Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
What Is Dumping
Enviado por
pixie128Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What Is Dumping
Enviado por
pixie128Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CHINA DUMPING AS A CASE OF PRICE DISCRIMINATION & CHINA DUMPING IN INDIA
PRESENTED BY:
ASHITA SAKARIA - 1 NIKITA - 13 PRIYANKA KALE - 23 MASSOM - 49 VARUN ALIMCHANDANI - 58
DEFINITION OF DUMPING
Definition: Dumping is an informal name for the practice of selling a product in a foreign country for less than either (a) the price in the domestic country, or (b) the cost of making the product. It is illegal in some countries to dump certain products into them, because they want to protect their own industries from such competition.
EASY ILLUSTRATION OF DUMPING
Definition: Dumping is an informal name for the practice of selling a product in a foreign country for less than either (a) the price in the domestic country, or (b) the cost of making the product. It is illegal in some countries to dump certain products into them, because they want to protect their own industries from such competition.
DUMPING MARGIN
IT HOW U CALCULATE THE MARGIN DURING THE DUMPING Dumping is an informal name for the practice of selling a product in a foreign country for less than either (a) the price in the domestic country, or (b) the cost of making the product. It is illegal in some countries to dump certain products into them, because they want to protect their own industries from such competition.
WHAT IS ANTI-DUMPING?????
The WTO agreement allows governments to act against dumping where there is genuine (material) injury to the competing domestic industry. In order to do that the government has to be able to show that dumping is taking place, calculate the extent of dumping (how much lower the export price is compared to the exporters home market price), and show that the dumping is causing injury or threatening to do so.
WHAT IS ANTI-DUMPING
Anti-dumping action means charging extra import duty on the particular product from the particular exporting country in order to bring its price closer to the normal value or to remove the injury to domestic industry in the importing country.
ADAM SMITH APPOSING THE DUMPING ACTIVITY
Quoting Adam Smith, by restraining, either by duties, or by absolute prohibitions, the importation of such goods from foreign countries as can be produced at home, the monopoly of the home market is more or less secured to the domestic industry employed in producing them. Thus Adam Smith was of the opinion, that, the importing countries should discourage those imports which will harm the domestic industries, by imposing duties on such items. arises for imposing anti-dumping duties.
ADAM SMITH APPOSING THE DUMPING ACTIVITY
Here he was referring to import duties but in the present economic scenario, import duties alone cannot discourage dumping. Thus the need arises for imposing antidumping duties.
ANTI-DUMPING MEASURES
1) Anti-dumping duty: This is imposed at the time of imports, in addition to other customs duties. The purpose of antidumping duty is to raise the price of the commodity when introduced in the market of the importing country. 2) Price undertaking: If the exporter himself undertakes to raise the price of the product then the importing country can consider it and accept it instead of imposing antidumping duty.
HOW TO CALCULATE THE EXTENT OF DUMPING????
GATT (Article 6) provides three methods to calculate a products normal value. The main one is based on .price of the product in exporters domestic market When this method cannot be used the other two alternatives arePrice charged by exporters in other country &calculation based on combination of
CASE STUDY 1
This case study supports the hypothesis that the dumping country need not be very developed so as to indulge in dumping. China is the worlds largest producer of apples. China has flooded the US market with apple juice concentrate along with textiles and garments. In the beginning of May 2000, an anti-dumping duty to the extent of 51.74% was imposed on Chinese apple concentrate. In United States, the price of Chinese apple concentrate is still low even after the imposition of antidumping duties due to their extremely low cost of production. China does not occupy a
CASE STUDY 2
In a recent post, I mentioned the U.S. government imposing additional duties on Chinese products because of dumping; that is, selling us cheap products. In what has got to be the ultimate case of dumping, pharmacies at Publix Supermarkets in Florida are still giving away certain prescription drugs. Evidently, this has been going on for some time. Quick, call the Commerce Department. Publix is obviously trying to put locallyowned pharmacies out of business. Then Publix will start charging to fill these prescriptions. Soon the price will be so high
THREAT OF DUMPING
In developing countries, especially those neighbouring the non-market economies, dumping can pose a serious threat. Dumping from China in India is an example of this. More than one-third cases decided by the Designated Authority in India involve China. These exporters are indulging in very aggressive pricing which is evident from the huge dumping margin. Moreover, in a majority of the cases, the exporters and producers of
STEPS INVOLED IN PRICING OF PRODUCT
One of the four major elements of the marketing mix is price. Pricing is an important strategic issue because it is related to product positioning. Furthermore, pricing affects other marketing mix elements such as product features, channel decisions, and promotion. While there is no single recipe to determine pricing, the following is a general sequence of steps that might be followed for developing the pricing of a new product: Develop marketing strategy - perform marketing analysis, segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
STEPS INVOLED IN PRICING OF PRODUCT
Calculate cost - include fixed and variable costs associated with the product. Understand environmental factors - evaluate likely competitor actions, understand legal constraints, etc. Set pricing objectives - for example, profit maximization, revenue maximization, or price stabilization (status quo). Determine pricing - using information collected in the above steps, select a pricing method, develop the pricing structure, and define discounts. Estimate the demand curve - understand how quantity demanded varies with price.
ESTIMATION OF DEMAND CURVE
Because there is a relationship between price and quantity demanded, it is important to understand the impact of pricing on sales by estimating the demand curve for the product. For existing products, experiments can be performed at prices above and below the current price in order to determine the price elasticity of demand. Inelastic demand indicates that price increases might be feasible.
MAIN OBJECTIVE OF PRICING
The firm's pricing objectives must be identified in order to determine the optimal pricing. Common objectives include the following: Current profit maximization - seeks to maximize current profit, taking into account revenue and costs. Current profit maximization may not be the best objective if it results in lower long-term profits. Current revenue maximization - seeks to maximize current revenue with no regard to profit margins. The underlying objective often is to maximize long-term profits by increasing market share and lowering costs. Maximize quantity - seeks to maximize the number of units sold or the number of customers served in order to decrease long-term costs as predicted by the experience curve.
MAIN OBJECTIVE OF PRICING
Maximize profit margin - attempts to maximize the unit profit margin, recognizing that quantities will be low. Quality leadership - use price to signal high quality in an attempt to position the product as the quality leader. Partial cost recovery - an organization that has other revenue sources may seek only partial cost recovery. Survival - in situations such as market decline and overcapacity, the goal may be to select a price that will cover costs and permit the firm to remain in the market. In this case, survival may take a priority over profits, so this objective is considered temporary.
MAIN OBJECTIVE OF PRICING
Psychological pricing - base the price on factors such as signals of product quality, popular price points, and what the consumer perceives to be fair.
In addition to setting the price level, managers have the opportunity to design innovative pricing models that better meet the needs of both the firm and its customers. For example, software traditionally was purchased as a product in which customers made a one-time payment and then owned a perpetual license to the software. Many software suppliers have changed their pricing to a subscription model in which the customer subscribes for a set period of time, such as one year. Afterwards, the subscription must be renewed or the software no longer will function. This model offers stability to both the
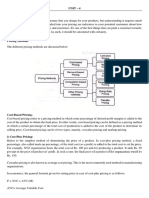
DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRICING
To set the specific price level that achieves their pricing objectives, managers may make use of several pricing methods. These methods include:
Cost-plus pricing - set the price at the production cost plus a certain profit margin. Target return pricing - set the price to achieve a target return-on-investment. Value-based pricing - base the price on the effective value to the customer relative to alternative products.
WHAT IS PRICE DISCRIMINATION????
Practice of selling goods or services at different prices to different buyers, even though sales costs are the same for all the transactions. Buyers may be discriminated against on the basis of income, ethnicity, age, or geographic location. For price discrimination to succeed, other entrepreneurs must be unable to purchase goods at the lower price and resell them at a higher one.
ADAM SMITH APPOSING THE DUMPING ACTIVITY
Quoting Adam Smith, by restraining, either by duties, or by absolute prohibitions, the importation of such goods from foreign countries as can be produced at home, the monopoly of the home market is more or less secured to the domestic industry employed in producing them. Thus Adam Smith was of the opinion, that, the importing countries should discourage those imports which will harm the domestic industries, by imposing duties on such items. arises for imposing anti-dumping duties.
DUMPING AS A CASE OF PRICE DISCRIMINATION
Increasing volumes of apple juice concentrate imports from China into the U.S. began in the mid 90s as a result of low Chinese prices. In 1999, the U.S. Apple Association launched a complaint with the US International Trade Commission (USITC) regarding the Chinese price strategy. During the course of investigation, the U.S. Apple Association requested that the Department of Agricultural Economics at Washington State University analyze the impact on the total value of juice apples utilized in Washington during the span of the USITC investigation. To determine the magnitude of the effect of the USITC investigation, not only on finished apple juice prices but also on the Washington raw product price, an inverse demand for finished product and an input demand function for raw product was developed and parametrically estimated. Results from a derived demand analysis for juice apples revealed that a decrease in Chinese apple juice price reduced the prices paid by the processing sector by approximately 0.07 percent. However, throughout the course of the investigation process, juice apple prices increased significantly, resulting in an increase in the value of the juice apples purchased by
DUMPING OF CHINA GOODS IN INDIA
The government of India has levied anti-dumping duties on certain types of stainless steel that are shipped in from countries like China and Japan. The anti-dumping duties were imposed after finding that certain types of imported steel are landing at below the normal value in the country's port. The Central Board of Customs and Excise imposed the duties by saying that the domestic industry has suffered badly due to the imports from other countries. As per a notification of Central Board of Customs and Excise, the duties will remain effective till October 21, 2009. The subject countries will pay the duties in Indian currency, notified the board. Apart from China and Japan, other countries include South Korea, European Union, South Africa, Taiwan, Thailand and the US. The type of steel on which duties have been imposed is called cold-rolled flat steel products. The subject countries will have to pay duties ranging from $12.74 to $2,011 per tonne. The anti-dumping duties will be charged depending on the type of steel, the country of manufacture, the origin of import and the producer. The firms that are mentioned in the notification include Arcelor Mittal from France and Belgium, Lianzhong and Shanxi Taigang from China, Acrinox from Spain and Malaysia, Columbus from South Africa, Posco from South Korea and Yeih United of Taiwan. India is the fifth largest producer of steel in the world with a capacity of producing 53 million tonnes of steel annually.
DUMPING OF CHINA GOODS IN INDIA
The type of steel on which duties have been imposed is called cold-rolled flat steel products. The subject countries will have to pay duties ranging from $12.74 to $2,011 per tonne. The anti-dumping duties will be charged depending on the type of steel, the country of manufacture, the origin of import and the producer. The firms that are mentioned in the notification include Arcelor Mittal from France and Belgium, Lianzhong and Shanxi Taigang from China, Acrinox from Spain and Malaysia, Columbus from South Africa, Posco from South Korea and Yeih United of Taiwan. India is the fifth largest producer of steel in the world with a capacity of producing 53 million tonnes of steel annually.
EFFECT OF CHINA DUMPING ON THE FDI OF JAPAN
THE dumping of Chinese goods is not only threatening India's domestic industry but is also likely to affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows. The dragon has cast its shadow even on the domestic industries of developed nations such as Japan. While th e dumping is hitting the small-scale sector and the chemical industry in India, it is the textile industry that threatened in Japan. Both India and Japan are on their feet to counter the dumping, but their approaches are different. While India is using antidumping measures and tariffs to shield its domestic industry, Japan is using economic measure -- that is, by investing more in Ch ina to produce and sell to its own domestic market at half the price of similar products produced in Japan.
EFFECT OF CHINA DUMPING ON THE FDI OF JAPAN
For instance, Japanese apparel major, Itokin Co, exported 1718 million pieces of garments from China to Japan in 2000, treble the 1999 figure. In 2000, other leading Japanese apparel companies -- Fast Retailing and Cecile -- set up shop in Shanghai to p roduce low-priced apparels for export to Japan. Thus, Japanese apparel-makers have increasingly been relocating their manufacturing base to China to capitalise on the cheap labour and nullify the latter's competitive edge in the Japanese market. To counter the dumping, the US and Europe may also take Japan's route -- by investing more in China, that is. What does this imply for India? Going by the current trend, and coupled with its imminent entry into the WTO, China will once again become an at tractive destination for foreign investments
EFFECT OF CHINA DUMPING ON THE FDI OF INDIA
The dumping by China has further dampened India's potential to attract foreign investors. With the removal of quantitative restrictions (QRs) from April 1, 2001, it is feared that the dumping would increase. Moreover, the world FDI trends are that the ea rlier attraction of local markets is giving way to global integration. Global integration means development of borderless production to cater to the needs of both the domestic and export markets. In this changed situation, if India wants to compete with China, it will have to strengthen its manufacturing facilities. But thi s is not easy. Hence, the only alternative would be to open up its service sector more boldly, that is, well before China does so after gaining WTO entry.
EFFECT OF CHINA DUMPING ON THE FDI OF INDIA
India, for instance, has a vast potential to attract FDI into retail and wholesale trading. Following the removal of the QRs and the gradual reduction in tariffs, the distribution industry has emerged as a high-potential area for investment. Considering India's size and the diversified nature of its regional markets, the domestic private sector alone cannot pump in the investment required. Hence, foreign investors should be encouraged to supplement the enlarged distribution industry with resources and t echnology, rather than be paranoid about protecting the domestic players.
Você também pode gostar
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesNo EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Staregies and TacticsDocumento40 páginasPricing Staregies and TacticsrithikkumuthaAinda não há avaliações
- Developing the International Pricing Mix Objectives and StrategiesDocumento3 páginasDeveloping the International Pricing Mix Objectives and StrategiesAngelica Macaraeg CañedoAinda não há avaliações
- Bem102 7Documento22 páginasBem102 7Mellisa AndileAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Business Decisions - SEction IDocumento4 páginasPrinciples of Business Decisions - SEction ISheethalAinda não há avaliações
- Economic Analysis Policy - IDocumento30 páginasEconomic Analysis Policy - IThaddeus De MenezesAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Methods ExplainedDocumento15 páginasPricing Methods ExplainedmussaiyibAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing StrategyDocumento5 páginasPricing StrategyShantonu RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 3: Pricing Strategy Objectives & Pricing MethodsDocumento13 páginasUnit - 3: Pricing Strategy Objectives & Pricing MethodssreedeviAinda não há avaliações
- PricingDocumento4 páginasPricingSrikanth ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- NEW Lesson 3 in ST 2, Economics of Agriculture, December 25, 2023Documento249 páginasNEW Lesson 3 in ST 2, Economics of Agriculture, December 25, 2023beberliepangandoyonAinda não há avaliações
- International MarketDocumento21 páginasInternational MarketNathish RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Export PricingDocumento21 páginasExport PricingSushant KaushalAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 3 International Marketing 1Documento19 páginasUNIT 3 International Marketing 1Pari SweetuAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Strategy: Internal Factors in Pricing A ProductDocumento5 páginasPricing Strategy: Internal Factors in Pricing A Productainsyasya 98Ainda não há avaliações
- Pricing Decision Unit IIIDocumento3 páginasPricing Decision Unit IIIGovind TrivediAinda não há avaliações
- Various Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeDocumento5 páginasVarious Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeGis PeeAinda não há avaliações
- CH 6 Cost IIDocumento3 páginasCH 6 Cost IIfirewAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing MangementDocumento26 páginasMarketing MangementPopuri Nagasai KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing StrategyDocumento5 páginasPricing StrategyAbhishek MenonAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of Pricing StrategyDocumento7 páginasDefinition of Pricing StrategyYvonne WongAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Management Price StrategyDocumento30 páginasMarketing Management Price StrategyChali KumaraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Export MarketingDocumento13 páginasChapter 11 Export MarketingShayza KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Pili Pricing Methods&Strategy Ac33arDocumento3 páginasPili Pricing Methods&Strategy Ac33arMary Jannica Azul PiliAinda não há avaliações
- Cost Analysis and Pricing DecisionsDocumento20 páginasCost Analysis and Pricing DecisionsKalkidan NigussieAinda não há avaliações
- Exim Unit 2Documento32 páginasExim Unit 2Aditi SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Boost profits sustainably with Navetti pricingDocumento12 páginasBoost profits sustainably with Navetti pricingarmenmalawaniAinda não há avaliações
- Termeni Engleza 2Documento18 páginasTermeni Engleza 2andrey7coAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Management.Documento12 páginasMarketing Management.Purvi ShethAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing MethodsDocumento4 páginasPricing Methodssatya narayanaAinda não há avaliações
- Module-3 Pricing: "Price Is The Amount of Money or Goods For Which A Thing Is Bought or Sold"Documento7 páginasModule-3 Pricing: "Price Is The Amount of Money or Goods For Which A Thing Is Bought or Sold"murshidaman3Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Strategy: I. What Is Strategy?Documento5 páginasIntroduction To Strategy: I. What Is Strategy?Satheesh VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeDocumento4 páginasPricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeClaudette ClementeAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Methods and Strategies GuideDocumento3 páginasPricing Methods and Strategies GuideMary Jannica Azul PiliAinda não há avaliações
- Price StrategyDocumento8 páginasPrice StrategyBry KaparangAinda não há avaliações
- Ppropriate Marketing Strategy For Your Company:-: Assignment-MBA (Sem-I) ECO7748-Managerial EconomicsDocumento7 páginasPpropriate Marketing Strategy For Your Company:-: Assignment-MBA (Sem-I) ECO7748-Managerial EconomicsGaurav ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Pricing ApprochesDocumento8 páginas6 Pricing ApprocheskmvilasAinda não há avaliações
- Step 4: Export Pricing Strategies at Your DisposalDocumento5 páginasStep 4: Export Pricing Strategies at Your DisposalVignesh RavindranAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing StrategiesDocumento9 páginasPricing StrategiesramyagolluAinda não há avaliações
- Different Pricing StrategiesDocumento12 páginasDifferent Pricing Strategiesfahimahmed786Ainda não há avaliações
- 7_Pricing Decisions.pptxDocumento12 páginas7_Pricing Decisions.pptxCharisse Ahnne TosloladoAinda não há avaliações
- PricingDocumento3 páginasPricingcarnivalofpainAinda não há avaliações
- Name and Explain Costing MethodsDocumento6 páginasName and Explain Costing MethodsOgutuEricJeanAinda não há avaliações
- Meaning of PricingDocumento13 páginasMeaning of PricingChera HabebawAinda não há avaliações
- Export Pricing 4Documento17 páginasExport Pricing 4Rohit JindalAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Decisions: Ii Element of Marketing MixDocumento25 páginasPricing Decisions: Ii Element of Marketing MixKrishna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing StrategiesDocumento7 páginasPricing StrategiesPrakhyathThejveerAinda não há avaliações
- Methods To Price Your ProductsDocumento11 páginasMethods To Price Your ProductsosamamusaAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Business Analysis IIDocumento46 páginasStrategic Business Analysis IIAngel Chane OstrazAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Pricing ConceptsDocumento15 páginasBasic Pricing ConceptsJoshi DrcpAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Strategy Review in Telecom SectorDocumento40 páginasPricing Strategy Review in Telecom SectorSonam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Five Pricing Strategy ExplainedDocumento42 páginasChapter Five Pricing Strategy ExplainedAmanuel AbebawAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of PriceDocumento10 páginasDefinition of PricesunnyrictoAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Strategy (Economics - KU Lesson Notes)Documento6 páginasPricing Strategy (Economics - KU Lesson Notes)Platonic100% (12)
- Marketing pricing strategiesDocumento4 páginasMarketing pricing strategiesSabaAinda não há avaliações
- International Trade Test 2Documento3 páginasInternational Trade Test 2api-257363860Ainda não há avaliações
- Managerial Economics 1st SemDocumento39 páginasManagerial Economics 1st SemAmrutha GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Pricing (Review and Analysis of Raju and Zhang's Book)No EverandSmart Pricing (Review and Analysis of Raju and Zhang's Book)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- DaburDocumento27 páginasDaburPriyanka Kale100% (1)
- IPL ORIGIN AND CONTROVERSIESDocumento9 páginasIPL ORIGIN AND CONTROVERSIESpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Retail StoresDocumento3 páginasTypes of Retail Storespixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Retail Management Part-1: Prepared By: Presented byDocumento33 páginasRetail Management Part-1: Prepared By: Presented bypixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Coca Cola Marketing StrategiesDocumento52 páginasCoca Cola Marketing Strategiesfakhar94% (163)
- Benefit Available in Personal Accidential PolicyDocumento3 páginasBenefit Available in Personal Accidential Policypixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- HR FinalDocumento33 páginasHR Finalpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Organisational Behaviour FinalDocumento43 páginasOrganisational Behaviour Finalpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Benefit Available in Personal Accidential PolicyDocumento3 páginasBenefit Available in Personal Accidential Policypixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- India Trade Before & After Liberlisation: Presented by Group 7Documento39 páginasIndia Trade Before & After Liberlisation: Presented by Group 7rajsinhain100% (13)
- Bank Recruitment - FinalDocumento14 páginasBank Recruitment - Finalpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- 2003Documento7 páginas2003pixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- IPL ORIGIN AND CONTROVERSIESDocumento9 páginasIPL ORIGIN AND CONTROVERSIESpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.Documento22 páginasMahindra & Mahindra Ltd.pixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- India As A Dumping Ground For ChinaDocumento24 páginasIndia As A Dumping Ground For Chinapixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- FedEx Packaging GuidelinesDocumento5 páginasFedEx Packaging GuidelinesChicago TribuneAinda não há avaliações
- Benefit Available in Personal Accidential PolicyDocumento3 páginasBenefit Available in Personal Accidential Policypixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Education Sector - Jan09Documento150 páginasEducation Sector - Jan09gauravskhuranaAinda não há avaliações
- The Oriental Insurance Company LimitedDocumento11 páginasThe Oriental Insurance Company Limitedpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Rbi Final FinalDocumento17 páginasRbi Final Finalpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- AbsenteeismDocumento26 páginasAbsenteeismpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Compensation ManagementDocumento15 páginasCompensation ManagementDevraj Singh ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Production ManagementDocumento8 páginasProduction Managementpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Store Based RetailingDocumento15 páginasStore Based RetailingAmit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Organisational Behaviour FinalDocumento42 páginasOrganisational Behaviour Finalpixie1280% (1)
- Final PPT of RuralDocumento4 páginasFinal PPT of Ruralpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Components of A Business PlanDocumento4 páginasComponents of A Business Planpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Production ManagementDocumento8 páginasProduction Managementpixie128Ainda não há avaliações
- Inflation Accounting: A Presentation by - ITM XMBA - 33 Dinesh M Manghani Sharon RodriguesDocumento15 páginasInflation Accounting: A Presentation by - ITM XMBA - 33 Dinesh M Manghani Sharon RodriguesDinesh Manghani100% (1)
- Professional Members Directory As On 13-02-2023Documento532 páginasProfessional Members Directory As On 13-02-2023Saddam HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank Principles of Cost Accounting 16th Edition VanderbeckDocumento75 páginasTest Bank Principles of Cost Accounting 16th Edition VanderbeckNhel AlvaroAinda não há avaliações
- Boston Condo InfoDocumento7 páginasBoston Condo InfoDaisy MaryAinda não há avaliações
- Examination: Subject CT1 Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalDocumento211 páginasExamination: Subject CT1 Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalMfundo MshenguAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation Digital Day 09112021 0Documento92 páginasPresentation Digital Day 09112021 0Nizar MTechAinda não há avaliações
- Business Case - Amy Baker Nature's CureDocumento19 páginasBusiness Case - Amy Baker Nature's CurerasyidazmiAinda não há avaliações
- Pengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan, Remunerasi Ceo Dan Modal IntelektualDocumento9 páginasPengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan, Remunerasi Ceo Dan Modal IntelektualdayaninurhandayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Trinity2013 Bill MatzDocumento14 páginasTrinity2013 Bill MatzRusu VaseaAinda não há avaliações
- Completing Test On Sales and Collection Cycles: Account ReceivableDocumento14 páginasCompleting Test On Sales and Collection Cycles: Account ReceivableunigaluhAinda não há avaliações
- IUMC - Management Accounting - Fall 2019 - QuizDocumento2 páginasIUMC - Management Accounting - Fall 2019 - QuizM Usama Ahmed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Ent300 Assignment 3 Business Plan General Guidelines 2021Documento18 páginasEnt300 Assignment 3 Business Plan General Guidelines 2021anisAinda não há avaliações
- ABM 009 Business Enterprise SimulationDocumento4 páginasABM 009 Business Enterprise SimulationMarvin EduarteAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10Documento28 páginasChapter 10YourMotherAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Strategy Internship ReportDocumento37 páginasMarketing Strategy Internship ReportA H LabuAinda não há avaliações
- Tony Kripas Sept 27, 2011 MKTSales ResumeDocumento3 páginasTony Kripas Sept 27, 2011 MKTSales ResumeAnthony KripasAinda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Accounting 1A 2019 by Millan Chapter 1-Summary (Accounting Process)Documento5 páginasIntermediate Accounting 1A 2019 by Millan Chapter 1-Summary (Accounting Process)Shaina DellomesAinda não há avaliações
- CAT 1 Module (NIAT Encoded)Documento245 páginasCAT 1 Module (NIAT Encoded)UFO CatcherAinda não há avaliações
- Investment Analysis Icmss 2013Documento20 páginasInvestment Analysis Icmss 2013Panzi Aulia RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- C Accomplishment Report Service Credits - TeachersDocumento7 páginasC Accomplishment Report Service Credits - TeachersCamelle MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Managing The Competition in Frozen Food AisleDocumento12 páginasManaging The Competition in Frozen Food AisleAnangsa BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- B2B Marketing Case Analysis: Arcelik's Transition to an Omnichannel ExperienceDocumento4 páginasB2B Marketing Case Analysis: Arcelik's Transition to an Omnichannel ExperienceAnsh LakhmaniAinda não há avaliações
- MBA in PM Strategic ManagementDocumento55 páginasMBA in PM Strategic Managementmohamed aktharAinda não há avaliações
- Observing Sales Activities & Direct Coverage Secondary Data Analysis at Rollick IndiaDocumento11 páginasObserving Sales Activities & Direct Coverage Secondary Data Analysis at Rollick Indiasouvikpal904Ainda não há avaliações
- Account PaperDocumento8 páginasAccount PaperAhmad SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Tarang LaunchDocumento10 páginasTarang LaunchBatool Yousuf0% (1)
- Cirque Du Soleil (Blue Ocean Strategy) : - by Group 6Documento7 páginasCirque Du Soleil (Blue Ocean Strategy) : - by Group 6KHALKAR SWAPNILAinda não há avaliações
- Contemporary Project Management 3rd Edition Timothy Kloppenborg Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasContemporary Project Management 3rd Edition Timothy Kloppenborg Solutions Manualmiscallcallipee462q100% (37)
- Achieving Excellence in After-Sales Services - BCG PDFDocumento16 páginasAchieving Excellence in After-Sales Services - BCG PDFAndrey Doran GambaAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 4 PROBLEMS BOND AND STOCK VALUATIONDocumento4 páginasLECTURE 4 PROBLEMS BOND AND STOCK VALUATIONDahniar AmalinaAinda não há avaliações