Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Peralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan Luis
Enviado por
Alfredo Zavaleta GonzalezDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Peralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan Luis
Enviado por
Alfredo Zavaleta GonzalezDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Peralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Tpac, Alejandra Tataje, Jos Yanamango Salazar , Juan Luis
INTRODUCTION
The Reproductive System passes genetic material to a new generation and ensures that the human race continues.
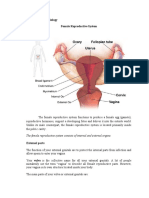
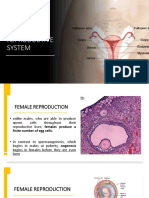
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The female reproductive system is located inside the body in the pelvis. The female reproductive system has four main parts: the vagina the uterus the fallopian tubes the ovaries
VAGINA
The vagina is about three to five inches (eight to 12 centimeters) long in a grown woman. It can expand and contract to allow for birth of a baby. It is lined with mucous membranes. The vagina has several functions: sexual intercourse, as the birth canal in childbirth, and as the exit for menstrual blood.
UTERUS
The uterus looks like an upside-down pear. It is made of some of the strongest muscles in the female body. These muscles expand during pregnancy and contract to push the baby out at birth. A non-pregnant uterus is about three inches (seven and a half centimeters) long and two inches (five centimeters) wide.
FALLOPIAN TUBES
The fallopian tubes connect the uterus to the ovaries. When an egg leaves the ovary, it goes into the fallopian tube. In the lining of the fallopian tube are tiny hairs that push the egg toward the uterus.
OVARIES
The ovaries are two ovalshaped organs above the uterus on the right and left. Ovaries produce store, and release eggs into the fallopian tubes during ovulation. The ovaries are also part of the Endocrine System. They produce the female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The male reproductive system is located outside of the body. Parts of the male reproductive system are: the testes the duct system the accessory glands the penis
TESTES
After puberty, the testes produce and store millions of sperm cells. They produce the hormone testosterone. Testosterone creates the bodily changes in males during puberty and starts the production of sperm.
EPIDIDYMIS
The epididymis and the vas deferens make up the duct system of the male reproductive organs.It transports the sperm-containing fluid called semen. The epididymis and the testes hang in a sac-like structure outside the pelvis called the scrotum.
SEMINAL VESICLES
The seminal vesicles attach to the vas deferens. The prostate gland produces some of the parts of semen. It is located at the base of the urethra below the bladder. The urethra carries semen to the outside of the body through the penis.
PENIS
The penis has two parts: the shaft the glans The shaft is the main part of the penis and the glans is the tip. At the end of the glans is an opening, where semen and urine exit the urethra. The foreskin is a fold of skin at the end of the penis covering the glans. Circumcision is a surgical removal of the foreskin.
PREGNANCY AND BIRTH
If a female and male have sex within several days of the female's ovulation, fertilization can occur. The fertilized egg burrows itself into the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. As the fertilized egg grows, it becomes an embryo. At about 9 weeks after fertilization, the embryo becomes a fetus.
Pregnancy lasts around 280 days about nine months. During labor, the cervix relaxes, and the amniotic sac breaks, releasing its fluid The baby is pushed out of the uterus through the cervix and the vagina. The placenta is delivered last.
After birth, the breasts and mammary glands are important to the reproductive process. The mammary glands are in the breasts. During pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone stimulate the production of milk.
MAINTAINING A HEALTHY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Just as all other systems of the body need to be cared for, there are rules to keep the Reproductive System healthy: Eat a healthy diet. Decrease caffeine intake. Stop smoking Limit alcohol Exercise regularly Wash fresh food before eating Maintain safe sex practices
DISEASES OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
CHLAMYDIA
Is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the United States. It causes painful intercourse, urinary burning and a discharge. Without treatment, it can cause severe conditions.
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Happens when a fertilized egg attaches itself and grows inside the fallopian tube. This causes severe abdominal pain and is a serious condition requiring medical attention.
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Happens when tissue normally found only in the uterus starts to grow inside the pelvic cavity. It can cause abnormal bleeding, painful periods, and general pelvic pain.
HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS (HPV)
Is thought to be one of the main causes of cervical cancer. A vaccine is available to prevent HPV infection.
INGUINAL HERNIA
Happens when a portion of the intestines push through an abnormal opening or weakening of the abdominal wall into the groin or scrotum. The hernia may look like a bulge or swelling in the groin area.
THANK YOU
Você também pode gostar
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento42 páginasFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosAinda não há avaliações
- Human ReproductionDocumento5 páginasHuman ReproductionKrishna SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System: Sexual Health UnitDocumento47 páginasFemale Reproductive System: Sexual Health UnitСухоставець Наталія ПетрівнаAinda não há avaliações
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocumento16 páginasThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocumento31 páginas1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductionjose mari chanAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System SlidesDocumento30 páginasFemale Reproductive System SlidesNyakie MotlalaneAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of The Reproductive OrganDocumento64 páginasParts of The Reproductive OrganFrancez Anne GuanzonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4&5Documento35 páginasLesson 4&5Miss JhemAinda não há avaliações
- Gender & Society 2Documento20 páginasGender & Society 2Anna Rose T. MarcelinoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 101 Reproductive SystemDocumento52 páginasLesson 101 Reproductive SystemtheacielaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4-Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocumento38 páginasLesson 4-Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDiana Hernandez100% (1)
- Group2 PPT ReportDocumento72 páginasGroup2 PPT ReportAbdulhakim BasirAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento23 páginasCase StudyLucero HyacinthAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System - ramoNJUANBASILANDocumento14 páginasFemale Reproductive System - ramoNJUANBASILANJericho TanalgoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Women HealthDocumento47 páginasIntroduction To Women HealthDarren LimAinda não há avaliações
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocumento14 páginasThe Male Reproductive SystemmarkkkkkkkheeessAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology OvaryDocumento6 páginasAnatomy and Physiology OvaryFretchell Aripal MontesAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCEDocumento3 páginasSCIENCEjoannalyn gregorioAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento4 páginasFemale Reproductive SystemDeepak VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Gender & Society Lo4Documento6 páginasGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive System HandoutDocumento21 páginasReproductive System HandoutJei SanAinda não há avaliações
- Human ReproductionDocumento17 páginasHuman Reproductionmyisha dailyAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Revision NotesDocumento29 páginasCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Revision Notesunnatidwivedi9568Ainda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento4 páginasFemale Reproductive SystemDeepak VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocumento17 páginasMale Reproductive System PDFN DrewAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive SystemDocumento33 páginasReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive System LessonDocumento3 páginasReproductive System LessonmargemunozAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction: Haniel & DaniellaDocumento30 páginasReproduction: Haniel & DaniellafriedAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System2Documento41 páginasFemale Reproductive System2joel1414Ainda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento5 páginasFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- Pandapatan Paler AnaPhyDocumento3 páginasPandapatan Paler AnaPhyShara Lailanie A. AzisAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System & Menstrual CycleDocumento77 páginasFemale Reproductive System & Menstrual Cyclebrandonbrandino624Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento7 páginasAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive SystemDocumento34 páginasReproductive Systemsyifa alawiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocumento211 páginasMale & Female Reproductive SystemDanica Marie SibayAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento30 páginasFemale Reproductive Systemsaranya amuAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento9 páginasFemale Reproductive Systembyata pausanosAinda não há avaliações
- The Female Reproductive System Is A Group of Organs That Work Together To Enable ReproductionDocumento5 páginasThe Female Reproductive System Is A Group of Organs That Work Together To Enable ReproductionNica Gobaliza EsquilonaAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento53 páginasUntitledPrincess Diane M. RagusAinda não há avaliações
- Human Reproductive SystemDocumento23 páginasHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronAinda não há avaliações
- Powerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageDocumento25 páginasPowerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageAngel CauilanAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento18 páginasFemale Reproductive SystemMama moAinda não há avaliações
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewDocumento49 páginasREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaAinda não há avaliações
- 10FRSDocumento27 páginas10FRSWakanda ForeverAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal and Child (Family Concepts)Documento22 páginasMaternal and Child (Family Concepts)Lenny SucalditoAinda não há avaliações
- Gender and Society CompileDocumento32 páginasGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento17 páginasFemale Reproductive SystemJasmaine RivoAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive System Ovarian Cycle &: Dr. Muhjah Falah Hasan PH.D in Infertility & Clinical ReproductionDocumento35 páginasFemale Reproductive System Ovarian Cycle &: Dr. Muhjah Falah Hasan PH.D in Infertility & Clinical Reproductionsuad aliAinda não há avaliações
- FeMale Reproductive SystemDocumento16 páginasFeMale Reproductive SystemArlenBalagotAinda não há avaliações
- MCN NotesDocumento71 páginasMCN NotesAbmil Ching TinggalongAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive OrgansDocumento42 páginasFemale Reproductive Organsaliyah nerz83% (6)
- Inbound 4525214668487640543Documento12 páginasInbound 4525214668487640543Neña Bautista PagalAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive Science 10Documento22 páginasReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50Ainda não há avaliações
- Human ReproductionDocumento96 páginasHuman Reproductionsanya razaAinda não há avaliações
- GE9 Module Lesson 3Documento6 páginasGE9 Module Lesson 3agnesAinda não há avaliações
- Repoductive SystemDocumento14 páginasRepoductive SystemJhoanna Marie RebutAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive FinalDocumento121 páginasReproductive FinalJasmine Nicole OsallaAinda não há avaliações
- Human Reproduction-1Documento50 páginasHuman Reproduction-1altheyafider615Ainda não há avaliações
- FEMALEDocumento60 páginasFEMALETri JaraAinda não há avaliações
- Additol-Xw-330 en LetterDocumento2 páginasAdditol-Xw-330 en Letternicolas chAinda não há avaliações
- Master Spreadsheet 2 - With Charts 2024 - ShcheglovaMDocumento23 páginasMaster Spreadsheet 2 - With Charts 2024 - ShcheglovaMМария ЩегловаAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment: Engineering Drawing & GraphicsDocumento2 páginasAssignment: Engineering Drawing & GraphicsSOCIAL WiseAinda não há avaliações
- Eye Brain and Vision PDFDocumento2 páginasEye Brain and Vision PDFBrett0% (1)
- Drives of MachinesDocumento2 páginasDrives of MachinesSimon AmboiseAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter IV Kaivalya PådaDocumento5 páginasChapter IV Kaivalya PådaAnonymous gqSpNAmlWAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-3 Op AmpDocumento19 páginasChapter-3 Op Ampmubs73Ainda não há avaliações
- Group 2 Presentation: El NiñoDocumento25 páginasGroup 2 Presentation: El NiñoFernan Lee R. ManingoAinda não há avaliações
- Emmvee Solarizer Elite Hybrid BrochureDocumento4 páginasEmmvee Solarizer Elite Hybrid BrochurePushkraj PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Ophthalmology: An International Journal of Clinical and Investigative OphthalmologyDocumento3 páginasVeterinary Ophthalmology: An International Journal of Clinical and Investigative OphthalmologyBlanca A SerranoAinda não há avaliações
- LAS MAPEH 9 Q3 W5 ArtsDocumento4 páginasLAS MAPEH 9 Q3 W5 ArtsJemalyn Hibaya LasacaAinda não há avaliações
- Ergonomics For Product DesignDocumento45 páginasErgonomics For Product DesignNORASHIKEN BINTI OTHMANAinda não há avaliações
- ABPK2203 Perception and Emotion Module PDFDocumento147 páginasABPK2203 Perception and Emotion Module PDFPhoebeilsie RaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Symphony II To RNS-E RetrofitDocumento26 páginasSymphony II To RNS-E Retrofitgeorge murphyAinda não há avaliações
- Phase A MaticDocumento2 páginasPhase A MatictheimproviserAinda não há avaliações
- After 4000 RH & 2000 RH After 1000 RHDocumento2 páginasAfter 4000 RH & 2000 RH After 1000 RHadeel ghouseAinda não há avaliações
- CMCA Case ScenarioDocumento3 páginasCMCA Case ScenarioPatricia DoAinda não há avaliações
- AnnunakiDocumento39 páginasAnnunakiCristian Stoica100% (10)
- About WELDA Anchor PlateDocumento1 páginaAbout WELDA Anchor PlateFircijevi KurajberiAinda não há avaliações
- Making Inferences 3Documento38 páginasMaking Inferences 3JayieepearlAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix DatabankDocumento4 páginasAppendix DatabankMiriam Torres TorresAinda não há avaliações
- BCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021Documento21 páginasBCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021hyperloop707 designAinda não há avaliações
- Beyond Today Magazine - March/April 2021Documento32 páginasBeyond Today Magazine - March/April 2021United Church of GodAinda não há avaliações
- Free 2019 Preakness Stakes Past PerformancesDocumento5 páginasFree 2019 Preakness Stakes Past PerformancesJonathan83% (6)
- Practical Acoustics of Instruments of The Violin FamilyDocumento13 páginasPractical Acoustics of Instruments of The Violin Familyapi-287441447100% (1)
- Shoulder Hypertrophy Specialization ProgramDocumento3 páginasShoulder Hypertrophy Specialization ProgramEli Harris100% (1)
- 03 Welding Control Procedure - Asf QC WCP 001Documento7 páginas03 Welding Control Procedure - Asf QC WCP 001el_sharkawy2011100% (1)
- DEBUT ScriptDocumento9 páginasDEBUT ScriptKen NethAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics PresentationDocumento21 páginasBiomechanics PresentationkylenddbsAinda não há avaliações
- David Shin Notes 05-02-19Documento6 páginasDavid Shin Notes 05-02-19ykk5qvx6gcAinda não há avaliações