Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
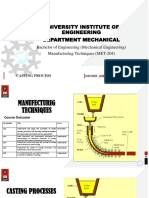
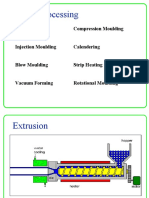
In Jection Moulding
Enviado por
Abhinandan PatilDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
In Jection Moulding
Enviado por
Abhinandan PatilDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Designed by :-Monde Sagar Baban
(13721)
EFINATION
Injection molding is a manufacturing process
where heated molten plastic is forced into a
mold cavity under pressur.
YPES
Reaction injection moulding.
Liquid injection moulding.
Gas assist injection moulding.
Co-injection moulding.
2-shot injection moulding.
Fusible core injection moulding.
Rapid injection moulding.
REACTION INJECTION
MOULDING
Process for molding polyurethane, epoxy, and
other liquid chemical systems. A mixture of two
to four components in the proper chemical ratio
is accomplished by a high-pressure
impingement-type mixing head, from which the
mixed material is delivered into the mold at low
pressure, where it reacts (cures).
IQUID INJECTION MOULDING
Process that involves an integrated system for
proportioning, mixing, and dispensing dual-
component liquid resin formulations and
directly injecting the resultant mix into a mold
which is clamped under pressure. See Injection
molding.
GAS ASSIST INJECTION
MOULDING
Plastic molding process in which a high-
pressure gas is co-injected along with the
plastic part to produce discrete internal hollow
sections. It differs from blow molding in that
one large hollow product is not created; rather,
a solid piece with hollow sections is produced.
O INJECTION MOULDING
This is a process that creates a skin and core
material arrangement in a molded part. The skin
material is injected first into the mold cavity,
and is immediately followed by a core material.
As the skin material flows into the cavity, the
material next to the cavity walls freezes and
material flows down a center channel. When the
core material enters it displaces the skin
material in the center of the channel by pushing
the skin ahead. As it flows ahead it continues to
freeze on the walls producing the skin layer
2-SHOT INJECTION MOULDING
This technology produces a part with two
different raw materials or colors in a single
operation. The machine has two injection units:
one vertical and one horizontal. By using a
rotating mold, the machine automatically
produces a substrate of one resin or color and
overmolds the part with the second resin or
color
FUSIBLE INJECTION MOULDING
It is used in the manufacture of molded
components with cavities or undercuts, which
would not be possible with tools having
demoldable cores
APID INJECTION MOULDING
Rapid Injection Molding allows us to make
prototype injection molded parts in a
production thermoplastic resin in 2-5 weeks.
These parts may be used for full functional and
fit testing as well as test marketing.
PROCESSES
Clamping
Injection
Cooling
Ejection
LAMPING
Prior to the injection of the material into the mold,
the two halves of the mold must first be securely
closed by the clamping unit. Each half of the mold is
attached to the injection molding machine and one
half is allowed to slide. The hydraulically powered
clamping unit pushes the mold halves together and
exerts sufficient force to keep the mold securely
closed while the material is injected. The time
required to close and clamp the mold is dependent
upon the machine - larger machines (those with
greater clamping forces) will require more time. This
time can be estimated from the dry cycle time of the
machine.
NJECTION
The raw plastic material, usually in the form of pellets, is
fed into the injection molding machine, and advanced
towards the mold by the injection unit. During this
process, the material is melted by heat and pressure.
The molten plastic is then injected into the mold very
quickly and the buildup of pressure packs and holds the
material. The amount of material that is injected is
referred to as the shot. The injection time is difficult to
calculate accurately due to the complex and changing
flow of the molten plastic into the mold. However, the
injection time can be estimated by the shot volume,
injection pressure, and injection power.
OOLING
The molten plastic that is inside the mold begins to
cool as soon as it makes contact with the interior
mold surfaces. As the plastic cools, it will solidify
into the shape of the desired part. However, during
cooling some shrinkage of the part may occur. The
packing of material in the injection stage allows
additional material to flow into the mold and reduce
the amount of visible shrinkage. The mold can not
be opened until the required cooling time has
elapsed. The cooling time can be estimated from
several thermodynamic properties of the plastic and
the maximum wall thickness of the part.
JECTION
After sufficient time has passed, the cooled part
may be ejected from the mold by the ejection
system, which is attached to the rear half of the
mold. When the mold is opened, a mechanism is
used to push the part out of the mold. Force must
be applied to eject the part because during cooling
the part shrinks and adheres to the mold. In order to
facilitate the ejection of the part, a mold release
agent can be sprayed onto the surfaces of the mold
cavity prior to injection of the material. The time that
is required to open the mold and eject the part can
be estimated from the dry cycle time of the machine
and should include time for the part to fall free of
the mold. Once the part is ejected, the mold can be
clamped shut for the next shot to be injected.
DVANTAGES
The injection molding process has several advantages over other
molding processes. The following is a short list of what you can
expect from utilizing Injection Molding as your form of production.
Injection molding allows for high production output rates.
When producing your product you may use inserts within the mold.
You may also use fillers for added strength.
Close tolerances on small intricate parts is possible with Injection
Molding.
More than one material may be used at the same time when utilizing
co-Injection Molding.
There is typically very little post production work required because
the parts usually have a very finished look upon ejection.
All scrap may be reground to be reused, therefor there is very little
waste.
Full automation is possible with Injection Molding.
ISADVANTAGES
The molding process has several disadvantages to
other molding processes. The following is a short
list of some of the disadvantages to Injection
Molding.
This is not a preferred method of manufacturing for
short production runs. This is mainly due to the cost
of tooling and the cost of operation. However B.J.
Molding can handle smaller runs than most shops.
Design and development of parts that will work well
with Injection Molding often takes a very long time.
Many parts are just not suited to the process.
PPLICATIONS
Injection molding is used to create many things
such as wire spools, packaging, bottle caps,
automotive dashboards, pocket combs, some
musical instruments (and parts of them), one-
piece chairs and small tables, storage
containers, mechanical parts (including gears),
and most other plastic products available today.
Injection molding is the most common modern
method of manufacturing parts; it is ideal for
producing high volumes of the same object.
OOLING ASICS
Cavity Plate
Cavity
Moulding
Core
Core Plate
Basic mould consisting of cavity and core plate
Runner
Cavity
Gate
Nozzle
Sprue
Melt Delivery
OOLING FOR A PLASTIC CUP
Runner
Part
Cavity
Nozzle
Part
Cavity
Knob
Stripper
plate
Runner
Part
Cavity
Nozzle
Você também pode gostar
- Molding & CastingDocumento8 páginasMolding & CastingxangolekonAinda não há avaliações
- How Voids Form in Thick Plastic PartsDocumento4 páginasHow Voids Form in Thick Plastic PartsRavindra ErabattiAinda não há avaliações
- Injection Moulding Process OverviewDocumento144 páginasInjection Moulding Process OverviewMohamed YahiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Injection Molding Process ExplainedDocumento12 páginasInjection Molding Process ExplainedMuhammad Usama KhokharAinda não há avaliações
- Rubber MoldingDocumento33 páginasRubber MoldingFurqan AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Casting!Documento12 páginasIntro To Casting!api-443709779Ainda não há avaliações
- Prepared By-Chaudhari M.M SVCP (Sinhgad), PUNE (INDIA) Dept. of Mech. EnggDocumento39 páginasPrepared By-Chaudhari M.M SVCP (Sinhgad), PUNE (INDIA) Dept. of Mech. EnggMitul patelAinda não há avaliações
- Berger Paints Internship Report 2017 by Muhammad JunaidDocumento17 páginasBerger Paints Internship Report 2017 by Muhammad JunaidRehan AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDocumento51 páginasSheet Metal Forming ProcessesLeo Dev WinsAinda não há avaliações
- Windmill Tutorial 13Documento6 páginasWindmill Tutorial 13Azhar A. QaziAinda não há avaliações
- Allaboutcolor 090828165733 Phpapp02Documento62 páginasAllaboutcolor 090828165733 Phpapp02Ilyana KamalAinda não há avaliações
- Heat TreatmentDocumento2 páginasHeat TreatmentUsman MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet MATALDocumento9 páginasSheet MATALSunil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Color Calculations enDocumento31 páginas09 Color Calculations enJayaminAinda não há avaliações
- Silicone MoldingDocumento6 páginasSilicone Moldingkats2404Ainda não há avaliações
- Advances in Casting TechnologiesDocumento34 páginasAdvances in Casting Technologiesvijaykumarn100% (1)
- Calculating Plastic Component Shrinkage and DistortionDocumento4 páginasCalculating Plastic Component Shrinkage and DistortionRajendra Kumar SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Treat Definitions PDFDocumento3 páginasHeat Treat Definitions PDFmastorfaizalAinda não há avaliações
- Principle of Spot WeldingDocumento2 páginasPrinciple of Spot Weldingkgggani100% (1)
- Limit, Fit, ToleranceDocumento15 páginasLimit, Fit, ToleranceTejwinderSinghAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages of LPDCDocumento2 páginasAdvantages of LPDCSuhas KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Jimma Institute of Technology: Product Design Unit II: Assembly and JoiningDocumento10 páginasJimma Institute of Technology: Product Design Unit II: Assembly and JoiningfayzaAinda não há avaliações
- Injection Molded Part Problems & Solutions With: SkillbuilderDocumento2 páginasInjection Molded Part Problems & Solutions With: SkillbuilderradzAinda não há avaliações
- Metals Extrusion and Drawing Processes ExplainedDocumento26 páginasMetals Extrusion and Drawing Processes ExplainedArvind BhosaleAinda não há avaliações
- Color Models and the CIE Chromaticity DiagramDocumento61 páginasColor Models and the CIE Chromaticity DiagramAmaresh DashAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to the Manufacturing Process of GlassDocumento12 páginasIntroduction to the Manufacturing Process of GlassSanjeev ShekherAinda não há avaliações
- Resins PDFDocumento11 páginasResins PDFZaib AdilAinda não há avaliações
- 1.0 Mould Intro On PlasticsDocumento17 páginas1.0 Mould Intro On Plasticsnurul ainiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 4: Color MeasurementDocumento37 páginasChapter - 4: Color Measurementmuhamed ademAinda não há avaliações
- Ivo BaseDocumento23 páginasIvo BasehomerjwongAinda não há avaliações
- Car Paint MaterialDocumento1 páginaCar Paint MaterialAbriel HaqqaniAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-V Design of Moulds Molding PartsDocumento8 páginasUnit-V Design of Moulds Molding Partsyuvaraj4509Ainda não há avaliações
- ACC's Introduction to Australian Kaolin OperationsDocumento134 páginasACC's Introduction to Australian Kaolin OperationsSerdar Akyildiz100% (1)
- Heat Treatment ProcessDocumento4 páginasHeat Treatment ProcessSuhaib AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Surface TreatmentDocumento24 páginasSurface TreatmentLingarajan RamasamyAinda não há avaliações
- All About Stainless and Heat-Resistant SteelDocumento8 páginasAll About Stainless and Heat-Resistant SteelsaeidianAinda não há avaliações
- Plastics Processing TechniquesDocumento59 páginasPlastics Processing TechniquesSusmit NimjeAinda não há avaliações
- 5674620Documento30 páginas5674620Amrik SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Casting Process Overview: Sand Mould Preparation and Pattern MakingDocumento31 páginasCasting Process Overview: Sand Mould Preparation and Pattern MakingChirag TaterAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 18 - Powder MetallurgyDocumento13 páginasLecture 18 - Powder MetallurgyKonark PatelAinda não há avaliações
- FoundryTerms PDFDocumento5 páginasFoundryTerms PDFFIREREALM66Ainda não há avaliações
- Unicorn Cat Coloring Pages for KidsDocumento6 páginasUnicorn Cat Coloring Pages for KidsIkennaAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Factors To Be Considered in Injection Molding Process Cannot Be Ignored. (158) DocxDocumento8 páginas7 Factors To Be Considered in Injection Molding Process Cannot Be Ignored. (158) DocxGiap NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- of ManuDocumento87 páginasof ManuVaibhav BaggaAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Lubricants On ProcessingbehaviourDocumento5 páginasImpact of Lubricants On ProcessingbehaviourMi Li50% (2)
- Engineering Drawings Practice PDFDocumento27 páginasEngineering Drawings Practice PDFSuriyakumar SundaramAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of Statistical Process Control (SPC) : X-Bar and Range ChartsDocumento4 páginasBasics of Statistical Process Control (SPC) : X-Bar and Range ChartsprabhupipingAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Treatment of Al-Si-Cu-Mg Casting AlloysDocumento60 páginasHeat Treatment of Al-Si-Cu-Mg Casting AlloysRocio LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between Forging and CastingDocumento2 páginasDifference Between Forging and CastingMOHAMMAD ALIAinda não há avaliações
- Heat TreatmentDocumento16 páginasHeat TreatmentPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Living Hinge Design: The Ultimate GuideDocumento18 páginasLiving Hinge Design: The Ultimate GuidesansagithAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic WeldingDocumento13 páginasPlastic Weldingakshay tapkirAinda não há avaliações
- NANOTECHNOLOGY IN CONSTRUCTION: BENEFITS AND APPLICATIONSDocumento10 páginasNANOTECHNOLOGY IN CONSTRUCTION: BENEFITS AND APPLICATIONSPrabhu KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Casting DefectDocumento5 páginasCasting DefectSaurabhAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingDocumento88 páginasPlastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingBhushan Shankar Kamble100% (2)
- Extrusion Molding Process PDFDocumento2 páginasExtrusion Molding Process PDFFrankieAinda não há avaliações
- Injection MouldingDocumento4 páginasInjection MouldinganipcatalyzerAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Injection MoldingDocumento15 páginasAdvances in Injection MoldingPranav PatilAinda não há avaliações
- INDUSTRIAL TRANING SEMINAR - PPTX AnshuDocumento31 páginasINDUSTRIAL TRANING SEMINAR - PPTX Anshuanshu rajAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Injection MoldingDocumento24 páginasPlastic Injection MoldingelectroternalAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop DIARY Sem-2Documento21 páginasWorkshop DIARY Sem-2Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Porous Concrete Project Report SummaryDocumento17 páginasPorous Concrete Project Report SummaryAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Report Sugarcane LifterDocumento44 páginasReport Sugarcane LifterAbhinandan Patil71% (7)
- Academic Caleder 2016-17Documento5 páginasAcademic Caleder 2016-17Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Training ReportDocumento31 páginasHospital Training ReportAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- SCHEME - G Third Semester (AU)Documento34 páginasSCHEME - G Third Semester (AU)Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Impact of ReservoirsDocumento18 páginasEnvironmental Impact of ReservoirsAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- 5th Answer SheetDocumento13 páginas5th Answer SheetAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Deforestration NeweDocumento17 páginasDeforestration NeweAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Toll plaza online payment systemDocumento1 páginaToll plaza online payment systemAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- SCHEME - G Third Semester (AE)Documento41 páginasSCHEME - G Third Semester (AE)Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Geology LectureDocumento32 páginasGeology LectureAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Indian EconomyDocumento14 páginasIndian EconomyAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Caleder 2016-17Documento5 páginasAcademic Caleder 2016-17Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Smoke DetectorDocumento22 páginasSmoke DetectorAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Guide to Photovoltaics (39Documento15 páginasGuide to Photovoltaics (39Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- SE Syllabus V2Documento28 páginasSE Syllabus V2Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Calendar 2015 16Documento5 páginasAcademic Calendar 2015 16Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento13 páginasAbrasive Jet MachiningAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- DSE CutOff2013 08 17Documento1.631 páginasDSE CutOff2013 08 17Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Rainwater HarvestingDocumento7 páginasAn Introduction To Rainwater HarvestingAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- 2012POSTSSC CAP1 CutOff PDFDocumento3.809 páginas2012POSTSSC CAP1 CutOff PDFAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Advance MaterialDocumento21 páginasAdvance MaterialAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Whatisacd?Documento6 páginasWhatisacd?Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Multi VibratorDocumento10 páginasMulti VibratorAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Bio-Data of Vishal TeliDocumento1 páginaBio-Data of Vishal TeliAbhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Whatisacd?Documento6 páginasWhatisacd?Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Sports New2Documento16 páginasImportance of Sports New2Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Sports New2Documento16 páginasImportance of Sports New2Abhinandan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Moulding and Pattern NotesDocumento28 páginasMoulding and Pattern Notesprabhu100% (1)
- Pengaruh Temperatur Cetakan Pada Cacat Visual Produk Piston Dengan Metode Die CastingDocumento10 páginasPengaruh Temperatur Cetakan Pada Cacat Visual Produk Piston Dengan Metode Die Castingrico doangAinda não há avaliações
- Die FormingDocumento4 páginasDie FormingMohit KambojAinda não há avaliações
- Trapezoidal Nut Type FTN - Flanged Bronze: Material: GB-Cu Sn5 Zn5 PB DIN 17656Documento1 páginaTrapezoidal Nut Type FTN - Flanged Bronze: Material: GB-Cu Sn5 Zn5 PB DIN 17656scooba84Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet MetalDocumento8 páginasSheet MetalPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Casting 1 X 1 PDFDocumento373 páginasCasting 1 X 1 PDFSumit Suman100% (1)
- C12 Jaw Crusher Toggle Kit AssemblyDocumento4 páginasC12 Jaw Crusher Toggle Kit AssemblyJustice MachiwanaAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Casting Technology OverviewDocumento4 páginasMetal Casting Technology OverviewTasnim ArifAinda não há avaliações
- iso3408-4-2006_standard5105-ballscrewDocumento26 páginasiso3408-4-2006_standard5105-ballscrewsomenameAinda não há avaliações
- Molds and Orthopedic HardwareDocumento33 páginasMolds and Orthopedic HardwareyelbonifacioAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Data Krasco ComDocumento3 páginasTechnical Data Krasco ComSHANEAinda não há avaliações
- Injection Moulding Process ExplainedDocumento24 páginasInjection Moulding Process ExplainedAbdulRehman Ahmed SoomroAinda não há avaliações
- Drill Hole SizeDocumento17 páginasDrill Hole SizeCTN2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet Metal Bending: A. ElbadanDocumento24 páginasSheet Metal Bending: A. ElbadanSuleman KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer Processing (Molding) : D. Jim Livingston Faculty of Chemistry, St. John's CollegeDocumento26 páginasPolymer Processing (Molding) : D. Jim Livingston Faculty of Chemistry, St. John's CollegeJim LivingstonAinda não há avaliações
- Thermowell Flare Tip Issue - Page 1Documento1 páginaThermowell Flare Tip Issue - Page 1Arif HakimAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 9-Blow Molding PDFDocumento24 páginasLecture 9-Blow Molding PDFAhmed WaelAinda não há avaliações
- E-Learning Modules Form 2020Documento2 páginasE-Learning Modules Form 2020dwimukh360Ainda não há avaliações
- MCQ PPT IDocumento4 páginasMCQ PPT IAditya MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Questions of The Forging and Casting ProcessesDocumento2 páginasQuestions of The Forging and Casting ProcessesMohamed IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Thread Height Gage Standards and Contact PointsDocumento1 páginaThread Height Gage Standards and Contact PointsCarlos Enrique Guzman CastellonAinda não há avaliações
- PTB profile rod seal dimensions and specificationsDocumento10 páginasPTB profile rod seal dimensions and specificationsAditiyo Umara WijayantoAinda não há avaliações
- Lal Kitab Vol 2 1952 CompressedDocumento228 páginasLal Kitab Vol 2 1952 CompressedsunitaranpiseAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocumento27 páginasSheet Metal OperationsbmvinayAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of Metal CastingDocumento43 páginasChapter 1 - Fundamentals of Metal CastingSeab PisethAinda não há avaliações
- Un Thread ClassDocumento1 páginaUn Thread ClassRazvan Andrei GiuscaAinda não há avaliações
- Special Steels RE60S: For Structural ProductsDocumento1 páginaSpecial Steels RE60S: For Structural ProductsRollpass DesignAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Forming-Cold WorkingDocumento79 páginasMetal Forming-Cold Workinganjaiah_19945Ainda não há avaliações
- IMM Process SetupsDocumento25 páginasIMM Process Setupslam nguyen100% (1)
- Types of Pattern Allowances in CastingDocumento7 páginasTypes of Pattern Allowances in CastingDr.S.Ravi CITAinda não há avaliações