Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
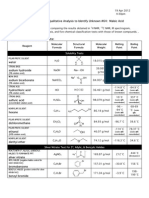
Analytical Chemistry
Enviado por
LovelyfaithN.Nadua0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
556 visualizações21 páginasIntroduction
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoIntroduction
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
556 visualizações21 páginasAnalytical Chemistry
Enviado por
LovelyfaithN.NaduaIntroduction
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 21
To define what analytical chemistry is;
To identify the difference between qualitative and
quantitative analysis;
To differentiate and familiarize among gravimetric,
volumetric and instrumental methods of analysis;
To outline the steps involved in a typical quantitative
analysis;
Participate in class discussion;
Appreciate the broad areas in which Analytical Chemistry
is commonly involved.
Objectives:
What is Analytical Chemistry?
Chemistry
Analytical
The science of the composition,
structure, properties, and reactions of
matter, especially of atomic and
molecular systems.
Of or relating to analysis or
analytics.
Dividing into elemental parts or
basic principles
Is the chemistry that is used in connection with the
separation and analysis of chemical substances.
What is Analytical Chemistry?
Analytical Chemistry provides the methods and tools
needed for insight into our material worldfor answering
four basic questions about a material sample?
What?
Where?
How much?
What arrangement, structure or form?
Science of Chemical Measurements
Classification
Chemical Analysis
(Separation)
Qualitative Analysis
(Identification)
What is present?
Quantitative Analysis
(Quantification)
How much is present?
A qualitative method yields
information about the identity
of atomic or molecular species
or the functional groups in the
sample.
A quantitative method in
contrast, provides numerical
information as to the relative
amount of one or more of
these components.
Nutritional Facts
Label
Analytical
Chemistry
Establishing
economic value
Diagnosing
disease
Relating
properties to
composition or
structure
Quality Control
Conducting
research
Determining
health hazards
Areas in which Analytical Chemistry is commonly involved
Analytical
Methods
Classical
Gravimetric
Volumetric
Instrumental
Spectroscopy
Electro
analytical
method
Category of Analytical Methods
Methods of Analysis
Method in which weight
of substance is measured.
Methods of Analysis
Refers to measurement of a volume.
Methods of Analysis
Methods are based on measurement of some
physical and chemical property, through the use of
instruments.
Steps in Analysis:
An analysis involves
several steps and
operations which
depend on:
the particular
problem
your expertise
the apparatus or
equipment available.
The analyst should be
involved in every step.
Standards bodieshierarchy
Gary Christian, Analytical Chemistry, 6th Ed. (Wiley)
Different methods provide a range of precision,
sensitivity, selectivity, and speed capabilities.
Method in testing Chocolate:
CODEX STAN 87-1981, Rev. 1 - 2003
Gary Christian, Analytical Chemistry, 6th Ed. (Wiley)
The sample size dictates what measurement
techniques can be used.
Calculate the result and report
Laboratory safety is a must!
Learn the rules.
Você também pode gostar
- Physics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONDocumento9 páginasPhysics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONHulwan Mukhlis76% (25)
- Experiment 4Documento7 páginasExperiment 4Pratik PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Introductory Titrimetric and Gravimetric Analysis: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo EverandIntroductory Titrimetric and Gravimetric Analysis: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Isa-Tr75 25 02-2000Documento40 páginasIsa-Tr75 25 02-2000Daniel Leonardo Barrera EspartaAinda não há avaliações
- Acid-Base Titrations 2Documento27 páginasAcid-Base Titrations 2John Henrick G. Uy100% (2)
- General Chemistry Lab Manual PDFDocumento232 páginasGeneral Chemistry Lab Manual PDFCharles Mintah100% (1)
- Calculations of Analytical ChemistryDocumento411 páginasCalculations of Analytical ChemistryMark Cliffton Badlon89% (9)
- Chemistry - Introduction To Environmental Analysis - Wiley 2002 PDFDocumento311 páginasChemistry - Introduction To Environmental Analysis - Wiley 2002 PDFRoberto Quiroz MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- FWEFJLNIY4QKLQXDocumento13 páginasFWEFJLNIY4QKLQXSoldan MihaiAinda não há avaliações
- Nebular Theory WsDocumento5 páginasNebular Theory WsSheila MaliitAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 400: Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry 8th Edition by Skoog, West, Holler, CrouchDocumento17 páginasCHEM 400: Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry 8th Edition by Skoog, West, Holler, CrouchJen MaramionAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Chemistry EBT 253/3: Prepared By, Dr. Salmie Suhana Che AbdullahDocumento12 páginasAnalytical Chemistry EBT 253/3: Prepared By, Dr. Salmie Suhana Che Abdullahmnfirdaus93100% (1)
- The Nature of Analytical ChemistryDocumento18 páginasThe Nature of Analytical ChemistryAzalia Tugade PanizalesAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Introduction To Analytical Chemistry PDFDocumento18 páginasUnit 1 Introduction To Analytical Chemistry PDFKim Yu100% (1)
- 01 Analytical ChemistryDocumento3 páginas01 Analytical ChemistryZenPhi100% (1)
- Chim H406 2017 - HVDocumento215 páginasChim H406 2017 - HVRavi Sharma100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry UnfinishedDocumento3 páginasAnalytical Chemistry UnfinishedJobeth Presto AlonzoAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumental Methods of AnalysisDocumento75 páginasInstrumental Methods of Analysismahbub133293% (14)
- Chapter 1 The Nature of Analytical ChemistryDocumento35 páginasChapter 1 The Nature of Analytical ChemistryAnalie RavinaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocumento25 páginasIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryDanice ConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual SK 2020Documento60 páginasLab Manual SK 2020Nrl MysrhAinda não há avaliações
- Anachem Module 1 ReviewerDocumento5 páginasAnachem Module 1 Reviewerleinra dela dullonAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Analytical Chemistry Fundamentals PDFDocumento7 páginas1-Analytical Chemistry Fundamentals PDFmoa muleAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Laboratory ManualDocumento8 páginasInorganic Laboratory ManualDhika AmeliaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 2014Documento16 páginasChemistry 2014veluselvamani100% (2)
- Spectroscopic Properties of Inorganic and Org A No Metallic Compounds - Vol1Documento406 páginasSpectroscopic Properties of Inorganic and Org A No Metallic Compounds - Vol1chemanalyserAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryMohamad Azani100% (1)
- Practical Titration: Training Manual For Titrimetric Volumetric AnalysisDocumento164 páginasPractical Titration: Training Manual For Titrimetric Volumetric AnalysisPanneer SelvamAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Analytical ChemistryDocumento300 páginasModern Analytical ChemistryOnime No IchinoseAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento223 páginasAnalytical ChemistryamitAinda não há avaliações
- Gravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaDocumento55 páginasGravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaasdfAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Analysis of UnknownDocumento10 páginasQualitative Analysis of UnknownJulie Edington100% (1)
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento303 páginasAnalytical ChemistryMuhammad Iqbal100% (2)
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDocumento48 páginas1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- Module in Organic Chemistry by Bse-III Physical Science MajorsDocumento96 páginasModule in Organic Chemistry by Bse-III Physical Science MajorsJade Noel Lapitan BalicatAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento14 páginasAnalytical ChemistryHarrizul Rivai100% (1)
- Acidity, Basicity and PkaDocumento39 páginasAcidity, Basicity and PkaZubaydah Abdullah100% (1)
- 5 SpectrosDocumento11 páginas5 SpectrosMuhammad kalimullahAinda não há avaliações
- Gravimetric AnalysisDocumento39 páginasGravimetric AnalysisPemilik Hatiku0% (1)
- Das Analytical Chemistry Second Edition Sample Chatper PDFDocumento39 páginasDas Analytical Chemistry Second Edition Sample Chatper PDFOkta Viya0% (1)
- Inorganic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualDocumento16 páginasInorganic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualAhmed ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Chemistry PDFDocumento168 páginasIndustrial Chemistry PDFHafiz Hamza100% (1)
- Differential Thermal Analysis and Differential Scanning CalorimetryDocumento12 páginasDifferential Thermal Analysis and Differential Scanning CalorimetryZahir Rayhan Jhon100% (1)
- Ebin - Pub Introduction To Modern Inorganic Chemistry 2nbsped 9843000870Documento840 páginasEbin - Pub Introduction To Modern Inorganic Chemistry 2nbsped 9843000870Sumiya Aziz100% (2)
- Precipitation TitrationDocumento3 páginasPrecipitation TitrationBanana SenpaiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesDocumento55 páginasLecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesS JAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento12 páginasAnalytical Chemistrybalaji1986Ainda não há avaliações
- INORGANIC CHEMISTRY - COURSE OUTLINE - Revised 2012Documento12 páginasINORGANIC CHEMISTRY - COURSE OUTLINE - Revised 2012Ianne FabianAinda não há avaliações
- NMR-1 BasicDocumento52 páginasNMR-1 Basicamit086Ainda não há avaliações
- Errors in Chemical AnalysisDocumento51 páginasErrors in Chemical AnalysisJeffrey PalconeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: HydrocarbonsDocumento14 páginasChapter 11 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: HydrocarbonsKatie-Nicole ChantalAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry For Aspiring Pharmacists PART 1Documento95 páginasOrganic Chemistry For Aspiring Pharmacists PART 1Jessica GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- General Chemistry Lab ManualDocumento68 páginasGeneral Chemistry Lab ManualEmin Ydds100% (2)
- Quantitative Chemical AnalysisDocumento1 páginaQuantitative Chemical AnalysisSimone Bordignon0% (4)
- Gattermann - Laboratory Methods of Organic ChemistryDocumento449 páginasGattermann - Laboratory Methods of Organic ChemistryGaurav DharAinda não há avaliações
- HPLC Detectors: Adapted From: HPLC For Pharmaceutical Scientists by Y.Kazakevich and R. LobruttoDocumento7 páginasHPLC Detectors: Adapted From: HPLC For Pharmaceutical Scientists by Y.Kazakevich and R. LobruttogunaseelandAinda não há avaliações
- STKK1702 Basic Analytical Chemistry Kimia Analisis Asas: Nurfaizah Abu TahrimDocumento53 páginasSTKK1702 Basic Analytical Chemistry Kimia Analisis Asas: Nurfaizah Abu TahrimMuhammad NaufalAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocumento22 páginasIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryCawen TaponAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ToolDocumento15 páginasBasic ToolAdi Kurniawan EffendiAinda não há avaliações
- Sch2105: Chemometrics and Classical Techniques of Chemical AnalysisDocumento48 páginasSch2105: Chemometrics and Classical Techniques of Chemical AnalysisJulius Miringu0% (1)
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryCHRISTINE JOY RETARDOAinda não há avaliações
- Flyer ChameleoBoost ConsolDocumento26 páginasFlyer ChameleoBoost ConsolAnchita MitraAinda não há avaliações
- SBM Probe 8Documento1 páginaSBM Probe 8Haroon GhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Sealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsDocumento13 páginasSealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsMohamed Abdou100% (1)
- MECN 4110 - Mechanisms Design - Fall 2012 - Lecture 01Documento59 páginasMECN 4110 - Mechanisms Design - Fall 2012 - Lecture 01florenceprasadAinda não há avaliações
- Dcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFDocumento236 páginasDcna Fixed Prosthodontics April 2004 PDFMiki FloreaAinda não há avaliações
- ∫…Δi… M……b˜M…‰ §……§…… +®…Æ˙…¥…i…" ¥…t… (…"'ˆ: ¥…Y……x… ¥…t…∂……J……Documento17 páginas∫…Δi… M……b˜M…‰ §……§…… +®…Æ˙…¥…i…" ¥…t… (…"'ˆ: ¥…Y……x… ¥…t…∂……J……YocobSamandrewsAinda não há avaliações
- 06 Instrument Transformer#Documento6 páginas06 Instrument Transformer#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- IDP Project DefinationDocumento9 páginasIDP Project DefinationDipak KardaniAinda não há avaliações
- Scanner Cobra en 201507Documento2 páginasScanner Cobra en 201507Shahbaz KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Hooke - S Law SVDocumento6 páginas11 Hooke - S Law SVTony GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Sections 4.6 - 4.7 Momentum Equation For Control Volume With Arbitrary Acceleration 4.7 The Angular-Momentum PrincipleDocumento10 páginasSections 4.6 - 4.7 Momentum Equation For Control Volume With Arbitrary Acceleration 4.7 The Angular-Momentum Principlepackman465100% (1)
- CE 632 Earth PressureDocumento18 páginasCE 632 Earth PressureBala Sutharshan100% (1)
- AcidBase Equilibrium WorksheetDocumento4 páginasAcidBase Equilibrium WorksheetAmirah SyahirahAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Various Accelerators On Different Strength Parameters of M - 20 Grade of ConcreteDocumento10 páginasEffect of Various Accelerators On Different Strength Parameters of M - 20 Grade of ConcreteTJPRC PublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- 4bak 4siz PeruDocumento8 páginas4bak 4siz PeruAnonymous cgKtuWzAinda não há avaliações
- Imbibition PressureDocumento11 páginasImbibition PressureMinette EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Ek Thesis 2003 05 12 Final 2Documento121 páginasEk Thesis 2003 05 12 Final 2tomdelfoAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage Sag PresentationDocumento26 páginasVoltage Sag Presentationpmandwani4687Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Notes - Scan ConversionDocumento7 páginasComputer Notes - Scan Conversionecomputernotes100% (1)
- ASphericDocumento5 páginasASpherickndprasad01Ainda não há avaliações
- Doubling Time and Half LifeDocumento2 páginasDoubling Time and Half Lifedrissdragon7100% (1)
- Library Book ListDocumento1.011 páginasLibrary Book ListKundan SavaliyaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 112-8: Grating and Prism SpectrometerDocumento6 páginasExperiment 112-8: Grating and Prism SpectrometerTuhinVariaAinda não há avaliações
- "Design of Jib Crane Type Rotating Derrick System" in EOT CRANE For Easy Lifting The Spare Parts During Heavy Maintenance in Confined SpaceDocumento7 páginas"Design of Jib Crane Type Rotating Derrick System" in EOT CRANE For Easy Lifting The Spare Parts During Heavy Maintenance in Confined SpaceijsretAinda não há avaliações
- Empirical Formulas For Ballistic Re-Entry TrajectoriesDocumento6 páginasEmpirical Formulas For Ballistic Re-Entry TrajectoriesMatthew AustinAinda não há avaliações