Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomi 3 - Cardiovascular System
Enviado por
Astri Ggamjong Xiao Lu0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
32 visualizações81 páginasmzzzzzzzzzzzzlllllllllllllllllllllllljvkjdcjklaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaadnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnjaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaksjbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbjfddddddddddddddddddddkaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentomzzzzzzzzzzzzlllllllllllllllllllllllljvkjdcjklaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaadnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnjaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaksjbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbjfddddddddddddddddddddkaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
32 visualizações81 páginasAnatomi 3 - Cardiovascular System
Enviado por
Astri Ggamjong Xiao Lumzzzzzzzzzzzzlllllllllllllllllllllllljvkjdcjklaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaadnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnjaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaksjbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbjfddddddddddddddddddddkaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 81
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 1
Dr. I Gusti Ayu Widianti, M.Biomed
ANATOMY DEPARTMENT
UDAYANA UNIVERSITY
Scientist / ilmuwan:
Lifelong study Internet international
communication
10/9/2014
2
Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
Leading causes of death
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
3
Heart disease
Malignant neoplasms
Cerebrovascular diseases,
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Pneumonia and influenza
Accidents
Diabetes mellitus
Suicide, nephritis, chronic liver disease, etc
etc
National Health Statistics, 1999
Major disorders
10/9/2014
Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
4
The heart: Coronary artery disease
ischemic heart disease
myocardial infarction
The blood vessels: atherosclerosis
hypertension
varicose vein
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 5
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 6
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 7
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 8
GENETIC PREDISPOSITION
EXCESSIVE CHOLESTEROL
SEDENTARY LIFE
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 9
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 10
LARGE QUANTITIES OF CHOLESTEROL
DEPOSITED BENEATH THE ENDOTHELIUM AT
MANY POINTS IN ARTERIES
INVADED BY FIBROUS TISSUE AND
FREQUENTLY CALCIFIED
NET RESULT IS DEVELOPMENT OF
ATHEROSCLEROTIC PLAQUES
BLOCK OR PARTIALLY BLOCK BLOOD FLOW
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 11
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 12
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 13
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 14
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 15
Weight reduction
Dietary sodium
Rich in vegetables & fruits
Physical activities
Stop smoking
Moderation alcohol
consumption
LIFE STYLE CHANGES
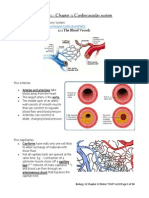
Circulatory System
1.Cardiovascular system
The heart (cor)
System of blood vessel
2. System of lymphatics
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 16
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 17
The site of exchange
10/9/2014
18
Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
Capillary Capillary
Cell
Arteriole Venule
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 19
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 20
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
21
Stroke volume: 70 ml
5 liter/minute
7,200 liters/day
216,000 liters/month
2,628,000 liters/year
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 22
Two major components:
The heart and system of blood vessels
Major functions:
Transport of oxygen and nutrients
Transport of CO
2
and waste products
Two major divisions
Major or systemic circulation
Lesser or pulmonary circulation
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 23
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 24
Oxygenated blood
(O
2
& nutrients)
Deoxygenated blood
(CO
2
& waste products)
Systemic circulation
Pulmonary
circulation
Oxygenated blood
Deoxygenated blood
RV
LA
RA LV
RA=right atrium, LA=left atrium, RV=right ventricle, LV=left
ventricle
Lungs
Heart
Whole body
Heart
Veins Arteries
15mmHg
Venules
Arterioles 60 mmHg
Capillaries
35 mmHg
10/9/2014
25
Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
Circulation
Venules=very small veins; arterioles=very small arteries
Aorta
120mmHg
Vena cava
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 26
OVERVIEW OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 27
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 28
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 29
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 30
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 31
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 32
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 33
PULMONARY
CIRCULATION
SYSTEMIC
CIRCULATION
VALVE
VEIN
LYMPH NODE
LYMPH
CAPILLARIES
HEART
THORACICUS
DUCT
CAPILLARIES
ARTERIES
LYMPH NODE
LYMPH
CAPILLARIES
20 l / day
BLOOD
7200 l
/day
LYMPH
BLOOD
CAPILLARIES
3 l / day
17 l /day
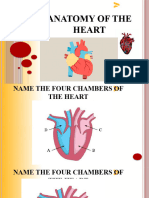
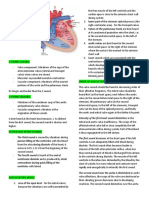
The Heart
A four-chamber, powerful, muscular pump
Divided into two halves: left heart & right
heart.
Left heart: left atrium & left ventricle
Receives oxygenated blood (arterial
blood) from the lungs
Distributes it to the whole body.
Right heart: right atrium & right ventricle
Receives deoxygenated blood (venous
blood) from the whole body, sends it to the
lungs.
The walls of the left ventricle is the thickest.
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 34
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 35
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 36
Boundaries:
left and right pleural cavities,
diaphragm,
anterior and posterior leaves of fibrous
pericardium, and
superior aspect of the left and right pulmonary
arteries
Contents:
Heart and pericardium
Roots of the great vessels
Arch of azygos vein
Main bronchi
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 37
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 38
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 39
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 40
Double-walled fibroserous sac, encloses the
heart and the roots of its great vessels
Pericardial cavity:
The potential space between the opposing
layers of the parietal and visceral of serous
pericardium
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 41
The wall consist of three layers:
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
The fibrous skeleton of the heart
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 42
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 43
A special system for generating rhytmical
electrical impuls to cause rhytmical contraction
of the heart muscle and conducting these
impulses rapidly through the heart
Allow all portions of the ventricles to contract
simultaneously which essential for most
effective pressure generation in the ventricular
chamber
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 44
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 45
A-V node (atrioventricular
node)
Conduction through the atrial wall
Sinoatrial node (sinus node)
A-V bundle (bundle of His)
Right & left branches
Purkinje fibers
PACE-MAKER
10/9/2014
Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD
46
A GROUP OF CELLS AS S-A NODE THAT SERVES
TO ESTABLISH AND MAINTAINING A
RHYTHMIC ACTIVITY
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 47
Number of heart beats per minute
Classification of heart rate
Normal heart rate; 60 100/minute
Bradycardia: 60 beats per minute
Tachycardia: 100 beats per minute
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 48
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 49
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 50
Two most common sites:
In the side of the neck: carotid pulse by
palpating the common carotid artery
At the wrist: radial pulse by palpating the
radial artery
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 51
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 52
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 53
Normal and optimal: 120/80 (adults)
Abnormal high: Hypertension
Systolic Hypertension (wide pulse pressure)
Systolic and diastolic hypertension: Increased
peripheral vascular resistance
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 54
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 55
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 56
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 57
THE FUNCTIONS OF LYMPHATICS
DRAINAGE OF TISSUE FLUID, COLLECTION OF
LYMPH PLASMA AND TRANSPORT OF LYMPH
TO THE VENOUS SYSTEM
ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT OF FAT FROM
THE INTESTINE.
FORMATION OF A DEFENCE MECHANISM
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 58
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 59
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 60
Right lymphatic duct (ductus lymphaticus
dexter):
The right halves of head, neck and thorax,
and the right upper limb
The thoracic duct (ductus lymphaticus
sinister):
The remainder of the body
Both duct eventually open into the
corresponding subclavian veins (venous
angles)
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 61
Lymphatic plexuses (lymphatic capillary)
Lymphatics vessels
Lymph nodes
Lymphocytes
Lymphoid tissue
10/9/2014 Bagian Anatomi FK UNUD 62
Vascularization of head
and neck.
Você também pode gostar
- Anatomy of The Coronary ArteriesDocumento102 páginasAnatomy of The Coronary ArteriesMoa Salloum67% (3)
- Cardiac Embryology 1Documento18 páginasCardiac Embryology 1Natalia IhalauwAinda não há avaliações
- Arterial Lines GuideDocumento38 páginasArterial Lines GuideRabeed MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Cardiology Notes on Personal History and Presenting SymptomsDocumento19 páginasClinical Cardiology Notes on Personal History and Presenting SymptomsRachitha GuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary Catheter Learning Package PDFDocumento36 páginasPulmonary Catheter Learning Package PDFnisar khanAinda não há avaliações
- 3g.gingival Retraction TechniquesDocumento9 páginas3g.gingival Retraction Techniquesdeepakmahla6248Ainda não há avaliações
- 0256 Version 2019Documento66 páginas0256 Version 2019vanessa armeliaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocumento3 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento10 páginasCardiovascular Systemtheglobalnursing75% (4)
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocumento15 páginasPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyAinda não há avaliações
- 5.10 Cardiac AuscultationDocumento47 páginas5.10 Cardiac AuscultationDenisseRangelAinda não há avaliações
- Circulation: Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsDocumento66 páginasCirculation: Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsGlen MangaliAinda não há avaliações
- IABP Handouts - Singapore March 2018 Color SlideDocumento243 páginasIABP Handouts - Singapore March 2018 Color SlideBima RizaldyAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio Anapyhy Session1Documento24 páginasCardio Anapyhy Session1Louise Anne Agnazata GayoAinda não há avaliações
- Webb - Thoracic Imaging - Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Radiology, 2nd Ed.Documento923 páginasWebb - Thoracic Imaging - Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Radiology, 2nd Ed.Iulia Campanu100% (2)
- OXY-Cardio Care ManagementDocumento114 páginasOXY-Cardio Care Managementlalaine22daleAinda não há avaliações
- Benedek Theodora - Curs Cardiologie Interventionala FinalDocumento102 páginasBenedek Theodora - Curs Cardiologie Interventionala FinalBianca IlieAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocumento11 páginasCardiopulmonary Bypass - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfhadeel fahimAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report - Complete Denture - 2Documento4 páginasCase Report - Complete Denture - 2Astri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Gr10 Topic 7 - Transport Systems in Mammals CCDocumento34 páginasGr10 Topic 7 - Transport Systems in Mammals CCkopilive54Ainda não há avaliações
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocumento6 páginas8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0Ainda não há avaliações
- WEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Documento44 páginasWEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Marc Jeff GabasaAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart of The MatterDocumento33 páginasThe Heart of The MatterSETH VILORIAAinda não há avaliações
- EHRA consensus on management of asymptomatic arrhythmiasDocumento32 páginasEHRA consensus on management of asymptomatic arrhythmiasDewiAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart of The MatterDocumento33 páginasThe Heart of The MatterhuangsoulAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Asymptomatic Arrhythmias - EHRA 2019Documento32 páginasManagement of Asymptomatic Arrhythmias - EHRA 2019Edgardo Vargas AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- ANMCO POSITION PAPER Role of Intra-Aortic BalloonDocumento17 páginasANMCO POSITION PAPER Role of Intra-Aortic BalloonapipAinda não há avaliações
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) System.: Atrial Septal DefectDocumento10 páginasExtracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) System.: Atrial Septal DefectDhina KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Pulse Oximetry Design for Developing WorldDocumento54 páginasPulse Oximetry Design for Developing WorldrijowanAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Anesthesia for Valve ProceduresDocumento30 páginasCardiac Anesthesia for Valve ProceduresSayed NourAinda não há avaliações
- Subject Seminar On Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation - ECMODocumento32 páginasSubject Seminar On Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation - ECMOAimhigh_PPMAinda não há avaliações
- Intra-Aortic Balloon Counterpulsation Therapy and Its Role in Optimizing Outcomes in Cardiac SurgeryDocumento31 páginasIntra-Aortic Balloon Counterpulsation Therapy and Its Role in Optimizing Outcomes in Cardiac SurgeryHendrik AbrahamAinda não há avaliações
- Vascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaDocumento47 páginasVascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaJose PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes: A Powerpoint PresentationDocumento105 páginasLecture Notes: A Powerpoint PresentationDutchsMoin Mohammad100% (1)
- The Anatomy of HeartDocumento46 páginasThe Anatomy of HeartPrincess NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Transport in AnimalsDocumento24 páginas8 Transport in AnimalsMariam ShehabAinda não há avaliações
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - CopyDocumento13 páginasCIRCULATORY SYSTEM - Copy2015.562fatimazaherakhanumAinda não há avaliações
- Chest 1975 Capone 577 82Documento8 páginasChest 1975 Capone 577 82ativonAinda não há avaliações
- Bio 12 Ch12 Cardiovascular Sys Notes PackageDocumento16 páginasBio 12 Ch12 Cardiovascular Sys Notes Packagekw2533Ainda não há avaliações
- Download Eacvi Handbook Of Cardiovascular Ct Oliver Gaemperli full chapterDocumento67 páginasDownload Eacvi Handbook Of Cardiovascular Ct Oliver Gaemperli full chaptermilton.alvarado146100% (2)
- 2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutDocumento16 páginas2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutMaggieHameedAinda não há avaliações
- V. Trachea: Zoology-IIDocumento22 páginasV. Trachea: Zoology-IIVenkatesh JoguAinda não há avaliações
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocumento37 páginasWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsAfnan MoeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology Training OverviewDocumento50 páginasAnatomy & Physiology Training OverviewAlisa BrownAinda não há avaliações
- Heart and PericardiumDocumento26 páginasHeart and PericardiumpalAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Bioligic CrisisDocumento141 páginasAcute Bioligic CrisisJanelle MatamorosaAinda não há avaliações
- CVSassignement 1 AnatomyDocumento12 páginasCVSassignement 1 AnatomyRista SimamAinda não há avaliações
- ARDS and Pul Edema SeminarDocumento48 páginasARDS and Pul Edema SeminaryohannesAinda não há avaliações
- EACVI Handbook of Cardiovascular CT 2023Documento385 páginasEACVI Handbook of Cardiovascular CT 2023Munkhjin MAinda não há avaliações
- 2 CardioDocumento26 páginas2 Cardiorashmi_harryAinda não há avaliações
- SimulatorDocumento16 páginasSimulatorMuhammad Farid AriffinAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Learning ObjectivesDocumento5 páginasCardiopulmonary Bypass: Learning ObjectivesAnonymous zPwXqwAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocumento62 páginasCardiopulmonary BypassNidya Putri100% (1)
- Extracorporeal Circulation in Cardiac Surgery Inflmmatory Response, Controversies and Future DirectionsDocumento13 páginasExtracorporeal Circulation in Cardiac Surgery Inflmmatory Response, Controversies and Future DirectionsInternational Medical PublisherAinda não há avaliações
- 10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)Documento31 páginas10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)vidisha bhansaliAinda não há avaliações
- What Is CPB CircuitDocumento4 páginasWhat Is CPB CircuitkhanAinda não há avaliações
- Last Moment Revision in Anatomy To Practice of MedicineDocumento30 páginasLast Moment Revision in Anatomy To Practice of Medicinevavij71588Ainda não há avaliações
- CardioDocumento46 páginasCardiodinglasanerica57Ainda não há avaliações
- Hayu 7Documento20 páginasHayu 7abdimoh926Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Invasive Diagnostic Tests GuideDocumento19 páginasCardiac Invasive Diagnostic Tests GuideSimran JosanAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Lung Machine PumpDocumento31 páginasHeart Lung Machine Pumpmapas_salem100% (2)
- The Vascular System - EditedDocumento5 páginasThe Vascular System - Editedgilbert michaelAinda não há avaliações
- 4 CVS - Arterial SupplyDocumento35 páginas4 CVS - Arterial SupplySepo CaciousAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 Focused Update of The ESC Guidelines For The Management of Atrial FibrillationDocumento29 páginas2012 Focused Update of The ESC Guidelines For The Management of Atrial FibrillationAna MariaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 9 Animal Transport 2023Documento46 páginasCH 9 Animal Transport 2023Mohamed AlyAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumopericardium Two Case Reports and A ReviewDocumento6 páginasPneumopericardium Two Case Reports and A ReviewYonasAinda não há avaliações
- AIPGMEE 2011 Question Paper With Answers PDFDocumento32 páginasAIPGMEE 2011 Question Paper With Answers PDFgayathri67% (3)
- Effects of Orthodontic Treatment With Fixed Appliances On Oral Health Status: A Comprehensive StudyDocumento4 páginasEffects of Orthodontic Treatment With Fixed Appliances On Oral Health Status: A Comprehensive StudyPutu WidiastriAinda não há avaliações
- Bahan Cetak Elastomer PDFDocumento4 páginasBahan Cetak Elastomer PDFAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Examination of The Temporomandibular JointDocumento6 páginasClinical Examination of The Temporomandibular JointAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 Article 499Documento10 páginas2014 Article 499Astri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- VITA 1511 VITA 1511E Prothetikleitfaden BA en V01 Screen enDocumento150 páginasVITA 1511 VITA 1511E Prothetikleitfaden BA en V01 Screen enAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Orthodontic Treatment With Fixed Appliances On Oral Health Status: A Comprehensive StudyDocumento4 páginasEffects of Orthodontic Treatment With Fixed Appliances On Oral Health Status: A Comprehensive StudyPutu WidiastriAinda não há avaliações
- Art:10.1186/s40510 016 0154 9 PDFDocumento6 páginasArt:10.1186/s40510 016 0154 9 PDFPutu WidiastriAinda não há avaliações
- Crown and Bridge RemoversDocumento8 páginasCrown and Bridge RemoversAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- DapusDocumento1 páginaDapusAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Idiopathic Antral Exostoses: Two Rare Cases in Maxillary SinusDocumento4 páginasIdiopathic Antral Exostoses: Two Rare Cases in Maxillary SinusAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- VITA 1511GB A Guide To Complete Denture Prosthetics PS EN V00 PDFDocumento150 páginasVITA 1511GB A Guide To Complete Denture Prosthetics PS EN V00 PDFAstri Ggamjong Xiao Lu0% (1)
- BDJ 2013. Oral Surgery - Part 3. Temporomandibular DisordersDocumento7 páginasBDJ 2013. Oral Surgery - Part 3. Temporomandibular DisordersAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- ATD Automatic Crown and Bridge Remover GuideDocumento7 páginasATD Automatic Crown and Bridge Remover GuideAntony SebastianAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Fissure Sealants in Children and Adolescents With A High Caries RiskDocumento9 páginasClinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Fissure Sealants in Children and Adolescents With A High Caries RiskAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Removing Bridge PDFDocumento6 páginasRemoving Bridge PDFElbanus WatriAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Inflammation HealingDocumento11 páginasChronic Inflammation HealingmemeyviaAinda não há avaliações
- ADocumento5 páginasAAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Jawetz, Melnick, and Adelberg. (2007) Medical Microbiology 24 Edition. MC Graw HillDocumento1 páginaJawetz, Melnick, and Adelberg. (2007) Medical Microbiology 24 Edition. MC Graw HillAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Module 16 Sawitri-Clinical-Trial 2015Documento29 páginasModule 16 Sawitri-Clinical-Trial 2015Astri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- 1472 6831 14 74Documento8 páginas1472 6831 14 74Astri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Base of Tongue VaricesDocumento2 páginasBase of Tongue VaricesAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Synthesis of PLGA Nanoparticles of Tea Polyphenols and Their Strong in Vivo Protective Effect Against Chemically Induced DNA DamageDocumento29 páginasSynthesis of PLGA Nanoparticles of Tea Polyphenols and Their Strong in Vivo Protective Effect Against Chemically Induced DNA DamageAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarDocumento25 páginas6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- The Recombinant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Outer Membrane Protein Has Carriers Properties For Conjugated Antigenic PeptideDocumento18 páginasThe Recombinant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Outer Membrane Protein Has Carriers Properties For Conjugated Antigenic PeptideAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Study of The Antibacterial Activities of Soursop (Annona Muricata L.) LeavesDocumento8 páginasStudy of The Antibacterial Activities of Soursop (Annona Muricata L.) LeavesAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Targeting Cancer Cells Using PLGA Nanoparticles Surface Modified With Monoclonal AntibodyDocumento17 páginasTargeting Cancer Cells Using PLGA Nanoparticles Surface Modified With Monoclonal AntibodyAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Outer Membrane Protein A From Klebsiella Pneumoniae Activates Bronchial Epithelial Cells Implication in Neutrophil RecruitmentDocumento21 páginasOuter Membrane Protein A From Klebsiella Pneumoniae Activates Bronchial Epithelial Cells Implication in Neutrophil RecruitmentAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuAinda não há avaliações
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Documento2 páginasAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeAinda não há avaliações
- The Lenke Classification System for Spinal CurvatureDocumento1 páginaThe Lenke Classification System for Spinal CurvatureFederico Nelson FreisAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory InsectsDocumento7 páginasCirculatory Insectsmith777Ainda não há avaliações
- PAVSDMAPCAsDocumento3 páginasPAVSDMAPCAsRajesh SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The HeartDocumento7 páginasAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Heartrapunzel777Ainda não há avaliações
- Left Vs Right: Heart FailureDocumento3 páginasLeft Vs Right: Heart FailureRosalinda PerigoAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Disease in PregnancyDocumento84 páginas2018 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancyasm obginAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Sounds GuideDocumento2 páginasHeart Sounds GuideShmuel BarshalomAinda não há avaliações
- Review The Causes of Decreased Breath SoundsDocumento1 páginaReview The Causes of Decreased Breath SoundsArvinth Guna SegaranAinda não há avaliações
- JV Electrophysiology of HeartDocumento19 páginasJV Electrophysiology of HeartRiya GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Naitik Trivedi & Dr. Upama Trivedi: Cardiovascular SystemDocumento20 páginasDr. Naitik Trivedi & Dr. Upama Trivedi: Cardiovascular SystemAhmed ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Jason Figueroa - 12 - Virtual Sheep Heart DissectionDocumento5 páginasJason Figueroa - 12 - Virtual Sheep Heart DissectionJason FigueroaAinda não há avaliações
- PENETRATING CHEST INJURY TREATED FOR MASSIVE HEMOTHORAXDocumento40 páginasPENETRATING CHEST INJURY TREATED FOR MASSIVE HEMOTHORAXAla'a Emerald AguamAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento40 páginasCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Joints of Axial SkeletonDocumento24 páginasJoints of Axial SkeletonPraney SlathiaAinda não há avaliações
- Loreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanDocumento4 páginasLoreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanJean CabigaoAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento8 páginasAcute Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Heart DiseaseHASNIZZAM BIN AHMAD AMIN -Ainda não há avaliações
- Trachea and LungsDocumento25 páginasTrachea and LungsDr.pallavi kumariAinda não há avaliações
- The International Association For The Study of Lung Cancer Lymph Node Map: A Radiologic Atlas and ReviewDocumento11 páginasThe International Association For The Study of Lung Cancer Lymph Node Map: A Radiologic Atlas and ReviewRikaAinda não há avaliações
- BI Furcati Otracheae Bronchus PRI NCI Pali S SI NI Ster: TracheaDocumento4 páginasBI Furcati Otracheae Bronchus PRI NCI Pali S SI NI Ster: TracheaWilliem ChandraAinda não há avaliações
- Inferior Vena Cava Cross-SectionDocumento3 páginasInferior Vena Cava Cross-SectionPriyanshu SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Thorax Card Final ExaminationDocumento3 páginasThorax Card Final ExaminationAbdul QuaiyumAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ECG Interpretation Review Questions Flashcards - QuizletDocumento5 páginasBasic ECG Interpretation Review Questions Flashcards - Quizletdina sharafAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Pathways for Rib FractureDocumento1 páginaClinical Pathways for Rib FractureIkhdin SaadhiAinda não há avaliações