Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1monopolistic Competition
Enviado por
Swet TiwariDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1monopolistic Competition
Enviado por
Swet TiwariDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MONOPOLISTIC
COMPETITION
Perfect competition , where all goods are
homogenous and all firms are price takers , is
rarely seen. Imperfect competition is very
common . In this kind of a market , there are few
sellers and product differentiation and price wars
are common
Differences between
monopolistic and perfect
competition.
While firms in a monopolistic markets are
price dictators , in perfect competition they are
price takers.
The demand curve for a market based on
perfect competition is a horizontal straight
line, while in imperfect competition the
demand curve slopes downwards from left to
right
Differences between monopolistic and perfect
competition.
In perfect competition there is constant returns to
scale, while imperfect competition is based on
the the principal of increasing returns to scale.
Under perfect competition increase in output is
equal to increase in input. But under imperfect
competition , an increase in input leads to more
than proportionate increase in output.This allows
some firms to occupy a dominant position in the
industry. These firms set the price for the entire
industry
Characteristis of mperfect
competition
An imperfect market can be defined as a market
with many producers offering goods which are
close substitutes, but not identicals as is the case
in the perfect competition. Since the products
vary in their features , the pricing also varies.
Under imperfect competition sellers try to
differentiate their products mainly on the basis of
four aspects
Physical features
Location
Services
Product image
Market structure characteristics
of monopolistic competition
Number and size distribution of sellers
Number and size distribution of buyers
Product differentiation
Conditions of entry and exit
Many small sellers. Actions of
individual sellers go unheeded by
other firms
Many small buyers
Slightly differentiated. Product of
one firm is a close substitute for
that of other sellers
Easy entry and exit
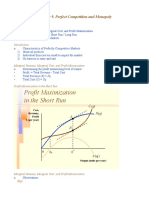
Profit maximizing price and
output in the short run
price
p
MC AC
D
MR
Qc
Long run profit maximization in
the monopolistic competition
mc
ac
Pc
The manager of a firm has the
following demand equation given by
P=309.75-Q and the long run cost
equation is TC=400Q-
20Q
2
+Q
3
Where Qis quantity. What is
the long run equilibrium price and
quantity how much economic profit
will the firm earn?
Você também pode gostar
- 1monopolistic CompetitionDocumento9 páginas1monopolistic CompetitionRaj AdakAinda não há avaliações
- Market StructureDocumento19 páginasMarket StructureNazmul HudaAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic CompDocumento32 páginasMonopolistic Compharsh guptaAinda não há avaliações
- 8 - Monopolistic CompetitionDocumento22 páginas8 - Monopolistic CompetitionShashwat JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Market and Its EquilbriumDocumento14 páginasMarket and Its Equilbrium4058AMAN ANANDAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Documento36 páginasMonopolistic Competition: Chapter 16-1Balwinder SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmDocumento20 páginasMonopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmalpha fiveAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmDocumento20 páginasMonopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmalpha fiveAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmDocumento20 páginasMonopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmalpha fiveAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmDocumento20 páginasMonopolistic Comp 08052020 042834pmalpha fiveAinda não há avaliações
- Perfect CompetitionDocumento22 páginasPerfect CompetitionDeepak kr. patelAinda não há avaliações
- Market Structures Recap Lecture (FLT) 2Documento72 páginasMarket Structures Recap Lecture (FLT) 2Cheng KysonAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT-4 Introduction To Markets and Pricing Policies: Size of The MarketDocumento10 páginasUNIT-4 Introduction To Markets and Pricing Policies: Size of The Marketarzun666Ainda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Competition & OligopolyDocumento19 páginasMonopolistic Competition & Oligopolysidmathur2010Ainda não há avaliações
- OligopolyDocumento16 páginasOligopolyMd. Amran HossainAinda não há avaliações
- Competitive Market - BKFSDocumento21 páginasCompetitive Market - BKFSNishtha GargAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocumento33 páginasMonopolistic CompetitionVedant KarwandeAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial Economics & Business StrategyDocumento31 páginasManagerial Economics & Business StrategyYokie RadnanAinda não há avaliações
- Market CompetitionDocumento43 páginasMarket CompetitiontamimAinda não há avaliações
- Perfect CompitionDocumento24 páginasPerfect Compitionsano_rockfolksAinda não há avaliações
- Perfect CompetitionDocumento24 páginasPerfect Competitionzishanmallick0% (1)
- IB Micro Monopolistic CompetitionDocumento18 páginasIB Micro Monopolistic CompetitionAnushkaa DattaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two: Demand and SupplyDocumento71 páginasChapter Two: Demand and Supplykasech mogesAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Strategies and TacticsDocumento142 páginasPricing Strategies and TacticsKRITIKA NIGAMAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Market Structure Perfect and Imperfect MarketsDocumento32 páginas2 Market Structure Perfect and Imperfect MarketsTechyAinda não há avaliações
- Colander Ch11 Perfect CompetitionDocumento84 páginasColander Ch11 Perfect CompetitionVishal JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Topic Five Market Structure, Pricing and Output Decisions 1Documento43 páginasTopic Five Market Structure, Pricing and Output Decisions 1Mister PhilipsAinda não há avaliações
- Rup Ratan Pine 01552438118: Economics For Managers Course No: 401Documento32 páginasRup Ratan Pine 01552438118: Economics For Managers Course No: 401rifath rafiqAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 09Documento8 páginasChap 09Thabo MojavaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit VII Pricing and Output Decisions: Perfect Competition and MonopolyDocumento36 páginasUnit VII Pricing and Output Decisions: Perfect Competition and MonopolyIshan PalAinda não há avaliações
- MonopolisticDocumento25 páginasMonopolisticDharshini RajkumarAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8E Baye Chap. 8Documento49 páginasManagerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8E Baye Chap. 8love100% (2)
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocumento13 páginasMonopolistic CompetitionSamrawit EndalamawAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 009Documento17 páginasChap 009Wendors WendorsAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic: A2 (Axis Achievers)Documento36 páginasMonopolistic: A2 (Axis Achievers)Saket AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Firms With Market PowersDocumento40 páginasFirms With Market PowersSwati PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Business Economics Session 2 - Market StructuresDocumento24 páginasBusiness Economics Session 2 - Market StructuresNeha GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Monopoly PDFDocumento12 páginasMonopoly PDFzofuAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial Decisions For Firms With Market PowerDocumento33 páginasManagerial Decisions For Firms With Market Powernur ardini binti jaafarAinda não há avaliações
- PERFECT COMPETITION Eccoooooooooooo Final PresentationDocumento23 páginasPERFECT COMPETITION Eccoooooooooooo Final Presentationbhartisingh4222Ainda não há avaliações
- Managerial Economics:: Perfect CompetitionDocumento43 páginasManagerial Economics:: Perfect CompetitionPhong VũAinda não há avaliações
- I Mcom Bus EcoDocumento39 páginasI Mcom Bus Ecokirthi nairAinda não há avaliações
- Session 7 - Market StructuresDocumento46 páginasSession 7 - Market StructuressusithsathsaraAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 5 - MEDocumento47 páginasChap 5 - MEladdooparmarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Managing in CompetitiveDocumento28 páginasChapter 8 Managing in CompetitiveAngela WaganAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Strategies and TacticsDocumento33 páginasPricing Strategies and Tacticssathvik RekapalliAinda não há avaliações
- Group Report. Perfect CompetitionDocumento31 páginasGroup Report. Perfect CompetitionMary Ann Manalo PanopioAinda não há avaliações
- Forms of Markets Forms of MarketsDocumento55 páginasForms of Markets Forms of MarketsAkhil NeyyattinkaraAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 6 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets Learning ObjectivesDocumento13 páginasCHAPTER 6 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets Learning ObjectivesJericho James Madrigal CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- Eco 101 FinalDocumento4 páginasEco 101 FinalShahidin ShirshoAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocumento29 páginasMonopolistic CompetitionJuanita CabigonAinda não há avaliações
- Monopolistic Competition (For Students)Documento18 páginasMonopolistic Competition (For Students)adillawa100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Business EconomicsDocumento15 páginasLecture 4 Business EconomicsTayyaba JawedAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of MonopolyDocumento3 páginasCharacteristics of Monopolywakeup_5550% (1)
- Pricing StrategiesDocumento16 páginasPricing StrategiesSHEKHAR SHUKLAAinda não há avaliações
- CH 14Documento77 páginasCH 14hartinahAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Market Structures AND Pricing Policies: Unit Iii Part-IDocumento39 páginasIntroduction To Market Structures AND Pricing Policies: Unit Iii Part-Igoyal_khushbu88Ainda não há avaliações
- Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic and Monopolistically Competitive MarketDocumento27 páginasManaging in Competitive, Monopolistic and Monopolistically Competitive MarketPutri AmandhariAinda não há avaliações
- 104-Me 1443017742071Documento82 páginas104-Me 1443017742071Hardik SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Market Makers (Review and Analysis of Spluber's Book)No EverandThe Market Makers (Review and Analysis of Spluber's Book)Ainda não há avaliações
- Economic PolicyDocumento14 páginasEconomic PolicySwet TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Business EnvironmentDocumento21 páginasBusiness EnvironmentSwet TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Costs-16Documento6 páginasAnalysis of Costs-16Swet TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Rexona CaseDocumento15 páginasRexona CaseSwet TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Chap01-Mtg Concepts1Documento9 páginasChap01-Mtg Concepts1Swet TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- COSMDocumento2 páginasCOSMRuchi Rabuya BaclayonAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To: International Business Rise of GlobalizationDocumento20 páginasIntroduction To: International Business Rise of GlobalizationBiajoy MesiasAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Economics - Economics Stack ExchangeDocumento5 páginasMathematical Economics - Economics Stack ExchangeJoseph JungAinda não há avaliações
- D&D 5.0 - Aventura (Nível 7) O Refúgio Perdido Do ArquimagoDocumento30 páginasD&D 5.0 - Aventura (Nível 7) O Refúgio Perdido Do ArquimagoMurilo TeixeiraAinda não há avaliações
- (Advances in Strategic Management) SZULANSKI ET AL - Strategy Process (Advances in Strategic Management Vol. 22) - Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2005)Documento553 páginas(Advances in Strategic Management) SZULANSKI ET AL - Strategy Process (Advances in Strategic Management Vol. 22) - Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2005)Andra ModreanuAinda não há avaliações
- PTGAC - Written AssessmentDocumento10 páginasPTGAC - Written AssessmentEsme AlcarazAinda não há avaliações
- Application Format For Scheme For Creation/expansion of Food Processing & Preservation CapacitiesDocumento3 páginasApplication Format For Scheme For Creation/expansion of Food Processing & Preservation CapacitiesA RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Trade ConfirmationDocumento1 páginaTrade ConfirmationHavid KurniaAinda não há avaliações
- Circular 14062023-Vivad Se Vishwas-1Documento4 páginasCircular 14062023-Vivad Se Vishwas-1Priya SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Guide: Please Reword The Answers To Essay Type Parts So As To Guarantee That Your Answer Is An Original. Do Not Submit As Your OwnDocumento2 páginasSolutions Guide: Please Reword The Answers To Essay Type Parts So As To Guarantee That Your Answer Is An Original. Do Not Submit As Your OwnKumar SonalAinda não há avaliações
- Take It From NT:-Cash Book Plays Role of Both Journal As Well As LedgerDocumento17 páginasTake It From NT:-Cash Book Plays Role of Both Journal As Well As LedgerAnonymous b4qyneAinda não há avaliações
- Birkenstock Orthopaedie GMBH and Co. KG (Formerly Birkenstock Orthopaedie GMBH) Philippine Shoe Expo Marketing CorporationDocumento2 páginasBirkenstock Orthopaedie GMBH and Co. KG (Formerly Birkenstock Orthopaedie GMBH) Philippine Shoe Expo Marketing CorporationbrigetteAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 Subsidiary BookDocumento17 páginasUnit 4 Subsidiary Bookkim kAinda não há avaliações
- Curing of A Credit Impaired Financial Asset SlidesDocumento27 páginasCuring of A Credit Impaired Financial Asset SlidesAsghar AliAinda não há avaliações
- Canadian Jeweller Magazine November 2009Documento88 páginasCanadian Jeweller Magazine November 2009rivegaucheAinda não há avaliações
- MJ's Home and Commercial Cleaning Services Comparative Statement of Financial Performance As of December 31, 2021 - 2025 (In Philippine Peso)Documento16 páginasMJ's Home and Commercial Cleaning Services Comparative Statement of Financial Performance As of December 31, 2021 - 2025 (In Philippine Peso)Jasmine ActaAinda não há avaliações
- INDOQUARTZDocumento10 páginasINDOQUARTZyip.kendalAinda não há avaliações
- National Foods LTDDocumento16 páginasNational Foods LTDSufiyan Alaam0% (1)
- Boq vs. ActualDocumento13 páginasBoq vs. Actualsri projectssAinda não há avaliações
- Optimal Portfolio Strategy To Control Maximum DrawdownDocumento35 páginasOptimal Portfolio Strategy To Control Maximum DrawdownLoulou DePanamAinda não há avaliações
- Cvol Calculation ExampleDocumento29 páginasCvol Calculation ExamplebhomenkovAinda não há avaliações
- HE6 W3aDocumento4 páginasHE6 W3aMa Theresa BambaoAinda não há avaliações
- Main Campus Map RevisedDocumento2 páginasMain Campus Map Revisedm.rautenbach00Ainda não há avaliações
- The Wedge PatternDocumento56 páginasThe Wedge PatternMohaAinda não há avaliações
- 516-70 DiffDocumento8 páginas516-70 DiffMohammad HassanAinda não há avaliações
- March Bank StatementDocumento2 páginasMarch Bank Statementvicky.sharon2Ainda não há avaliações
- MKII Spearhead Assembly BrochureDocumento2 páginasMKII Spearhead Assembly Brochuretomas caputoAinda não há avaliações
- Cost of Capital Math SolutionDocumento8 páginasCost of Capital Math SolutionArafatAinda não há avaliações
- MS40 / MS40EX: Magnetic Level Gauge SwitchDocumento4 páginasMS40 / MS40EX: Magnetic Level Gauge SwitchMahdi PiranhaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1 (Answer All Questions) : Saraswati Vidya NiketanDocumento3 páginasPaper 1 (Answer All Questions) : Saraswati Vidya Niketanyuvita prasadAinda não há avaliações