Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
FRQ Modern Physics
Enviado por
ericpwuTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
FRQ Modern Physics
Enviado por
ericpwuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AP Physics Summer Institute
2007
Free-Response-Questions
MODERN PHYSICS
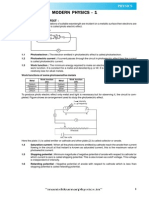
1980B3. In a photoelectric experiment, radiation of several
different frequencies was made to shine on a metal surface
and the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons was
measured at each frequency. Selected results of the
experiment are presented in the table below:
Frequency (Hz)
Maximum Kinetic Energy
of Electrons (eV)
0.5 x 10
15
No electrons ejected
1.0 x 10
15
1.0
1.5 x 10
15
3.0
2.0 x 10
15
5.0
a. On the axes below, plot the data from this photoelectric
experiment.
b. Determine the threshold frequency of the metal surface.
c. Determine the work function of the metal surface.
d. When light of frequency 2.0 x 10
15
Hz strikes the metal
surface, electrons of assorted speeds are ejected from the
surface. What minimum retarding potential would be
required to stop all of the electrons ejected from the surface
by light of frequency 2.0 x 10
15
Hz?
e. Investigation reveals that some electrons ejected from the
metal surface move in circular paths Suggest a reasonable
explanation for this electron behavior.
1983B6. An experiment is conducted to investigate the
photoelectric effect. When light of frequency 1.0 x 10
15
Hz is
incident on a photo cathode, electrons are emitted. Current due to
these electrons can be cut off with a 1.0-V retarding potential. Light
of frequency 1.5 x 10
15
Hz produces a photoelectric current that
can be cut off with a 3.0-V retarding potential.
a. Calculate an experimental value of Planck's constant based on
these data.
b. Calculate the work function of the photo cathode.
c. Will electrons be emitted from the photo cathode when
green light of wavelength 5.0 x 10
-7
m is incident on the photo
cathode? Justify your answer.
a. Determine the frequency of the lowest energy photon that
could ionize the atom, initially in its ground state.
1985B6. An energy-level
diagram for a hypothetical
atom is shown
b. Assume the atom has
been excited to the state
at -1.0 eV.
i. Determine the wavelength of the photon for each possible
spontaneous transition.
ii. Which, if any, of these wavelengths are in the visible
range?
c. Assume the atom is initially in the ground state. Show on the
following diagram the possible transitions from the ground state
when the atom is irradiated with electromagnetic radiation of
wavelengths ranging continuously from 2.5x10
-7
m to 10.0x10
-7
m.
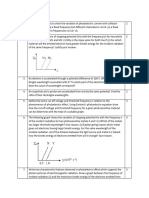
1987B6. In a photoelectric experiment, light is incident on a
metal surface. Electrons are ejected from the surface,
producing a current in a circuit. A reverse potential is applied
in the circuit and adjusted until the current drops to zero.
That potential at which the current drops to zero is called the
stopping potential. The data obtained for a range of
frequencies are graphed below.
a. For a frequency of light that has a stopping potential of 3 V, what
is the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons?
b. From the graph and the value of the electron charge,
determine an experimental value for Planck's constant.
c. From the graph, determine the work function for the metal.
d. On the axes above, draw the expected graph for a different
metal surface with a threshold frequency of 6.0 x 10
14
Hz.
Você também pode gostar
- FRQ Modern PhysicsDocumento22 páginasFRQ Modern PhysicsIvycrazeAinda não há avaliações
- Photoelectric OLD EXAM QsDocumento4 páginasPhotoelectric OLD EXAM QsericpwuAinda não há avaliações
- Atoms: Photons and The Photoelectric Effect Questions: SODIUM LAMPS (2012 2)Documento7 páginasAtoms: Photons and The Photoelectric Effect Questions: SODIUM LAMPS (2012 2)muhammadfaisal327170% (1)
- Nbts 2014 Photoelectric Q ADocumento20 páginasNbts 2014 Photoelectric Q Amustafa alasadyAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Phy Assi SubDocumento4 páginasModern Phy Assi SubNikhilPrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Photoelectric Effect2Documento40 páginasChapter 3 Photoelectric Effect2moxsueAinda não há avaliações
- Dual NatureDocumento19 páginasDual NaturebenitxmxnuAinda não há avaliações
- Alevel PhysicsDocumento4 páginasAlevel PhysicsDora AyeAinda não há avaliações
- PYL100 Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum Mechanics Exercise SheetDocumento2 páginasPYL100 Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum Mechanics Exercise SheetFranklin GarysonAinda não há avaliações
- Compton Effect, Photoelectric Effect, Blackbody Radiation, PhotoelectronsDocumento2 páginasCompton Effect, Photoelectric Effect, Blackbody Radiation, PhotoelectronsAnand KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocumento13 páginasPhysics Investigatory ProjectDêêpák Sîñgh ÑîtwálAinda não há avaliações
- Read Important Questions Class 12 Physics of Chapter 11Documento67 páginasRead Important Questions Class 12 Physics of Chapter 11SanjukthAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics QuestionsDocumento27 páginasModern Physics Questionsmehalingam nainarAinda não há avaliações
- LILAVATIBAI PODAR SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL (ISC) ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS questionsDocumento3 páginasLILAVATIBAI PODAR SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL (ISC) ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS questionsAnkit BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 - Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation-Saju-HssliveDocumento7 páginasChapter 11 - Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation-Saju-HssliveAmiAinda não há avaliações
- Q Bank Dual Nature & Semiconductor PDFDocumento3 páginasQ Bank Dual Nature & Semiconductor PDFSoham GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 3 Photoelectric Effect PDFDocumento37 páginasChap 3 Photoelectric Effect PDFNiesa IrdinaAinda não há avaliações
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Physics Exam QuestionsDocumento2 páginasJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Physics Exam QuestionsAyush TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics (Nitin M Sir) PDFDocumento14 páginasModern Physics (Nitin M Sir) PDFZaheer Ahmed TanoliAinda não há avaliações
- Photoelectric Effect PhET SimulationDocumento5 páginasPhotoelectric Effect PhET SimulationAnil KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Test Series 3 With Answer KeyDocumento7 páginasTest Series 3 With Answer KeysumithcsujithAinda não há avaliações
- Serway 6 e Problems 40Documento11 páginasSerway 6 e Problems 40Melikşah TürkmenAinda não há avaliações
- Problems For Practice - Dual NatutreDocumento2 páginasProblems For Practice - Dual NatutreSankar KumarasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics (CPP 1 To 3)Documento11 páginasModern Physics (CPP 1 To 3)Priyansh Vaibhav100% (3)
- Dual Nature Worksheet TUITIONDocumento5 páginasDual Nature Worksheet TUITIONAltaf Hussain KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Kvpy Pee PDFDocumento9 páginasKvpy Pee PDFstudysteps.inAinda não há avaliações
- Reg QDocumento78 páginasReg Qruppal42Ainda não há avaliações
- Photoelectric EffectDocumento7 páginasPhotoelectric EffectrujintoAinda não há avaliações
- Class Xi Sample PapersDocumento3 páginasClass Xi Sample PapersAastha ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- M38 Knig9404 Ism C38 PDFDocumento22 páginasM38 Knig9404 Ism C38 PDFnorma_jeannAinda não há avaliações
- New Modern PhysicsDocumento3 páginasNew Modern PhysicsshabbirtechnicalAinda não há avaliações
- Dual Nature Notes - 2014Documento13 páginasDual Nature Notes - 2014Chirag AsarpotaAinda não há avaliações
- Dual Nature Assignment1Documento2 páginasDual Nature Assignment1hsofficial910Ainda não há avaliações
- Atomic Physics 2.photoelectric Effect Points To RememberDocumento10 páginasAtomic Physics 2.photoelectric Effect Points To RememberMAHESH DAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Physics 2.photoelectric Effect Points To RememberDocumento10 páginasAtomic Physics 2.photoelectric Effect Points To RememberMAHESH DAinda não há avaliações
- Dawn of Modern PhysicsDocumento16 páginasDawn of Modern Physicsالفيزيائي MSAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 Quantum Physics StudentDocumento3 páginasChapter 6 Quantum Physics StudentKhairul AznizamAinda não há avaliações
- Modern PhysicsDocumento34 páginasModern PhysicsAditya BansalAinda não há avaliações
- All India Senior Secondary School Certificate Examination (AISSCE-2013-14)Documento10 páginasAll India Senior Secondary School Certificate Examination (AISSCE-2013-14)ScientistAinda não há avaliações
- Photoelectric EffectDocumento10 páginasPhotoelectric EffectScientistAinda não há avaliações
- Planks ConstantDocumento5 páginasPlanks Constantprateekjain01100% (4)
- D NaeDocumento4 páginasD Naehardikharsh.official.hgAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabDocumento3 páginas03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabJuan David ParraAinda não há avaliações
- Homework Set3 ParticlenatureofmatterDocumento2 páginasHomework Set3 Particlenatureofmatteryobrosky0% (1)
- Photoelectric Effect PDFDocumento7 páginasPhotoelectric Effect PDFVenu GopalAinda não há avaliações
- Photo ElectricDocumento7 páginasPhoto Electrictalha aliAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Planck'S ConstantDocumento4 páginasDetermination of Planck'S Constanthoangnghia_hcmupAinda não há avaliações
- EMTL 4 Units Important QuestionsDocumento27 páginasEMTL 4 Units Important Questionsganesh4u_p71% (7)
- Problem Set 1 NewDocumento2 páginasProblem Set 1 Newgm_navyAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions for Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Chapter 11Documento35 páginasNCERT Solutions for Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Chapter 11Parvatham VijayAinda não há avaliações
- APhO2001 Theory Prob 3Documento3 páginasAPhO2001 Theory Prob 3Popovici DraganAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics PDFDocumento46 páginasModern Physics PDFMarcos ShepardAinda não há avaliações
- 6705858915a075e6c3247ac7f051671fDocumento21 páginas6705858915a075e6c3247ac7f051671fAAVANIAinda não há avaliações
- Richard Modern Physics Solved QuestionsDocumento33 páginasRichard Modern Physics Solved Questionsmurugan_kribhcoAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyAinda não há avaliações
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7No EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Ainda não há avaliações
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNo EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Case 2Documento2 páginasCase 2Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Arabic Exam 4 - 1Documento6 páginasArabic Exam 4 - 1Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- ChingLiu Install NotesDocumento1 páginaChingLiu Install NotesLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Multi Gravity Separation Systems 20111Documento2 páginasMulti Gravity Separation Systems 20111Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Hindu Arabic Numeration SystemDocumento10 páginasHindu Arabic Numeration SystemLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 6Documento3 páginasLab 6Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Psychoacoustic Analysis Methods in ArtemiS SoftwareDocumento13 páginasPsychoacoustic Analysis Methods in ArtemiS SoftwareLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- HAAD Exam TipsDocumento3 páginasHAAD Exam TipsLowry Guetta100% (1)
- Sample Questions For HaadDocumento15 páginasSample Questions For HaadBrian Balan79% (14)
- Conjungo Com Technology Outsourcing Bpo Types of BusDocumento3 páginasConjungo Com Technology Outsourcing Bpo Types of BusLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Contract InterpretationDocumento30 páginasContract InterpretationLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Hello world greetingsDocumento1 páginaHello world greetingsLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 EC Social Networks Auctions PortalsDocumento46 páginas12 EC Social Networks Auctions PortalsRayhan AtunuAinda não há avaliações
- Hindu Arabic Numeration SystemDocumento10 páginasHindu Arabic Numeration SystemLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- History 102 Paper 2Documento5 páginasHistory 102 Paper 2Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Read MeDocumento2 páginasRead MeLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- NamesDocumento1 páginaNamesLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Hello world greetingsDocumento1 páginaHello world greetingsLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- LettersDocumento1 páginaLettersLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- MIT RecommendationsDocumento1 páginaMIT RecommendationsLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- OlympiadDocumento1 páginaOlympiadLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Booklet - Hold On 'Til The NightDocumento19 páginasDigital Booklet - Hold On 'Til The NightLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Character Sheet - Nomad V3.5adfasfDocumento2 páginasCharacter Sheet - Nomad V3.5adfasfLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- UCLA Physics6C Lab ManualDocumento86 páginasUCLA Physics6C Lab ManualLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Quotes For TatoosDocumento1 páginaQuotes For TatoosLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- OIOIOIOIOIOIDocumento1 páginaOIOIOIOIOIOILowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Lego City - 30150Documento2 páginasLego City - 30150Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- LEGO TechniquesDocumento37 páginasLEGO TechniquesBunnyCoder1100% (3)
- Hakan, Convoker of The WildDocumento2 páginasHakan, Convoker of The WildLowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações