Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The Midbrain 2
Enviado por
Vensun Reddy0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
66 visualizações43 páginasmid
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentomid
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
66 visualizações43 páginasThe Midbrain 2
Enviado por
Vensun Reddymid
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 43
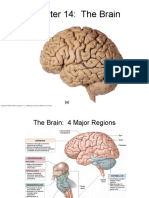
The Midbrain
Josephine M. Lumitao MD, MHPED, FPOGS
Section of Neuroanatomy
Department of Anatomy
USTFMS
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 2
Functions of the Midbrain
Conduit for ascending and descending fiber
tracts
Contains nuclei of cranial nerves III and IV and
midline nuclei with diverse functions
Center for pupillary light reflex
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 3
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 4
Developmental Features of the
Midbrain
Dorsoventral orientation of alar-basal plates
Neural cavity- Cerebral aqueduct
Alar plate derivatives :
Inferior colliculus
Superior colliculus
Substantia nigra
Red nucleus
Basal plate derivatives :
Trochlear nucleus
Oculomotor nucleus
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
Marginal zone invaded by fibers that form crus
cerebri/cerebral peduncles
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 5
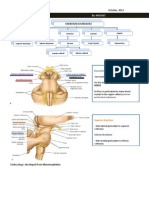
Boundaries of the midbrain
Ventral surface:
Caudal boundary- Superior pontine sulcus where
crus cerebri enters the pons
Rostral boundary exit of crura cerebri from
cerebral hemispheres and mammillary bodies
Dorsal surface:
- Caudal boundary Exit of trochlear nerves
- Rostral boundary- midbrain-diencephalic
boundary formed by posterior commissure
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 6
External Features Dorsal Surface
Caudal boundary: Exit of
trochlear nerves
Rostral boundary:
Posterior commissure
Four elevations- Corpora
quadrigemina
Inferiorcolliculus(caudal)
Superior colliculus
(rostral)
Pineal gland extends
posteriorly above and
between the superior
colliculus
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 7
External Features Ventral Surface
Caudal boundary: Superior
pontine sulcus
Rostral boundary:
Mammillary bodies
Crura cerebri pair of
large axon bundles from
cerebral hemisphere
caudal to the optic tract
Oculomotor nerves exit at
interpeduncular fossa
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 8
Lateral View of Midbrain
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 9
Internal Anatomy of Midbrain
Tectum area posterior to
cerebral aqueduct; contains
the superior and inferior
colliculus
Tegmentum extends from
base of tectum; does not
include substantia nigra;
contains ascending and
descending fiber tracts and
cranial nerve nuclei
Basis pedunculi
Anterolateral portion of
midbrain on each side made
up of Substantia nigra and
Crus cerebri
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 10
Caudal Midbrain Level of the Inferior Colliculus
-TECTUM:
Inferior colliculus made up of a
large central nucleus, dorsal
nucleus and lateral nucleus;
auditory relay nuclei receiving
fibers of the lateral lemniscus
Brachium of the inferior colliculus
projects to medial geniculate body
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 11
Inferior Colliculus
Central nucleus- egg shaped core of the inferior
colliculus at the base of afferent fibers of the lateral
lemniscus; consist of parallel shaped layers of cells
with disc shaped dendritic fields; receives and
integrates information from multiple hindbrain
auditory sources and projects to medial geniculate
nucleus; ascending projections converge in a point-
to-plane order, low frequencies posterolaterally and
high frequencies anteromedially
Paracentral nuclei made up of pericentral nucleus
(posterior) and external (lateral) nucleus; receive input
from central nucleus, cerebral cortex and non-auditory
input from spinal cord and superior colliculus;
projects to MGN, superior colliculus and reticular
formation; involved in functions related to attention,
multisensory integration and auditory-motor reflex
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 12
Inferior Colliculus receives auditory input from
Lateral lemniscus; projects to medial geniculate body
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 13
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 14
Caudal Midbrain Level of the Inferior Colliculus
TEGMENTUM:
- Periaqueductal gray collection of
nerve cell bodies that surround the
cerebral aqueduct; opiate receptors;
receives spinomesencephalic tract and
projects to nucleus raphe magnus; for
modulation of pain transmission
-Trochlear nucleus supplies superior
oblique muscle
-Medial longitudinal fasciculus
-Mesencephalic nucleus and tract
-Decussation of superior cerebellar
peduncle- crossed fibers from deep
cerebellar nuclei to red nucleus and/or
thalamus
-Anterolateral system and medial
lemniscus; Central tegmental tract
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 15
Trochlear Nerve
Only motor cranial nerve formed by axons that
cross the midline before their exit
Longest intracranial course
Trochlear nucleus provides GSE fibers to
superior oblique which functions to direct the
eyeball down when turned inwards (intorsion,
depression)
Receives projections from neurons in frontal
eye field via the rostral interstitial nucleus of
the MLF (medial longitudinal fasciculus)
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 16
Caudal Midbrain Level of the Inferior Colliculus
-BASIS PEDUNCULI:
-Substantia nigra pars compacta
(dopamine rich) and pars
reticulata (GABA)
-Crus cerebri middle 3/5
Corticospinal and corticobulbar;
medial 1/5 frontopontine (Arnolds
bundle); lateral 1/5 temporo-
parieto-occipito pointine fibers
(Turcks bundle)
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 17
Substantia Nigra
Functionally associated with the basal nuclei
Made up of pars compacta and pars reticulata
Pars compacta large number of neuromelanin
containing cells rich in dopamine; project to
neostriatum(caudate nucleus and putamen) as part of
nigrostriatal pathway
Pars reticulata- loose aggregations of medium to large
sized neurons rich in GABA; project to superior
colliculus, thalamus and pontine reticular formation
Parkinson disease- associated with loss of dopamine ;
resting tremors, akinesia, bradykinesia , blank stare,
paucity of movement
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 18
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 19
Parkinsons Disease
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 20
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 21
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 22
TECTUM:
Superior Colliculus- made up of
alternating gray matter and white matter;
layers I-III receive input from retina and
visual cortices and project to thalamus;
layers IV-VII subserve gaze changes
including eye movement and project to
thalamus, brain stem and spinal cord
-Detection of movements in visual fields
for visual orientation, searching and
tracking
-For audiovisual reflexes as it receives
input from inferior colliculus
-Connects with the lateral geniculate
nucleus via brachium of superior
colliculus
Features of Rostral Midbrain Level of
Superior Colliculus
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 23
TEGMENTUM:
Red nucleus Magnocellular division
send axons which cross the midline at
ventral tegmental decussation of Forel to
form the rubrospinal tract that innervates
the proximal limb flexors
Parvocellular division (rostral)
axons form the rubroolivary tract that
descends in the central tegmental tract
and terminates in the ipsilateral inferior
olives
Receives afferents from the
contralateral deep cerebellar nuclei and
ipsilateral cerebral cortex
Features of Rostral Midbrain Level of
Superior Colliculus
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 24
TEGMENTUM:
Dorsal tegmental decussation of
Meynert crossed projections of
superior colliculus to brain stem areas
(tectoreticular, tectoolivary and
tectospinal cervical spinal cord)
Tectobulbospinal system of brain stem
MLF
Medial lemniscus
Anterolateral system
Central tegmental tract
Ventral tegmental decussation of
Forel-crossed axons from red nucleus
that form ruprospinal tract
Features of Rostral Midbrain Level of
Superior Colliculus
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 25
Oculomotor Nucleus
Composed of:
- central nucleus of Perlia that supplies the
ciliary muscle for convergence and accommodation
- lateral dorsal somatic cell column that innervates all extraocular muscles
except the lateral rectus and superior oblique
- Midline dorsal subnucleus(caudal central subdivision) supply the levator
palpebrae superioris
- midline dorsal visceral cell column (Edinger-Westphal nucleus) , origin of
preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the ciliary ganglion, postganglionic
fibers of which innervate sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
Does not receive direct cortical projections via corticobulbar pathway; cortex of
frontal eye field exerts its control over oculomotor neurons via projections to
rostral interstitial nucleus of the MLF (riMLF, the vertical gaze center) and the
superior colliculus
Accessory nuclei: interstitial nucleus of Cajal, nucleus of Darkschewtisch,
nucleus of posterior commissure and riMLF
Oculomotor nerve emerge at interpeduncular fossa medial to crus cerebri
Ipsilateral lesion will result in an abducted and depressed eye, diplopia (double
vision), mydriasis (dilated pupil) non reactive to light and cannot accommodate
and drooping of eyelids (ptosis)
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 26
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 27
Reticular and Raphe Nuclei of
Midbrain
Reticular Nuclei are
cuneiform and
subcuneiform nuclei
which forms part of
ARAS for maintaining
alertness and
wakefulness
Dorsal raphe nucleus
serotonergic neurons
that modulate neuronal
activity involved in
sleep/dream cycles
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 28
Midbrain-Diencephalic junction
Pretectal Area consist of groups of cells related to visual
system; brainstem center for pupillary light reflex; receives input
from superior colliculus and project bilaterally to Edinger-
Westphal nucleus mediating direct and consensual pupillary light
reflex
Posterior commissure rostral boundary of midbrain;
functionally, contains fibers from the pretectal nuclei that project
to contralateral Edinger Westphal nucleus and upgaze fibers
from riMLF; important in consensual pupillary light reflex and
upward vertical gaze
Ventral tegmental area of Tsai- diffuse cell group
ventromedial to red nucleus and continuous with lateral
hypothalamic area; contains dopaminergic neurons that project
to cortical and subcortical structures of limbic system (emotional
behavior); fibers directed to nucleus accumbens that constitute
the mesolimbic or reward pathway
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 29
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 30
Pupillary Light Reflex
Four neuron reflex arc:
Ganglion cells of retina
forms the OPTIC
NERVE
Pretectal area
Edinger-Westphal
nucleus (bilateral) of
OCULOMOTOR
NERVE
Ciliary Ganglion to
sphincter pupillae to
produce pupillary
constriction
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 31
BLOOD SUPPLY OF
MIDBRAIN:
Superior cerebellar
artery supply the
tectum
Quadrigeminal artery
supply the posterior
midbrain and
ventrolateral regions
Posteromedial group
of branches from circle
of Willis (P1 and P2)
from posterior
cerebral artery supply
ventromedial region of
midbrain
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 32
Vascular Syndromes of the Midbrain
Webers syndrome ipsilateral
paralysis of extraocular
muscles except superior
oblique and lateral rectus,
dilated pupil ipsilaterally,
contralateral paralysis of
extremities
Claude syndrome Ipsilateral
paralysis of all extraocular
muscles except LR and SO;
ipsilateral dilated pupil,
contralateral ataxia, tremor
and incoordination
Benedikt syndrome
ipsilateral paralysis of
extraocular muscles except
SO and LR; ipsilateral dilated
pupil; contralateral paralysis
of extremities and
contralateral tremor and ataxia
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 33
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 34
1. Which of the ff. serves as caudal
boundary of dorsal midbrain?
A. Superior pontine sulcus
B. Exit of trochlear nerve
C. Mammillary body
D. Posterior commissure
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 35
2. Which of the ff. forms the tectum in
rostral midbrain?
A. Superior colliculus
B. Inferior colliculus
C. Cerebral peduncles
D. Cerebral aqueduct
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 36
3. Which of the ff. is center for
pupillary light reflex?
A. Dorsal raphe nucleus
B. Pretectal area
C. Posterior commissure
D. Ventral tegmental area of Tsai
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 37
4. Which of the ff. nuclei of the inferior colliculus
shows plane-to-order convergence of
projections?
A. Central nucleus
B. Pericentral nucleus
C. Lateral nucleus
D. Paracentral nuclei
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 38
5. The pars compacta of the
substantia nigra is rich in _____.
A. GABA
B. Serotonin
C. Dopamine
D. Norepinephrine
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 39
6. What is the functional significance
of posterior commissure?
A. Direct pupillary light reflex
B. Consensual pupillary light reflex
C. Upward vertical gaze
D. Both B and C
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 40
7. Which of the ff. is a manifestation of
a lesion of R oculomotor nerve?
A. Ptosis of L eye
B. Medially deviated R eye
C. Dilated R pupil
D. Dilated L pupil
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 41
8. Where do the superior colliculus
fibers project?
A. Medial geniculate body
B. Lateral geniculate body
C. Red nucleus
D. Both A and B
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 42
9. Which of the ff. structures is found
in caudal midbrain?
A. Superior colliculus
B. Red nucleus
C. Oculomotor nucleus
D. Decussation of superior cerebellar
peduncle
8/20/2014 Free PowerPoint Template from www.brainybetty.com 43
10. Which of the. ff. occupies the
middle 3/5 of the crus cerebri?
A. Frontopontine fibers
B. Corticospinal fibers
C. Occipitopontine fibers
D. Temporopontine fibers
Você também pode gostar
- 2016-17 CPL FellowsDocumento150 páginas2016-17 CPL FellowsBrent Godfrey100% (1)
- 11 Online Trading AcademyDocumento16 páginas11 Online Trading AcademyVensun Reddy100% (9)
- History of Clinical PsychologyDocumento4 páginasHistory of Clinical PsychologyAnanya67% (3)
- Venn Football Tennis P 6Documento2 páginasVenn Football Tennis P 6Hartanto100% (1)
- 2006 Business CalculationsDocumento13 páginas2006 Business CalculationsthatasianpersonAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking: How to Start and Why it's ImportantDocumento33 páginasCritical Thinking: How to Start and Why it's ImportantSankalp ShandilyaAinda não há avaliações
- ISM Substitute Teacher HandbookDocumento10 páginasISM Substitute Teacher HandbookInternational School Manila100% (1)
- The Stock Market Update: 2016 © David H. WeisDocumento1 páginaThe Stock Market Update: 2016 © David H. WeisVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Theories Venn Diagram 1Documento1 páginaLearning Theories Venn Diagram 1api-489318508Ainda não há avaliações
- Esmé Weijun Wang's Insightful Look at Mental HealthDocumento4 páginasEsmé Weijun Wang's Insightful Look at Mental Healthgghyo88Ainda não há avaliações
- Childhood and Adolescent Research Paper 1Documento12 páginasChildhood and Adolescent Research Paper 1Spencer Pitoc100% (4)
- Midbrain and PonsDocumento8 páginasMidbrain and PonsMatet Monje100% (3)
- Google Analytics Guide for BeginnersDocumento21 páginasGoogle Analytics Guide for BeginnersMartin LloydAinda não há avaliações
- Guide For Good AssessmentDocumento35 páginasGuide For Good AssessmentMarila EdisonAinda não há avaliações
- Preschool Developmental Milestones GuideDocumento2 páginasPreschool Developmental Milestones GuideLacy2DaycareAinda não há avaliações
- The Power of AccountabilityDocumento5 páginasThe Power of AccountabilityGonzalo AlcalaAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching ResponsibilityDocumento0 páginaTeaching ResponsibilityhlariveeAinda não há avaliações
- Sara Educational Psychology BOOK-1342411Documento128 páginasSara Educational Psychology BOOK-1342411Anonymous 74EiX2MzgcAinda não há avaliações
- Important Life Lessons from Silence Queue OneDocumento38 páginasImportant Life Lessons from Silence Queue Onekookie12in100% (1)
- Harvard Core Concepts in The Science of Early Childhood DevelopmentDocumento7 páginasHarvard Core Concepts in The Science of Early Childhood DevelopmentSandra MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Neps Special Needs Resource PackDocumento27 páginasNeps Special Needs Resource PackMarta SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Reading To Children With Ds 08Documento15 páginasTeaching Reading To Children With Ds 08carmenbolosAinda não há avaliações
- Happy, Confident Successful: What Children Need To BeDocumento180 páginasHappy, Confident Successful: What Children Need To BeMarco Fidel ZambranoAinda não há avaliações
- Positive Disciplines Training ManualDocumento47 páginasPositive Disciplines Training Manualinnova_humanoAinda não há avaliações
- OTSM-TRIZ EducationDocumento41 páginasOTSM-TRIZ EducationPaurake MantarrayaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Think SidewaysDocumento1 páginaHow To Think SidewayshypatiaphdAinda não há avaliações
- Form Four Term Two Worksheet Three Consumer Arithmetic PDFDocumento2 páginasForm Four Term Two Worksheet Three Consumer Arithmetic PDFmissy100% (1)
- Backward Design-1Documento22 páginasBackward Design-1api-239641222Ainda não há avaliações
- Edu 4400 Bully Management PlanDocumento12 páginasEdu 4400 Bully Management Planaliciarae6Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 CerebellumDocumento61 páginas6 CerebellumNishanth LakshmanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 BrainDocumento150 páginasChapter 14 BrainMbi1965Ainda não há avaliações
- Auditory & Vestibular SystemDocumento20 páginasAuditory & Vestibular SystemMichael GuzikAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of BrainstemDocumento66 páginasAnatomy of BrainstemFitria OctavianiAinda não há avaliações
- 23 Level 6 Anatomy of Brain Stem DR Mostafa KandilDocumento36 páginas23 Level 6 Anatomy of Brain Stem DR Mostafa KandilMustafa Kandil SolimanAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem CranialnervesDocumento93 páginasBrainstem CranialnervesmarykristiroseAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Stem AnatomiDocumento55 páginasBrain Stem AnatomiNor Ubudiah SetiAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocumento71 páginasCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Embryological Development of the Central Nervous SystemDocumento28 páginasEmbryological Development of the Central Nervous Systemtenshi315Ainda não há avaliações
- Development of Nervous System - NewkeynoteDocumento49 páginasDevelopment of Nervous System - Newkeynotejesse716Ainda não há avaliações
- The Brainstem: Midbrain and IntroductionDocumento28 páginasThe Brainstem: Midbrain and Introductionانس ابوهيبةAinda não há avaliações
- Ainstem IDocumento86 páginasAinstem INishanth LakshmanAinda não há avaliações
- Embryology of Cns and AnomaliesDocumento111 páginasEmbryology of Cns and AnomaliesBaguma MichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem EnglDocumento28 páginasBrainstem EnglNasrudin EfendiAinda não há avaliações
- Cranial Nerve Nadz FinalDocumento58 páginasCranial Nerve Nadz Finalnadzirah ruslanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment On Nervous System of Amphibia, Reptilia and Aves-1Documento30 páginasAssignment On Nervous System of Amphibia, Reptilia and Aves-1MD Taufique Hussain100% (1)
- The Differentiation of Nervous System-2018Documento36 páginasThe Differentiation of Nervous System-2018NadhillaHauraWahyudianaAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem (Yuni)Documento34 páginasBrainstem (Yuni)Ayi Abdul Basith100% (2)
- Cerebellum LesionsofbrainstemDocumento50 páginasCerebellum LesionsofbrainstemAira LorenzoAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsDocumento43 páginasCerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsHarmas Novryan FarezaAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Brainstem 1Documento28 páginas7 Brainstem 1sjs6r8wwv9Ainda não há avaliações
- Lect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54Documento74 páginasLect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54nopporn2520Ainda não há avaliações
- Brainstem FunctionsDocumento94 páginasBrainstem FunctionsInchic MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- NS 5. Cerebrum SEPDocumento28 páginasNS 5. Cerebrum SEPsanthiya rajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebellardisordersppt 200731144621Documento108 páginasCerebellardisordersppt 200731144621Dr.Aman SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem & LesionsDocumento4 páginasBrainstem & LesionsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDAinda não há avaliações
- Oculomotor Nerve 3Documento30 páginasOculomotor Nerve 3Sanreet RandhawaAinda não há avaliações
- BRAINSTEM Anatom - in .Ua 04.04.2015Documento101 páginasBRAINSTEM Anatom - in .Ua 04.04.2015Sevval OzcelikAinda não há avaliações
- (OS 202A) Neuroembryology.2Documento4 páginas(OS 202A) Neuroembryology.2mark_mondiaAinda não há avaliações
- p7. The CerebellumDocumento37 páginasp7. The CerebellumGedefaw TegegneAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of BrainstemDocumento30 páginasAnatomy of BrainstemAliyah Tofani PawelloiAinda não há avaliações
- Brain AnatomyDocumento37 páginasBrain AnatomyDr. Jayesh PatidarAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Midbrain and HindbrainDocumento58 páginasDevelopment of Midbrain and HindbrainBramwell K. MiteiAinda não há avaliações
- Synaptic Circuitry in The Cerebellum: Lecture 2 Part 2Documento39 páginasSynaptic Circuitry in The Cerebellum: Lecture 2 Part 2DeanAinda não há avaliações
- DR MartinDocumento42 páginasDR MartindeycallmebudAinda não há avaliações
- CEREBELUMDocumento48 páginasCEREBELUMMarian GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem: Joel P. Carreon M.DDocumento79 páginasBrainstem: Joel P. Carreon M.DAfAinda não há avaliações
- 25085ADocumento45 páginas25085AVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- 25085ADocumento45 páginas25085AVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Bitdefender Total Security 2016 Download GuideDocumento2 páginasBitdefender Total Security 2016 Download GuideRao_Surender_KosaliaAinda não há avaliações
- English IDocumento82 páginasEnglish IVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Vsa Basics PDFDocumento31 páginasVsa Basics PDFdiogonbig100% (1)
- The Stock Market Update: 2016 © David H. WeisDocumento1 páginaThe Stock Market Update: 2016 © David H. WeisVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Memory Voltage PinoutsDocumento24 páginasMemory Voltage PinoutsVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- 25085ADocumento45 páginas25085AVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Error LogDocumento18 páginasError LogVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- ذفنم يلاوتلا وذ 9 فارطا .. Serial portsDocumento16 páginasذفنم يلاوتلا وذ 9 فارطا .. Serial portsVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- How To Trade Using Multiple Time FramesDocumento1 páginaHow To Trade Using Multiple Time FramesVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Communism and Zen Fire, Zen WindDocumento1 páginaCommunism and Zen Fire, Zen WindVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- English IDocumento82 páginasEnglish IVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Date & Time:2016/06/17 09:06:147 Exchange: Ncdex SR No Instrumensymbol Expirydatltp Pricing Qulot Size (Lot Value (Span MargDocumento6 páginasDate & Time:2016/06/17 09:06:147 Exchange: Ncdex SR No Instrumensymbol Expirydatltp Pricing Qulot Size (Lot Value (Span MargVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- What Does A Daily Practice of Heartfulness Meditation Achieve? How Is This Form of Meditation Different From Contemplation As We Understand It?Documento3 páginasWhat Does A Daily Practice of Heartfulness Meditation Achieve? How Is This Form of Meditation Different From Contemplation As We Understand It?Vensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- ChipsetDocumento2 páginasChipsetFredy DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Adminsion GuidelineDocumento20 páginasAdminsion GuidelineAnandh GaneshAinda não há avaliações
- Vsa Basics PDFDocumento31 páginasVsa Basics PDFdiogonbig100% (1)
- Prospectus VI 2016Documento66 páginasProspectus VI 2016Vensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Instructions of GamesDocumento6 páginasInstructions of GamesDeepak BaraiAinda não há avaliações
- Dhavin Nifty IntradayDocumento20 páginasDhavin Nifty IntradayVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Seagate Diagnostic CommandDocumento45 páginasSeagate Diagnostic CommandMiodragAinda não há avaliações
- Following The Tracks of LionsDocumento27 páginasFollowing The Tracks of LionsVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Yoga (Kundalini)Documento168 páginasYoga (Kundalini)Alesha Rose100% (25)
- ZaspDocumento3 páginasZaspVensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Windows 7 (G2) X64 12in1 OEM ESD en-US May 2015Documento3 páginasWindows 7 (G2) X64 12in1 OEM ESD en-US May 2015Vensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Res 7Documento8 páginasRes 7Vensun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Clean Your Chakras, Clean Your Life! by Reena Johar: New Chakra Research Challenges SkepticsDocumento5 páginasClean Your Chakras, Clean Your Life! by Reena Johar: New Chakra Research Challenges SkepticsAditi RosyAinda não há avaliações
- Bloom Learning DomainsDocumento3 páginasBloom Learning DomainsMohiyulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Physioex Modul MusketDocumento65 páginasLaporan Physioex Modul MusketAfifah Marwah Al-Qadrie100% (1)
- Introduction to Education B.Ed. Mcqs SolvedDocumento37 páginasIntroduction to Education B.Ed. Mcqs SolvedALI SHERAinda não há avaliações
- Factor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoDocumento19 páginasFactor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoFourthMolar.comAinda não há avaliações
- Eustress FinallyDocumento13 páginasEustress FinallysiyanvAinda não há avaliações
- Williams Et Al 1996, The Emotional Stroop Task and Psychopathology PDFDocumento22 páginasWilliams Et Al 1996, The Emotional Stroop Task and Psychopathology PDFAnamarisamachadoAinda não há avaliações
- Language Development, Language Diversity and Immigrant EducationDocumento22 páginasLanguage Development, Language Diversity and Immigrant EducationKERTLY EMMANUELAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Stress Management 13th Edition Greenberg Test BankDocumento35 páginasComprehensive Stress Management 13th Edition Greenberg Test Bankabetterguerillal4o2100% (29)
- Bagan Perilaku KonsumenDocumento3 páginasBagan Perilaku KonsumenEdwina Putri PrimanandaAinda não há avaliações
- Course Summary:: Course Title: Course Code: InstructorDocumento2 páginasCourse Summary:: Course Title: Course Code: Instructor薇娅薇娅Ainda não há avaliações
- Raymond J. Corsini - Handbook of Innovative Therapy, Second Edition (Wiley Series On Personality Processes) (2001) PDFDocumento764 páginasRaymond J. Corsini - Handbook of Innovative Therapy, Second Edition (Wiley Series On Personality Processes) (2001) PDFFelipe Concha Aqueveque100% (3)
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation To Students' Academic Performance at Batasan Hills National High SchoolDocumento13 páginasThe Effects of Sleep Deprivation To Students' Academic Performance at Batasan Hills National High SchoolAngela ErandioAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 B9780444626042000113 MainDocumento10 páginas1 s2.0 B9780444626042000113 Mainyee yeeAinda não há avaliações
- A Neuropsychoanalytic Viewpoint: Commentary On Paper by Steven H. KnoblauchDocumento26 páginasA Neuropsychoanalytic Viewpoint: Commentary On Paper by Steven H. KnoblauchPaul ScallanAinda não há avaliações
- Wolfskill Gagnes 9 EventsDocumento12 páginasWolfskill Gagnes 9 EventsCristi BuscaAinda não há avaliações
- Stroop Effect TestDocumento8 páginasStroop Effect TestSehaj BediAinda não há avaliações
- Schema theory cognitive approachDocumento3 páginasSchema theory cognitive approachНекит СухловAinda não há avaliações
- Sherrie All - The Neuroscience of MemoryDocumento226 páginasSherrie All - The Neuroscience of MemoryDaniela Buliga bbn100% (1)
- Neurobiology of EmotionDocumento5 páginasNeurobiology of EmotionUpama PoudelAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Addiction and Depression, Anxiety and Stress: I O J E SDocumento11 páginasInternet Addiction and Depression, Anxiety and Stress: I O J E SShari' Si WahyuAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamic Supportive PsyichotherapyDocumento50 páginasDynamic Supportive PsyichotherapyGusti Andhika Azwar100% (2)
- ReferencesDocumento4 páginasReferencesapi-290353359Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Psychology Definitions, Roles, and ChallengesDocumento9 páginasClinical Psychology Definitions, Roles, and ChallengesMissy VillahermosaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical ScriptsDocumento28 páginasPractical ScriptsIslam TahaAinda não há avaliações
- Motivation 1980007641Documento12 páginasMotivation 1980007641kshitizAinda não há avaliações
- PREDYS - How To Prepare Children For The Process of Literacy AcquisitionDocumento81 páginasPREDYS - How To Prepare Children For The Process of Literacy AcquisitionEvija KasaAinda não há avaliações