Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Amino Acid Metabolism
Enviado por
akmalsatibi0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações48 páginasAmino acids can be formed from the citrate cycle intermediates in a human body a) -ketoglutarate - glutamate b) succinyl-CoA - isoleucine c) oxaloacetate - aspartate d) malate - threonine the amino acids can also be synthesized from a variety of branched chain amino acids.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoAmino acids can be formed from the citrate cycle intermediates in a human body a) -ketoglutarate - glutamate b) succinyl-CoA - isoleucine c) oxaloacetate - aspartate d) malate - threonine the amino acids can also be synthesized from a variety of branched chain amino acids.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações48 páginasAmino Acid Metabolism
Enviado por
akmalsatibiAmino acids can be formed from the citrate cycle intermediates in a human body a) -ketoglutarate - glutamate b) succinyl-CoA - isoleucine c) oxaloacetate - aspartate d) malate - threonine the amino acids can also be synthesized from a variety of branched chain amino acids.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 48
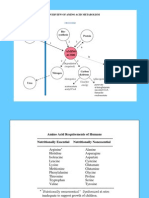
Metabolism of amino acids
Choose essential amino acids
a) Asp, Glu
b) Val, Leu, Ile
c) Ala, Ser, Gly
d) Phe, Trp
Choose essential amino acids
a) Asp, Glu
b) Val, Leu, Ile
c) Ala, Ser, Gly
d) Phe, Trp
Essential amino acids
1) branched chain: Val, Leu, Ile
2) basic: His, Arg, Lys
3) aromatic: Phe ( Tyr), Trp
4) sulfur-containing: Met ( Cys)
5) other: Thr
10
Choose amino acids from which the
other amino acid can be synthesized in
a human body
a) valine leucine
b) aspartate asparagine
c) phenylalanine tyrosine
d) methionine + serine cysteine
Choose amino acids from which the
other amino acid can be synthesized in
a human body
a) valine leucine leucine is the essential AA
b) aspartate asparagine
c) phenylalanine tyrosine
d) methionine + serine cysteine
Synthesis of
ASPARAGINE
needs glutamine as
NH
2
group donor
(it is not ammonia as
in the Gln synthesis)
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
The figure is from http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/amino-acid-metabolism.html (Jan 2007)
Synthesis of Tyr from Phe
The figure is from http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/amino-acid-metabolism.html (Jan 2007)
Synthesis of Cys from Met and Ser
The amino acids can be formed from the
citrate cycle intermediates
in a human body
a) -ketoglutarate glutamate
b) succinyl-CoA isoleucine
c) oxaloacetate aspartate
d) malate threonine
The amino acids can be formed from
the citrate cycle intermediates
in a human body
a) -ketoglutarate glutamate
b) succinyl-CoA isoleucine Ile is the essential AA
c) oxaloacetate aspartate
d) malate threonine Thr is the essential AA
The figure is from
http://www.tcd.ie/Biochemistry/IUBMB-Nicholson/gif/13.html (Dec 2006)
Amphibolic
character
of citrate cycle
The compound(s) can be synthesized
from the amino acid
a) tyrosine serotonin
b) serine ethanolamine
c) tryptophan catecholamines
d) cysteine taurine
The compound(s) can be synthesized
from the amino acid
a) tyrosine serotonin Tyr catecholamines
b) serine ethanolamine formed by decarboxylation
c) tryptophan catecholamines Trp serotonin
d) cysteine taurine
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
taurin is used in conjugation reactions in the liver
it is bound to hydrophobic substances to increase their solubility
(e.g. conjugation of bile acids)
If the amino acid is metabolised the
substance is formed:
a) methionine gives homocysteine
b) serine gives glycine and folic acid
derivative: methylene tetrahydrofolate
c) glutamine releases ammonia
d) some amino acides can be degraded to
acetoacetate
If the amino acid is metabolised the
substance is formed:
a) methionine gives homocysteine
b) serine gives glycine and folic acid
derivative: methylene tetrahydrofolate
c) glutamine releases ammonia
d) some amino acides can be degraded to
acetoacetate = one of ketone bodies
The figure is from http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/amino-acid-metabolism.html (Jan 2007)
B12
Regeneration of
Met
(vitamins: folate+B
12
)
The figure is from http://www.biocarta.com/pathfiles/GlycinePathway.asp (Jan 2007)
Synthesis of serine and glycine
glycolysis
Choose products of the transamination
reactions
a) alanine pyruvate
b) glutamate 2-oxoglutarate
c) aspartate oxaloacetate
d) phenylalanine tyrosine
Choose products of the transamination
reactions
a) alanine pyruvate
b) glutamate 2-oxoglutarate
c) aspartate oxaloacetate
d) phenylalanine tyrosine it is not transamination
The figure is from http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/nitrogen-metabolism.html (Jan 2007)
Transamination reaction
! REVERSIBLE !
enzymes: amino transferases
coenzyme: pyridoxal phosphate (vit. B6 derivative)
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
alanine aminotransferase
(ALT = GPT)
aspartate aminotransferase
(AST = GOT)
Amino transferases important in medicine
(transaminases)
Amino nitrogen released from carbon
sceletons of AAs can be transported in
blood as
a) NH
4
+
b) alanine
c) glutamine
d) urea
Amino nitrogen released from carbon
sceletons of AAs can be transported in
blood as
a) NH
4
+
physiologically up to 35 mol/l
(NH
3
+ H
+
NH
4
+
)
b) alanine formed by transamination from pyruvate
c) glutamine the most important transport form of NH
2
d) urea it is the end product of degradation of amino nitrogen
(liver kidneys urine)
Transport of
amino nitrogen
from degraded
muscle proteins
products
excreted
with urine
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook
of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss,
Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
Glucose-alanine cycle
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
alanine transfers
both the carbon
sceleton for
gluconeogenesis
and NH
2
group
glutamine synthetase
GLUTAMINE
= the most important
transport form af amino
nitrogen in blood
it transfers two amino
groups released by
degradation of AAs
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
Choose glucogenic amino acids
a) alanine
b) lysine
c) leucine
d) glutamine
Choose glucogenic amino acids
a) alanine
b) lysine
c) leucine
d) glutamine
7 degradation products of AAs
1. pyruvate Gly, Ala, Ser, Thr, Cys, Trp
2. oxaloacetate Asp, Asn
3. -ketoglutarate Glu, Gln, Pro, Arg, His
4. succinyl-CoA Val, Ile, Met, Thr
5. fumarate Phe, Tyr
6. acetyl-CoA Ile
7. acetoacetyl-CoA Lys, Leu, Phe, Tyr, Trp
glucogenic AAs
ketogenic AAs
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GMD)
a) catalyzes conversion of Glu to oxaloacetate
b) is found in mitochondria of hepatocytes
c) produces ammonia
d) needs pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GMD)
a) catalyzes conversion of Glu to oxaloacetate
b) is found in mitochondria of hepatocytes
c) produces ammonia
d) needs pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme
The figure is from http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/nitrogen-metabolism.html (Jan 2007)
GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE
removes amino group from carbon sceleton of Glu in the liver
1. NH
2
from AAs was transfered by transamination Glu
2. free ammonia is released by oxidative deamination of Glu
Choose correct statement(s) about
metabolism of amino acids
a) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) transforms
pyruvate to alanine
b) aspartate aminotransferase (AST) transforms
aspartate to -ketoglutarate
c) glutamine synthetase transforms glutamate to
glutamine
d) glutaminase catylyzes conversion of glutamine
to ammonia and -ketoglutarate
Choose correct statement(s) about
metabolism of amino acids
a) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) transforms
pyruvate to alanine
b) aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
transforms aspartate to -ketoglutarate
c) glutamine synthetase transforms glutamate
to glutamine
d) glutaminase catylyzes conversion of
glutamine to ammonia and -ketoglutarate
The figure was adopted from Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed.
Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2
alanine aminotransferase
(ALT = GPT)
aspartate aminotransferase
(AST = GOT)
Amino transferases important in medicine
(transaminases)
Glutamine is principal
transport form of amino nitrogen
The figure is from http://www.sbuniv.edu/~ggray/CHE3364/b1c25out.html (Dec 2006)
The amino acids can enter the citrate
cycle as the molecules
a) alanine acetyl-CoA
b) aspartate oxaloacetate
c) valine succinyl-CoA
d) glutamine -ketoglutarate
The amino acids can enter the citrate
cycle as the molecules
a) alanine acetyl-CoA
b) aspartate oxaloacetate
c) valine succinyl-CoA
d) glutamine -ketoglutarate
The figure is from http://www.biocarta.com/pathfiles/glucogenicPathway.asp (Jan 2007)
The entrance of amino acids into the citrate cycle
Ornithine cycle
a) proceeds only in the liver
b) produces uric acid
c) includes arginine as an intermediate
d) produces energy in a form of ATP
Ornithine cycle
a) proceeds only in the liver
b) produces uric acid
c) includes arginine as an intermediate
d) produces energy in a form of ATP
The figure is from http://www.biocarta.com/pathfiles/ureacyclePathway.asp (Jan 2007)
Detoxication of ammonia in the liver
The figure is from http://courses.cm.utexas.edu/archive/Spring2002/CH339K/Robertus/overheads-3/ch18_TCA-Urea_link.jpg
(Jan 2007)
Interconnection of the urea cycle with the
citrate cycle
In the urea synthesis
a) ammonia reacts with ornithine citrulline
b) carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (=
mitochondrial) regulates the cycle
c) aspartate is used as a NH
2
group donor
d) urea is formed it can be used as an energy
substrate for extrahepatic tissues
In the urea synthesis
a) ammonia reacts with ornithine citrulline
b) carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (=
mitochondrial) regulates the cycle
c) aspartate is used as a NH
2
group donor
d) urea is formed it can be used as an energy
substrate for extrahepatic tissues
regulatory enzyme activation inhibition
carbamoyl phosphate
synthetase I
(= mitochondrial)
N-acetylglutamate
N-acetylglutamate
synthetase
arginine
Regulation of urea cycle
allosteric regulation + enzyme induction by protein rich diet or
by metabolic changes during starvation
Urea synthesis is inhibited by acidosis
HCO
3
-
is saved
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- How Bacterial Imbalances May Predispose To Seizure DisorderDocumento5 páginasHow Bacterial Imbalances May Predispose To Seizure DisorderDr. Amy Yasko100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocumento10 páginasDaftar PustakaakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento10 páginasDaftar PustakaakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- SyphilisDocumento94 páginasSyphilisakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Overview Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento7 páginasOverview Amino Acid MetabolismakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Overview Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento7 páginasOverview Amino Acid MetabolismakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Kata Lo Gene Loop 2011Documento24 páginasKata Lo Gene Loop 2011akmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Metabolic Breakdown of Individual Amino Acids: To Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates or Their PrecursorsDocumento36 páginasMetabolic Breakdown of Individual Amino Acids: To Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates or Their PrecursorsakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- Bleaching3 Konser2Documento3 páginasBleaching3 Konser2akmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- 2623 4831 1 SMDocumento6 páginas2623 4831 1 SMakmalsatibiAinda não há avaliações
- 2023 BCH313 Gluconeogenesis and Synthesis of Complex Carbohydrates NotesDocumento9 páginas2023 BCH313 Gluconeogenesis and Synthesis of Complex Carbohydrates NotesNOLUBABALOAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid PathwayDocumento15 páginas2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid Pathwaylovelots1234100% (1)
- AS Bio Lesson on Cell RespirationDocumento3 páginasAS Bio Lesson on Cell RespirationrutendoAinda não há avaliações
- Krebs CycleDocumento26 páginasKrebs CycleTanChiaZhiAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry-Exam 2 Heinz SchwarzkopfDocumento162 páginasBiochemistry-Exam 2 Heinz SchwarzkopfthomasAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise Physiology-LecturDocumento102 páginasExercise Physiology-Lecturworku kassieAinda não há avaliações
- Gluconeogenesis: An Overview of Glucose Formation from Non-Carbohydrate SourcesDocumento10 páginasGluconeogenesis: An Overview of Glucose Formation from Non-Carbohydrate SourcesManila Med100% (1)
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento56 páginasCarbohydrate MetabolismloijhonmuchillasAinda não há avaliações
- Lista de Enzimas y Reacciones Clase 4 - LiasasDocumento261 páginasLista de Enzimas y Reacciones Clase 4 - LiasasgustasconAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Metabolism of Carbohydrates, Fats and ProteinsDocumento19 páginasUnderstanding Metabolism of Carbohydrates, Fats and ProteinsShaira BayubayAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento14 páginasChapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle: Multiple Choice QuestionshielAinda não há avaliações
- CAPE Biology 2005 U1 P1Documento19 páginasCAPE Biology 2005 U1 P1Reshana SimonAinda não há avaliações
- Gluconeogenesis Metabolic PathwayDocumento36 páginasGluconeogenesis Metabolic PathwayDayledaniel Sorveto0% (1)
- Plant Respiration ExplainedDocumento6 páginasPlant Respiration ExplainedAadil ShakulAinda não há avaliações
- Kerbs CycleDocumento11 páginasKerbs CycleVarun bharathiAinda não há avaliações
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocumento26 páginasHow Cells Harvest EnergyMarita YaghiAinda não há avaliações
- Presented by 15 Batch 1 Fhcs - EuslDocumento453 páginasPresented by 15 Batch 1 Fhcs - EuslAfk SystemAinda não há avaliações
- SAS For Biochemistry (BIO 024) Module #9Documento35 páginasSAS For Biochemistry (BIO 024) Module #9jeannikkavAinda não há avaliações
- 2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better PicturesDocumento12 páginas2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better Pictureslovelots1234Ainda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry 1St Edition Miesfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento57 páginasBiochemistry 1St Edition Miesfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrebeccagomezearndpsjkc100% (12)
- Metabolism & Starvation CHEM 124Documento19 páginasMetabolism & Starvation CHEM 124Andi9993Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 23 Metabolism and Energy ProductionDocumento68 páginasChapter 23 Metabolism and Energy ProductionZahid HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Crystal - Res.ku - Edu Taksnotes Biol 638 Notes CHP 16Documento19 páginasCrystal - Res.ku - Edu Taksnotes Biol 638 Notes CHP 16shahjafferAinda não há avaliações
- Bchemistry - Exercises 14-15Documento30 páginasBchemistry - Exercises 14-15NIYONSHUTI VIATEUR100% (1)
- The Krebs Cycle ExplainedDocumento5 páginasThe Krebs Cycle ExplainedCarlo CondeAinda não há avaliações
- Amino Acid SynthesisDocumento70 páginasAmino Acid SynthesisBhavesh BatraAinda não há avaliações
- Technology: ApplicationsDocumento12 páginasTechnology: ApplicationsGRishab GRishabAinda não há avaliações
- Amino Acid DegradationDocumento44 páginasAmino Acid DegradationTanvi ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Citric Acid 1Documento10 páginasCitric Acid 1Tawakal MuzaffarAinda não há avaliações