Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Right Bundle Branch Block
Enviado por
Kweenie QueenieDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Right Bundle Branch Block
Enviado por
Kweenie QueenieDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK
BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK
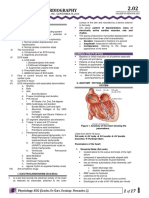
bundle branch block refers to a conduction block in one or both of the ventricular bundle branches FASICULAR BLOCK- only a part of one of the bundle branches is blocked
The right and left bundle branches deliver the current to the right and left ventricles, respectively QRS complex= representing ventricular depolarization from start to finish, is narrow less than 0.10 seconds in duration muscle mass of the left ventricle is so much larger than that of the right ventricle, left ventricular electrical forces dominate those of the right ventricle, and the resultant electrical axis is leftward, lying between 0 and +90
Thus, with normal ventricular depolarization, the QRS complex is narrow and the electrical axis lies between 0 and 90 Bundle branch block is diagnosed by looking at the width and configuration of the QRS complexes.
Intrinsic impairment of conduction in either left or right bundle system (intraventicular conduction disturbances)--- prolongation of the QRS interval.
COMPLETE BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCKS: QRS interval is >120ms INCOMPLETE BLOCKS: QRS interval is between 100 and 120 ms in duration
QRS VECTOR is usually oriented in the myocardial region where depolarization is delayed.
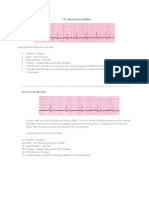
RIGHT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK
In right bundle branch block, conduction through the right bundle is obstructed. As a result, right ventricular depolarization is delayed; it does not begin until the left ventricle is almost fully depolarized. The terminal QRS vector is oriented to the right and anteriorly.
The delay in right ventricular depolarization prolongs the total time for ventricular depolarization. As a result, the QRS complex widens beyond 0.12 seconds. The wide QRS complex assumes a unique, virtually diagnostic shape in those leads overlying the right ventricle: V1 and V2. the normal QRS complex in these leads consists of a small positive R wave and a deep negative S wave, reflecting the electrical dominance of the left ventricle.
With right bundle branch block, you can still see the initial R and S waves as the left ventricle depolarizes, but as the right ventricle then begins its delayed depolarization, unopposed by the now fully depolarized and electrically silent left ventricle, the electrical axis of current flow swings sharply back toward the right. This inscribes a second R wave, called R', in leads V1 and V2. The whole complex is called RSR', Meanwhile, in the left lateral leads overlying the left ventricle (I, AVL, V5, and V6), late right ventricular depolarization causes reciprocal late deep S waves to be inscribed.
V1& V2:rSR I, AVL, V5, and V6 : qRS
In subjects without structural heart disease, right bundle branch block is seen more commonly than left bundle branch block. RBBB is also seen in both congenital (ASD)and acquired conditions (ischemic).
Você também pode gostar
- Raza's ECGDocumento45 páginasRaza's ECGcozmoxxxAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookDocumento118 páginasECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookOana Anghel100% (9)
- Podrid's Real-World ECGs Volume 6 (2016) PDFDocumento635 páginasPodrid's Real-World ECGs Volume 6 (2016) PDFRyan Kadavil100% (2)
- Cardiac Pacing and ICDDocumento74 páginasCardiac Pacing and ICDBernadixta Winda Dwi Cahyani100% (3)
- Complete Guide To ECGDocumento78 páginasComplete Guide To ECGAnas YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Jugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionDocumento53 páginasJugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionJoshua JayakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Arrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1Documento34 páginasArrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1preethi preethaAinda não há avaliações
- Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-AnswersDocumento2 páginasDisorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answersapi-281108263Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Physiology:: Circuitry, Hemodynamics, ElectrophysiologyDocumento27 páginasCardiovascular Physiology:: Circuitry, Hemodynamics, Electrophysiologyrsmoney3Ainda não há avaliações
- Pericardial EffusionDocumento1 páginaPericardial EffusionAlfrin Antony100% (1)
- Coronary Circulation FDocumento36 páginasCoronary Circulation FjefferyAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral Blood FlowDocumento39 páginasCerebral Blood FlowRajat ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Action PotentialDocumento41 páginasCardiac Action PotentialRadijska Postaja KoprivnicaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Tubular NecrosisDocumento60 páginasAcute Tubular NecrosisYedesney C. LinaresAinda não há avaliações
- Frank-Starling LawDocumento5 páginasFrank-Starling LawNTA UGC-NETAinda não há avaliações
- CerebellumDocumento14 páginasCerebellumapi-508474347Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11-The Normal ElectrocardiogramDocumento18 páginasChapter 11-The Normal Electrocardiogrammuna s100% (1)
- The Cardiac Cycle: Chapter 19Documento62 páginasThe Cardiac Cycle: Chapter 19BishwambherAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood VesselDocumento3 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of Blood Vesselneleh grayAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Major Veins of The BodyDocumento26 páginas3-Major Veins of The BodyTJPlayz100% (1)
- CVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologyDocumento13 páginasCVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologySherwan R Shal100% (5)
- 3rd Lecture On Arrythmias by Dr. RoomiDocumento16 páginas3rd Lecture On Arrythmias by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- Bundle Branch BlockDocumento37 páginasBundle Branch BlocksyukronchalimAinda não há avaliações
- Nose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018Documento63 páginasNose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018yasrul izadAinda não há avaliações
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDocumento35 páginas1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The AortaDocumento19 páginasAnatomy of The AortaUma Sanggari ThirunavukarasuAinda não há avaliações
- Action Potential of Cardiac MusclesDocumento16 páginasAction Potential of Cardiac Muscleswaqas_xsAinda não há avaliações
- GI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Documento41 páginasGI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Abby LiewAinda não há avaliações
- Jugular Venous PressureDocumento9 páginasJugular Venous Pressuremoh86-Ainda não há avaliações
- Anaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationDocumento15 páginasAnaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationNaresh Dhawan100% (1)
- Case 1 - Sickle Cell Disease - PPSXDocumento44 páginasCase 1 - Sickle Cell Disease - PPSXNICHOLAS KAUMBA100% (1)
- Sickle Cell Disease: Everything You Ever Wanted To KnowDocumento23 páginasSickle Cell Disease: Everything You Ever Wanted To KnowAnastasiafynn100% (1)
- Diabetes InsipidusDocumento39 páginasDiabetes Insipidusกรคุง ภิญโญพจนารถAinda não há avaliações
- Anastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockageDocumento5 páginasAnastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockagemcwnotesAinda não há avaliações
- Congestive Heart FailureDocumento86 páginasCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System NotesDocumento4 páginasCirculatory System Notesputri aisheAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Supply of HeartDocumento7 páginasBlood Supply of Heartmariposa_0612Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Cycle - DR Rakesh JainDocumento97 páginasCardiac Cycle - DR Rakesh JainEmmieAinda não há avaliações
- CH 11 Heart NotesDocumento2 páginasCH 11 Heart Notesummnicole0% (1)
- Schematic Diagram Wilson'S DiseaseDocumento2 páginasSchematic Diagram Wilson'S DiseaseAmira CharmaineAinda não há avaliações
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocumento69 páginasFluids and ElectrolytesHarold DiasanaAinda não há avaliações
- Arrythmic DrugsDocumento43 páginasArrythmic DrugsjanakaAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Documento182 páginasCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot MotAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pancreatitis: J Koh & D ChengDocumento7 páginasAcute Pancreatitis: J Koh & D ChengGloriaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerulonephritis 10Documento5 páginasGlomerulonephritis 10Eden Jay Calija AgoyAinda não há avaliações
- Myasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderDocumento16 páginasMyasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderHibba NasserAinda não há avaliações
- Stroke FullDocumento10 páginasStroke Fullshowkat3Ainda não há avaliações
- Physiology Chap9 (Cardiac Muscle)Documento5 páginasPhysiology Chap9 (Cardiac Muscle)Man DejeloAinda não há avaliações
- SepsisDocumento33 páginasSepsisv_vijayakanth7656Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiac CycleDocumento31 páginasCardiac CycleAdwaitha KrAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary BladderDocumento28 páginasHistology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary Bladderkhairul_azhar_27Ainda não há avaliações
- Progenitor Heart Cells Lie in The Epiblast, Immediately Adjacent To TheDocumento15 páginasProgenitor Heart Cells Lie in The Epiblast, Immediately Adjacent To TheJehangir AllamAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Cycle: Mechanical Event and Their Electrical and Clinical CorrelationDocumento28 páginasCardiac Cycle: Mechanical Event and Their Electrical and Clinical Correlationhawas muhammed100% (1)
- Histology of LungsDocumento30 páginasHistology of LungsShahir21Ainda não há avaliações
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocumento44 páginasCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarctionalejandrino_leoaugustoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of External Features of HeartDocumento45 páginasAnatomy of External Features of HeartSurajit KunduAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemDocumento89 páginasChapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemOliver Namyalo100% (1)
- Chapter 26: The Urinary System: Chapter Objectives Overview of Kidney FunctionDocumento14 páginasChapter 26: The Urinary System: Chapter Objectives Overview of Kidney FunctionAnkit SwainAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of RespirationDocumento2 páginasPhysiology of RespirationIOSRjournalAinda não há avaliações
- Lung Volume & CapacitiesDocumento32 páginasLung Volume & CapacitiesGaurav SinghAinda não há avaliações
- MNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryDocumento38 páginasMNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryJosephine A. Bertulfo100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to Brain Hypoxia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Brain Hypoxia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Normal ECG: - P Wave: Between 3 - 5 Little Square - Lead V1 Is A Good Place To StartDocumento80 páginasNormal ECG: - P Wave: Between 3 - 5 Little Square - Lead V1 Is A Good Place To Startkuchniaat123Ainda não há avaliações
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocumento10 páginasNormal Sinus RhythmNakul GaurAinda não há avaliações
- The Main Applications of The ECG Nursing Lecture NotesDocumento19 páginasThe Main Applications of The ECG Nursing Lecture NotesMaria Rowena O. SalvoAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento169 páginasElectrocardiogramjitendra magarAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 6.advance 12 Lead InterpretationDocumento30 páginasModule - 6.advance 12 Lead InterpretationFerry SofyanriAinda não há avaliações
- ECG ExamplesDocumento25 páginasECG Examplesvinsonpeng26Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecg in DogsDocumento107 páginasEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Ele&Arr&Com&Rev&Das&Zip&1 STDocumento492 páginasEle&Arr&Com&Rev&Das&Zip&1 STeuinpersoana100% (3)
- Ecg Interpretation: Intervals and ComplexesDocumento7 páginasEcg Interpretation: Intervals and ComplexesBobet ReñaAinda não há avaliações
- (Mebooksfree Net) Car&Arr&Int&Dia&Tre&2ndDocumento529 páginas(Mebooksfree Net) Car&Arr&Int&Dia&Tre&2ndBÁCH NGUYỄN ĐẮC100% (1)
- ECG IntroDocumento52 páginasECG IntroljgutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- 2 02-Electrocardiography PDFDocumento17 páginas2 02-Electrocardiography PDFMiguel DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- 12-Lead ECG &: StemiDocumento58 páginas12-Lead ECG &: StemiSarah-kate PatersonAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction AbnormalitiesDocumento9 páginasECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction Abnormalitiesradha1000100% (1)
- Quick Reference GuideDocumento2 páginasQuick Reference GuideHoàng Anh NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Intern TutorialDocumento288 páginasIntern TutorialtoffeepolAinda não há avaliações
- Syncope in Adults - Clinical Manifestations and Initial Diagnostic Evaluation - UpToDateDocumento21 páginasSyncope in Adults - Clinical Manifestations and Initial Diagnostic Evaluation - UpToDateBruno FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- Backwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultDocumento120 páginasBackwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultAndra Elena Pricop100% (2)
- Ekg BasicDocumento24 páginasEkg BasicGhica CostinAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormalities Caused by LBBBDocumento6 páginasAbnormalities Caused by LBBBLiliappAinda não há avaliações
- ECG LectureDocumento37 páginasECG LectureAmit Pannu100% (1)
- s1c11 ECG - Supplement PDFDocumento108 páginass1c11 ECG - Supplement PDFVisan Andreea Mihaela RamonaAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocumento8 páginasNormal Sinus RhythmRosalyn YuAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Pain: Caitlin Everson (Clinical Fellow AED)Documento194 páginasChest Pain: Caitlin Everson (Clinical Fellow AED)lisserranoAinda não há avaliações
- Ehab364 SuppDocumento32 páginasEhab364 SuppEffika Nurningtyas PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Left Bundle Branch Block LBBBDocumento5 páginasLeft Bundle Branch Block LBBBFathimah afifah zahrahAinda não há avaliações