Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
How To Read Electrocardiography
Enviado por
Andi WiraTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
How To Read Electrocardiography
Enviado por
Andi WiraDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
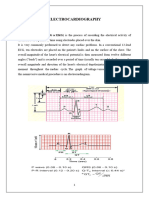
HOW TO READ
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine
Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia
National Cardiovascular Center Harapan Kita
Aryo Soeryo Kuncoro, MD, FIHA
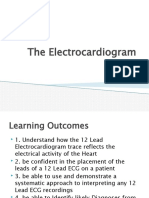
How to read ECG
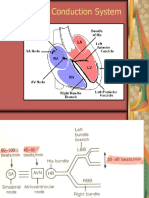
Anatomy and electrophysiology of the
heart
The purpose of ECG recording
ABC of ECG recording
Interpretation of normal ECG
Normal variant
Anatomy and electrophysiology of
the heart
Anatomy of THE HEART
V
6
V
5
V
4
V
3
V
2
V
1
V
6R
V
5R
V
4R
V
3R
Midclavicular line
Anterior axillary line
Midaxillary line
Unipolar Precodial (Chest) Leads
Mervin J. Goldman, MD. 11
th
edition Principles of clinical Electrocardiography. Clinical Professor of Medicine University of
California School of Medicine San Francisco @1995-1982
V
7
V
8
V
9
V
9R
V
8R
V
7R
Horizontal plane of V
4-6
Unipolar Precodial (Chest) Leads
Mervin J. Goldman, MD. 11
th
edition Principles of clinical Electrocardiography. Clinical Professor of Medicine University of
California School of Medicine San Francisco @1995-1982
ATTACHMENT OF THE LEADS
EINTHOVENS TRIANGLE
The purpose of ECG recording
Morphology of ECG tracing
Is any abnormality of P wave, QRS complex, ST, T wave
Hypertrophy?
Ischemia/infarction
Electrolyte imbalance
Disturbance of AVN, specific disease (Brugada, Long QT,WPW
syndrome)
To look whether any rhythm disturbance (arrhythmias)
Normal
Abnormal
Irregular
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
P wave
Absent (really absent or buried within QRS complex)
Present
Axis
Normal (its vector, from upper right to lower left)
Abnormal
Its vector goes up (it is retrograde from the ventricle or abnormal site of
its origin)
Morphology
Normal morphology
Abnormal morphology (LAH, RAH)
Rate
Regular (normal, brady or tachy)
Irregular (atrial extra systole oratrial fibrillation)
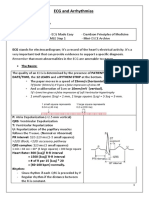
CARA MENGHITUNG HEART RATE
2. RHYTHM
Karakteristik Sinus Ritme:
Rate : 60-100x/menit
Ritme : Interval P-P regular, interval R-R reguler
Gelombang P : Positif (upright) di lead II, selalu diikuti kompleks QRS
PR interval : 0.12-0.20 detik dan konstan dari beat to beat
Durasi QRS : kurang dari 0.10 detik kecuali ada gangguan konduksi
intraventrikel
3. AXIS
4. HYPERTROPHIC SIGNS
5. MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA OR
INFARCTION
Ischemia
Injury
Necrosis
6. ARRHYTHMIA
WHATS WRONG??
Lead Error: V1 and V3 are Transposed!
In this normal 12-lead ECG the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are
interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this
lead placement error.
DISCUSSION
Sinus arrhythmia
Limb lead reversal
Early repolarization
Subendocardial ischemia.
Anterolateral ST-segment depression
Unstable angina
acute anterolateral myocardial infarction
High lateral infarction
Lateral myocardial infarction
Right ventricular infarction
Acute inferoposterior myocardial infarction
left ventricular aneurysm
Mobitz I
High-grade atrioventricular block
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
premature ventricular contraction
Supraventricular tachycardia
Wide complex tachycardia
Ventricular flutter
Idioventricular rhythm
Você também pode gostar
- ECG InterpretationDocumento81 páginasECG InterpretationRidyah Ning Tyas100% (2)
- ECG InterpretationDocumento81 páginasECG Interpretationd.ramadhan100% (3)
- ECG InterpretationDocumento81 páginasECG InterpretationK'RiBo Siahaan PaRt IIAinda não há avaliações
- Dasar Dasar Interpretasi Ekg Radityo Prakoso Hary S MuliawanDocumento69 páginasDasar Dasar Interpretasi Ekg Radityo Prakoso Hary S MuliawanKinanta Dewi100% (1)
- ECG TutorialDocumento74 páginasECG TutorialIrina Triboi AmariiAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Utah EduDocumento87 páginasEcg Utah EduMos Viorel DanutAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Tutorial PDFDocumento82 páginasEcg Tutorial PDFpacpacpac123Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0Documento84 páginasIntroduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0TrickyRooAinda não há avaliações
- A El Outline June 2007Documento82 páginasA El Outline June 2007neysaonlineAinda não há avaliações
- ECG FILEDocumento29 páginasECG FILEneha miriAinda não há avaliações
- EcgDocumento57 páginasEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- Ekg Normal PapdiDocumento51 páginasEkg Normal PapdifennyaliskaAinda não há avaliações
- Hotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PDocumento145 páginasHotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PkangheriAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Documento91 páginasIntroduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Muhammad AsrudinAinda não há avaliações
- ECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyDocumento103 páginasECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyGhaidaa Sadeq100% (1)
- Ecg 01Documento103 páginasEcg 01Bandar al ghamdi100% (1)
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento52 páginasElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentDocumento54 páginasDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentadela_97line100% (2)
- EkgDocumento75 páginasEkgRamot Tribaya Recardo PardedeAinda não há avaliações
- ECG PresentationDocumento52 páginasECG PresentationShah NahidAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Reading Made EasyDocumento59 páginasEcg Reading Made EasyAngealyn GaviolaAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)Documento53 páginasBasics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)CloudySkyAinda não há avaliações
- Ekg Kds Kardio OkDocumento54 páginasEkg Kds Kardio OkDai Muhammad AbdiAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrocardiographyDocumento4 páginasElectrocardiographyJho BuanAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Varient ECGDocumento64 páginasNormal Varient ECGShah NahidAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg PDFDocumento87 páginasEcg PDFSabir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Elektrokardiografi Dasar: Dr. Eka Ginanjar, SPPDDocumento81 páginasElektrokardiografi Dasar: Dr. Eka Ginanjar, SPPDNur Rahmat WibowoAinda não há avaliações
- The 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideDocumento31 páginasThe 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideJay JiangAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocumento52 páginasElectrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoAinda não há avaliações
- DR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg TracingDocumento39 páginasDR Amao Core Principles of Interpreting Ecg Tracingdan ekelemeAinda não há avaliações
- ECG and ArrhythmiasDocumento25 páginasECG and ArrhythmiasRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Perkembangan EKGDocumento51 páginasPerkembangan EKGevhyajahAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Approach by DR SSSDocumento51 páginasECG Approach by DR SSSAritro DasguptaAinda não há avaliações
- Dysrhythmia Interpretation GuideDocumento26 páginasDysrhythmia Interpretation GuideSarah ChadnickAinda não há avaliações
- IV A Ecg Preparation 12 Lead Placements NCM 118 Nursing Care of Clients With Life Threatening CondDocumento13 páginasIV A Ecg Preparation 12 Lead Placements NCM 118 Nursing Care of Clients With Life Threatening CondRio DanteAinda não há avaliações
- ECG EKG InterpretationDocumento11 páginasECG EKG InterpretationGunma AkagiAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Made EasyDocumento130 páginasEcg Made EasyJOHN ARBIE TATTAO, RN96% (49)
- (PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackDocumento33 páginas(PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackTheany Be SmilerAinda não há avaliações
- A Noob's Guide to ECG InterpretationDocumento103 páginasA Noob's Guide to ECG InterpretationTeodorescu Claudia GabrielaAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Booklet PDFDocumento35 páginasECG Booklet PDFyuhuma_qyu6841Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecg Guidelines: Donna J. Castillo, MDDocumento76 páginasEcg Guidelines: Donna J. Castillo, MDBheck Magat100% (1)
- ECG Interpretation UnismaDocumento178 páginasECG Interpretation UnismadefinaAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Essentials Quick ReviewDocumento45 páginasECG Essentials Quick Reviewjaikishan marathe 69Ainda não há avaliações
- Kamis 10 September 2015 - IPD 2 - Kuliah-Ekg-Blok-KegawatdaruratanDocumento118 páginasKamis 10 September 2015 - IPD 2 - Kuliah-Ekg-Blok-KegawatdaruratanIrfanArifZulfikarAinda não há avaliações
- Electrocardiograph Y: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, Kemd, FinasimDocumento118 páginasElectrocardiograph Y: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, Kemd, FinasimTommy WidjayaAinda não há avaliações
- Dasar Ekg Iwe - RSPP Seminar RSPPDocumento89 páginasDasar Ekg Iwe - RSPP Seminar RSPPMabro CahyoAinda não há avaliações
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiografiDocumento60 páginasInterpretasi ElektrokardiografiYogi GustriansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Sistimatika Membaca EKG-FINALDocumento62 páginasSistimatika Membaca EKG-FINALEdi HidayatAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Ekg UnswagatiDocumento75 páginasKuliah Ekg UnswagatiiikAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Study GuideDocumento70 páginasECG Study GuideFatima Chrystelle NuñalAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding 12-Lead ECGsDocumento53 páginasUnderstanding 12-Lead ECGsJEM93Ainda não há avaliações
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Ainda não há avaliações
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasNo EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (5)
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationNo EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasNo EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookAinda não há avaliações
- An Apgar Score For SurgeryDocumento8 páginasAn Apgar Score For Surgerybagnerd2Ainda não há avaliações
- NHS Lanarkshire Palliative Care GuidelinesDocumento82 páginasNHS Lanarkshire Palliative Care GuidelinesAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Trakeostomi PerkutanDocumento7 páginasTrakeostomi PerkutanAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- ICU Admission Discharge Triage GuidelinesDocumento50 páginasICU Admission Discharge Triage GuidelinesNindya Anggi SinantaraAinda não há avaliações
- 216 2674 1 PBDocumento5 páginas216 2674 1 PBAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- IHOP - 09.01.26 - Admission Discharge Transfer Criteria To SICUDocumento4 páginasIHOP - 09.01.26 - Admission Discharge Transfer Criteria To SICUAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Jama PDFDocumento8 páginasJama PDFmaria isabelAinda não há avaliações
- Jama PDFDocumento8 páginasJama PDFmaria isabelAinda não há avaliações
- 1012 Lipofundinmctlct20Documento2 páginas1012 Lipofundinmctlct20Andi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- 1012 Lipofundinmctlct20Documento2 páginas1012 Lipofundinmctlct20Andi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Standards For Postanesthesia CareDocumento2 páginasStandards For Postanesthesia CareywdAinda não há avaliações
- Lower Limb AmputationDocumento4 páginasLower Limb AmputationAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign International.15Documento67 páginasSurviving Sepsis Campaign International.15Tanawat SingboonAinda não há avaliações
- Infectious Diseases: I. Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento18 páginasInfectious Diseases: I. Antibiotic ResistanceAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- NHS Lanarkshire Palliative Care GuidelinesDocumento82 páginasNHS Lanarkshire Palliative Care GuidelinesAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines Presentation FinalDocumento60 páginasSurviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines Presentation FinalailedAinda não há avaliações
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocumento3 páginasUndifferentiated SchizophreniaAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- 2005 8 4 45Documento10 páginas2005 8 4 45Andi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- IPD IPD: Jadwal Mingguan Semester Vii Kelas A Dan B Blok Tropical Medicine Minggu: 1 (Satu)Documento11 páginasIPD IPD: Jadwal Mingguan Semester Vii Kelas A Dan B Blok Tropical Medicine Minggu: 1 (Satu)Andi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- EctopicDocumento5 páginasEctopicAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- General Information On Antibiotics and Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento3 páginasGeneral Information On Antibiotics and Antibiotic ResistanceAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Josh Zimmerman, Survival in The orDocumento11 páginasJosh Zimmerman, Survival in The orAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Walkthrough Mhp3Documento41 páginasWalkthrough Mhp3Andi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Part 9 Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines PDFDocumento20 páginasPart 9 Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines PDFAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Part 5 Adult Basic Life Support 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines PDFDocumento22 páginasPart 5 Adult Basic Life Support 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines PDFAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Part 9 Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association GuidelinesDocumento20 páginasPart 9 Post Cardiac Arrest Care 2010 American Heart Association GuidelinesAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- Anestesi Pada Sistem KardioDocumento72 páginasAnestesi Pada Sistem KardioAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- WHO AdultsDocumento4 páginasWHO AdultsAndi WiraAinda não há avaliações
- CKDDocumento16 páginasCKDAnny AunAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento208 páginasChronic Kidney DiseaseDaveyf123Ainda não há avaliações
- ECON 121 Principles of MacroeconomicsDocumento3 páginasECON 121 Principles of MacroeconomicssaadianaveedAinda não há avaliações
- CV Jan 2015 SDocumento4 páginasCV Jan 2015 Sapi-276142935Ainda não há avaliações
- Overview of Isopanisad, Text, Anvaya and TranslationDocumento7 páginasOverview of Isopanisad, Text, Anvaya and TranslationVidvan Gauranga DasaAinda não há avaliações
- QHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONDocumento25 páginasQHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONherisb100% (1)
- Subarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal FluidDocumento41 páginasSubarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal Fluidharjoth395Ainda não há avaliações
- Shortcut To Spanish Component #1 Cognates - How To Learn 1000s of Spanish Words InstantlyDocumento2 páginasShortcut To Spanish Component #1 Cognates - How To Learn 1000s of Spanish Words InstantlyCaptain AmericaAinda não há avaliações
- Engb546 NP RevisedDocumento5 páginasEngb546 NP RevisedRafaelaAinda não há avaliações
- mc1776 - Datasheet PDFDocumento12 páginasmc1776 - Datasheet PDFLg GnilAinda não há avaliações
- Course Outline Physics EducationDocumento3 páginasCourse Outline Physics EducationTrisna HawuAinda não há avaliações
- Music 146 SyllabusDocumento4 páginasMusic 146 SyllabusNatAinda não há avaliações
- The Bachelor of ArtsDocumento6 páginasThe Bachelor of ArtsShubhajit Nayak100% (2)
- Emotion and Decision Making: FurtherDocumento28 páginasEmotion and Decision Making: FurtherUMAMA UZAIR MIRZAAinda não há avaliações
- Review Unit 10 Test CHP 17Documento13 páginasReview Unit 10 Test CHP 17TechnoKittyKittyAinda não há avaliações
- 15Documento74 páginas15physicsdocs60% (25)
- Audience AnalysisDocumento7 páginasAudience AnalysisSHAHKOT GRIDAinda não há avaliações
- Portal ScienceDocumento5 páginasPortal ScienceiuhalsdjvauhAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics Machine Learning Python DraftDocumento319 páginasStatistics Machine Learning Python DraftnagAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Evidence of College Readiness: A Tri-Level Empirical & Conceptual FrameworkDocumento66 páginasAnalyzing Evidence of College Readiness: A Tri-Level Empirical & Conceptual FrameworkJinky RegonayAinda não há avaliações
- Bunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesDocumento6 páginasBunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesBunga RefiraAinda não há avaliações
- Olimpiada Engleza 2017 CL A 7 A PDFDocumento4 páginasOlimpiada Engleza 2017 CL A 7 A PDFAnthony Adams100% (3)
- Bhavartha Ratnakara: ReferencesDocumento2 páginasBhavartha Ratnakara: ReferencescrppypolAinda não há avaliações
- Reducing Healthcare Workers' InjuriesDocumento24 páginasReducing Healthcare Workers' InjuriesAnaAinda não há avaliações
- Title Iii 1 30Documento3 páginasTitle Iii 1 30CheriferDahangCoAinda não há avaliações
- IS-LM Model Analysis of Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocumento23 páginasIS-LM Model Analysis of Monetary and Fiscal PolicyFatima mirzaAinda não há avaliações
- Araminta Spook My Haunted House ExtractDocumento14 páginasAraminta Spook My Haunted House Extractsenuthmi dihansaAinda não há avaliações
- CPARDocumento22 páginasCPARAngelo Christian MandarAinda não há avaliações
- Rhodes Solutions Ch4Documento19 páginasRhodes Solutions Ch4Joson Chai100% (4)
- PNP P.A.T.R.O.L. 2030 Score Card Dashboard FormulationDocumento89 páginasPNP P.A.T.R.O.L. 2030 Score Card Dashboard FormulationMark Payumo83% (41)
- Community Action and Core Values and Principles of Community-Action InitiativesDocumento5 páginasCommunity Action and Core Values and Principles of Community-Action Initiativeskimberson alacyangAinda não há avaliações
- AREVA Directional Over Current Relay MiCOM P12x en TechDataDocumento28 páginasAREVA Directional Over Current Relay MiCOM P12x en TechDatadeccanelecAinda não há avaliações