Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Fungsi Mata Dan Kulit
Enviado por
Nova SuryatiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fungsi Mata Dan Kulit
Enviado por
Nova SuryatiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
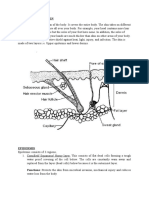
The function of the parts of eye
Part Palpebral, eyelashes, eyebrows lacrimal gland) Function Eye protection Produce lacrimal. Lacrimal secretion containing mucus, salt, and antibacterial enzymes lizozim. To : cleaning, protecting, moisturizing and lubricating the eye surface (conjunctiva and cornea) Produce an oily secretion that forms a layer on the surface of the tear film. This function prevents the evaporation of the tear film Produce secretions that are drawn to the eyelash follicles
Tarsal glands
Sweat glands
Cornea
Sclera Humour aquous
Transmits light and focuses the light beam
Maintain eye shape and protect delicate structures beneath and as a attachment point for muscles extrinsic Is a product of epithelial siliaris that flowing into the camera eye anterior and posterior. It will rinse the cornea and lens nonvascular and deliver nutrients and oxygen The entry of light into the interior of the eye
Pupil
Part Iris
Function Set the amount of light entering the eye. The muscles of the iris: smooth muscle - When the circular muscle contraction will shrink pupils, stimulated by the light that protects the retina - Radial muscles from the edge of the pupil, the contract cause dilated pupils. When the light is weak, the muscles contract it cause pupillary dilation to include more light Preventing internal retina reflection light beam, give the nutrients to the retina and vitreous corpus, and can pull the suspensory ligament Role in the refraction of light (refraction) and also bend the light to be focused on the retina Lens capsule: change the shape of the lens and protects the corpus vitreous and aquosus humor, and was instrumental in the process of accommodation Deliver incoming light, is nonrefractive in relation to the lens, forming role intraocular eye pressure, and hold the retina in the pigmented layer of the eyeball Photoreceptor
Choroid
Lensa
The corpus vitreous
Retina
The main function of skin:
1. protection Epithelial-coated with a layer of horn protects against mechanical abrasion of the body surface and form a physical barrier against foreign pathogens or other microorganisms. Because there glycolipid layer between the stratum granulosum, epidermis also permeable to water. This layer also prevents the loss of body fluids through dehydration. Increased synthesis of the melanin pigment to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation 2. temperature regulation Sweating allows partial loss of body heat through the evaporation of sweat from the body surface. In addition to sweat, thermoregulation involves dilation of blood vessels allowing maximum blood flow to the skin. This function increases the heat expenditure. And in the cold temperatures, body heat is maintained by constricting blood vessels and decrease blood flow to the skin 3. sensory perception In the skin there are many sensory nerves
4. excretion through the formation of sweat by the sweat glands of water, saline solution, urea and nitrogenous waste products can be excreted through the skin's surface 5. Formation of vitamin D When skin is exposed to ultraviolet rays from the sun, vitamin D is formed from precursor molecules are
Você também pode gostar
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocumento6 páginasIntegumentary System ReviewerKrize Colene dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- The Eye and The SkinDocumento19 páginasThe Eye and The SkinFezel HamiltonAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5No EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Chapter One Basic Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye: BY DR - Sawsan Hussein Mahgoub Consultant OphthalmologistDocumento15 páginasChapter One Basic Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye: BY DR - Sawsan Hussein Mahgoub Consultant OphthalmologistMarceloAinda não há avaliações
- Skin PhysiologyDocumento7 páginasSkin PhysiologyYash PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary SystemDocumento19 páginasThe Integumentary SystemInigo Galima SusanAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Anatomy of The Eye BallDocumento6 páginas1-Anatomy of The Eye BalltressAinda não há avaliações
- The Physiology of The SkinDocumento39 páginasThe Physiology of The SkinElvisAinda não há avaliações
- Your Guide to the Integumentary SystemDocumento4 páginasYour Guide to the Integumentary SystemShyeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of External EyeDocumento39 páginasAnatomy of External EyeUzma KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Topical Relief From Tropical Prickly HeatDocumento5 páginasTopical Relief From Tropical Prickly HeatavijeetAinda não há avaliações
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasesDocumento181 páginasThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasessanjivdasAinda não há avaliações
- IntegumentaryDocumento6 páginasIntegumentarytrisha anne uberasAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER5 Form2Documento14 páginasCHAPTER5 Form2basraawi379Ainda não há avaliações
- Integumentary SystemDocumento16 páginasIntegumentary SystemFlorinel B. LACATANAinda não há avaliações
- Unit III. The Integumentary SystemDocumento73 páginasUnit III. The Integumentary SystemLara C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento12 páginasChapter 2basraawi379Ainda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System HandoutDocumento18 páginasIntegumentary System HandoutbarchlrAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento45 páginasUntitledc/risaaq yuusuf ColoowAinda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary System: Your Skin and Its FunctionsDocumento42 páginasThe Integumentary System: Your Skin and Its FunctionsGabAinda não há avaliações
- Notes On Eye of RabbitDocumento3 páginasNotes On Eye of RabbitShailesh NiroulaAinda não há avaliações
- ANAPHY Reviewer IntegumentaryDocumento6 páginasANAPHY Reviewer Integumentaryjade tanAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary SystemDocumento5 páginasIntegumentary Systemrubelyn.caratikitAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System: Skin, Glands, Hair & NailsDocumento20 páginasIntegumentary System: Skin, Glands, Hair & NailsMarielle Ann RumbaoaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYDocumento40 páginasAnatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYhenok birukAinda não há avaliações
- The Structure and Functions of SkinDocumento6 páginasThe Structure and Functions of SkinJad JawhariAinda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary System: Functions and Disorders of the Largest OrganDocumento24 páginasThe Integumentary System: Functions and Disorders of the Largest OrganMichael Ramirez100% (1)
- Medical Students Guide to the Integumentary SystemDocumento32 páginasMedical Students Guide to the Integumentary SystemZea Mae AgirAinda não há avaliações
- EyeDocumento9 páginasEyeMont HanaAinda não há avaliações
- Yoga & Eye - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento73 páginasYoga & Eye - Anatomy and Physiologysachi sharma0% (1)
- PBL Eye No1,2,3Documento9 páginasPBL Eye No1,2,3adelaAinda não há avaliações
- Organ Systems ModuleDocumento6 páginasOrgan Systems ModuleJayAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3 Midterm LaboratoryDocumento4 páginasActivity 3 Midterm LaboratoryRej CosainAinda não há avaliações
- 3 The Integumentary System: Section IDocumento18 páginas3 The Integumentary System: Section IVõ ĐứcAinda não há avaliações
- The Skin NotesDocumento7 páginasThe Skin NotesSafeer SefiAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary SystemDocumento34 páginasIntegumentary SystemJerneth Nyka FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocumento3 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglAinda não há avaliações
- 16 A P Integumentary HandoutDocumento19 páginas16 A P Integumentary Handoutapi-300931855Ainda não há avaliações
- The Mammalian Skin and LiverDocumento7 páginasThe Mammalian Skin and LiverHarun IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocumento5 páginasAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemSmol PadernalAinda não há avaliações
- TDDSDocumento110 páginasTDDSp.ishaanpawarAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation Integumentary SystemDocumento11 páginasPresentation Integumentary SystemEstrella ApuyaAinda não há avaliações
- Skin and Breast HistologyDocumento8 páginasSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and Function of SkinDocumento4 páginasStructure and Function of SkinSarah AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EYEDocumento70 páginasANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EYEArif MohammadAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary Sytem ReviewerDocumento2 páginasIntegumentary Sytem ReviewerNors SulaboAinda não há avaliações
- 03 The Integumentary SystemDocumento48 páginas03 The Integumentary SystemLucy Kare100% (1)
- Embryology of the Integumentary System DevelopmentDocumento3 páginasEmbryology of the Integumentary System DevelopmentJonathan PaghubasanAinda não há avaliações
- Cuidado de La PielDocumento22 páginasCuidado de La PielSummer HorneAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocumento8 páginasChapter 5 IntegumentaryClark Jeth VicenteAinda não há avaliações
- By Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorDocumento14 páginasBy Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorOphthalmology DiscussionAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocumento22 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBalkos 61Ainda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary SystemDocumento23 páginasThe Integumentary Systemtareqhaddad123Ainda não há avaliações
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: INNER EYEDocumento71 páginasANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: INNER EYEGermanyAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology of Lacrimal Secretion & Outflow: DR - Nurcahya Ab, SPMDocumento51 páginasAnatomy & Physiology of Lacrimal Secretion & Outflow: DR - Nurcahya Ab, SPMsaddamAinda não há avaliações
- Pragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinDocumento4 páginasPragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinNeelofur Ibran AliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter I - DermatologyDocumento2 páginasChapter I - DermatologyIndranil SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury: Review: Blood Research & Transfusion JournalDocumento4 páginasRenal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury: Review: Blood Research & Transfusion JournalNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Miringitis BulosaDocumento1 páginaMiringitis BulosaNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury An Update PDFDocumento8 páginasAcute Kidney Injury An Update PDFAmanda Besta RizaldyAinda não há avaliações
- Injuria Renal Aguda Enfoque Moderno Terapeutico 2014Documento5 páginasInjuria Renal Aguda Enfoque Moderno Terapeutico 2014s4nty13Ainda não há avaliações
- Ijcri 1056610201566 AbdelreheemDocumento6 páginasIjcri 1056610201566 AbdelreheemNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- GuillainDocumento1 páginaGuillainNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart Disease: Mitral RegurgitationDocumento33 páginasValvular Heart Disease: Mitral RegurgitationyantoAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah ECG 1Documento64 páginasKuliah ECG 1Adriyan SikumalayAinda não há avaliações
- MITRAL VALVE REPAIR SURGERYDocumento22 páginasMITRAL VALVE REPAIR SURGERYNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- JURNALDocumento6 páginasJURNALNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Aortic Stenosis: Yerizal Karani MD Cardiology Division Faculty of Medicine Andalas UniversityDocumento29 páginasAortic Stenosis: Yerizal Karani MD Cardiology Division Faculty of Medicine Andalas UniversityNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Review For General PractitionersDocumento6 páginasIdiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Review For General PractitionersNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Heart Disease: Aortic RegurgitationDocumento14 páginasValvular Heart Disease: Aortic Regurgitationnurul ramadhiniAinda não há avaliações
- SGBDocumento6 páginasSGBNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseDocumento9 páginasBacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Herpes Zoster, New Preventive PerspectiveDocumento4 páginasHerpes Zoster, New Preventive PerspectiveNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Miringitis TreatmenDocumento7 páginasMiringitis TreatmenAnsh NviariyntiAinda não há avaliações
- Randomized Clinical Trial of Antibiotic Therapy Versus Appendicectomy As Primary Treatment of Acute Appendicitis in Unselected PatientsDocumento9 páginasRandomized Clinical Trial of Antibiotic Therapy Versus Appendicectomy As Primary Treatment of Acute Appendicitis in Unselected PatientsNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Varicella GuidelineDocumento6 páginasVaricella GuidelineMonika Margareta Maria ElviraAinda não há avaliações
- JOURNALDocumento8 páginasJOURNALNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- 869 840 1 PBDocumento11 páginas869 840 1 PBNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- HydrosefalusDocumento19 páginasHydrosefalusarina windri rivartiAinda não há avaliações
- Miringitis BulosaDocumento1 páginaMiringitis BulosaNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- VARICELADocumento11 páginasVARICELANova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Journal About VaricellaDocumento9 páginasJournal About VaricellaNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Health20100200010 76627800 PDFDocumento10 páginasHealth20100200010 76627800 PDFNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- JURNALDocumento6 páginasJURNALNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal VariselaDocumento7 páginasJurnal VariselaNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Varisela ZosterDocumento19 páginasJurnal Varisela ZosterNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah GGN PubertasDocumento56 páginasKuliah GGN PubertasNova SuryatiAinda não há avaliações
- About Nysc Ict CD in Imo StateDocumento9 páginasAbout Nysc Ict CD in Imo StateIsoft PexAinda não há avaliações
- Mugunthan ResumeDocumento4 páginasMugunthan Resumeapi-20007381Ainda não há avaliações
- Professional Teaching ResumeDocumento2 páginasProfessional Teaching Resumeapi-535361896Ainda não há avaliações
- Work Breakdown StructureDocumento3 páginasWork Breakdown StructureEllie Annelle LazaroAinda não há avaliações
- ID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFDocumento17 páginasID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFsabila azilaAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDocumento26 páginasFundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDanielYoungabrn100% (60)
- Sugar Cane White FlyDocumento13 páginasSugar Cane White Flyvishnu0751Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 03Documento2 páginasAssignment 03Molto falsoAinda não há avaliações
- Eight Principles of Ethical Leadership in EducationDocumento2 páginasEight Principles of Ethical Leadership in EducationKimberly Rose Nativo100% (1)
- SPELD SA A Trip To The Top End-DSDocumento16 páginasSPELD SA A Trip To The Top End-DSThien Tho NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 8Documento2 páginasUnit 8The Four QueensAinda não há avaliações
- The CIA Tavistock Institute and The GlobalDocumento34 páginasThe CIA Tavistock Institute and The GlobalAnton Crellen100% (4)
- Case Study Analysis of Six Sigma Implementation Inservice OrganisationsDocumento30 páginasCase Study Analysis of Six Sigma Implementation Inservice OrganisationsMohammed AwolAinda não há avaliações
- Draft Resolution 1.1 SPECPOL LUMUN 2013Documento8 páginasDraft Resolution 1.1 SPECPOL LUMUN 2013Hamza Hashim100% (1)
- Class 6 - The Banyan TreeDocumento5 páginasClass 6 - The Banyan Tree7A04Aditya MayankAinda não há avaliações
- 1000arepas Maythuna Aceituna Una YogaDocumento164 páginas1000arepas Maythuna Aceituna Una YogaDaniel Medvedov - ELKENOS ABE100% (1)
- Thank You LetterDocumento2 páginasThank You LetterFathina57% (7)
- Worksheet Pirates of The Caribbean Curse of TheDocumento3 páginasWorksheet Pirates of The Caribbean Curse of TheAylin Acar0% (1)
- People v. Sandiganbayan (Evidence)Documento2 páginasPeople v. Sandiganbayan (Evidence)donnamariebollosAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Mesina v. PeopleDocumento7 páginas05 Mesina v. PeopleJason ToddAinda não há avaliações
- Compulsive Buying Tendency As A Predictor of Attitudes and PerceptionsDocumento4 páginasCompulsive Buying Tendency As A Predictor of Attitudes and PerceptionsvsharanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 01 Who Is A Contributor PDFDocumento28 páginasUnit 01 Who Is A Contributor PDFKumpavatJayarajsinhAinda não há avaliações
- scn625 Summativeeval SarahltDocumento6 páginasscn625 Summativeeval Sarahltapi-644817377Ainda não há avaliações
- Management Review, 32: 794-816.: Daftar PustakaDocumento8 páginasManagement Review, 32: 794-816.: Daftar PustakaNurulsalamah28Ainda não há avaliações
- A Summer's Reading - Sample Questions With AnswersDocumento11 páginasA Summer's Reading - Sample Questions With AnswersRoy SchwartzAinda não há avaliações
- Antenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineDocumento2 páginasAntenna & Wave Propagation - Course OutlineSabuj AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Rock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionDocumento7 páginasRock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionChad HorsleyAinda não há avaliações
- Corruption PDFDocumento11 páginasCorruption PDFkaleemullahAinda não há avaliações
- HI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Documento3 páginasHI6025 Assignment T3, 2016Abeer ArifAinda não há avaliações
- Dilo SpaDocumento2 páginasDilo SpajosefAinda não há avaliações