Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy and Physiology-Bones
Enviado por
pako182Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy and Physiology-Bones
Enviado por
pako182Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ANATOMY AND
PHYSIOLOGY
This is the structure and function of the body.
We have already looked at the physiology
(function) of the body when we studied the
CIRCULATORY and RESPIRATORY systems.
We will now look at the structure of the body,
and in particular:
1. BONES
2.FUNCTION OF THE SKELETON
3.JOINTS
4.MUSCLES
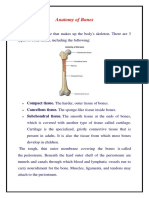
BONES
Some bones are hollow and inside them is the
red bone marrow from which our blood is
formed.
All bones are formed from CARTILAGE,
except the clavicle and some parts of the
cranium.
Bones begin to grow before children are born,
and as growth takes place the CARTILAGE,
which forms the temporary skeleton, is
hardened into bone by the addition of calcium.
Bone growth begins in the centre of each bone.
This is in the centre of the shaft. Growth
takes place upwards, downwards and around
the central marrow cavity.
Secondary growth appears at both ends.
CARTILAGE remains between the areas until
bone growth is completed.
This process of development from cartilage to
bone is known as OSSIFICATION.
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE
BONES AND THE SKELETON ?
1. MOVEMENT
2.Muscles are attached to bone by tendons,
and these allow us to apply POWER and
MOVEMENT.
3.PROTECTION of vital organs.
4.STORES CALCIUM which gives bones
hardness.
WHAT BONES DO WE NEED TO KNOW AND
WHERE THEY ARE SITUATED ?
1. CRANIUM
2.CLAVICLE
3.SCAPULA
4.STERNUM
5.RIBS
6.VERTEBRAL COLUMN
7.HUMERUS
8. RADIUS
9. ULNA
10. ILIUM
11. CARPALS
12. META CARPALS
13. PHALANGES
14. FEMUR
15. PATELLA
16. TIBIA
17. FIBULA
18. TARSALS
19. META TARSALS
20. PHALANGES
HOW DO WE CLASSIFY BONES ?
Bones are classified according to their
function.
1. (Protection) FLAT BONES
2.(Protection) IRREGULAR BONES
3.(levers) LONG BONES
4.SHORT BONES
CAN YOU PUT THE BONES OF THE
SKELETON INTO THESE GROUPS.
WHAT IS THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN
The vertebral column is very versatile. It has
strength and is flexible. We can use it as a
lever and it also protects the spinal chord.
We have 12 ribs and it is their job to protect
the organs of the chest and the upper
abdomen.
The vertebral column consists of 33 bones, or
vertebrae, which are divided into 5 groups:
1. 7 in the CERVICAL region which form the
neck, and allow a variety of movement.
2. 12 in the THORACIC region.
3. 5 in the LUMBAR region.
4. 5 in the SACRUM
5. 4 IN THE coccyx WHICH USED TO FORM
OUR TAIL.
All the vertebrae fit neatly together to
protect the spinal chord.
Between each vertebrae is an
INTERVERTEBRAL disc. These discs are very
delicate and if put out of action by slipping out
of place or tearing, the patient is said to have
slipped a disc.
JOINTS OF THE BODY
JOINT- A place where two or more bones
meet.
SYNOVIAL JOINTS- in order to prevent pain
through the friction that might be caused by
the bones rubbing together, the ends of the
bones in a SYNOVIAL JOINT are covered
with a layer of thick cartilage KNOWN AS
HYALINE CARTILAGE.
The cartilage is elastic and this enables it to
cushion and therefore protect the ends of the
bones involved in the joint.
Surrounding a synovial joint is a tough capsule,
which is reinforced by LIGAMENTS.
Inside the capsule is a SYNOVIAL
MEMBRANE which produces SYNOVIAL
FLUID to lubricate the joint.
There are 6 types of joints in which we need
to know 3 of them:
1. BALL AND SOCKET JOINTS
2.HINGE JOINTS
3.PIVOT JOINT
CAN YOU PUT THE FOLLOWING JOINTS
INTO THE ABOVE CATEGORIES AND NAME
A SPORTING ACTION THAT USES THE
JOINT ?
1. HIP
2.SHOULDER
3.KNEE
4.ELBOW
5.WRIST
6.ANKLE
WHAT SORT OF MOVEMENTS CAN BE
DONE AT A JOINT ?
There are 6 principle movements at a joint.
Can you name a joint that will perform this
movement and give examples in sport where
the following movements take place ?
1. FLEXION
2.EXTENSION
3.ABDUCTION
4.ADDUCTION
5.ROTATION
6.CIRCUMDUCTION
CAN YOU NAME THESE MOVEMENTS?
REVISION
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Anatomy of BonesDocumento6 páginasAnatomy of BonesAbdelrhman AboodaAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Exostoses: An Assessment of Two Hundred Years of Research Les Exostoses Orales: Bilan de Deux Siècles de RecherchesDocumento22 páginasOral Exostoses: An Assessment of Two Hundred Years of Research Les Exostoses Orales: Bilan de Deux Siècles de RecherchesYusuf DiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Nasal TraumaDocumento5 páginasNasal TraumaRae Marie AquinoAinda não há avaliações
- Functions and Deficiency Symptoms of MineralsDocumento12 páginasFunctions and Deficiency Symptoms of MineralsAshley Sparkles100% (1)
- Raymond - Peat - From Pms To MenopauseDocumento196 páginasRaymond - Peat - From Pms To MenopauseM. J.Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Physical Education 3rd and 4th QuarterDocumento31 páginasGrade 11 Physical Education 3rd and 4th QuarterYong YongAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report - HLH Case HistoryDocumento1 páginaCase Report - HLH Case HistoryVijayakanth VijayakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Titanium/HA FGM For Dental ImplantationDocumento18 páginasExperimental and Numerical Analysis of Titanium/HA FGM For Dental Implantationimen mehriAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactive Dating WorksheetDocumento3 páginasRadioactive Dating WorksheetJoshua Vasquez100% (1)
- 170+ Easy Mini Computer Projects For Beginners - Super Dooper Projects PDFDocumento928 páginas170+ Easy Mini Computer Projects For Beginners - Super Dooper Projects PDFhaji5100% (1)
- Specialized Connective TissueDocumento15 páginasSpecialized Connective TissueSebAinda não há avaliações
- Patologi Tulang Dan SendiDocumento79 páginasPatologi Tulang Dan SendiDio Reynaldi SusantoAinda não há avaliações
- Physeal Injuries FinalDocumento49 páginasPhyseal Injuries FinalAnkit KarkiAinda não há avaliações
- Wafer TechniquesDocumento10 páginasWafer TechniquesCeeta IndustriesAinda não há avaliações
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento7 páginasNew Microsoft Word DocumentBiancaPascuAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocumento19 páginasStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- TractionDocumento92 páginasTractionvasu_5iveAinda não há avaliações
- List of Mineral Function and DeficiencyDocumento16 páginasList of Mineral Function and Deficiencyketavmodi100% (8)
- Cell Injury-4Documento25 páginasCell Injury-4Nooria ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Bone Anatomy Viewer GameDocumento1 páginaBone Anatomy Viewer GameAngelica DiolataAinda não há avaliações
- Inside The Living BodyDocumento40 páginasInside The Living BodyEli Abram CabilinAinda não há avaliações
- SynoviomaDocumento28 páginasSynoviomaAnonymous bE4VegCcAinda não há avaliações
- Phosphorus: Nora Alnaqbi Huda Ibrahim AliaDocumento15 páginasPhosphorus: Nora Alnaqbi Huda Ibrahim Aliacaramel109Ainda não há avaliações
- Properties of Tilapia Bone Powder and Its Calcium Bioavailability Based On Transglutaminase AssayDocumento4 páginasProperties of Tilapia Bone Powder and Its Calcium Bioavailability Based On Transglutaminase AssayBabylyn OronanAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyDocumento62 páginasSCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyARLENE PINERAAinda não há avaliações
- Robert Thompson - The Calcium LieDocumento271 páginasRobert Thompson - The Calcium LieNorma Perez100% (9)
- 1.1 OSPE - Cells and TissuesDocumento11 páginas1.1 OSPE - Cells and TissuesAffan AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Testing in MedicineDocumento9 páginasAnimal Testing in MedicineCamilla SatteAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal System PDFDocumento24 páginasSkeletal System PDFJennifer LalondeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Class NotesDocumento57 páginasAnatomy Class NotesClinical Psychology0% (1)