Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Plant Reproduction Systems Explained
Enviado por
Izzati Zulaikha Amy0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
113 visualizações30 páginasplant reproduction system
Título original
Plant Reproduction System
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoplant reproduction system
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
113 visualizações30 páginasPlant Reproduction Systems Explained
Enviado por
Izzati Zulaikha Amyplant reproduction system
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 30
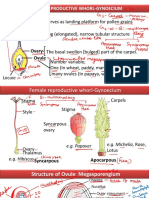
PLANT REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
The reproduction mechanism of a
particular plant species or the way
it reproduces determines
its genetic characteristics
the breeding approach.
1. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Using sex organs to form
next generation / to produce
seeds.
Important steps:
1. Production of gametes (gametogenesis)
2. Pollination Transfer of pollen from anther
(male organ) to the stigma (female organ).
3. Fertilization The union of male and female
gametes to produce new genotypes.
1. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION (CONT.)
POLLINATION
Transfer of pollen from anther
(male organ) to the stigma
(female organ).
Two kinds of pollination,
Self pollination
Cross pollination
Transfer of pollen from
anther to stigma of the
same flower / plant
SELF POLLINATION
Natural mechanisms that
encourages self pollination:
1. Cleistogamy
Pollination happens when
flower is still closed.
Example: Rice
SELF POLLINATION
2. Stigma protected by
anther
Anthesis and pollination
occur instantaneously
once the flower blooms.
Many pollen are
produced, covering the
stigma, hence
preventing pollination by
pollen from outside.
Example: lime, tomato
and chilli
SELF POLLINATION (CONT.)
Chilli flower
3. Stigma and anther
protected by other parts of
flower.
Male (stamen) and
female (pistil) organs
covered by keel, i.e. two
fused petals.
Example: Leguminosae
family, sub-family
Papilionoideae.
SELF POLLINATION (CONT.)
Transfer of pollen from
anther to stigma of flower of
different plant.
CROSS POLLINATION
Natural mechanisms to
promote cross pollination:
1. Dieocious
Male and female flowers are
formed on different plants.
Have male and female
plants.
Example: Papaya, salak
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
Male salak flower
Female salak flower
2. Monoecious
Male and female
flowers are in
separate positions
on the same plant
but mature at
slightly different
times.
Example: Oil palm, corn
and rubber.
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
3. Dichogamy
Anther and stigma from
hemaphrodite flower or
flower of monoecious
plant mature at different
times.
Protogyne
Stigma (female flower)
matures before anther (male
flower).
Example: Potato, cassava
and cashew.
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
Protogyne: Potato
flower
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
3. Dichogamy (cont.)
Protandry
Anther (male flower)
matures before stigma
(female flower).
Example: Starfruit and
rubber.
Protandry: Starfruit
flower
4. Self-incompatibility
Pollens are unable to fertilize
ovule (female gamete) of the
same flower/plant due to
genetic factor (self
incompatibility gene)
Example: Potato, passion fruit and
starfruit.
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
In some species, there are more than
one mechanism to promote cross
pollination:
1. Rubber and corn: monoecious and
protandry.
2. Potato, Sweet potato: Self-
incompatibility and protogyne
3. Starfruit & passion fruit: Self-
incompatibility and protandry
CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.)
METHODS TO DETERMINE
MODES OF POLLINATION
1. Identify flower formation system.
2. Isolate plants.
No fruit/seed cross pollinated
Fruit set/seed set self pollinated and
possibly cross pollinated
3. Selfing.
To observe the effects of inbreeding.
Present cross pollinated.
Absent / minimal self pollinated.
2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Does not involve sex or union
of male and female gametes.
Mechanisms:-
1. Vegetative reproduction
2. Apomixis
VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION
o Stem/branch/root cuttings
e.g. cassava
o Grafting e.g. rubber,
rambutan & durian
o Rhizome e.g. tumeric &
ginger
o Stolon e.g. grass
o Tuber e.g. potato & sweet
potato
o Tiller e.g. pineapple ,
sugarcane & banana
APOMIXIS
Formation of seeds without
union of gametes, i.e.
fertilization.
APOMIXIS (CONT.)
Apogamy Embryo formation from synergids or
antipodals
Apospory Embryo develops
from somatic cell such as
nucellus and integument.
Diplospory Embryo develops
from megasporocyte.
Adventitious embryo Embryo
develops directly from nucellus
and integument cells without
involving embryo sac cells.
Parthenogenesis Embryo
develops from unfertilized eggs.
APOMIXIS (CONT.)
1. Obligate apomixis
Apomixis reproduction
is the main method of
reproduction.
Example: mangosteen
APOMIXIS (CONT.)
2. Facultative
apomixis
Both apomixis and
sexual reproduction
occur.
Example: Guinea
grass (Panicum
maximum), Citrus
sp.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CROSS
POLLINATED, SELF POLLINATED AND
ASEXUAL PLANTS
Characteristic Cross
pollinated
Self pollinated Asexual
Population Heterogeneous Homogeneous Homogeneous
Genotype Heterozygous Homozygous Heterozygous
Gamete Different Similar Different
Progeny Different &
heterozygous
Similar &
homozygous
Similar &
heterozygous
Inbreeding
depression
Present Absent Present
Incompatibility Present Absent Present
Você também pode gostar
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3Ainda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Organisms ExplainedDocumento25 páginasReproduction in Organisms ExplainedSHRIRAM JOSHIAinda não há avaliações
- Gardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4No EverandGardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4Ainda não há avaliações
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento9 páginasSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDikansha JasaiwalAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionDocumento30 páginasSelf-Incompatibility Lecture Outlines Flower Structure and ReproductionlkokodkodAinda não há avaliações
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Documento12 páginas3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonAinda não há avaliações
- Plant reproduction: Asexual vs sexual processesDocumento9 páginasPlant reproduction: Asexual vs sexual processesregine gamaleAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Passing Pacakage KarthikDocumento22 páginasBiology Passing Pacakage Karthikvarshithajadhav6Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocumento80 páginasChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068Ainda não há avaliações
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento10 páginasSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsOmpriya SAinda não há avaliações
- Anther&Pollen CultureDocumento17 páginasAnther&Pollen CulturenadyaawlAinda não há avaliações
- Modes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in VegetablesDocumento46 páginasModes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in Vegetablessyamkavitha100% (4)
- How Do Org ReproduceDocumento32 páginasHow Do Org ReproducePankaj Kumar100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento11 páginasCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsNada NavasAinda não há avaliações
- ReproductionDocumento29 páginasReproductionWapapha Gen-Rev MuzilaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento7 páginas12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsJatin kumar100% (1)
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Documento25 páginasBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Plants NotesDocumento5 páginasReproduction in Plants Notesalviayaan807Ainda não há avaliações
- Flowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityDocumento4 páginasFlowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityJobadzAinda não há avaliações
- Female Reproductive Structure and FunctionDocumento21 páginasFemale Reproductive Structure and FunctionAyush bhadaniAinda não há avaliações
- Plus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionDocumento170 páginasPlus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionLena AlbertAinda não há avaliações
- Course Content: Flowers Embriogenesis 3. Mikrosporangium 4. Male Gametophyte 5. Megasporangium 6. Female GametophyteDocumento12 páginasCourse Content: Flowers Embriogenesis 3. Mikrosporangium 4. Male Gametophyte 5. Megasporangium 6. Female GametophyteChandra AdieAinda não há avaliações
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocumento7 páginasLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelAinda não há avaliações
- Plant and Animal Reproduction Processes ComparedDocumento16 páginasPlant and Animal Reproduction Processes Comparedhellohelloworld100% (1)
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Documento10 páginasReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesAinda não há avaliações
- Plant ReproductionDocumento8 páginasPlant ReproductionayanurhidayahAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento35 páginasSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKumar Munendra PrfAinda não há avaliações
- Hybrid Seed ProductionDocumento67 páginasHybrid Seed ProductionHarsh Vardhan Singh ShekhawatAinda não há avaliações
- Megasporangium and Female Gametophyte FormationDocumento16 páginasMegasporangium and Female Gametophyte FormationVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BAinda não há avaliações
- Final ReportDocumento41 páginasFinal ReportMickeyAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocumento26 páginasReproduction in OrganismsRakesh S. GourAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasDocumento26 páginasChapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasSNOWCHILL VINESAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual ReproductionDocumento19 páginasSexual ReproductionjojopebblesAinda não há avaliações
- MF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2Documento27 páginasMF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2PikuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4. Reproductive SystemsDocumento35 páginasChapter 4. Reproductive Systemsalemneh bayehAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeDocumento23 páginasLECTURE 6 Perpetuation of LifeJemuel LuminariasAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento75 páginasReproduction in Flowering PlantsEdward BradshawAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13Documento31 páginasCH 13Lynden100% (1)
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 6 by RajatDocumento32 páginasRajkumar Biology Unit - 6 by RajatayonavobrownAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocumento30 páginasClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerSufiyanAinda não há avaliações
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocumento15 páginasModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- Unit 8 Sy PollinationDocumento17 páginasUnit 8 Sy Pollinationvaibhavbarde287Ainda não há avaliações
- Plant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentDocumento22 páginasPlant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentNix TanAinda não há avaliações
- Flowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesDocumento76 páginasFlowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesRaja InaAinda não há avaliações
- 16. REPRODUCTIONDocumento32 páginas16. REPRODUCTIONArpita SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Documento8 páginasEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento17 páginasChapter 6sheisbonjing PHAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocumento3 páginasSexual Reproduction in Plantsmallorca albertAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Living OrganismsDocumento38 páginasReproduction in Living OrganismsRishi KeshAinda não há avaliações
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocumento53 páginasAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductioncriselAinda não há avaliações
- Asexual ReproductionDocumento3 páginasAsexual ReproductionmohangeneAinda não há avaliações
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocumento9 páginasGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaAinda não há avaliações
- 3. Reproduciton in crops Plant 2023Documento68 páginas3. Reproduciton in crops Plant 2023lemma4aAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocumento7 páginasChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocumento49 páginasPlant Reproduction and DevelopmentSK GamingAinda não há avaliações
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideDocumento3 páginasRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento22 páginasChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSushil RajbharAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento9 páginasClass 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsVerma AjjuAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Plants: Sexual vs AsexualDocumento12 páginasReproduction in Plants: Sexual vs AsexualAnand Philip PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Plant ReproductionDocumento6 páginasTypes of Plant ReproductionNaNa Liyana Elias IAinda não há avaliações
- Amaranthus Graecizans (Prostrate Pigweed)Documento4 páginasAmaranthus Graecizans (Prostrate Pigweed)Izzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Plant BreedingDocumento10 páginasPlant BreedingIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Bacillus Subtilis PlantDocumento5 páginasBacillus Subtilis PlantIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- BDocumento4 páginasBIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- ChapterDocumento48 páginasChapterIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Experemint 10Documento4 páginasExperemint 10Izzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- APA Referencing 6th Ed Quick GuideDocumento2 páginasAPA Referencing 6th Ed Quick GuidehartymAinda não há avaliações
- Azolla Fact Sheet - Benefits and Management of the Aquatic FernDocumento2 páginasAzolla Fact Sheet - Benefits and Management of the Aquatic FernSaurav GutgutiaAinda não há avaliações
- Azolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaDocumento29 páginasAzolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report ExampleDocumento7 páginasLab Report ExampleIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Azolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaDocumento29 páginasAzolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Azolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaDocumento29 páginasAzolla as a biofertiliser in AfricaIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Studies On Planktonic Blue-Green Algae 7Documento0 páginaStudies On Planktonic Blue-Green Algae 7Izzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Emission SpectrosDocumento18 páginasAtomic Emission Spectrosmatin5Ainda não há avaliações
- EPH 7112 Lecture 1 IntroductionDocumento22 páginasEPH 7112 Lecture 1 IntroductionSyed Zafirna W HAinda não há avaliações
- Musa Banana PlantainDocumento33 páginasMusa Banana Plantainrenato05100% (1)
- Protandric Simultaneous Hermaphroditism in Marine ShrimpDocumento9 páginasProtandric Simultaneous Hermaphroditism in Marine ShrimpANALIZEEEEEEEAinda não há avaliações
- Aquatic Sciences and Fisheries AbstractsDocumento298 páginasAquatic Sciences and Fisheries AbstractsRaja DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- ZK Article 4259 en 1Documento23 páginasZK Article 4259 en 1Luis sawakiAinda não há avaliações
- Un FruitfulnessDocumento20 páginasUn FruitfulnessVikas JainAinda não há avaliações
- The King Soldier Bream Auto Saved)Documento8 páginasThe King Soldier Bream Auto Saved)tariqmaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Hatchery Technology of GrouperDocumento68 páginasHatchery Technology of GrouperAbdul NazarAinda não há avaliações
- Life History Strategy Separate Sexes FinalDocumento18 páginasLife History Strategy Separate Sexes FinalFranco Xavier CalderónAinda não há avaliações
- Sex DifferentiationDocumento59 páginasSex DifferentiationAndreoli CorreiaAinda não há avaliações
- EarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod23 PerpetuationOfLife V1Documento23 páginasEarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod23 PerpetuationOfLife V1Roseman TumaliuanAinda não há avaliações
- Bruce Miller-Early Life History of Marine Fishes-University of California Press (2009)Documento377 páginasBruce Miller-Early Life History of Marine Fishes-University of California Press (2009)Daniel Fernández100% (3)
- Fish Reproduction StrategiesDocumento30 páginasFish Reproduction StrategiesWahyuniFanggiTasikAinda não há avaliações
- Palm 2016Documento13 páginasPalm 2016Boran KzAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Development and Reproductive Demography of The Green Humphead Parrotfish Bolbometopon Muricatum in The Solomon IslandsDocumento12 páginasSexual Development and Reproductive Demography of The Green Humphead Parrotfish Bolbometopon Muricatum in The Solomon IslandsHaliliAinda não há avaliações
- CRPSCI 1100-Module6Documento18 páginasCRPSCI 1100-Module6carbonel.carlaAinda não há avaliações
- Avocado Pollination StudyDocumento5 páginasAvocado Pollination StudyCarlos CarvajalAinda não há avaliações
- Sex Determination and Sex Differentiation in FishDocumento174 páginasSex Determination and Sex Differentiation in Fishtrunghieu85Ainda não há avaliações
- Reproductive Character of The Ricefield EelDocumento14 páginasReproductive Character of The Ricefield EelnesaAinda não há avaliações
- Diversity of Microbes and Life on EarthDocumento75 páginasDiversity of Microbes and Life on EarthSaulrj3Ainda não há avaliações
- Avocado Cultivation Guide for IndiaDocumento17 páginasAvocado Cultivation Guide for IndiadonbosskissAinda não há avaliações
- Problem of UnfruitfulnessDocumento6 páginasProblem of UnfruitfulnessRockyAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science Reproduction LessonDocumento2 páginasEarth and Life Science Reproduction LessonZild Frigg CorbitaAinda não há avaliações
- CSJGB-v42 ODocumento136 páginasCSJGB-v42 OCristinaIcamenAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Hermaphroditism in TeleostsDocumento43 páginasFunctional Hermaphroditism in TeleostsMaik_horaAinda não há avaliações
- Revista Botanica NR 18 2019 PDFDocumento122 páginasRevista Botanica NR 18 2019 PDFAlex IuziAinda não há avaliações
- Morphological Development of The Gonads in Zebrafish (Maack y Senger, 2003) PDFDocumento12 páginasMorphological Development of The Gonads in Zebrafish (Maack y Senger, 2003) PDFCrycel TapiaAinda não há avaliações
- Cruden 1977 EvolutionDocumento15 páginasCruden 1977 EvolutionReynaldo AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Sex Reversal in FishDocumento5 páginasSex Reversal in FishKgerbAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Reproduction Systems ExplainedDocumento30 páginasPlant Reproduction Systems ExplainedIzzati Zulaikha AmyAinda não há avaliações
- ICAR Pollination Manual Provides Guidance on Flowering Phenology StudiesDocumento47 páginasICAR Pollination Manual Provides Guidance on Flowering Phenology StudiesAdlin PricillaAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento13 páginasSample Detailed Lesson PlanRABANG, DIETHER KENJIEAinda não há avaliações