Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bab 3 Slide 1
Enviado por
Mohammad Rofii100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
49 visualizações11 páginaszs
Título original
Bab 3 slide 1.ppt
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentozs
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
49 visualizações11 páginasBab 3 Slide 1
Enviado por
Mohammad Rofiizs
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 11
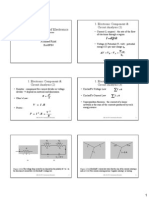
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 25
Mathematical Modeling
RECALL:
The Design of Control System requires Formulation of Mathematical
Model of the System
Why Mathematical Model?
So that we will able to Design and Analyze the control system
Examples:
How would we know the relationship between Input and Output?
How would we predict or describe the dynamic behavior of the
control system?
Two Methods to develop the Mathematical Model of Control System
1. Transfer Function in Frequency Domain (Using Laplace Transform)
2. State Space Equations in Time Domain
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 26
Review of Laplace Transform and Linearity
V(t)
L
R
C
i(t)
RECALL:
In EE301, We learned that Ordinary Differential Equation may describe
mathematically dynamic behavior, input vs. output relationship of
physical system such as Mechanical System using Newton Law and
Electrical System using Kirchoffs Law
Example: RLC Network
Lets assume that V(t) is Input; i(t) is Output
Using KVL:
0
( ) 1
( ) ( ) ( )
t
R
di t
v t v t L i d
dt C
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
R L C
v t v t v t v t
Using the differential equation (derived from KVL):
Is it a simple algebraic equation?
Is it easy to describe relationship between Input and Output and System?
i.e. Can you make them as a Separate Entities?
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 27
Laplace Transform
If you answered NO to all previous questions, then YOU NEED
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS
Laplace Transform provides:
Representation of Input, output, and system as separate entities
Simple Algebraic interrelationship between Input, Output, and
System
Limitation of Laplace Transfrom:
Works in Frequency Domain
Valid when the system is LINEAR
A System is called LINEAR when it possesses:
Superposition
Homogeneity
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 28
Superposition
The output response of a system to the sum of inputs is the sum of
the responses to individual inputs
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 29
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 30
Homogeneity
Describes the response of the system to a Multiplication of the input
by a scalar as compared to a Multiplication of output to the same input
by the same scalar
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 31
Will any LINEAR EQUATION/FUNCTION represent a LINEAR
SYSTEM?
Example: Try y = mx + b (where m and b are constants) is
a LINEAR function, but check to see
if it yields a LINEAR System
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 32
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 33
Linearization
BAD NEWS is Real World Physical Systems are NON-LINEAR
GOOD NEWS:
1. A great majority of Physical Systems are LINEAR within some range of
operating point
2. We have a Mathematical Tool that could perform Linear Approximation
of Non-Linear Systems, a process called LINEARIZATION
NOTE:
Linearization does NOT necessarily
yield a LINEAR system!
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 34
1st Revision 2007 Taufik
Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo 35
Você também pode gostar
- Review of Laplace Transforms: Laplace Transform of A Function F (T) Is Defined AsDocumento10 páginasReview of Laplace Transforms: Laplace Transform of A Function F (T) Is Defined AsRosyid RidhoAinda não há avaliações
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Control of Nonlinear SystemsDocumento9 páginasUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Control of Nonlinear SystemsSubhasish MahapatraAinda não há avaliações
- ME330- spring-2022 Part 1 فصل الربيع 2022Documento41 páginasME330- spring-2022 Part 1 فصل الربيع 2022saad SdAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 2 - Mathematical Models of Systems - W2015Documento75 páginasChapter - 2 - Mathematical Models of Systems - W2015120200421003nAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Modeling of Control SystemDocumento31 páginasMathematical Modeling of Control SystemMegiAinda não há avaliações
- Willems - Dissipative Dynamical StructuresDocumento57 páginasWillems - Dissipative Dynamical StructuresDoug DaltonAinda não há avaliações
- EE-503 Linear System Theory OverviewDocumento19 páginasEE-503 Linear System Theory OverviewWaseem ChAinda não há avaliações
- EC2255-Solved Problems in Control System IV Semester ECEDocumento182 páginasEC2255-Solved Problems in Control System IV Semester ECEBEKHITI BelkacemAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide to the Generation of Liapunov FunctionsDocumento12 páginasA Guide to the Generation of Liapunov Functionsfrank_grimesAinda não há avaliações
- Slide 2Documento89 páginasSlide 2EnesVSAinda não há avaliações
- Design Strategies For Iterative Learning Control Based On Optimal ControlDocumento8 páginasDesign Strategies For Iterative Learning Control Based On Optimal Controlsaadi0Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter1 16Documento11 páginasChapter1 16Ambuz VimalAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2Documento52 páginasLecture 2faruktokuslu16Ainda não há avaliações
- EC2255-Solved Problems in Control Systems PDFDocumento182 páginasEC2255-Solved Problems in Control Systems PDFmaheshbabu527100% (2)
- Control Engineering: Closed-Loop Poles Are The Positions of The Poles (OrDocumento9 páginasControl Engineering: Closed-Loop Poles Are The Positions of The Poles (OrWanambwa SilagiAinda não há avaliações
- System ModelingDocumento9 páginasSystem ModelingFyaAinda não há avaliações
- FLab-04 EXP4Documento20 páginasFLab-04 EXP4Carl Kevin CartijanoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Laplace and Inverse Transform, TF and TD ModelingDocumento20 páginasPresentation On Laplace and Inverse Transform, TF and TD ModelingHassan RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical ModelingDocumento8 páginasMathematical ModelingMourougapragash SubramanianAinda não há avaliações
- Physiological Control SystemsDocumento49 páginasPhysiological Control SystemsPrasidha PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- EEE 3201: Control System I: Week 2: Lecture 1Documento11 páginasEEE 3201: Control System I: Week 2: Lecture 1harun or rashidAinda não há avaliações
- Week 12Documento15 páginasWeek 12onuraktas1923Ainda não há avaliações
- Feedback Control System: Mathematical ModelDocumento59 páginasFeedback Control System: Mathematical ModelRachana GadeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report CS 2Documento9 páginasLab Report CS 2ubaidAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2Documento107 páginasLecture 2Nowrin JawedAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Introduction System ModelingDocumento9 páginas01 Introduction System ModelingFicky SaputraAinda não há avaliações
- ELM 322, Control Systems Control Systems Spring 2015Documento37 páginasELM 322, Control Systems Control Systems Spring 2015kaanAinda não há avaliações
- Pengantar Simulasi Sistem FisisDocumento22 páginasPengantar Simulasi Sistem FisisAulia RahmaAinda não há avaliações
- Fevirgen, IJOCTA Article 1073Documento11 páginasFevirgen, IJOCTA Article 1073Roodi AliAinda não há avaliações
- MODELING CONTROL SYSTEMSDocumento11 páginasMODELING CONTROL SYSTEMSAnonymous UrzdtCB0IAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Documento33 páginas1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Tahmid ShihabAinda não há avaliações
- First Order SystemDocumento45 páginasFirst Order SystemKrishna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Han LMI Struct Linear Cdc03Documento6 páginasHan LMI Struct Linear Cdc03Tensegrity WikiAinda não há avaliações
- Week 11Documento16 páginasWeek 11onuraktas1923Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 4 Group 3Documento10 páginasLab 4 Group 3AYESHA FAHEEMAinda não há avaliações
- Stability of Fractional-Order Dynamic SystemsDocumento12 páginasStability of Fractional-Order Dynamic SystemskarpagasenthilpandyAinda não há avaliações
- Navtej Mishra 19116043: Experiment - 1: Study of Linear-Time-Invariant Open-Loop Systems and Their RepresentationsDocumento24 páginasNavtej Mishra 19116043: Experiment - 1: Study of Linear-Time-Invariant Open-Loop Systems and Their RepresentationsNavtej MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Linear AlgebraDocumento67 páginasIntro To Linear AlgebraBevold LineAinda não há avaliações
- Passivity, Feedback Equivalence, and The Global Stabilization of Minimum Phase Nonlinear SystemsDocumento13 páginasPassivity, Feedback Equivalence, and The Global Stabilization of Minimum Phase Nonlinear SystemsgusalemanAinda não há avaliações
- The Stability of Input-Output Dynamical SystemsNo EverandThe Stability of Input-Output Dynamical SystemsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Gain and Phase Margin Multiloop LQG Regulators: TheoryDocumento7 páginasGain and Phase Margin Multiloop LQG Regulators: TheoryAyunda RahmayanaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report CS 1Documento7 páginasLab Report CS 1ubaidAinda não há avaliações
- Control in LabVIEW PDFDocumento104 páginasControl in LabVIEW PDFJuan PabloAinda não há avaliações
- Control Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsDocumento132 páginasControl Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsP POORNA CHANDRA REDDYAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 State SpaceDocumento57 páginasUnit 1 State SpaceJoseph AgboglaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture NotesDocumento517 páginasLecture NotesTech BoyAinda não há avaliações
- Singular PerturbationDocumento37 páginasSingular PerturbationshubhobrataAinda não há avaliações
- Simulink Basics TutorialDocumento143 páginasSimulink Basics TutorialHiếu HuỳnhAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDocumento45 páginasMathematical Models of SystemsSaid Ahmed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data setsDocumento60 páginasPractical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data setsjameelahmadAinda não há avaliações
- System Modeling MethodsDocumento51 páginasSystem Modeling MethodsJerc ZajAinda não há avaliações
- Feedback Linearization ExplainedDocumento4 páginasFeedback Linearization ExplainedmCmAlAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Analysis and Linear Control TheoryNo EverandFunctional Analysis and Linear Control TheoryAinda não há avaliações
- On Input-to-State Stability For Time Varying Nonlinear SystemsDocumento6 páginasOn Input-to-State Stability For Time Varying Nonlinear SystemsFathi MusaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 05Documento10 páginasLab 05Saad mubeenAinda não há avaliações
- W EE 418 - Lecture 2 ModelingDocumento20 páginasW EE 418 - Lecture 2 ModelingGGAP LASTAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringDocumento3 páginasGujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringMandy745Ainda não há avaliações
- Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems: Lecture Notes of ME 862Documento9 páginasModeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems: Lecture Notes of ME 862RajrdbAinda não há avaliações
- Control System Synthesis by Root Locus MethodDocumento6 páginasControl System Synthesis by Root Locus MethodcastrojpAinda não há avaliações
- IcaDocumento1 páginaIcaMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Bab2 Mode AddressingDocumento29 páginasBab2 Mode AddressingMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Bio Medical Instrumentation The Technology of Patient CareDocumento245 páginasIntroduction To Bio Medical Instrumentation The Technology of Patient CareAtziri Miranda88% (8)
- Texture Analysis of Aggressive and Nonaggressive Lung Tumor CE CT Images PDFDocumento9 páginasTexture Analysis of Aggressive and Nonaggressive Lung Tumor CE CT Images PDFMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- ReadmedDocumento1 páginaReadmedMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- BrosurgDocumento4 páginasBrosurgMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- WekaManual 3 7 8 PDFDocumento327 páginasWekaManual 3 7 8 PDFEduardoMendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Kementerian Agama Republik Indonesia: Jadwal Shalat Propinsi: JAWA TENGAH Daerah: SEMARANGDocumento1 páginaKementerian Agama Republik Indonesia: Jadwal Shalat Propinsi: JAWA TENGAH Daerah: SEMARANGMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- RULATIKAHBINTIABDGHANI2013Documento78 páginasRULATIKAHBINTIABDGHANI2013Mohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Learn MATLABDocumento61 páginasLearn MATLABsayyanAinda não há avaliações
- RangkaianDocumento1 páginaRangkaianMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- User Manual1 2Documento56 páginasUser Manual1 2Mohammad Rofii100% (1)
- Bok Mark FirefoxsDocumento2 páginasBok Mark FirefoxsMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentasi Sistem Hayati: Kode MK: TM216 2 (Dua) SKSDocumento26 páginasInstrumentasi Sistem Hayati: Kode MK: TM216 2 (Dua) SKSMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Icml TutorialDocumento85 páginasIcml TutorialMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Bab3 - ElectriccircuitreviewDocumento5 páginasBab3 - ElectriccircuitreviewDefika FiantiAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE Outline FormatDocumento3 páginasIEEE Outline FormatAlex HerrmannAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentasi Sistem HayatiDocumento21 páginasInstrumentasi Sistem HayatiMohammad Rofii100% (1)
- F 1Documento10 páginasF 1Srinivas AmbalaAinda não há avaliações
- Icml TutorialDocumento85 páginasIcml TutorialMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Bab3 - ElectriccircuitreviewDocumento5 páginasBab3 - ElectriccircuitreviewDefika FiantiAinda não há avaliações
- Computers in Biology and Medicine: B. Nayebifar, H. Abrishami MoghaddamDocumento8 páginasComputers in Biology and Medicine: B. Nayebifar, H. Abrishami MoghaddamMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Nota TransferDocumento1 páginaNota TransferMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Invoice-G3bawDocumento1 páginaInvoice-G3bawMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- DCT Theory and ApplicationDocumento32 páginasDCT Theory and ApplicationAhmed SoulimanAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE Outline FormatDocumento3 páginasIEEE Outline FormatAlex HerrmannAinda não há avaliações
- 2009-IJRTE Analysis of Foveal Avascular Zone in Color Fundus Image For Grading of DRDocumento4 páginas2009-IJRTE Analysis of Foveal Avascular Zone in Color Fundus Image For Grading of DRMohammad RofiiAinda não há avaliações
- Intro Sci LabDocumento87 páginasIntro Sci LabandysarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- Solving linear programming problems (Graphical, Simplex, Two phase and Big M methodDocumento3 páginasSolving linear programming problems (Graphical, Simplex, Two phase and Big M methodG sai supreethAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Mathematics A or Better Revison SheetsDocumento47 páginasGCSE Mathematics A or Better Revison SheetsHannah PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Real Life Exponential FunctionsDocumento11 páginasReal Life Exponential FunctionsValentine DimitrovAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocumento34 páginasIntroduction To Linear ProgrammingDeepika Raj100% (1)
- Doppler Broadening: 1 Wavelength and TemperatureDocumento5 páginasDoppler Broadening: 1 Wavelength and Temperatureakhilesh_353859963Ainda não há avaliações
- Ee 301 - Circuit Theory & Networks: Multiple Choice Type QuestionsDocumento5 páginasEe 301 - Circuit Theory & Networks: Multiple Choice Type QuestionsGsn ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- NUMERICAL METHODS IN QUANTUM MECHANICSDocumento101 páginasNUMERICAL METHODS IN QUANTUM MECHANICSAnderson Buarque100% (1)
- Inverse Trig Functions Domain & RangeDocumento7 páginasInverse Trig Functions Domain & RangeArya NairAinda não há avaliações
- ch19 PDFDocumento23 páginasch19 PDFDonita BinayAinda não há avaliações
- Vector Integral Calculus OutlineDocumento65 páginasVector Integral Calculus OutlineTarek Hajj ShehadiAinda não há avaliações
- Kosmann Nonlin PDFDocumento342 páginasKosmann Nonlin PDFscualoboy2010Ainda não há avaliações
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 11Documento14 páginasNational Senior Certificate: Grade 11rowan chibiAinda não há avaliações
- 0606 w14 Ms 11Documento7 páginas0606 w14 Ms 11AKRAMAinda não há avaliações
- IFS Mathematics 2016Documento10 páginasIFS Mathematics 2016SreekanthPamuluruAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Openqbmm and Quadrature-Based Moment MethodsDocumento53 páginasIntroduction To Openqbmm and Quadrature-Based Moment MethodsMohamed BoukhelefAinda não há avaliações
- Zlib - Pub Nonparametric Statistics 3rd Isnps Avignon France June 2016Documento388 páginasZlib - Pub Nonparametric Statistics 3rd Isnps Avignon France June 2016Chaker MeraïhiAinda não há avaliações
- 4) Simulink S Function Miniguide Rev06Documento15 páginas4) Simulink S Function Miniguide Rev06Motasim_mAinda não há avaliações
- Vladimir Gordin (Author) - Mathematical Problems and Methods of Hydrodynamic Weather Forecasting (2000, CRC Press) (10.1201 - 9781482287417) - Libgen - LiDocumento843 páginasVladimir Gordin (Author) - Mathematical Problems and Methods of Hydrodynamic Weather Forecasting (2000, CRC Press) (10.1201 - 9781482287417) - Libgen - LiLibrarian BUASCAinda não há avaliações
- Martin Josefsson - A New Proof of Yuns InsequalityDocumento4 páginasMartin Josefsson - A New Proof of Yuns InsequalityKevin MesićAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3.1 g7Documento1 páginaActivity 3.1 g7Honeylyn TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Problems On Two Dimensional Random VariableDocumento15 páginasProblems On Two Dimensional Random VariableBRAHMA REDDY AAKUMAIIAAinda não há avaliações
- Nays2dFlood PDFDocumento28 páginasNays2dFlood PDFFranco QuispeAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment CLO 1: Relation, Function, and Recurrence: Discrete Mathematics (CII1G3)Documento10 páginasAssignment CLO 1: Relation, Function, and Recurrence: Discrete Mathematics (CII1G3)maulanbach riburaneAinda não há avaliações
- Algorithms Chapter 10 Exercises and SolutionsDocumento43 páginasAlgorithms Chapter 10 Exercises and Solutionsc_noneAinda não há avaliações
- 5-person car seating arrangementsDocumento18 páginas5-person car seating arrangementsJohn Paul Marin ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Methods: GEC-R14 M. Tech II Semester Regular/Suppl. Examinations, July 2016Documento2 páginasFinite Element Methods: GEC-R14 M. Tech II Semester Regular/Suppl. Examinations, July 2016venkat subbuAinda não há avaliações
- Differential Geometry and Computer VisionDocumento41 páginasDifferential Geometry and Computer VisionApple ForScaleAinda não há avaliações
- Week 001 - Course Module RandomVariablesDocumento44 páginasWeek 001 - Course Module RandomVariablesHikari AkariAinda não há avaliações
- Solving fluid equations with Navier-StokesDocumento3 páginasSolving fluid equations with Navier-StokesositisAinda não há avaliações
- Graphs of Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento8 páginasGraphs of Trigonometric FunctionsJohn-ZelDomingoAinda não há avaliações