Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Potassium - Sparing Diuretics
Enviado por
rhimineecat710 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
80 visualizações12 páginasPotassium – Sparing Diuretics
Título original
Potassium – Sparing Diuretics
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoPotassium – Sparing Diuretics
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
80 visualizações12 páginasPotassium - Sparing Diuretics
Enviado por
rhimineecat71Potassium – Sparing Diuretics
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 12
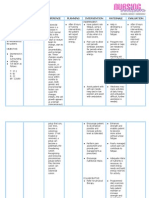
Potassium-sparing diuretics:
reduce Na+ reabsorption
reduce K+ secretion
These are not potent diuretics when used
alone
They are primarily used in combination
with other diuretics.
Amiloride (Midamor)
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Interfere with sodium-potassium exchange in
collecting ducts and convoluted tubules
Competitively bind to aldosterone receptors
Block the reabsorption of sodium and water
Prevent potassium from being pumped into the
tubule, thus preventing its secretion
Sodium and water are excreted
These drugs are generally used in combination
with a thiazide or loop diuretic to treat
hypertension
CHF
refractory edema
They are also used to induce diuresis in clinical
situations associated with hyperaldosteronism:
adrenal hyperplasia
in the presence of aldosterone-producing
adenomas when surgery is not feasible.
these drugs are well absorbed protein bound,
and widely distributed
they are metabolized in the liver and primarily
excreted in urine
these diuretics cross the placenta and enter
breast milk
* routine use during pregnancy is not appropriate,
and they should be saved for situations in which the
mother has pathological reasons for use, not pregnancy
manifestations or complications , and the benefit to
the mother clearly outweighs the risk to the fetus.
* If one of these drugs is needed during lactation,
another method of feeding the baby should be used,
because of the potential for adverse effects on fluid and
electrolyte changes in the baby.
these drugs are contraindicated for use in
patients with allergy to the drug,hyperkalemia,
renal disease , or anuria.
are given cautiously during pregnancy and
lactation.
These agents can cause hyperkalemia,
hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and
arrhythmias.
Spironolactone is associated with
gynecomastia and can also cause menstrual
abnormalities in women.
These drugs are contraindicated in renal
insufficiency, especially in diabetic patients.
They are contraindicated in the presence of
other potassium-sparing diuretics and should
be used with extreme caution in individuals
taking an angiotensin-converting enzyme
(ACE) inhibitor.
Spironolactone
Act as antagonists to aldosterone, competes
with aldosterone for receptor sites in DCT
Results in decreased Na
+
reabsorption in DCT
Promotes Na
+
and water loss
Decreased Na
+
reabsorption balanced by K
+
retention at this site (and H
+
).
Used in combination with diuretic e.g..
frusomide
Triamterene and Amiloride
Similar effect to spironolactone by reducing Na
+
absorption and H
+
/K
+
secretion in DCT
Independent of aldosterone
Have little diuretic effect
Used in conjunction with diuretics
In low doses blocks entry of Na+ into tubule
cells across luminal membrane
Decrease availability of Na
+
to Na
+
-K
+
-ATPase at
basal cell membrane
Called Na
+
channel blockers
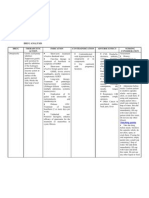
Drug Name Usual Dosage Usual Indications
amiloride (Midamor) 15 -20 mg/d PO with
monitoring of
electrolytes
All of the potassium
sparing diuretics are
indicated for the
adjunctive treatment of
edema caused by
congestive heart failure,
liver disease, or renal
disease; hypertension;
hyperkalemia; and
hyperaldosteronism;
Special considerations:
Not for use in children
Spironolactone
(Aldactone)
100 200 mg/d PO for
edema; 100 400 mg/d
PO for
hyperaldosteronism;
50 100 mg/d PO for
hypertension
Pediatric: 3.3 mg/kg per
day PO
Special considerations:
Can be used in children
with careful monitoring
of electrolytes
Triamterene (Dyrenium) 100 mg/D PO b.i.d Special considerations:
Not for use in children
Você também pode gostar
- Other Diuretics Final 2017Documento4 páginasOther Diuretics Final 2017Anonymous sSuBudwdAinda não há avaliações
- DrugDocumento13 páginasDrugkhesler BacallaAinda não há avaliações
- Potassium SpariDocumento13 páginasPotassium SpariOmkar RaviAinda não há avaliações
- DiureticsDocumento42 páginasDiureticsKeziah TampusAinda não há avaliações
- TriamtereneDocumento2 páginasTriamtereneapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- Oral Rehydration SaltDocumento3 páginasOral Rehydration SaltVincent ManganaanAinda não há avaliações
- GRP 6.pharmaDocumento29 páginasGRP 6.pharmaLjc JaslinAinda não há avaliações
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocumento5 páginasSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinAinda não há avaliações
- DiureticsDocumento10 páginasDiureticsAyla NacariøAinda não há avaliações
- Plain LRDocumento3 páginasPlain LRlovlyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocumento5 páginasDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- CVS PART 1 DiureticsDocumento31 páginasCVS PART 1 Diureticshishamasmaa5Ainda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocumento98 páginasDrugs Acting On Renal SystemIsmael JaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Diuretics TabulationDocumento3 páginasDiuretics TabulationAna Rika Javier HarderAinda não há avaliações
- DiureticsDocumento3 páginasDiureticsCarl Simon CalingacionAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VDocumento9 páginasName: Ellaine Jhane T. Domede Bsn1VNeil Floyd VenturaAinda não há avaliações
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocumento12 páginasDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioAinda não há avaliações
- Labs Drug Study 1Documento17 páginasLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento19 páginasDrug StudyAngelica Bestre De La CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Kee: Pharmacology, 8th Edition: Chapter 43: Diuretics Downloadable Key PointsDocumento3 páginasKee: Pharmacology, 8th Edition: Chapter 43: Diuretics Downloadable Key PointsLondera BainAinda não há avaliações
- Lasilactone PI 201801Documento9 páginasLasilactone PI 201801Shivam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocumento12 páginasDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocumento5 páginasDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoana Marie GuanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit VI Drugs Used On Urinary SystemDocumento46 páginasUnit VI Drugs Used On Urinary SystemHarshika KDGAinda não há avaliações
- DiureticsDocumento3 páginasDiureticsarshu98172Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento10 páginasDrug StudyHelen ReonalAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Renale Disease-1Documento20 páginasManagement of Renale Disease-1Abdur RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Indapamid SR Pliva 15 MG Tablete S Produljenim Oslobadjanjem SPCDocumento10 páginasIndapamid SR Pliva 15 MG Tablete S Produljenim Oslobadjanjem SPCDuje ErcegovicAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoAinda não há avaliações
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasFurosemide Drug StudyYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On GitDocumento119 páginasDrugs Acting On GitNathaniel Mbiu Tim100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsDocumento5 páginasGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZAinda não há avaliações
- SPIRONOLACTONEDocumento2 páginasSPIRONOLACTONERj AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- DrugsDocumento20 páginasDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drugs GCDocumento7 páginasDrugs GCJharene BasbañoAinda não há avaliações
- Important Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease: Continuing Medical EducationDocumento4 páginasImportant Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease: Continuing Medical EducationAn-Nisa Khoirun UmmiAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Ana - FurosemideDocumento3 páginasDrug Ana - FurosemideIngrid Sasha FongAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyAbdurrahim MlntdAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasDrug StudyCyric Jyn Fadul Full100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento11 páginasDrug StudyNedemar OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Nikki Logan - Friends To Forever - Sahabat Selamanya (BM)Documento10 páginasNikki Logan - Friends To Forever - Sahabat Selamanya (BM)Arie Yanti YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6-1Documento50 páginasLecture 6-1Vijita PriyaAinda não há avaliações
- SpironolactoneDocumento3 páginasSpironolactoneapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- Antipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsDocumento6 páginasAntipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsLeevi Paul LaviñaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento96 páginasDrug StudyirismirzigAinda não há avaliações
- The Management of Cirrhotic Ascites: DisclosuresDocumento3 páginasThe Management of Cirrhotic Ascites: DisclosuresJiaaaahAinda não há avaliações
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Diuretics 1Documento34 páginasDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrointestinal Tract DisordersDocumento4 páginasGastrointestinal Tract DisordersCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaAinda não há avaliações
- AntacidsDocumento7 páginasAntacidsrosita d. ramosAinda não há avaliações
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationDocumento4 páginasFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento18 páginasDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamAinda não há avaliações
- Medfact Pocket Guide Drug Interaction: FurosemideDocumento7 páginasMedfact Pocket Guide Drug Interaction: FurosemideParis Yayuk JacksonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento5 páginasDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (MS)Documento9 páginasDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoAinda não há avaliações
- Archer Review Note 5Documento11 páginasArcher Review Note 5karan SinghAinda não há avaliações
- BAENA, Nicole - Compilation of PharmacardsDocumento11 páginasBAENA, Nicole - Compilation of PharmacardsnicoletbaenaAinda não há avaliações
- Fusid®: TabletsDocumento8 páginasFusid®: Tabletsddandan_2Ainda não há avaliações
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of NursingDocumento38 páginasFundamentals of NursingabigailxDAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Problems: An Excerpt From Our Book, The Natural Remedies EncyclopediaDocumento12 páginasCardiovascular Problems: An Excerpt From Our Book, The Natural Remedies Encyclopediarhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- To Do Notebook Template 3Documento2 páginasTo Do Notebook Template 3rhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- What To Include in Your Yellow Card of An Adverse Drug ReactionDocumento3 páginasWhat To Include in Your Yellow Card of An Adverse Drug Reactionrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- TSS NEJM ReadingDocumento16 páginasTSS NEJM Readingrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Tube FeedingDocumento55 páginasTube Feedingrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular System: Claire R. Hatton, RN, MANDocumento63 páginasCardiovascular System: Claire R. Hatton, RN, MANrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Tests and DiagnosisDocumento5 páginasTests and Diagnosisrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- In The Name of Allah, The Beneficient, The Merciful: Articles of Faith 1. Unity of GodDocumento11 páginasIn The Name of Allah, The Beneficient, The Merciful: Articles of Faith 1. Unity of Godrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Poliomyelitis: Abarca, Mark Nerza, Lourelie BSN3-ADocumento45 páginasPoliomyelitis: Abarca, Mark Nerza, Lourelie BSN3-Arhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Report On AmoebiasisDocumento36 páginasReport On Amoebiasisrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Scabies PresentationDocumento15 páginasScabies Presentationrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- A Book of Religious KnowledgeDocumento27 páginasA Book of Religious Knowledgerhimineecat710% (1)
- Humanistic Learning TheoryDocumento4 páginasHumanistic Learning Theoryrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Filariasis: By: Barrantes, Patrick and Garcia, Charina JaneDocumento17 páginasFilariasis: By: Barrantes, Patrick and Garcia, Charina Janerhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Eyes and Vision PresentationDocumento142 páginasEyes and Vision Presentationrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Pediculosis CorporisDocumento14 páginasPediculosis Corporisrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- RA 9173 & Legal Responsibilities of NursesDocumento8 páginasRA 9173 & Legal Responsibilities of Nursesrhimineecat71Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Colorectal CancerDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Colorectal Cancerderic88% (34)
- 9650-0301-01 Rev. MDocumento48 páginas9650-0301-01 Rev. MCarlos AndresAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyDocumento5 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology'Riku' Pratiwie TunaAinda não há avaliações
- Bleeding Disorder (Paediatrics)Documento95 páginasBleeding Disorder (Paediatrics)Nurul Afiqah Mohd YusoffAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Atherosclerosis - SummaryDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Atherosclerosis - SummaryJohn OsborneAinda não há avaliações
- NAET Infor GuideDocumento7 páginasNAET Infor GuideAlejo Ribas SalaAinda não há avaliações
- Care of Older Adult HWDocumento6 páginasCare of Older Adult HWJenny AjocAinda não há avaliações
- Ivermectina - Profilaxis Covid-19 - DR HirschDocumento8 páginasIvermectina - Profilaxis Covid-19 - DR HirschAlheni Fabiola Miranda GomezAinda não há avaliações
- DSDRelease Medical v1 EUDocumento2 páginasDSDRelease Medical v1 EUTania FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- 2024-Article Text-6560-1-10-20230128Documento4 páginas2024-Article Text-6560-1-10-20230128Adniana NareswariAinda não há avaliações
- OLHS COVID Phase-IV BackToSchool FlyerDocumento1 páginaOLHS COVID Phase-IV BackToSchool FlyerRachael ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - O - Shubham BorkarDocumento9 páginas5 - O - Shubham Borkarumapati 1505Ainda não há avaliações
- Haemodialysis Access UKDocumento19 páginasHaemodialysis Access UKmadimadi11Ainda não há avaliações
- J of Ultrasound Medicine 2022 Demi New International GuidelinesDocumento36 páginasJ of Ultrasound Medicine 2022 Demi New International Guidelineslilo serranoAinda não há avaliações
- Kerala University of Health Sciences Thrissur: (2010 Scheme)Documento1 páginaKerala University of Health Sciences Thrissur: (2010 Scheme)subiAinda não há avaliações
- AsdsDocumento5 páginasAsdsGerald MasagandaAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Pushing During Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor and Perineal Outcomes: A ReviewDocumento7 páginasMethods of Pushing During Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor and Perineal Outcomes: A ReviewToqa DabbasAinda não há avaliações
- Manesar Design Competition NoticeDocumento15 páginasManesar Design Competition NoticeAsna DTAinda não há avaliações
- The Metamorphosis of Pharmacy Education in Ethiopia The Case of Mekelle UniversityDocumento10 páginasThe Metamorphosis of Pharmacy Education in Ethiopia The Case of Mekelle UniversityGatwech DechAinda não há avaliações
- A235B300D8AF49669FA4CE74DD0BB90EDocumento2 páginasA235B300D8AF49669FA4CE74DD0BB90EMalyn DilagAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Plan ProposalDocumento27 páginasStrategic Plan ProposalMaya Fahel LubisAinda não há avaliações
- Introductory Welcome To Avicenna Medical and Dental CollegeDocumento63 páginasIntroductory Welcome To Avicenna Medical and Dental Collegeshahreen KAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal and Obstetric Risk Assessment (NORA) Pregnancy Cohort Study in SingaporeDocumento7 páginasNeonatal and Obstetric Risk Assessment (NORA) Pregnancy Cohort Study in SingaporePremier PublishersAinda não há avaliações
- 4th Week Health ModulesDocumento13 páginas4th Week Health ModulesYza VelleAinda não há avaliações
- Region X: January 1, 2021 Advanced Life Support Standard Operating ProceduresDocumento126 páginasRegion X: January 1, 2021 Advanced Life Support Standard Operating ProceduresC ScribAinda não há avaliações
- M. Pharm Review NAPLEX38Documento1 páginaM. Pharm Review NAPLEX38JUSASBAinda não há avaliações
- WIDALDocumento17 páginasWIDALNasti YL HardiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Presepsin in Determining The Incidence of Septic Shock and Mortality in Patients With SepsisDocumento8 páginasRole of Presepsin in Determining The Incidence of Septic Shock and Mortality in Patients With Sepsisfaraz.mirza1Ainda não há avaliações
- UNIT II MedicalDocumento34 páginasUNIT II Medicalangelax1.1Ainda não há avaliações
- Ethics and Mental HealthDocumento15 páginasEthics and Mental Healthapi-3704513100% (1)
- Overview of Anesthesia - UpToDateDocumento11 páginasOverview of Anesthesia - UpToDateFernandoVianaAinda não há avaliações