Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Photosynthesis Summary Powerpoint
Enviado por
Santhiya Madhavan0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
44 visualizações8 páginasPhotosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using energy from sunlight. The glucose produced can be converted into other compounds like starch, cellulose, lipids, and proteins. The rate of photosynthesis is affected by factors like light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration. Plants require minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and iron in ionic forms to support photosynthesis, respiration, and overall growth. Deficiencies in these minerals can result in symptoms such as stunted growth, yellow leaves, and purple or dead spots on leaves.
Descrição original:
Título original
photosynthesis summary powerpoint.ppt
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoPhotosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using energy from sunlight. The glucose produced can be converted into other compounds like starch, cellulose, lipids, and proteins. The rate of photosynthesis is affected by factors like light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration. Plants require minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and iron in ionic forms to support photosynthesis, respiration, and overall growth. Deficiencies in these minerals can result in symptoms such as stunted growth, yellow leaves, and purple or dead spots on leaves.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
44 visualizações8 páginasPhotosynthesis Summary Powerpoint
Enviado por
Santhiya MadhavanPhotosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using energy from sunlight. The glucose produced can be converted into other compounds like starch, cellulose, lipids, and proteins. The rate of photosynthesis is affected by factors like light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration. Plants require minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and iron in ionic forms to support photosynthesis, respiration, and overall growth. Deficiencies in these minerals can result in symptoms such as stunted growth, yellow leaves, and purple or dead spots on leaves.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 8
photosynthesis
A summary of what you should
know
WITH THANKS TO LRGS
Revision of third form photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
What happens to the glucose formed in photosynthesis?
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
GLUCOSE STARCH
CELLULOSE
LIPIDS
PROTEINS
CARBON
DIOXIDE AND
WATER
Required to make plant cell walls. It is made
of 100s of glucose molecules bonded
together.
Glucose is chemically converted to fatty acids and
glycerol to make lipids, which are needed to make
plant cell membranes and seed storage oils.
Is used by roots and leaves to store excess
glucose in an osmotically inactive form. It is
made of 100s of glucose molecules.
Using nitrate ions absorbed by plant roots,
glucose is converted first to amino acids
then to protein.
The carbon dioxide can be used again in
photosynthesis or may diffuse out of the
leaf via the stomata
respiration
ATP
Factors necessary for photosynthesis
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
light intensity
The main external factors affecting
the rate of photosynthesis are:
R
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
temperature (degrees C)
Heat energy increases
kinetic energy. More
collisions, with more force,
thus the rate increases
Enzyme protein
denatures. They lose
their catalytic ability to
catalyse
photosynthesis
Optimum
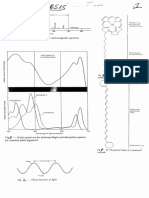
Increasing light intensity increases the energy
entering chlorophyll and thus the amount of ATP
and produced to drive photosynthesis
The effect of light intensity
on photosynthetic rate
The effect of
temperature on
photosynthetic
rate
The rate is limited by another
factor such as carbon dioxide
concentration
Light
intensity
limiting.
light wavelength
light intensity
temperature
carbon dioxide
Notice how increasing the light intensity
beyond a certain point causes no further
increase in rate of photosynthesis.
Something else is now holding the reaction
back. Light is no longer the limiting factor.
Photosynthetic sugar production is catalysed by
enzymes. If the temperature is raised too high
the enzymes denature and photosynthesis stops.
Factors necessary for photosynthesis
Limiting factors
25
O
C and 0.04% CO
2
25
O
C and 0.4% CO
2
15
O
C and 0.04% CO
2
R
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
Light intensity
0 5 10 15 20 25
R
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
temperature (degrees C)
High light intensity
Low light intensity
The effect of temperature
and light
At low light intensities increasing the temperature has little
effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
At high light intensities the rate of photosynthesis increases
much more rapidly over the same temperature range.
This is an example of the law of limiting factors.
THE LAW OF LIMITING FACTORS If a
process is influenced by more than 1
factor, the rate will be limited by the
factor nearest its lowest value
Here is another example of
the law of limiting factors
What 3 factors are limiting in regions A, B, C
respectively?
ANSWERS:
At B temperature limiting
At A CO2 limiting
A
B
C
At C light limiting
Plant mineral requirements
Plants require small quantities of minerals for healthy growth
Minerals are absorbed by the root hairs, either by diffusion or active
transport, depending on their concentration in the soil see next topic.
The most important minerals for plants are:
Nitrogen
Potassium
Magnesium
Iron
Phosphorous
usually as nitrate, nitrite or ammonium ions, NO
3
-
, NO
2
-
, NH
4
+
often in the form of phosphate ions, PO
4
- ions.
in the form of K
+
ions.
in the form of Mg
2+
ions
in the form of Fe
2+
ions
Mineral requirements of plants
Nitrogen (nitrate ions: Needed
to make proteins and
chlorophyll
Deficiency: Poor growth and
leaf yellowing
NO
3
-
Potassium: Helps enzymes in
photosynthesis and respiration
Deficiency: Yellow leaves with
dead spots
K
+
Phosphorous: Required for
photosynthesis and respiration
Deficiency: Poor root growth
and purple younger leaves
PO
4
-
Iron is required by the enzymes
that make chlorophyll
Deficiency: Leaf yellowing
Fe
2+
Magnesium is required as part
of the chlorophyll molecule
Deficiency: Yellowing of
leaves and poor growth
Mg
+
REMEMBER
THESE ARE
REQUIRED
IN IONIC
FORM!
The photosynthesis word equation. That light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in
chloroplasts and used to make sugar from carbon dioxide. Oxygen is a by-product.
The rate of photosynthesis may by limited by: low temperature, shortage of carbon
dioxide, shortage of light.
The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be converted to insoluble starch. Start does
not attract water by osmosis.
The energy from respiration is used to build smaller molecules into larger ones, including:
sugars into starch, sugars into cellulose for cell walls, sugars, nitrates and other nutrients
into amino acids and then proteins. Sugars into lipids for seed storage.
For healthy growth plants need mineral ions including: nitrate for protein synthesis,
phosphate and potassium for photosynthesis and respiration.
Symptoms shown by mineral ion-deficient plants include:
Any 1 of light, temperature and carbon dioxide will be limiting the rate of photosynthesis at
any particular time.
WHAT YOU SHOULD
KNOW AT THE END
OF THIS UNIT
Plant cells use some of the photosynthetic glucose for respiration. In addition, nitrates,
absorbed by the roots, are needed for healthy growth.
Stunted growth and yellow older leaves if nitrate ions are deficient
Poor root growth and purple younger leaves if phosphate ions are deficient
Yellow leaves with dead spots if potassium ions are deficient.
Você também pode gostar
- Photosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Documento14 páginasPhotosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Lo ViAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition in PlantsDocumento33 páginasNutrition in PlantsBenedicta SarfoAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Nutrition NotesDocumento13 páginasPlant Nutrition NotesErwin Mauricio Padilla RocaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Nutrition NotesDocumento13 páginasPlant Nutrition NotesErwin Mauricio Padilla RocaAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisDocumento5 páginasFactors Affecting PhotosynthesisGISRemoteSensingAinda não há avaliações
- BioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisDocumento34 páginasBioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisNADIAAinda não há avaliações
- Logical ThinkingDocumento3 páginasLogical ThinkingLiquartervoisAinda não há avaliações
- CRP 101 Lecture No. 13Documento10 páginasCRP 101 Lecture No. 13AnandKuttiyanAinda não há avaliações
- 8 PhotosynthesisDocumento8 páginas8 PhotosynthesisRAVINDRA PRASADAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleAinda não há avaliações
- b4 Bioenergetics Mastery Booklet Arb v2Documento22 páginasb4 Bioenergetics Mastery Booklet Arb v2laurnawhittakerAinda não há avaliações
- Ecosystem Life EnergyDocumento34 páginasEcosystem Life EnergyKeith C CabbabAinda não há avaliações
- ChapterDocumento3 páginasChaptercontroller playerAinda não há avaliações
- Carbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDocumento2 páginasCarbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDavidIsmailBarkerAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsDocumento8 páginasPhotosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsBonny Ya SakeusAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsAinda não há avaliações
- L6 PhotosynthesisDocumento28 páginasL6 PhotosynthesisNaomi AceroAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento23 páginasPhotosynthesisBLESSING UHUOAinda não há avaliações
- Notes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9Documento5 páginasNotes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9PranatiAinda não há avaliações
- #4 Limiting Factors in PhotosynthesisDocumento2 páginas#4 Limiting Factors in PhotosynthesisJayson cheekAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE 6 Plant Nutrition 2020Documento35 páginasIGCSE 6 Plant Nutrition 2020Harry is the coolestAinda não há avaliações
- PP14 Photosynthesis The ProcessDocumento63 páginasPP14 Photosynthesis The Processsaishabhawanipersad81Ainda não há avaliações
- Definition of PhotosynthesisDocumento10 páginasDefinition of PhotosynthesisYSAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento182 páginasPhotosynthesisparashakthi PRAinda não há avaliações
- Plant NutritionDocumento46 páginasPlant NutritionJaved SohawonAinda não há avaliações
- (25774) Photosynthesis Limiting FactorsDocumento5 páginas(25774) Photosynthesis Limiting Factorsηυѕαувαн ツAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocumento6 páginasPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis 5.2.1Documento5 páginasPhotosynthesis 5.2.1bexAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocumento20 páginasPhotosynthesis and RespirationAdriana CentenoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsDocumento36 páginasChapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento3 páginasPhotosynthesisJanapareddi VenkataramanaAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free EncyclopediaDocumento3 páginasPhotosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopediaapi-253604375Ainda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento59 páginasPhotosynthesisAima AzharAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocumento54 páginasBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Nutrition NotesDocumento12 páginasPlant Nutrition NotesTHAMSANQA SIBANDAAinda não há avaliações
- Apex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchDocumento35 páginasApex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchSHEKHAR PRASADAinda não há avaliações
- PP14 Photosynthesis The ProcessDocumento63 páginasPP14 Photosynthesis The Process8wb9xfbjpvAinda não há avaliações
- Fertilizer Management For Greenhouse Vegetables - Florida Greenhouse Vegetable Production HandbooDocumento36 páginasFertilizer Management For Greenhouse Vegetables - Florida Greenhouse Vegetable Production HandbooGerman Antonio Aviles Orellana100% (1)
- G-10 Biology, 4.2 PhotosynthesisDocumento6 páginasG-10 Biology, 4.2 Photosynthesisjohn nigussieAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition in Plants Edexcel IGCSEDocumento7 páginasNutrition in Plants Edexcel IGCSETZ AZAinda não há avaliações
- Plant NutritionDocumento6 páginasPlant NutritionMemona KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Revision GuideDocumento22 páginasBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariAinda não há avaliações
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocumento5 páginasBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6.1 PhotosynthesisDocumento16 páginasLesson 6.1 PhotosynthesisrajzemjeoimojicaAinda não há avaliações
- Sameeha Rida 20OSB1200 IGCSE VIII A Biologyworksheetonphotosynthesis 1Documento6 páginasSameeha Rida 20OSB1200 IGCSE VIII A Biologyworksheetonphotosynthesis 1Sameeha RidaAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento14 páginasPhotosynthesisArvind KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Synoptic Essay PackDocumento29 páginasSynoptic Essay Packriri_p_94100% (1)
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureDocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio-Inorganic Allied ChemistryDocumento19 páginasBio-Inorganic Allied ChemistrymohanAinda não há avaliações
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisDocumento36 páginasBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- UNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterDocumento10 páginasUNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterNeha HenstridgeAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosyntesisDocumento16 páginasPhotosyntesisMariaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic PhotosynthesisDocumento2 páginasTopic PhotosynthesisJacob AssoulineAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis 123Documento4 páginasPhotosynthesis 123Alyssa L.J. Dela Cruz (Aly)Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocumento29 páginasBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Nutrition 2021Documento8 páginasPlant Nutrition 2021lowkeydeadAinda não há avaliações
- Plant NutritionDocumento37 páginasPlant NutritionWen Shan ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- NutritionDocumento7 páginasNutritionsemasingheAinda não há avaliações
- Plant NutritionDocumento39 páginasPlant Nutritionapi-3059093250% (1)
- By Marinela BuzoDocumento13 páginasBy Marinela BuzoSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is? Collision Theory?: Factors Affecting?Documento63 páginasWhat Is? Collision Theory?: Factors Affecting?Santhiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Rainforest PowerpointDocumento11 páginasRainforest PowerpointSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Documento19 páginasSexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Santhiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsDocumento36 páginasChapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Bananas in Pyjamas RecipeDocumento1 páginaBananas in Pyjamas RecipeSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento25 páginasReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Chap15 Periodic TableDocumento32 páginasChap15 Periodic TableSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Blowing Up Balloons With CO2Documento1 páginaBlowing Up Balloons With CO2Santhiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Report Card CommentsDocumento15 páginasReport Card CommentsSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Ionic and Covalent Bond WorksheetDocumento1 páginaIonic and Covalent Bond WorksheetSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- AA IGCSE Unit 1 TESDocumento60 páginasAA IGCSE Unit 1 TESSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Division (JM)Documento15 páginasCell Division (JM)Santhiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Menstrual CycleDocumento2 páginasMenstrual CycleSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- Bio CH 4-Repdoduction NewDocumento70 páginasBio CH 4-Repdoduction NewSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- 2021-Recent Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Adsorbents For Wastewater TreatmentDocumento27 páginas2021-Recent Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Adsorbents For Wastewater TreatmentCARLOS ALBERTO RAMIREZ BARRAGANAinda não há avaliações
- MSC Chemistry Oct16Documento142 páginasMSC Chemistry Oct16Kundan DeoreAinda não há avaliações
- Amine Gas TreatingDocumento3 páginasAmine Gas Treatinghmudassir_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Steve Talbott Getting Over The Code DelusionDocumento57 páginasSteve Talbott Getting Over The Code DelusionAlexandra DaleAinda não há avaliações
- Two Phase Flow Course-1Documento522 páginasTwo Phase Flow Course-1sarmadAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 6 Laboratory ProcedureDocumento7 páginasActivity 6 Laboratory ProcedureAinie JuripaeAinda não há avaliações
- HTC Summary and Discussion of Chemical Mechanisms For Process EngineeringDocumento18 páginasHTC Summary and Discussion of Chemical Mechanisms For Process EngineeringJoseCuevasMartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Arkema POF Brochure 2019Documento6 páginasArkema POF Brochure 2019julioAinda não há avaliações
- Bokashi Making Leaflet 3Documento1 páginaBokashi Making Leaflet 3glvl88Ainda não há avaliações
- Rahmania Et Al-2017-Jurnal Kefarmasian IndonesiaDocumento10 páginasRahmania Et Al-2017-Jurnal Kefarmasian IndonesiaBellinda ZalzabillahAinda não há avaliações
- Pineapple Peel Waste For Bioethanol ProductionDocumento1 páginaPineapple Peel Waste For Bioethanol ProductionAnge Cantor-dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Milk: Under The Guidence ofDocumento16 páginasAnalysis of Milk: Under The Guidence ofK Rajesh BabuAinda não há avaliações
- PowerpointDocumento33 páginasPowerpointZain HashmiAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic AcidsDocumento23 páginasBiological Molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic AcidsAMEER HANAFI JIKIRI. JUL-ASRIAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Dissociation ConstantDocumento4 páginasAcid Dissociation ConstantJair RangelAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 3Documento6 páginasLab 3Anonymous eGc6IFJc8GAinda não há avaliações
- Hazard Classification of Process Operations For Spacing RequirementsDocumento3 páginasHazard Classification of Process Operations For Spacing RequirementsAlejandra Diaz Rojas100% (3)
- Us 6645428Documento20 páginasUs 6645428JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Cosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsDocumento8 páginasCosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsmasorAinda não há avaliações
- Auxiliary: Product ListDocumento7 páginasAuxiliary: Product ListNguyễn Huy CườngAinda não há avaliações
- 8-The Chemistry of The Environment PDFDocumento52 páginas8-The Chemistry of The Environment PDFJewel LimAinda não há avaliações
- F.J. Gutiérrez Ortiz, A. Serrera, S. Galera, P. Ollero: Sciverse SciencedirectDocumento13 páginasF.J. Gutiérrez Ortiz, A. Serrera, S. Galera, P. Ollero: Sciverse SciencedirectJuanPabloGuerreroAinda não há avaliações
- CochleamyciDocumento4 páginasCochleamyciOscar Martin OrdoñezAinda não há avaliações
- Literature Reviewof Poly Lactic AcidDocumento23 páginasLiterature Reviewof Poly Lactic AcidSamirisAinda não há avaliações
- SetyaningrumrahmawatyDocumento3 páginasSetyaningrumrahmawatyBoh Cucu KaraengAinda não há avaliações
- Reactor TubularDocumento9 páginasReactor TubularPaulina Ibarra SánchezAinda não há avaliações
- Phytochemical Analysis and Biological Properties of Cyperus Rotundus LDocumento12 páginasPhytochemical Analysis and Biological Properties of Cyperus Rotundus LWesley SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- IITJEE2006 CheDocumento9 páginasIITJEE2006 CheLokesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Epa 1664a - EnglishDocumento3 páginasEpa 1664a - EnglishSaydee De vaqueraAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Form4 Chapter9Documento8 páginasBiology Form4 Chapter9Wei EnAinda não há avaliações