Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ag-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab Reactions
Enviado por
summiya0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
20 visualizações36 páginasAg Ab Reaction
Título original
Ag Ab Reactions08
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoAg Ab Reaction
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
20 visualizações36 páginasAg-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab Reactions
Enviado por
summiyaAg Ab Reaction
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 36
Ag-Ab reactions
Tests for Ag-Ab reactions
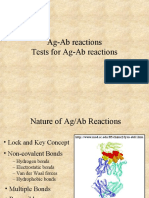
Nature of Ag/Ab Reactions
Lock and Key Concept
Non-covalent Bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Electrostatic bonds
Van der Waal forces
Hydrophobic bonds
Reversible
Multiple Bonds
Source: Li, Y., Li, H., Smith-Gill, S. J.,
Mariuzza, R. A., Biochemistry 39, 6296, 2000
http://www.med.sc.edu:85/chime2/lyso-abfr.htm
Affinity = attractive and repulsive forces
Ab
Ag
High Affinity
Ab
Ag
Low Affinity
Affinity
Strength of the reaction between a single antigenic
determinant and a single Ab combining site
Calculation of Affinity
Ag + Ab Ag-Ab
K
eq
=
[Ag-Ab]
[Ag] x [Ab]
Applying the Law of Mass Action:
Avidity
The overall strength of binding between an Ag
with many determinants and multivalent Abs
K
eq
=
10
4
Affinity
10
6
Avidity
10
10
Avidity
Specificity
The ability of an individual antibody combining
site to react with only one antigenic determinant.
The ability of a population of antibody molecules
to react with only one antigen.
Cross Reactivity
The ability of an individual Ab combining site to
react with more than one antigenic determinant.
The ability of a population of Ab molecules to
react with more than one Ag
Anti-A
Ab
Ag A
Anti-A
Ab
Ag B
Shared epitope
Anti-A
Ab
Ag C
Similar epitope
Cross reactions
Factors Affecting Measurement of
Ag/Ab Reactions
Affinity
Avidity
Ag:Ab ratio
Physical form of Ag
Ab excess Ag excess
Equivalence Lattice formation
Tests Based on Ag/Ab Reactions
All tests based on Ag/Ab reactions will
have to depend on lattice formation or they
will have to utilize ways to detect small
immune complexes
All tests based on Ag/Ab reactions can be
used to detect either Ag or Ab
Agglutination Tests
Lattice Formation
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition - tests that have as their endpoint
the agglutination of a particulate antigen
Agglutinin/hemagglutinin
+
Qualitative agglutination test
Ag or Ab
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Quantitative agglutination test
Titer
Prozone
1
/
2
1
/
4
1
/
8
1
/
1
6
1
/
3
2
1
/
6
4
1
/
1
2
8
1
/
2
5
6
1
/
5
1
2
1
/
1
0
2
4
P
o
s
.
N
e
g
.
Titer
64
8
512
<2
32
128
32
4
Patient
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition
Qualitative test
Quantitative test
Applications
Blood typing
Bacterial infections
Fourfold rise in titer
Practical considerations
Easy
Semi-quantitative
1
/
2
1
/
4
1
/
8
1
/
1
6
1
/
3
2
1
/
6
4
1
/
1
2
8
1
/
2
5
6
1
/
5
1
2
Passive Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition - agglutination test done with a
soluble antigen coated onto a particle
+
Applications
Measurement of antibodies to soluble antigens
Coombs (Antiglobulin)Tests
Incomplete Ab
Direct Coombs Test
Detects antibodies on erythrocytes
+
Patients RBCs Coombs Reagent
(Antiglobulin)
Coombs (Antiglobulin)Tests
Indirect Coombs Test
Detects anti-erythrocyte antibodies in serum
Patients
Serum
Target
RBCs
+
Step 1
+
Coombs Reagent
(Antiglobulin)
Step 2
Coombs (Antiglobulin)Tests
Applications
Detection of anti-Rh Ab
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Agglutination/Hemagglutination Inhibition
Definition - test based on the inhibition of
agglutination due to competition with a soluble Ag
+
Prior to Test
+
+
Test
Patients sample
Agglutination/Hemagglutination Inhibition
Applications
Measurement of soluble Ag
Practical considerations
Same as agglutination test
Definition
Precipitation Tests
Lattice Formation
Radial Immunodiffusion (Mancini)
Interpretation
Diameter of ring is
proportional to the
concentration
Quantitative
Ig levels
Method
Ab in gel
Ag in a well
Ag Concentration
D
i
a
m
e
t
e
r
2
Ag Ag Ag Ag
Ab in gel
Immunoelectrophoresis
Method
Ags are separated by electrophoresis
Interpretation
Precipitin arc represent individual antigens
Ag
-
+
Ag
Ab
Ag
Ab
Ab is placed in trough cut in the agar
Immunoelectrophoresis
Method
Interpretation
Qualitative
Relative concentration
Countercurrent electrophoresis
Method
Ag and Ab migrate toward each other by
electrophoresis
Used only when Ag and Ab have opposite charges
Qualitative
Rapid
Ag
Ab
-
+
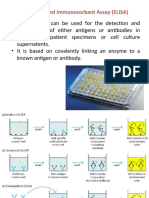
Radioimmuoassays (RIA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
Assays (ELISA)
Lattice formation not required
Competitive RIA/ELISA for Ag
Method
Determine amount
of Ab needed to bind
to a known amount
of labeled Ag
+
Prior to Test
Labeled
Ag
+
Test
+
Patients
sample
Labeled
Ag
+
Use predetermined
amounts of labeled Ag
and Ab and add a
sample containing
unlabeled Ag as a
competitor
Competitive RIA/ELISA for Ag
Method cont.
Determine amount
of labeled Ag bound
to Ab
NH
4
SO
4
anti-Ig
Immobilize the Ab
Quantitative
Most sensitive test
+
Test
+
Patients
sample
Labeled
Ag
+
Concentration determined from a standard curve
using known amounts of unlabeled Ag
Solid
Phase
Solid
Phase
Solid Phase Non-Competitive RIA/ELISA
Ab detection
Immobilize Ag
Incubate with sample
Add labeled anti-Ig
Amount of labeled Ab
bound is proportional
to amount of Ab in the
sample
Quantitative
Solid
Phase
Ag
Immobilized
Ab in
Patients
sample
Labeled
Anti-Ig
Solid Phase Non-Competitive RIA/ELISA
Ag detection
Immobilize Ab
Incubate with sample
Add labeled antibody
Amount of labeled Ab
bound is proportional to
the amount of Ag in the
sample
Quantitative
Solid
Phase
Ag
Immobilized
Ag in
Patients
sample
Labeled
Ab
Tests for Cell Associated
Antigens
Lattice formation not required
Immunofluorescence
Direct
Ab to tissue Ag is labeled with fluorochrome
Ag
Fluorochrome
Labeled Ab
Tissue Section
Immunofluorescence
Indirect
Ab to tissue Ag is
unlabeled
Fluorochrome-labeled anti-
Ig is used to detect binding
of the first Ab.
Ag
Fluorochrome
Labeled Anti-Ig
Tissue Section
Unlabeled
Ab
Qualitative to Semi-
Quantitative
Immunofluorescence
Flow Cytometry
Cells in suspension are labeld with fluorescent tag
Direct or Indirect Fluorescence
Cells analyzed on a flow cytometer
Flow
Tip
Laser
FL
Detector
Light
Scatter
Detector
Immunofluorescence
Flow Cytometry cont.
Data displayed
Green Fluorescence Intensity
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
C
e
l
l
s
Unstained cells
FITC-labeled cells
One Parameter Histogram
Red Fluorescence Intensity
G
r
e
e
n
F
l
u
o
r
e
s
c
e
n
c
e
I
n
t
e
n
s
i
t
y
Two Parameter Histogram
Assays Based on Complement
Lattice formation not required
Complement Fixation
Ag mixed with test serum to be assayed for Ab
Standard amount of complement is added
Erythrocytes coated with Abs is added
Amount of erythrocyte lysis is determined
Ag
Patients
serum
Ag No Ag
Ag
Methodology
Você também pode gostar
- A Laboratory Manual of Physical PharmaceuticsNo EverandA Laboratory Manual of Physical PharmaceuticsNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationNo EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of ImmunologyDocumento27 páginasAntigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of ImmunologysummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Immunoassay TechniquesDocumento35 páginasPrinciples of Immunoassay TechniquesBRENDA NHERERAAinda não há avaliações
- Serology NewDocumento116 páginasSerology NewFarlogyAinda não há avaliações
- SerologyDocumento43 páginasSerologyAlvin OccianoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 - Antigen-Antibody Reaction & Diagnostic TestsDocumento30 páginasLecture 5 - Antigen-Antibody Reaction & Diagnostic TestsJeanPaule JoumaaAinda não há avaliações
- Ag Ab ReactionsDocumento43 páginasAg Ab ReactionsNiyaz ShahriarAinda não há avaliações
- Immuno As SayDocumento33 páginasImmuno As SayShankar RajAinda não há avaliações
- Antibody and Soluble Antigen Precipitation Reactions PrecipitinsDocumento25 páginasAntibody and Soluble Antigen Precipitation Reactions PrecipitinsRakin Bin RaihanAinda não há avaliações
- ElisaDocumento76 páginasElisaSobha MatthewAinda não há avaliações
- SerologyDocumento34 páginasSerologyJennifer HerediaAinda não há avaliações
- Agglutination & NTII - PPT 28.04.Documento31 páginasAgglutination & NTII - PPT 28.04.Meenakshisundaram CAinda não há avaliações
- Ag-Ab Interactions: K.Prameela Department of Biotechnology Gitam UniversityDocumento16 páginasAg-Ab Interactions: K.Prameela Department of Biotechnology Gitam UniversityGayatri TallapragadaAinda não há avaliações
- Ag - Ab ReactionsDocumento37 páginasAg - Ab ReactionsJennifer DixonAinda não há avaliações
- Ag Ab Reaction - 30th August 2013Documento34 páginasAg Ab Reaction - 30th August 2013Rajkishor YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Agglutination TestDocumento34 páginasAgglutination TestAJAYAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen - Antibody Reactions: DR - Gomathi M.D.Documento22 páginasAntigen - Antibody Reactions: DR - Gomathi M.D.Meenakshisundaram CAinda não há avaliações
- Agglutination and PrecipitationDocumento35 páginasAgglutination and PrecipitationIsak Isak IsakAinda não há avaliações
- Ag-Ab Interactions & Immunologic TestsDocumento18 páginasAg-Ab Interactions & Immunologic TestsDr. Tapan Kr. DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Antigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Documento44 páginasAntigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Azhar Clinical Laboratory TubeAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen - Antibo-WPS OfficeDocumento10 páginasAntigen - Antibo-WPS OfficePalagiri MadhuAinda não há avaliações
- Immunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationDocumento29 páginasImmunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationBassem AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Chap. 6 - Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Characterized AsDocumento17 páginasChap. 6 - Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Characterized AsmaniiiiiiiiAinda não há avaliações
- Radioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay: M K Unnikrishnan (Aug 2006)Documento16 páginasRadioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay: M K Unnikrishnan (Aug 2006)May AbusalahAinda não há avaliações
- Ag - Ag InteractionDocumento22 páginasAg - Ag Interactionaaryasuxena16Ainda não há avaliações
- Antiglobulin TestDocumento28 páginasAntiglobulin TestAvi Verma100% (1)
- Serologic ProceduresDocumento77 páginasSerologic ProceduresWynlor AbarcaAinda não há avaliações
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Elisa) : Definition and TypesDocumento10 páginasEnzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Elisa) : Definition and TypesPalagiri MadhuAinda não há avaliações
- TurbidimetryDocumento11 páginasTurbidimetryalexis mae IsonAinda não há avaliações
- Immunological ReationsDocumento76 páginasImmunological ReationsSaba AmanAinda não há avaliações
- 15.antigen - Antibody Reactions Part 2Documento34 páginas15.antigen - Antibody Reactions Part 2Manas DixitAinda não há avaliações
- PracticDocumento5 páginasPracticGheorghe MaryaAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen and Antibody ReactionDocumento27 páginasAntigen and Antibody ReactionHusnain AliAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen Antibody InteractionsDocumento62 páginasAntigen Antibody Interactionsshivangi_vyasAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Precipitation Reactions 1Documento50 páginas5 Precipitation Reactions 1Christine Joy ManzanillaAinda não há avaliações
- Antiglobulin Test and Antibody Detection: AHLS 311Documento29 páginasAntiglobulin Test and Antibody Detection: AHLS 311Purple basketAinda não há avaliações
- RadioimmunoassaysDocumento16 páginasRadioimmunoassaysSonali DasAinda não há avaliações
- Ag-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab ReactionsDocumento36 páginasAg-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab ReactionsRiya KvAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen and Antibody ReactionDocumento43 páginasAntigen and Antibody ReactionSubash SubaAinda não há avaliações
- RadioimmunoassayDocumento35 páginasRadioimmunoassayRekha ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- RadioimmunoassayDocumento16 páginasRadioimmunoassaysr_bakegAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10 - Ag Ab Reactions PDFDocumento34 páginasLecture 10 - Ag Ab Reactions PDFUPENDRA KUMAR SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Antigen Antibody Precipitation ReactionsDocumento21 páginasAntigen Antibody Precipitation Reactionsvinupv88Ainda não há avaliações
- Serology: Precipitation ReactionsDocumento18 páginasSerology: Precipitation ReactionsSirine AjourAinda não há avaliações
- Radioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocumento16 páginasRadioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent AssayPavan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Immunology and Serology Part 3Documento117 páginasImmunology and Serology Part 3UnixoftAinda não há avaliações
- Week 9 Slide Agglutination TestDocumento14 páginasWeek 9 Slide Agglutination TestJae TAinda não há avaliações
- Ria ImmunoassayDocumento10 páginasRia ImmunoassayDinkey SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Cross Matching-Wps OfficeDocumento22 páginasCross Matching-Wps Officeashwini priyaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Immunological TestsDocumento71 páginas10 Immunological Testsozerbilge24Ainda não há avaliações
- Antigen and Antibody Reactions Agglutination TestsDocumento74 páginasAntigen and Antibody Reactions Agglutination Teststummalapalli venkateswara rao0% (1)
- Agglutination and Preceptation (Recovered)Documento19 páginasAgglutination and Preceptation (Recovered)Rizwan AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Ag Ab ReactionDocumento31 páginasAg Ab ReactionmaniiiiiiiiAinda não há avaliações
- ELISA (Aslam Sir), Pharmaceutical BiotechnologyDocumento8 páginasELISA (Aslam Sir), Pharmaceutical Biotechnologypolashsd091Ainda não há avaliações
- Imunologi SMT IDocumento66 páginasImunologi SMT IArdilla DewiAinda não há avaliações
- Troubleshooting in CXMDocumento3 páginasTroubleshooting in CXMquerokeropi100% (1)
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay (ELISA)Documento7 páginasEnzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay (ELISA)Asmat UllahAinda não há avaliações
- بنك الدم ٥Documento30 páginasبنك الدم ٥hussien shelbayeAinda não há avaliações
- Thermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNo EverandThermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryAinda não há avaliações
- Candidiasis MedscapeDocumento36 páginasCandidiasis MedscapesummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Update 2014, 7 Discontinuation of Salmonella Serology Test AKUHDocumento1 páginaUpdate 2014, 7 Discontinuation of Salmonella Serology Test AKUHsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Candida UTI DiagnosisDocumento5 páginasCandida UTI DiagnosissummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Candida Urinary Tract Infections-TreatmentDocumento10 páginasCandida Urinary Tract Infections-TreatmentsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Candidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalDocumento5 páginasCandidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Candida UTI TreatmentDocumento10 páginasCandida UTI TreatmentsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Trypanosoma MCQDocumento2 páginasTrypanosoma MCQsummiya100% (2)
- Vaccine Updates UkDocumento4 páginasVaccine Updates UksummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Candidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalDocumento5 páginasCandidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Critically Ill 75 Year Old Man With ComplicationsDocumento20 páginasCritically Ill 75 Year Old Man With ComplicationssummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Cases in TransplantationDocumento59 páginasCases in TransplantationsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Case 1 EsblDocumento15 páginasCase 1 EsblsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) : Mohammad Zeeshan Resident MicrobiologyDocumento30 páginasC-Reactive Protein (CRP) : Mohammad Zeeshan Resident MicrobiologysummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- CASE FILES Hiv MeaslesDocumento15 páginasCASE FILES Hiv MeaslessummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Case 8 TBDocumento41 páginasCase 8 TBsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Infection in Cancer Patients: Department of MedicineDocumento18 páginasDengue Infection in Cancer Patients: Department of MedicinesummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Case OsteomyelitisDocumento32 páginasCase OsteomyelitissummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio SafetyDocumento68 páginasBio SafetysummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Id SuggestionDocumento2 páginasId SuggestionsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial ShapesDocumento28 páginasBacterial ShapessummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Culture Collection 2Documento14 páginasBlood Culture Collection 2summiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio SafetyDocumento68 páginasBio SafetysummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- An Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinDocumento43 páginasAn Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Aspergillus and AspergillosisDocumento35 páginasAspergillus and AspergillosissummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- An Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinDocumento43 páginasAn Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)Documento41 páginasAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)summiya100% (1)
- 4-ZN StainDocumento66 páginas4-ZN StainsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Act 2Documento6 páginasAct 2JHON LHOYD CORPUZAinda não há avaliações
- 985 22647-R02 Installation Manual ORCA Offshore Part1Documento21 páginas985 22647-R02 Installation Manual ORCA Offshore Part1dumpuu100% (1)
- AS NZS 3992-1998 Amdt 1-2000 Pressure Equipment - Welding and Brazing Qualification PDFDocumento6 páginasAS NZS 3992-1998 Amdt 1-2000 Pressure Equipment - Welding and Brazing Qualification PDFEsapermana RiyanAinda não há avaliações
- Nanotechnology Roadmap 2007 WG ProcDocumento210 páginasNanotechnology Roadmap 2007 WG Proc2mdotyAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion RingsDocumento1 páginaCorrosion RingsAnonymous JMuM0E5YOAinda não há avaliações
- Three Fundamental Chemical Laws WorksheetDocumento1 páginaThree Fundamental Chemical Laws WorksheetJuventie PrimastutiAinda não há avaliações
- Norma C177-04 PDFDocumento22 páginasNorma C177-04 PDFJimmy AnticonaAinda não há avaliações
- EE Catalogue PDFDocumento27 páginasEE Catalogue PDFssnAinda não há avaliações
- Sanyo Alarm Codes PDFDocumento6 páginasSanyo Alarm Codes PDFomarAinda não há avaliações
- Tube Repair and Protection For DamageDocumento112 páginasTube Repair and Protection For Damagesandipwarbhe1234100% (1)
- g115 Ws Us PDFDocumento60 páginasg115 Ws Us PDFNiku HAinda não há avaliações
- Sikasil 670 Fire - Pds enDocumento4 páginasSikasil 670 Fire - Pds enTRI MINTO WIDODOAinda não há avaliações
- Installation Dresser MeterDocumento32 páginasInstallation Dresser MeterCoco GalindoAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry 8Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasOrganic Chemistry 8Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtonya.paongo686100% (11)
- The Aqueous Geochemistry of Gallium, Germanium, Indium and ScandiumDocumento46 páginasThe Aqueous Geochemistry of Gallium, Germanium, Indium and ScandiumLeon MutambalaAinda não há avaliações
- Rotogravure Printing Learn MoreDocumento15 páginasRotogravure Printing Learn Moreumangashling100% (1)
- Transformers&ReactorsDocumento56 páginasTransformers&ReactorsDilip KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Action Potentials and Synapses HandoutsDocumento6 páginasAction Potentials and Synapses HandoutsKelly TrainorAinda não há avaliações
- Dichtomatik Handbook PDFDocumento225 páginasDichtomatik Handbook PDFErick LedezmaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec1 PDFDocumento3 páginasLec1 PDFusmanAinda não há avaliações
- BioEx.D.Foam Anglais Web PDFDocumento2 páginasBioEx.D.Foam Anglais Web PDFhectorAinda não há avaliações
- Growth Promotion Test Guide For Media Used in Sterility TestsDocumento5 páginasGrowth Promotion Test Guide For Media Used in Sterility Testshoria96Ainda não há avaliações
- Mobil Dte 20Documento3 páginasMobil Dte 20alexander900616Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of ValvesDocumento53 páginasFundamentals of Valvesnatezenmaster100% (4)
- 05 34228 AnalyserDocumento17 páginas05 34228 AnalyserOliver TwisteAinda não há avaliações
- Thermoregulasi Pada BurungDocumento29 páginasThermoregulasi Pada BurungBillyTanumihardjaAinda não há avaliações
- Chevron Rykon Hydraulic OilDocumento7 páginasChevron Rykon Hydraulic OilAbu Saleh ImamAinda não há avaliações
- PolyolsDocumento12 páginasPolyolsA MahmoodAinda não há avaliações
- Empirical Bond Strength Bond Length Curves For OxDocumento18 páginasEmpirical Bond Strength Bond Length Curves For OxGary DunnAinda não há avaliações
- Etil Acetate Total Production RDDocumento6 páginasEtil Acetate Total Production RDJuan Camilo Rodriguez SandovalAinda não há avaliações