Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Set of Education Problem and Multicultural Education
Enviado por
Inggrid Ayu Putri0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
10 visualizações68 páginasThe problem is how the education system can provide the opportunity for all citizens to get education. There are many citizens, especially school-age children who can not be accommodated in the education system or educational institution because of the lack of facilities available. Education quality is come, if the result of education have not reached the level as expected.
Descrição original:
Título original
SET OF EDUCATION PROBLEM AND MULTICULTURAL EDUCATION.pptx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe problem is how the education system can provide the opportunity for all citizens to get education. There are many citizens, especially school-age children who can not be accommodated in the education system or educational institution because of the lack of facilities available. Education quality is come, if the result of education have not reached the level as expected.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
10 visualizações68 páginasSet of Education Problem and Multicultural Education
Enviado por
Inggrid Ayu PutriThe problem is how the education system can provide the opportunity for all citizens to get education. There are many citizens, especially school-age children who can not be accommodated in the education system or educational institution because of the lack of facilities available. Education quality is come, if the result of education have not reached the level as expected.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 68
Disusun Oleh :
- Siti Nur Shafriani
- Siska Sugih
- Rica Oktoria
- Nadia Farhana
Pendidikan Fisika Bilingual 2013
How all the citizens can enjoy
educational opportunities ?
How can education have the suply
student with the skills work steady
directly into the public life?
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
Type of Main Problems in Indonesia
A. Educational Equity
The problem is how the education system can provide the opportunity
for all citizens to get education.
This problem appear
when there are many
citizens, especially
school-age children who
can not be
accommodated in the
education system or
educational institution
because of the lack of
facilities available.
Figure 1 The situasion of class that have
good facilities.
Source: blog.pinkemma.com (August 30,
2013)
Figure 2 The situasion of class that
doesnt have good facilities.
Source : blog.tp.ac.id (oktober
22,2012)
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
B. Quality of Education
Education quality is come, if the result of education have not reached the level as
expected.
There are any reasons for the low quality of
education in Indonesia :
Eficiency of Education in Indonesia
Effectifity of Education in Indonesia
Standardization of Education in Indonesia
Figure 5 National examination
always make the controfertion
Sumber : edukasi.kompasiana.com
(Maret,18 2013)
Figure 3 Curriculum change in
Indonesia
Source :
amirullah2407.blogspot.com
(Desember,2 2012)
Figure 4 people opinion , about
education only to formality to get a
sertificat
Source : holiparent.blogspot.com/
(Juni,22 2013)
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
C. Efficiency of Education
The problem of education efficiency, its relation with the process
transformation raw input into output.
Thats the problem of education effiency is:
i. How the function of educator staff?
ii. How to used the education facilities?
iii. How the education can be held?
D. Relevance of Education
This problem relation with the rasio between the result of graduate on unit
education with instituation that need workers. Thats the problem of relation with
relevance of education is:
a. Many various of status educational institution
b. Education system doesnt produces graduated already.
c. Unavailable the necessity of working staff with requirements that are used as
guidelines by educational institutions to develop its program
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
FACTORS AFFECTING THE DEVELOPMENT OF EDUCATION
PROBLEMS
I. Progress IPTEK & ART
o There is a strengthen relationship between education and iptek ( science and
technology)
o With the development of globalization in our country, especially with the rapid increase
in communication technologies, making everything must be done quickly and precisely.
o Science is the result of an exploration system about the universe, and then technology is
planned application of science to satisfy the needs of society.
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
II. Population growth rate
Total population in Indonesia : 241 million person (www.bps.go.id)
Tota area in Indonesia : 1.919.443 km2 (indonesiadata.co.id)
The problems of population and education stem from 2 things:
Population Growth
If the population growth is rapidly increasing, the number of school-age
children will be greater.
Distribution of Population
Uneven distribution of the population will pose new problems.
Educational facilities must be matching with the number of
population in the area.
Figure 6 graphic of population growth in Indonesia
Source: 110.138.206.53/bahan-
ajar/modul_online/geografi (April,11 2011)
Figure r 7 population density map of Indonesia
Sumber : potretpendudukindonesia.blogspot.com
(Juli,2 2012)
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
III. Aspiration of The People
Lately aspirations of the people is
increasing in line with the increase in
public awareness of 'reform'. The
aspirations regarding education
opportunities, feasibility study and
guarantees the standard of living after
they undergo the process of education.
IV. Cultural Backwardness
Cultural backwardness caused by several
things, for example the geographical
location isolated and difficult to reach,
the public rejection of the new culture
elements, because feared would erode
cultural, and economical concerns the
inability of these cultural elements.
Figure 7 the demonstrators were expressing their
aspirations
Source : bahasa.kompasiana.com (Maret,29 2011)
Figure 8 isolated geography
Source:kuburayaforindonesia.b
logspot.com
Figure 9 portrait of poverty life
Source : baltyra.com ( Februari,6
2011)
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
THE PROBLEMS OF EDUCATION ACTUAL
The problem of education actual in Indonesia is very complex and is
growing in line with the times and the establishment of human resources.
And the problem is :
a. Achievement
integrity problems
b. Curriculum issue
c. The Role of Teacher
d. 9-year basic
education
Gambar 12 Seorang guru yang
sedang mengarahkan siswa dalam
praktikum
Sumber : panduanguru.com
(Januari,2 2013)
Figure 13 program 9-years basic
education
Source:muhammadsyamlawi.blogs
pot.com ( Agustus,20 2012)
Figure 11 A student who
headache with the curriculum
now.
Source : iwansmtri.blogspot.com (
Oktober, 4 2012)
Figure 10 Someone who wants to
shoot the right target.
Source: muslimin88.blogspot.com
Source : Tirtarahardja, Umar dan La Sula.2005.Pengantar Pendidikan.Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta
Study of
Case
3.3 million children every year could not continue education
Neneng Zubaidah
Wednesday, 30 October 2013 16:32 WIB
Sindonews.com - The Government considered can not educate all the
children of Indonesia. Because, of the total 5.6 million elementary school
children (SD) every generation, there are 3.3 million children who can not
attend school because quantity of school is less.
Paramadina University Rector Anies Baswedan said, if we compared to South
Korea (ROK) and Japan, the number of children who enter primary school has
been equal with their.
But the high school level there are only 2.3 million children who graduated
from high school. He said there were 3.3 million children every generation
lost on the road, because there is championed his right to education., "He
concluded.
Sumber : http://nasional.sindonews.com/read/2013/10/30/15/800111/pertahun-3-3-juta-anak-tak-bisa-lanjutkan-pendidikan
Sumber : http://nasional.sindonews.com/read/2013/10/30/15/800111/pertahun-3-3-juta-anak-tak-bisa-lanjutkan-pendidikan
"If it is multiplied by 10 years, then there are 33 million people in Indonesia
who are not educated," said anies in the Library, University of Indonesia (UI),
Depok, West Java, on Wednesday (30/10/2013).
Anies explained, causes them to lose his right to education because quantity
of schools that are not comparable. Compare the number of elementary
school in Indonesia as many as 146 967 units but only 35 492 units SMP
number.
"With so much of the population, not necessarily the quantity of schools in
the country so little. Prove low number of government schools does not
intend to educate all the children of Indonesia"
Input the Problem :
The Government considered can not educate all the children of Indonesia.
Because, of the total 5.6 million elementary school student (SD) every
generation, there are 3.3 million children who can graduated from High
School.
Process
Improve education aspiration to society in Indonesia. Increase the quantity of
public schools on the junior high school and senior high school. In addition it
provides scholarships to students - students who lack the cost that can still go
to college.
Output
Indonesia reduced the number of children who drop out of school. Increasing
the quality of graduates.
EDUCATION ISSUES
BACKGROUND OF THE ISSUES
Education has the task of preparing human
resources for development. Development has always
strived to demands of the times. The times bring new
challenges. As a logical consequence, education is
always faced with new problems. Problems facing the
world of education is so broad, the first since the goal of
human nature, both as a business education should
anticipate the future. Therefore there needs to be
formulated as key issues that can be used as a handle by
educators in carrying out their duties.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Goals can be achieved:
1. Transcribe 4 kinds of problems and explain about basic education,
2. Explain the relationship between the fundamental problems of the
education,
3. Explain the influence of science and technology development,
population growth, and aspirations towards development of education,
4. Explain the actual problems of education in our country as well as
efforts to overcome.
To achieve these objectives the material can be presented include:
a. Education and basic problems to overcome,
b. Type of education and overcome underlying problems,
c. Interrelations between the central issue of education,
d. The factors that influence the development of educational issues,
e. Actual problems of education in Indonesia and handling.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
A. PROBLEMS BASIC EDUCATION AND
ABATEMENT
Basically there are two main problems faced by the
education sector in our country, namely:
1. How citizens can enjoy educational opportunities,
2. How can education equip learners with the skills to be
able to work steady directly into public life.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
B. BASIC EDUCATION PROBLEMS
Four main issues that need to be prioritized national
agreement to overcome, namely:
1. Educational equity issues,
2. The problem of education quality,
3. Efficiency problems of education,
4. Relevance education issues.
Source Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
1. EDUCATIONAL EQUITY ISSUES
Educational equity problem is the issue of how the
education system can provide the broadest opportunity to all
citizens to education, so that education becomes a vehicle for
the development of human resources to support development.
Relating to compulsory Chapter VI, Article 10 Paragraph
1, states: "All children are entitled if they are already 6 years
old and 8 years old who are required to learn in school, at least
6 years,".
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
TROUBLESHOOTING EQUITABLE EDUCATION
Solving problems that have been and are being made by the
government to improve educational equity reached by way of:
Conventional ways, among others:
a. Such as elementary school building or classrooms inpress
b. Using the school building for a double shift (evening and night
alternately systems).
Innovative ways, among others:
a. Guardian System (education by society, parents, and teachers) or Inpacts
System (Instructional Management by Parent, Community and, Teacher).
The system was pioneered in Solo and applied to several provinces
b. Small SD in remote areas
c. Visit the Master System
d. Junior Open (ISOSA-In School Out off School Approach).
e. Packet A and B
f. Distance Learning, such as the Open University.
Source Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Innovative ways:
SD in remote
areas.
Conventional
Method:
Development of
learning spaces.
Source:
http://aurellyreresaputra.blogspot.com/2013/05/problematika-
pendidikan-bangsa-indonesia.html
2. EDUCATION QUALITY PROBLEMS
The quality of education in question, if the results have not
reached the level of education as expected.
Furthermore, the smooth processing of education
supported by an educational component. In the MPR RI 1998
on the Guidelines stated that the emphasis placed on the
development of education quality improvement all levels and
types of education, and in order to improve the quality of
education, especially for spur mastery of science and
technology needs to be further refined and improved the
teaching of science and mathematics.
Source Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
TROUBLESHOOTING QUALITY OF EDUCATION
Efforts to solve the problem of quality
education in the outline include things that are
physical and software, personnel, and
management as follows:
a. More rational selection of the raw input,
especially for high school and PT
b. The development of education personnel
capabilities through further studies
c. Completion of curriculum
d. Infrastructure development that creates a
peaceful environment for learning
e. Completion of a learning tool
f. The increase in administrative management
especially regarding budget
g. Adannya quality control activities.
Not achieving educational
quality learning outcomes
that are not optimal so that
students are not ready to
make the exams and finally
cheating.
Source: https://encrypted-
tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSzi0F2joc-
LrdJ_2z32k9ZlhiDqaYz7f1yEnWCKaDx5ZXIlc5P
Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Rineka
Cipta.
3. EDUCATION EFFICIENCY ISSUES
Problems questioned how the efficiency of education an educational system
utilizing existing resources to achieve educational goals.
Several issues are important educational efficiency, is:
a. How education personnel function
b. How infrastructure and educational facilities used
c. How education held
d. Problems in the functioning of energy efficiency.
This issue includes the removal, placement, and personnel development.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
4. PROBLEMS RELEVANCE EDUCATION
Relevance education covers a number of issues which the
education system can produce outputs in accordance with the needs
of development. Relevance criteria if the condition is associated with
the education system in general and an overview of the existing
work, such as:
The status of the institution itself is still bermavam-wide quality,
The education system never produces an output ready-made, that
there is ready to flower,
The need for labor with the requirements that could be used as a
guide by educational institutions to develop its program is not
available.
Of the four kinds of educational problems is said to be resolved
if the education:
1. Equalization can provide an opportunity to learn,
2. Can achieve quality results,
3. Can terlaksama efficiently,
4. The quality Relevance products.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
THE FOUR INTER-RELATED PROBLEMS IN THE
IMPLEMENTATION
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
C. FACTORS AFFECTING THE DEVELOPMENT OF
EDUCATION ISSUES
Factors affecting the development of education,
namely:
1. The development of science and art,
2. The rate of population growth,
3. Aspirations of the people,
4. Cultural backwardness and means of life.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Availability of classrooms with technology, such as computers because of the
development of science and technology.
One of the difficulties in educational
facilities, such as classrooms, thus
causing the learning process conducted
by the vehicle such as a bicycle parked
in one room.
Source: http://m.kompasiana.com/post/read/456635/3/fasilitas-pendidikan-
di-pulau-kayuadi-kabupaten-kepulauan-selayar.html
http://bimg.antaranews.com/jambi/2011/11/ori/20111115d68.jpg
One of the aspirations of a mother in
Pekanbaru Batang areas (remote areas)
who are eager to help in the education
process in the area so that he entered into
a process of learning to improvise
conditions.
Cultural backwardness and means of
livelihood due to geographic, cultural
rejection of new elements, and the
community has led to the inability of
the people in the Papua region (inland)
still wear penis gourds.
Source: http://herusupanji.blogspot.com/2012/06/papua.html
ACTUAL PROBLEMS OF EDUCATION AND
ABATEMENT
Some of the issues raised include the actual education issues:
a. Integrity of achievement goals, dealing with aspects of cognitive
development have obstacles in the experience.
b. Curriculum, concepts and issues related to its implementation.
c. The role of the teacher, the procedures relating to the system of
educating and interacting with students, the delivery of the material
to be taught, a teacher effective time to add their own knowledge,
and student learning process is assisted by a number of other
officers.
d. 9 years of basic education, the foundation associated with
Republic Act No. 2 of 1989 of Article 6 and Article 13 of
Government Regulation No. 28 of 1990 Article 2 of the Basic
Education Assessment Guidelines 1993 on the direction of the
realization of national education in item 26
e. Utilization of educational technology, touch on the use or function
of technology in support of the educational process.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
PREVENTION EFFORT
Some effort needs to be done to tackle the actual problems as noted,
among other things:
a. Programmatically enhanced affective education is not sufficiently
lasting only incidentally. Approach the skills that have been disseminated
spread the concept needs to be followed up with a guide book to the
schools. In this connection the implementation of arts education should be
given special attention so as not to be excluded subjects.
b. Implementation of such knockout (Event Organization) and
extracurricular done with full sincerity and the results are taken into
account in determining the final grade or the release. For that needs to be
associated with the provision of intensive for teachers.
c. The selection of groups of students who will continue studying high
keperguruan that will go into the community is a matter of principle
because basically all potential students are able to learn in college.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop a solid plan for it. For example,
among other top-level vocational schools propagated by various kinds.
On the other hand the establishment of private universities and
accreditation of private universities is restricted tightened.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
d. Education education personnel need to be given special attention,
especially because of the teacher education personnel became the major
cause of the birth of qualified human resources for development. PKG
(Center Teacher Training Teacher), MGBS (Teacher Field Studies
Council) and MGMPs (Subject Teachers Council) needs to be nurtured
continuously as a model of teacher development capabilities (self-
sustaining competencies). Utilization of diverse learning resources that
need to be improved. These efforts are the responsibility of the principal,
teachers, and technicians learning sources.
e. For the implementation of the 9-year basic education, especially if it is
associated with the movement of compulsory education, research needs to
be conducted extensively in the community to find the main factors
supporting and inhibiting factors.
To the general public need to be given information that is clear and
persuasive of the meaning of basic education. The realization of the
implementation of basic education is done in stages.
Source: Tirtarahardja, U., & Sulo, S. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
LAMPUNG EDUCATION COORDINATION MEETING TO DISCUSS
IMPLEMENTATION OF CURRICULUM 2013
REPUBLIKA.CO.ID, JAKARTA-Coordinating Meeting of the Forum of Regional Task Force for Education in Bandar
Lampung province , on Tuesday , to discuss the implementation of Curriculum 2013 readiness and the various programs and
other educational issues.
Coordination Meeting of the Forum on education that Education Dept. of Education opened Lampung tauhidi Drs MM , and
presents a number of speakers from Lampung Police Traffic Directorate (Commissioner Elviza Thamrin), Bappeda Lampung
(Evi Fatmawati / Head of Socio-Cultural), and Department of Education officials Lampung (Retno Setianingrum and Ria
Anda).
Secretary of Education Office of Lampung Maidasuri a guide Rakor on education that lasted until it was past noon.
Head of Education Lampung tauhidi stated that the coordination meetings specifically to discuss a number of issues and
identification of educational problems in Lampung , for the programmed efforts to handle it well. "All parties are expected to
actively provide input in coordination meetings," he said anyway.
He admits there are still problems of education in the area of Lampung, including education quality gap between regions in
Lampung, namely in urban and rural areas in the outlying regions of Lampung.
Source: http://www.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/daerah/14/03/12/n2anrq-
rakor-pendidikan-lampung-bahas-implementasi-kurikulum-2013
Department of Education Lampung according to him, will encourage every county and city in Lampung
develop and have excellent schools so that the quality of education in Lampung are becoming increasingly
prevalent.
A number of issues of concern to education and language coordination meetings participants, of whom
need the readiness of the whole school, teachers and students in Lampung to implement Curriculum
2013.
"No more excuses, in the academic year 2014/2015 which starts in July, all schools in Lampung
Curriculum 2013 must have been running it," said Head of Education Department of Elementary
Education Lampung Ria Anda.
According to him, in order to prepare the implementation of Curriculum 2013, teachers will be trained in
Lampung, books required will be prepared by the government , and schools will receive the necessary
assistance.
"Efforts will be made to the government run school readiness curriculum in 2013 's, so there is no reason
not to implement it," he said anyway.
In time , starting in July 2014, the Curriculum 2013 was to be implemented by all schools in Lampung,
according to Ria Anda.
Source: http://www.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/daerah/14/03/12/n2anrq-
rakor-pendidikan-lampung-bahas-implementasi-kurikulum-2013
INPUT
1. The necessity of readiness throughout the school,
teachers and students in Lampung to implement
Curriculum 2013.
2. A number of problems and identification of
educational problems in Lampung.
3. education quality gap between regions in Lampung,
namely in urban and rural areas in the outlying regions of
Lampung.
Source: http://www.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/daerah/14/03/12/n2anrq-
rakor-pendidikan-lampung-bahas-implementasi-kurikulum-2013
PROCESS
1. Holding coordination meetings Work Unit Area Forum
for Education in Bandar Lampung
2. Identify the issues of readiness curriculum in 2013 in
Lampung for programmed attempt to handle it well.
3. Providing curriculum efforts that performing well in
2013.
4. The implementation of the curriculum in 2013 by all
schools in Lampung.
Source: http://www.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/daerah/14/03/12/n2anrq-
rakor-pendidikan-lampung-bahas-implementasi-kurikulum-2013
OUTPUT
1. Curriculum 2013 can run well in Lampung.
2. Problems of education in Lampung can be resolved by 2013 that
the curriculum will be implemented.
3. There is no gap of education quality gap between regions in
Lampung.
Source: http://www.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/daerah/14/03/12/n2anrq-
rakor-pendidikan-lampung-bahas-implementasi-kurikulum-2013
CURRICULUM 2013
Sumber: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cguVdHGWUs0
Multicultural education is etymologically derived from
two terms: education and multiculturtal.
Education can be defined as the process of developing
attitudes and code of conduct a person or group of
people in human mature businesses through the efforts
of the teaching, training, processes, actions, and ways to
educate.
Multicultural means of cultural diversity, variety,
decency, or lots of maintenance.
Ainurrofiq Dawam said,
multicultural education is
the process of developing
the full potential of human
plurality and heterogeneity
appreciate cultural
diversity as a consequence
of ethnic, tribal, and flow
(religion).
Sources: Ainurrafiq Dawam, unwilling to School
Refused commercialization of education and
intellectual cannibalism manuju multicultural
education, 2003.
According to Zubaedi,
multicultural education is a
reform movement that is
changing the educational
component senua including
changing the basic values of
education, rules of
procedures, curriculum,
teaching materials,
organizational structure and
government policies that
reflect the cultural pluralism
as the reality of Indonesian
society.
Source: Zubaedi, Assessing the concept of
multiculturalism and its implementation in
education. 2004
Conclusion:
Multicultural education is a process of
development which does not recognize the
barriers to human interaction. As a vehicle for
potential development, multicultural education
is education that respects the heterogeneity and
plurality, education that values culture, ethnicity,
race, and religion.
Based on the Encyclopedia of Social Sciences,
Education Multicultural education began as a reform
movement in the U.S. during the struggle for civil
rights of African Americans in the 1960s and 1970s.
Source: Encyclopedia of Social Sciences. Kuper. 2000
According to Banks (2003),
describing the evolution of
multicultural education in four
phases:
There was an attempt to unite the
ethnic studies curriculum at all.
Multiethnic education followed by an
attempt to apply the equation of
education reform through the entire
education system.
Marginalized groups others, such as
women, disabled people, gay and
lesbian, began to demand
fundamental changes in the
educational institutions.
The development of the theory, and
practice triset, attention to race
relations, gender, and class have
produced a common goal for most
experts theorists, if not practitioners,
of multicultural education.
Source: James A. Banks. Educating Citizens in
Multicultural Society. 1993
Sumber:
https://www.google.com/search?q=james+a
.banks,+1993&client=firefox-
a&hs=lpW&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&
ei=mZ0lU-
qeHcyXrgeggoGAAw&ved=0CAkQ_AUoAQ
&biw=1024&bih=605#facrc=_&imgdii=_&im
grc=OV3r5RZHmype1M%253A%3BA6PFJFV
F32FNoM%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Ffacult
y.washington.edu%252Fjbanks%252FBanks-
James-A-8x10-
33%252520small.jpg%3Bhttp%253A%252F%
252Ffaculty.washington.edu%252Fjbanks%2
52Flongbio.htm%3B1680%3B2100
Nieto (1992) states that
multicultural education aims:
To be an anti-racist
education;
whose attention skills-skills
and basic knowledge for the
citizens of the world;
develop the attitudes,
knowledge, and skills that
enable students to work for
social justice;
a process in which teachers
and together students learn
the importance of cultural
variables to academic success
Source: Multicultural Education. Sonia
Nieto. 1992
Sumber:
https://www.google.com/search?q=nieto,+1992
&client=firefox-a&hs=5dC&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ei=
xqQlU4vNJYaYrgeU24CgBw&ved=0CAkQ_AU
oAQ&biw=1024&bih=605#q=sonia+nieto%2C+
1992&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&tbm=isch&facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgr
c=G-
puhqTSZa61EM%253A%3B8ILW38nJowdNkM
%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fgsep.pepperdine.e
du%252Fimages%252Fevents%252FDr.Sonia.Ni
eto.jpg%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fgsep.peppe
rdine.edu%252Fnews-
events%252Fevents%252Fdeans-
lecture%252F%3B116%3B133
According Parsudi
Suparlan, Multiculturalism
is a concept that is able to
meet the challenges of
changing times on the
grounds of
multiculturalism is an idea
that glorifies ologi cultural
differences, or a belief that
recognizes and encourages
the establishment of
cultural pluralism as a
mode of social life.
Sources: S, Parsudi. Culture and
Development. , 1982.
Sumber:
https://www.google.com/search?q=parsudi
+suparlan+sosiolog+UI&client=firefox-
a&hs=PPX&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&biw=1024&bih=605&noj=1&tbm
=isch&source=lnms&sa=X&ei=O6YlU7O-
FcaSrge7jIHICQ&ved=0CAgQ_AUoAQ#facr
c=_&imgdii=_&imgrc=qXVc_2fjwFJTOM%2
53A%3BjcrW374Gx2cjdM%3Bhttp%253A%2
52F%252Fcapcuskampus.files.wordpress.co
m%252F2013%252F08%252Fds.jpg%253Fw%
253D614%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fcapcus
kampus.wordpress.com%252Fseputar-ilmu-
antropologi%252F%3B196%3B257
While Resident Identity Change Model
Lysgaard develop a model of intercultural adjustment
consists of three phases that include initial
adjustment, crisis, and adjustment recovered.
Initial adjustment is optimistic phase of the seasonal
adjustment process of the population.
The second phase is formed and pressed when the
reality of their inability brimmed seasonal residents.
The third is the establishment phase, when seasonal
residents learned to deal with the new environment.
Source: Lysgraad, S. Multiculturalism. 1955
Lysgaard propose a model of the U-curve adjustment process
seasonal residents
Sumber: https://www.google.com/search?q=teori+kurva+u+sverre+lysgaard&client=firefox-a&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ei=hX0lU8bWGcS_rgfruICYBw&ved=0CAcQ_AUoAQ&biw=1024&bih
=629#q=sverre+lysgaard&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&tbm=isch&facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgrc=6d0dccnOnvGikM%253A%3BlZ9yMjW-
QqORsM%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.soulshineblog.com%252Fwp-
content%252Fuploads%252F2012%252F10%252FThe-Expat-
Curve.png%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.soulshineblog.com%252F2012%252F10%252F01%252Fthree-groups-
of-three%252F%3B525%3B344
(Lysgraad, S. Multiculturalism. 1955)
Sumber: https://www.google.com/search?q=Gullahorn&client=firefox-a&hs=RoU&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&tbm=isch&source=lnms&sa=X&ei=QH8lU4mHKcWNrQel34DgCg&ved=0CAkQ_AUoAw&bi
w=1024&bih=629#q=curve+w+Gullahorn&rls=org.mozilla:en-
US:official&tbm=isch&facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgrc=UF_aHFP2odd5YM%253A%3Bw92B8j2woHfe6M%3Bhtt
p%253A%252F%252Fwww.hotelmule.com%252Fmanagement%252Fattachments%252F2010%252F08%252
F26_2010081518564212nk3J.gif%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.hotelmule.com%252Fhtml%252F13%252F
n-3113-14.html%3B492%3B317
In developing the model curve-U, Gullahorn filed the W-curve
models with six levels
(Gollahorn. Multicultural Behavior and Global Business Environment. 1963)
Basically, the W-shaped adjustment models that have been
revised to emphasize some of the characteristics during the
process of changing the identity of the seasonal population:
1. They need to understand the peaks and low points, positive
and negative shift, which establish the identity of a change in the
foreign environment, be aware that changes up and down
feelings are part of the process of change and development,
2. They must be aware of and follow the instrumental purpose,
relational and identity in a new culture; successful in a particular
set of goals affect the success of achieving other goals,
3. They need to give themselves time and space to adjust,
4. They need to develop strong ties and weak ties to protect them
and where to seek help when needed,
5. They need to look for an opportunity to participate in a major
cultural event belongs to the host culture and immerse yourself
in the rare opportunity to enjoy the local culture and learn as
much as possible.
Source: Gollahorn. Multicultural Behavior and Global Business Environment. 1963
Model Changes in Immigrant and Minority Identity
Acculturation is a multidimensional process involving
and system level processes and individual change.
According to Berry, immigrants tend to promote the
maintenance of ethnic traditions and degrading
siginifikansi values and new cultural norms applying
traditional oriented option.
Source: Integration and Multiculturalism. John Berry. , 1984.
Incident Tarakan and Insulation Ethnic Regional Autonomy
Smelling ethnic conflict broke out in Tarakan, East Kalimantan (28/9). Events
triggered by the assassination of Abdullah (56), one Tidung stakeholders, indigenous
Tarakan, by a group of descendants of the Bugis (South Of Sulawesi).
Emotional ties of ethnic solidarity spontaneously rise up, be organized by the
Union of Indigenous Borneo (Heritage), especially after the security forces (police) to
find the killer acted sluggish Abdullah.
Two ethnic groups clashed eventually inevitable. Residents of the Bugis
community was a physical fight in the open. The security forces seem to be overwhelmed
or unable to anticipate that when this article was written, the victim died from both sides
grew to five people, is very alarming.
Conflicts of inter-ethnic different open with unbridled emotion appears it was
always inevitable. The citizens of warring dissolved or trapped in the tribal emotions. In
fact, on a large scale and the relatively long time span, an intertribal dispute has often
happened in this country.
We still remember, among others, the conflict triangle tribes in Sambas, West
Kalimantan, between ethnic Malays Dayaks and Madurese versus; conflict in Ambon,
Maluku, Ambon involving ethnic native versus newcomer (Bugis, Makassar, Buton and
Muna), and the Sampit conflict , Central Of Kalimantan, Madura VS Dayak.
The number of casualties and material in some of the events of civil war is
indeed very large, with a psychosocial impact of trauma and anxiety can happen again or
even warring tribal hatreds. It is an inherent part of the social life, including the younger
generation. This means, the degree of social sensitivity post-clash will be very high.
Source: kompas.com (Friday, October 1
th
, 2010)
Input:
The conflict stems from Tarakan ethnic conflict
between the two close neighbors. Early events just a
trivial matter of five young men in Bugis Juwata
Permai Housing is considered disturbing the peace
and comfort of the people as a party of Alcohol
(liquor) offended when reprimanded by youth, local
residents as well as the youths attacked.
Process:
The elder Tidung then waging war against the people
Bugis.Huru nutrient that lasts for several days it
nenyebabkan falling dead and wounded. Tarakan city
had lumpuh.Pasar, shops, and schools closed.
Output:
Mediation was held regarding a peace agreement between the Tribe
Tidung with the Bugis settlers who became a mediator and was the
Governor of East Kalimantan. In a statement to the press invited the
parties to submit the agreement. The agreement was read alternately
by two groups of Tidung and South Sulawesi. Here is a 10-point peace
agreement between the two parties:
1. Communities asked to end the conflict.
2. People are asked to understand that the events are purely criminal in
Tarakan
3. Police asked to disperse the crowd that clustered
4. Police asked firmly and prohibits citizens carrying weapons
5. People are asked to respect local customs
6. The residents who had fled asked back to normal activities
7. Police asked to prosecute perpetrators allegedly involved
8. People are asked not easily provoked
9. Both communities will hold religious gatherings facilitated by local
government
10. This agreement to immediately socialized to all warga.The point is
that both sides agreed to stop the action and agreed to bury the hatchet
Implementation Steps Unity
in Diversity in education
Ones of school education adjustment
efforts with diversity of social
backgrounds Indonesias culture
impose Local Content in the school
curriculum
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
For example: regional
languagess lesson.
Social and cultural diversity
is manifested in the
diversity of customs,
manners and etiquette
association, arts, language
and literature as well as
proficiency and skills grew
and preserved in a specific
area
Figure 1. Indonesia, which
has many islands and has
diverse languages of each
region.
Image Source: Fardelyn Hacky. 2012 http://fardelynhacky.blogspot.com/2012/06/bangga-berbahasa-indonesia-dan-
bahasa.html
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
UU years 1989 2 paragraph 2 of article I emphasized that
what is meant by Indonesian national education system is
rooted in the culture of education and the Indonesian nation
based on Pancasila and the 1945 Constitution."
Laws regarding National Education of
Indonesia on the culture
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Image Source: Zein_sasak. 2009. http://bangkusekolah-id.blogspot.com/2012/09/lembaga-sosial-
dalam-pendidikan.html
Involve formal institution specially
formed for destination education.
Figure
2. Example of
how formal
education is
learning in
school with
teachers
Ways to transmit Culture
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Image Source: Fauzi EP. 2012. http://fauziep.blogdetik.com/2012/02/10/hukum-positif-pendidikan-
informal-dan-asa-sekolahrumah/foto-25-agt-05-060-2/
Non formal
nature community Continuous and in daily life
sosialization .
Figure 3.
examples of
non-formal
education that
occurs in the
environment
due to the
interaction of
friendship
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Informal is in family
Image Source: Oddyjordy 2012. http://dieudonnejordy.wordpress.com/2012/10/10/peran-keluarga-dalam-
perkembangan-kepribadian-anak/
Figure 4.
Examples of
informal way in
many homes
when familytime
Source: Tirtahardja, U., & Sulo, S. L. (2005). Pengantar Pendidikan (Edisi Revisi). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
5 Dimensions of Multicultural Education
Expected to Help Teachers in the Implementing
the philosophy of Unity in Diversity
Content integration.
Knowledge construction.
Pprejudice ruduction.
Equitable pedagogy.
Empowering school culture and social structure.
Source: Banks, J., Bangks, C., & Mac.Gee. (1997). Multicultural Education-Issues and Prespective. Boston: Ellyn and Bacon.
Teacher qualifications required in the
context of the development of a
multicultural learning
Having a teacher skill, understanding, experience and values of the
cultures with either
Always reflect his own
Enrich understanding not only about the teacher and learning
Have knowledge of the history, characteristics and internal
differences within each ethnic group and certain races.
Able to conduct comparative analyzes and able to take a
conclusion about the theories that can be used
Source: Banks, J., Bangks, C., & Mac.Gee. (1997). Multicultural Education-Issues and Prespective. Boston: Ellyn and Bacon.
Bali Threatened Languages,
Curriculum 2013 Denied
Denpasar - Students from various
universities in 2013 rejected the implementation
of curriculum that integrates local content with
art and culture. The rejection was motivated
curriculum threatening the existence of the
Balinese language.
The attitude shown by the hundreds of students
held demonstrations in front of the Parliament
Office Renon Denpasar Bali, Thursday
(17/01/2013).
While unfurled banners mass rejection of the
new curriculum continues speeches.
illustration balinese
language. (doc:
dasarbali.wordpress.com)
Thursday, January 17, 2013 15:16 pm
Rohmat - Okezone.com
"The incorporation of the area into the language of art and culture have an
impact on the extinction of the Balinese language," said coordinator of
action, I Nyoman Like Ardiyasa.
Penggabungan clearly can make Balinese increasingly endangered due to
the blurring that occurs Balinese language.
With the incorporation of the obvious implications for the reduction of
Balinese language subjects. That means threatening the existence of
Balinese culture.
To that end, the students called for all parties to maintain the Balinese
language because it is the pride of the people in this temple Thousand
Islands.
Not only that, Bahasa Bali Bali has become the identity of the person that
they refuse to Balinese replaced other languages.
In its claim, the students also assess, if the understanding of the local
culture declined, the preservation of local languages can not be maximal.
If the language of Bali slowly disappear, then the cultural symbols will also
be lost. "Language is a medium of expression Bali Hindu Balinese culture,"
he stated.
When they meet, Chairman of Commission IV DPRD Bali, Nyoman Parta
promised ready to fight for the demands students Bali
input:
Students who refuse demonstrations Curriculum 2013 which would
remove a lesson in "Local Content", one of the subjects in Bali is
Balinese Language Lessons. Because it is considered to destroy the
culture and language of Bali.
process:
The attitude shown by the hundreds of students held demonstrations
in front of the Parliament Office Renon Denpasar Bali, Thursday
(17/01/2013). While unfurled banners mass rejection of the new
curriculum continues speeches.
output:
Chairman of Commission IV DPRD Bali, Nyoman Parta promised to be
ready to fight for the demands students Bali.
Meanwhile, according to Government Regulation republic of
Indonesia. No. 32 years 2013 concerning amendments to the
Government Regulation No. 19 of 2005 on national education
standards, in Chapter XIA about curriculum, explained that the Local
content remains imprinted on the curriculum in 2013.
This is a wise decision as a form of cultural preservation in the world of
formal education.
Você também pode gostar
- Version SoftwareDocumento1 páginaVersion SoftwareSagita RochmanAinda não há avaliações
- Adjuvant PeDocumento1 páginaAdjuvant PeAlexandru IacobanAinda não há avaliações
- SkyWatcher Black Diamond ED120 Doublet Refractor TelescopeDocumento1 páginaSkyWatcher Black Diamond ED120 Doublet Refractor TelescopeInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- HGFDDocumento2 páginasHGFDInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Imitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenDocumento15 páginasImitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Adjuvant PeDocumento1 páginaAdjuvant PeAlexandru IacobanAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessDocumento3 páginasUnderstanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessRon QuerubinAinda não há avaliações
- HGFDDocumento2 páginasHGFDInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Terms of Use End User Lisence AgreementDocumento2 páginasTerms of Use End User Lisence AgreementInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Matkul GelombangDocumento2 páginasTugas Matkul GelombangInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Multi Lizer 4 PDFDocumento1 páginaMulti Lizer 4 PDFEdith LunaAinda não há avaliações
- Imitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenDocumento15 páginasImitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
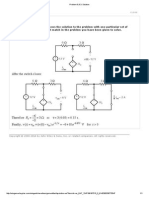
- Problem 3.2-12 PDFDocumento1 páginaProblem 3.2-12 PDFInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Imitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenDocumento15 páginasImitation of Aggressive Behavior in ChildrenInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 8.3-3Documento1 páginaProblem 8.3-3Inggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- ReferencesDocumento1 páginaReferencesInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- History of Indonesia Education and Inclusive EducationDocumento73 páginasHistory of Indonesia Education and Inclusive EducationInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Set of Education Problem and Multicultural EducationDocumento68 páginasSet of Education Problem and Multicultural EducationInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Print Assignment - 2014-L-01A - False PDFDocumento7 páginasPrint Assignment - 2014-L-01A - False PDFInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- MIT8 01SC Slides06 PDFDocumento21 páginasMIT8 01SC Slides06 PDFInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Hakikat Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocumento72 páginasHakikat Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisInggrid Ayu PutriAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- The Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageDocumento12 páginasThe Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageLuigie VazquezAinda não há avaliações
- English Week3 PDFDocumento4 páginasEnglish Week3 PDFLucky GeminaAinda não há avaliações
- National Advisory Committee For AeronauticsDocumento36 páginasNational Advisory Committee For AeronauticsSamuel ChristioAinda não há avaliações
- (Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingDocumento17 páginas(Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingKatherine Natalia Pino Arredondo100% (1)
- 13 Fashion Studies Textbook XIDocumento158 páginas13 Fashion Studies Textbook XIMeeta GawriAinda não há avaliações
- Product CycleDocumento2 páginasProduct CycleoldinaAinda não há avaliações
- SEO Design ExamplesDocumento10 páginasSEO Design ExamplesAnonymous YDwBCtsAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionDocumento2 páginasChapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionJoyce Ann May BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Suband Coding in MatlabDocumento5 páginasSuband Coding in MatlabZoro Roronoa0% (1)
- Living Nonliving DeadDocumento11 páginasLiving Nonliving DeadArun AcharyaAinda não há avaliações
- What is zone refining processDocumento1 páginaWhat is zone refining processKeshav MadanAinda não há avaliações
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogDocumento1 páginaCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaAinda não há avaliações
- AAU5243 DescriptionDocumento30 páginasAAU5243 DescriptionWisut MorthaiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 Family PlanningDocumento84 páginasLecture 1 Family PlanningAlfie Adam Ramillano100% (4)
- Unit 1 Writing. Exercise 1Documento316 páginasUnit 1 Writing. Exercise 1Hoài Thương NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Ecole Polytechnique Federale de LausanneDocumento44 páginasEcole Polytechnique Federale de LausanneSyed Yahya HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Ks3 Science 2008 Level 5 7 Paper 1Documento28 páginasKs3 Science 2008 Level 5 7 Paper 1Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBAinda não há avaliações
- 'K Is Mentally Ill' The Anatomy of A Factual AccountDocumento32 páginas'K Is Mentally Ill' The Anatomy of A Factual AccountDiego TorresAinda não há avaliações
- S2 Retake Practice Exam PDFDocumento3 páginasS2 Retake Practice Exam PDFWinnie MeiAinda não há avaliações
- Job Description Support Worker Level 1Documento4 páginasJob Description Support Worker Level 1Damilola IsahAinda não há avaliações
- Programming Language Foundations PDFDocumento338 páginasProgramming Language Foundations PDFTOURE100% (2)
- Ryerson EthicsDocumento20 páginasRyerson EthicssinghbabaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyDocumento4 páginasAssessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyVijay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Technology Syllabus-2019Documento2 páginasEnvironmental Technology Syllabus-2019Kxsns sjidAinda não há avaliações
- Basf Masterseal 725hc TdsDocumento2 páginasBasf Masterseal 725hc TdsshashiAinda não há avaliações
- Installation Instruction XALM IndoorDocumento37 páginasInstallation Instruction XALM IndoorVanek505Ainda não há avaliações
- SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSDocumento3 páginasSOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSwaleedAinda não há avaliações
- ER DiagramDocumento23 páginasER Diagramapi-2757091480% (20)
- Budget ControlDocumento7 páginasBudget ControlArnel CopinaAinda não há avaliações
- C Exam13Documento4 páginasC Exam13gauravsoni1991Ainda não há avaliações