Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
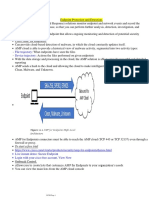
Network Security
Enviado por
Ahmad AliDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Network Security
Enviado por
Ahmad AliDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Network Security
Attacks
Technical Solutions
Acknowledgments
Material is sourced from:
CISA Review Manual 2011, 2010, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by
permission.
CISM Review Manual 2012, 2011, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by
permission.
Many other Network Security sources
http://www.csrc.nist.gov/publications/drafts/800-118/draft-sp800-118.pdf
Author: Susan J Lincke, PhD
Univ. of Wisconsin-Parkside
Reviewers/Contributors: Todd Burri, Kahili Cheng
Funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Course, Curriculum and
Laboratory Improvement (CCLI) grant 0837574: Information Security: Audit,
Case Study, and Service Learning.
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this
material are those of the author(s) and/or source(s) and do not necessarily
reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Objectives
The student should be able to:
Define attacks: script kiddy, social engineering, logic bomb, Trojan horse,
phishing, pharming, war driving, war dialing, man-in-the-middle attack, SQL
injection, virus, worm, root kit, dictionary attack, brute force attack, DOS,
DDOS, botnet, spoofing, packet reply.
Describe defenses: defense in depth, bastion host, content filter, packet filter,
stateful inspection, circuit-level firewall, application-level firewall, de-
militarized zone, multi-homed firewall, IDS, IPS, NIDS, HIDS, signature-
based IDS, statistical-based IDS, neural network, VPN, network access
server (RADIUS/TACACS), honeypot, honeynet, hash, secret key encryption,
public key encryption, digital signature, PKI, vulnerability assessment
Identify techniques (what they do): SHA1/SHA2, MD2/MD4/MD5, DES, AES,
RSA, ECC.
Describe and define security goals: confidentiality, authenticity, integrity, non-
repudiation
Define services & servers data in the correct sensitivity class and roles with
access
Define services that can enter and leave a network
Draw network Diagram with proper zones and security equipment
The Problem of Network Security
The Internet allows an
attacker to attack from
anywhere in the world
from their home desk.
They just need to find one
vulnerability: a security
analyst need to close
every vulnerability.
Hacking Networks
Phase 1: Reconnaissance
Physical Break-In
Dumpster Diving
Google, Newsgroups,
Web sites
Social Engineering
Phishing: fake email
Pharming: fake web pages
WhoIs Database &
arin.net
Domain Name Server
Interrogations
Registrant:
Microsoft Corporation
One Microsoft Way
Redmond, WA 98052
US
Domain name: MICROSOFT.COM
Administrative Contact:
Administrator, Domain domains@microsoft.com
One Microsoft Way
Redmond, WA 98052
US
+1.4258828080
Technical Contact:
Hostmaster, MSN msnhst@microsoft.com
One Microsoft Way
Redmond, WA 98052 US
+1.4258828080
Registration Service Provider:
DBMS VeriSign, dbms-support@verisign.com
800-579-2848 x4
Please contact DBMS VeriSign for domain updates,
DNS/Nameserver
changes, and general domain support questions.
Registrar of Record: TUCOWS, INC.
Record last updated on 27-Aug-2006.
Record expires on 03-May-2014.
Record created on 02-May-1991.
Domain servers in listed order:
NS3.MSFT.NET 213.199.144.151
NS1.MSFT.NET 207.68.160.190
NS4.MSFT.NET 207.46.66.126
NS2.MSFT.NET 65.54.240.126
NS5.MSFT.NET 65.55.238.126
Hacking Networks
Phase 2: Scanning
War Driving: Can I find a wireless network?
War Dialing: Can I find a modem to connect to?
Network Mapping: What IP addresses exist, and what
ports are open on them?
Vulnerability-Scanning Tools: What versions of software
are implemented on devices?
Passive Attacks
Eavesdropping: Listen to
packets from other
parties = Sniffing
Traffic Analysis: Learn
about network from
observing traffic patterns
Footprinting: Test to
determine software
installed on system =
Network Mapping
Bob
Jennie
Carl
Hacking Networks:
Phase 3: Gaining Access
Network Attacks:
Sniffing
(Eavesdropping)
IP Address Spoofing
Session Hijacking
System Attacks:
Buffer Overflow
Password Cracking
SQL Injection
Web Protocol Abuse
Denial of Service
Trap Door
Virus, Worm, Trojan
horse,
Login: Ginger Password: Snap
Some Active Attacks
Denial of Service: Message
did not make it; or service
could not run
Masquerading or Spoofing:
The actual sender is not
the claimed sender
Message Modification: The
message was modified in
transmission
Packet Replay: A past packet
is transmitted again in
order to gain access or
otherwise cause damage
Denial of Service
Joe
Ann
Bill
Spoofing
Joe (Actually Bill)
Ann
Bill
Message
Modification
Joe
Ann
Packet Replay
Joe
Ann
Bill
Bill
Man-in-the-Middle Attack
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.2
10.1.1.3
(1) Login
(3) Password
(2) Login
(4) Password
SQL Injection
Java Original: SELECT * FROM
users_table WHERE username= + +
username + + AND password = + +
password + ;
Inserted Password: Aa OR =
Java Result: SELECT * FROM
users_table WHERE username=anyname
AND password = Aa OR = ;
Inserted Password: foo;DELETE FROM
users_table WHERE username LIKE %
Java Result: SELECT * FROM
users_table WHERE username=anyname
AND password = foo; DELETE FROM
users_table WHERE username LIKE %
Inserted entry: |shell(cmd /c echo &
char(124) & format c:)|
Login:
Password:
Welcome to My System
NIST SP 800-118 Draft
Password Cracking:
Dictionary Attack & Brute Force
Pattern Calculation Result Time to Guess
(2.6x10
18
/month)
Personal Info: interests, relatives 20 Manual 5 minutes
Social Engineering 1 Manual 2 minutes
American Dictionary 80,000 < 1 second
4 chars: lower case alpha 26
4
5x10
5
8 chars: lower case alpha 26
8
2x10
11
8 chars: alpha 52
8
5x10
13
8 chars: alphanumeric 62
8
2x10
14
3.4 min.
8 chars alphanumeric +10 72
8
7x10
14
12 min.
8 chars: all keyboard 95
8
7x10
15
2 hours
12 chars: alphanumeric 62
12
3x10
21
96 years
12 chars: alphanumeric + 10 72
12
2x10
22
500 years
12 chars: all keyboard 95
12
5x10
23
16 chars: alphanumeric 62
16
5x10
28
Hacking Networks:
Phase 4: Exploit/Maintain Access
Backdoor
Trojan Horse
Spyware/Adware
Bots
User-Level Rootkit
Kernel-Level Rootkit
Replaces system
executables: e.g.
Login, ls, du
Replaces OS kernel:
e.g. process or file
control to hide
Control system:
system commands,
log keystrokes, pswd
Useful utility actually
creates a backdoor.
Slave forwards/performs
commands; spreads,
list email addrs, DOS
attacks
Spyware: Collect info:
keystroke logger,
collect credit card #s,
AdWare: insert ads,
filter search results
Botnets
Attacker
Handler
Bots: Host illegal movies,
music, pornography,
criminal web sites,
Forward Spam for
financial gain
China
Hungary
Botnets: Bots
Zombies
Distributed Denial of Service
Zombies
Victim
Attacker
Handler
Can barrage a victim
server with requests,
causing the network
to fail to respond to anyone
Russia
Bulgaria United
States
Zombies
Question
An attack where multiple computers send
connection packets to a server simultaneously
to slow the firewall is known as:
1. Spoofing
2. DDOS
3. Worm
4. Rootkit
Question
A man in the middle attack is
implementing which additional type of
attack:
1. Spoofing
2. DoS
3. Phishing
4. Pharming
Network Security
Network Defense
Encryption
Security: Defense in Depth
Border Router
Perimeter firewall
Internal firewall
Intrusion Detection System
Policies & Procedures & Audits
Authentication
Access Controls
Bastion Host
Computer fortified
against attackers
Applications turned
off
Operating system
patched
Security configuration
tightened
Attacking the Network
What ways do you see of getting in?
The Internet
De-Militarized
Zone
Private Network
Border Router/Firewall
Commercial Network
Private Network
WLAN
Filters
Route Filter: Verifies sources and destination of IP
addresses
Packet Filter: Scans headers of packets and discards if
ruleset failed (e.g., Firewall or router)
Content Filter: Scans contents of packets and discards if
ruleset failed (e.g., Intrusion Prevention System or
firewall)
The good, the bad &
the ugly
Filter
The bad &
the ugly
The Good
Packet Filter Firewall
Web Request
Ping Request
FTP request
Email Connect Request
Web Response
Telnet Request
Email Response
SSH Connect Request
DNS Request
Email Response
Web
Response
Illegal Source IP Address
Illegal Dest IP Address
Microsoft NetBIOS Name Service
Firewall
Configurations
A A
terminal
firewall
host
Router Packet Filtering:
Packet header is inspected
Single packet attacks caught
Very little overhead in firewall: very quick
High volume filter
A A
terminal
firewall
host
A
Stateful Inspection
State retained in firewall memory
Most multi-packet attacks caught
More fields in packet header inspected
Little overhead in firewall: quick
Firewall
Configurations
A B
terminal
firewall
host
Circuit-Level Firewall:
Packet session terminated and recreated
via a Proxy Server
All multi-packet attacks caught
Packet header completely inspected
High overhead in firewall: slow
A B
terminal
firewall
host
A
Application-Level Firewall
Packet session terminated and recreated
via a Proxy Server
Packet header completely inspected
Most or all of application inspected
Highest overhead: slow & low volume
A B
B
Router
External
DNS
IDS
Web
Server
E-Commerce VPN
Server
IDS
Protected
Internal
Network
Zone
IDS
Database/File
Servers
Internet
Multi-Homed Firewall:
Separate Zones
Demilitarized Zone
With Proxy
Interface
Screened
Host
The router serves as a screen for the
Firewall, preventing Denial of Service
attacks to the Firewall.
Screening
Device
Firewall
Writing Rules
Policies
Network Filter Capabilities
Write Rules
Protected Network
Audit Failures
Corrections
Services and Servers
Workbook
Service Sensitivity Roles Server
Grades Confidential For Graduates: Transcripts
For Current Students:
Advising, Students,
Faculty
StudentScholastic
Billing Confidential, For Current Students:
Registration, Accounting,
Advising
Payment: Students
StudentBilling
Web Pages Public Students, Employees,
Public
Web services
Path of Logical Access
How would access control be improved?
The Internet
De-Militarized
Zone
Private Network
Border Router/
Firewall
Router/Firewall
WLAN
Protecting the Network
The Internet
De-Militarized
Zone
Private Network
Border Router: Packet Filter
Bastion Hosts
Proxy server firewall
WLAN
Serviced Applications
Workbook
Applicatio
ns
Sources of
Entry
Servers Required Controls (e.g.,
Encryption)
Grades -
Graduates
University
Registration
Graduate
Scholastic
Confidentiality, Integrity,
Authentication
Grades
Current
Students
United States Student
Scholastic
Confidentiality, Integrity,
Authentication
Billing Payment:
International
Reports: Univ.
Student
Scholastic
Confidentiality,
Authentication, Integrity,
Non-repudiation
Web Pages International DMZ:
PublicFace
Router
External
DNS
Email
Public
Web
Server
E-Commerce
Firewall
Zone 1:
Student
Labs &
Files
Internet
Network Diagram
Workbook
Demilitarized Zone
Zone 2:
Faculty
Labs &
Files
Student
Records
Student
Billing
Transcripts
Student
Scholastic
Student
History
Zone 3:Student Data
Student
Billing
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Network IDS=NIDS
Examines packets for attacks
Can find worms, viruses, org-
defined attacks
Warns administrator of attack
IPS=Packets are routed
through IPS
Host IDS=HIDS
Examines actions or resources
for attacks
Recognize unusual or
inappropriate behavior
E.g., Detect modification or
deletion of special files
Router
Firewall
IDS
IDS Intelligence Systems
Signature-Based:
Specific patterns are recognized
as attacks
Statistical-Based:
The expected behavior of the
system is understood
If variations occur, they may be
attacks (or maybe not)
Neural Networks:
Statistical-Based with self-learning
(or artificial intelligence)
Recognizes patterns
Attacks:
NastyVirus
BlastWorm
N
a
s
t
y
V
i
r
u
s
NIDS:
ALARM!!!
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Mon. Tues. Wed. Thurs.
Sales
Personnel
Factory
N
o
r
m
a
l
Honeypot & Honeynet
Honeypot: A system with a special software application
which appears easy to break into
Honeynet: A network which appears easy to break into
Purpose: Catch attackers
All traffic going to honeypot/net is suspicious
If successfully penetrated, can launch further attacks
Must be carefully monitored
External
DNS
IDS
Web
Server
E-Commerce VPN
Server
Firewall
Honey
Pot
Data Privacy
Confidentiality: Unauthorized
parties cannot access
information (->Secret Key
Encryption
Authenticity: Ensuring that
the actual sender is the
claimed sender. (->Public Key
Encryption)
Integrity: Ensuring that the
message was not modified in
transmission. (->Hashing)
Nonrepudiation: Ensuring
that sender cannot deny
sending a message at a later
time. (->Digital Signature)
Confidentiality
Joe
Ann
Bill
Authenticity
Joe (Actually Bill)
Ann
Bill
Integrity
Joe
Ann
Non-Repudiation
Joe
Ann
Bill
Encryption Secret Key
Examples: DES, AES
Encrypt
K
secret
Decrypt
K
secret
plaintext
ciphertext
plaintext
P = D(K
secret
, E(K
secret
,P))
NIST Recommended: 3DES w. CBC
AES 128 Bit
Public Key Encryption
Examples: RSA, ECC, Quantum
Encrypt
K
public
Decrypt
K
private
Key owner Joe
Encryption
(e.g., RCS)
Decrypt
K
public
Encrypt
K
private
Message,
private key
Digital
Signature
Key
owner
Authentication,
Non-repudiation
Joe
P = D(k
PRIV
, E(k
PUB
,P))
P = D(k
PUB
, E(k
PRIV
,P))
NIST Recommended:
RSA 1024 bit
2011: RSA 2048 bit
Remote Access Security
Virtual Private Network (VPN) often implemented with
IPSec
Can authenticate and encrypt data through Internet (red line)
Easy to use and inexpensive
Difficult to troubleshoot, less reliable than dedicated lines
Susceptible to malicious software and unauthorized actions
Often router or firewall is the VPN endpoint
The Internet
Firewall
VPN
Concentrator
Secure Hash Functions
Examples: SHA1, SHA2, MD2, MD4, MD5
Message
H
H
E
Message H
Message H
D
H
H
H
Compare
Message Authentication Code
Message
H
Message Message
H
H H
H
H
Compare
One Way Hash
K
K
K
K
Ensures the message was not modified during transmission
NIST Recommended: SHA-1, SHA-2
2011: SHA-2
Encrypted
K(Senders Private)
Digital Signature
Electronic Signature
Uses public key
algorithm
Verifies integrity of
data
Verifies identity of
sender: non-
repudiation
Message
Msg Digest
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Digital
Certificate
User: Sue
Public Key:
2456
1. Sue registers with
CA through RA
Certificate Authority
(CA)
Register(Owner, Public Key)
2. Registration Authority
(RA) verifies owners
3. Send approved
Digital Certificates
5. Tom requests Sues DC
6. CA sends Sues DC
Sue
Tom
4. Sue sends
Tom message
signed with
Digital Signature
7. Tom confirms
Sues DS
Network Access Server
NAS: Network Access Server
Handles user authentication, access control and accounting
Calls back to pre-stored number based on user ID
Prone to hackers, DOS, misconfigured or insecure devices
RADIUS: Remote Access Dial-in User Service
TACACS: Terminal Access Control Access
1. Dial up and authenticate
2. Call back
RADIUS or
TACACS
3. Connect
Web Page Security
SQL Filtering: Filtering of web input for SQL
Injection
Encryption/Authentication: Ensuring
Confidentiality, Integrity, Authenticity, Non-
repudiation
Web Protocol Protection: Protection of
State
Vulnerability Assessment
Scan servers, work stations, and control
devices for vulnerabilities
Open services, patching, configuration
weaknesses
Testing controls for effectiveness
Adherence to policy & standards
Penetration testing
Serviced Applications
Workbook
Applicatio
ns
Sources of
Entry
Servers Required Controls (e.g.,
Encryption)
Grades
Current
Students
United States Student
Scholastic
Confidentiality: Encryption
Integrity: Hashing, IDS
Authentication: VPN/IPsec, secure
passwords
Billing Payment:
International
Reports: Univ.
Student
Scholastic
Confidentiality: Encryption,
HTTPs
Authentication: VPN/IPsec
Integrity, Hashing, IDS
Non-repudiation: Digital
Signature
Summary of Network Controls
Network Security Techniques
Encryption: Public and Private
key, Wireless WPA2
Virtual Private Network (VPN):
Secure communications tunnel
Secure Hashing
Digital Signature
Bastion Host Configuration
Certificate Authority: PKI
Network Protection Devices
Firewall: Packet, Stateful,
Circuit, Application-Level
Proxy server
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
Intrusion Detection System
Intrusion Prevention System
Network access server
(RADIUS or TACACS)
Honeypot, honeynet
Secure Protocols
SSL: Secure web
SSH: Secure telnet/rlogin or
file transfer
S/MIME: Secure email
Secure Information Mgmt: Log
mgmt
Question
A map of the network that shows where service
requests enter and are processed
1. Is called the Path of Physical Access
2. Is primarily used in developing security policies
3. Can be used to determine whether sufficient
Defense in Depth is implemented
4. Helps to determine where antivirus software
should be installed
Question
The filter with the most extensive filtering
capability is the
1. Packet filter
2. Application-level firewall
3. Circuit-level firewall
4. State Inspection
Question
The technique which implements non-
repudiation is:
1. Hash
2. Secret Key Encryption
3. Digital Signature
4. IDS
Question
Anti-virus software typically implements
which type of defensive software:
1. Neural Network
2. Statistical-based
3. Signature-based
4. Packet filter
Question
MD5 is an example of what type of
software:
1. Public Key Encryption
2. Secret Key Encryption
3. Message Authentication
4. PKI
Question
A personal firewall implemented as part
of the OS or antivirus software qualifies
as a:
1. Dual-homed firewall
2. Packet filter
3. Screened host
4. Bastion host
HEALTH FIRST CASE STUDY
Designing Network Security
Jamie Ramon MD
Doctor
Chris Ramon RD
Dietician
Terry
Licensed
Practicing Nurse
Pat
Software Consultant
Define Services & Servers
Which data can be grouped together by
role and sensitivity/criticality?
Service
Name
Sensitivity
Class.
Roles with
Access
Server Name
Confidential
Management
Public
Web Pages
Privileged
Contracts
Defining Services which can
Enter and Leave the Network
Service Source
(e.g., home,
world, local
computer)
Destination
(local server,
home, world,
etc.)
Defining Zones and Controls
Compartmentalization:
Zone = Region (E.g., DMZ, wireless,
internet)
Servers can be physical or virtual
Zone Service
Server Required Controls
(Conf., Integrity, Auth., Nonrepud.,
with tools: e.g., Encryption/VPN)
Router
External
DNS
Email
Public
Web
Server
E-Commerce
Firewall
Zone 1:
Student
Labs &
Files
Internet
Draw the Network Diagram
Demilitarized Zone
Zone 2:
Faculty
Labs &
Files
Student
Records
Student
Billing
Transcripts
Student
Scholastic
Student
History
Zone 3:Student Data
Student
Billing
Reference
Slide # Slide Title Source of Information
7 Passive Attacks CISA: page 331,333, 352
9 Some Active Attacks CISA: page 330, 332, 352
10 Man-in-the Middle Attack CISA: page 331
12 Password Cracking: dictionary Attack & Brute Force CISA: page 330
14 Botnets CISA: page 330
15 Distributed Denial of Service CISA: page 330
23 Packet Filter Firewall CISA: page 353, 354
24 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 353 355
25 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 354
26 Multi-Homed Firewall: Separate Zones CISA: page 355
33 Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
CISA: page 355, 356
34 IDS Intelligence Systems CISA: page 356
35 Honeypot & Honeynet CISA: page 356, 357
37 Encryption Secret Key CISA: page 357
38 Public Key Encryption CISA: page 357, 358
39 Remote Access Security CISA: page 361
40 Secure Hash Functions CISA: page 359, 361, 362
41 Digital Signature CISA: page 359
42 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) CISA: page 359, 360
Você também pode gostar
- Network Performance and Security: Testing and Analyzing Using Open Source and Low-Cost ToolsNo EverandNetwork Performance and Security: Testing and Analyzing Using Open Source and Low-Cost ToolsAinda não há avaliações
- Security Architecture and DesignDocumento38 páginasSecurity Architecture and DesigndonweenaAinda não há avaliações
- Testing of DDoS Protection SolutionsDocumento16 páginasTesting of DDoS Protection SolutionsSon Tran Hong NamAinda não há avaliações
- DDoS Attack Handbook CSP.Documento25 páginasDDoS Attack Handbook CSP.Bablish Jaiswal100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo EverandIntrusion Detection Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Cybersecurity Course Quiz With AnswersDocumento2 páginasCybersecurity Course Quiz With AnswersTarik AmezianeAinda não há avaliações
- Email Security Architecture A Clear and Concise ReferenceNo EverandEmail Security Architecture A Clear and Concise ReferenceAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Model Vs TCP-IP ModelDocumento1 páginaOSI Model Vs TCP-IP ModelSean RiceAinda não há avaliações
- Information SecurityDocumento72 páginasInformation SecurityManish MadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Network Security - KerberosDocumento15 páginasNetwork Security - KerberosebinVettuchirayilAinda não há avaliações
- D1T2 - Bypassing GSMA Recommendations On SS7 Networks - Kirill PuzankovDocumento51 páginasD1T2 - Bypassing GSMA Recommendations On SS7 Networks - Kirill Puzankovfouad boutatAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Network SecurityDocumento38 páginasPrinciples of Network SecurityMd Zahid HossainAinda não há avaliações
- 1 IoT SecurityDocumento49 páginas1 IoT Securitylakshmisudarshan100% (1)
- Security+ Chapter 8 AnswersDocumento2 páginasSecurity+ Chapter 8 AnswersFrank StevensonAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Awareness 2 0 2 1: BY Ayokunle OlaniyiDocumento31 páginasCyber Awareness 2 0 2 1: BY Ayokunle OlaniyiOludare OgunkoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Security Solution ArchitectureDocumento7 páginasSecurity Solution ArchitectureMohammed Jabir AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Information Security FinalDocumento13 páginasInformation Security FinalFadia ZulfiqarAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of Computer NetworksDocumento10 páginasBasics of Computer NetworkskunalAinda não há avaliações
- Incident Response and Digital ForensicsDocumento50 páginasIncident Response and Digital ForensicsJames EspinosaAinda não há avaliações
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocumento22 páginas18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01Ainda não há avaliações
- Security + Study GuideDocumento59 páginasSecurity + Study GuideDavid EdwardAinda não há avaliações
- Network SecurityDocumento17 páginasNetwork SecurityMimranB67% (3)
- Sample Network DesignDocumento25 páginasSample Network DesignHailay Weldegebriel MaruAinda não há avaliações
- Secure Email Gateway QuizDocumento2 páginasSecure Email Gateway Quizoviuap100% (1)
- Threats ConcernsDocumento5 páginasThreats ConcernsP PAinda não há avaliações
- Pentesting PresentationDocumento99 páginasPentesting PresentationMaqsood AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Data Security: Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption StandardDocumento12 páginasData Security: Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption Standardapi-19822376Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco Network Foundation Protection OverviewDocumento10 páginasCisco Network Foundation Protection OverviewRyanb378Ainda não há avaliações
- Cyber Risk Management FrameworkDocumento9 páginasCyber Risk Management Frameworkleo58800% (1)
- Network SecuurityDocumento25 páginasNetwork SecuurityDebopriyo SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- 1-DHCP Infrastructure Security Threats, Mitigation and AssessmentDocumento12 páginas1-DHCP Infrastructure Security Threats, Mitigation and AssessmentNirav AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Sec 01Documento11 páginasCCNA Sec 01Aissa ChaabiAinda não há avaliações
- Sy0 601 01Documento17 páginasSy0 601 01SABRINA NUR AISHA AZAHARI100% (1)
- Kerberos Authentication Protocol Simulation: Course: Cpe 597 B Advisor: Prof. Khaled ElleithyDocumento32 páginasKerberos Authentication Protocol Simulation: Course: Cpe 597 B Advisor: Prof. Khaled ElleithyPhani PatibandlaAinda não há avaliações
- Insident ResponseDocumento8 páginasInsident Responseraghuram medapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Network SecurityDocumento62 páginasChapter 4 Network SecurityNurlign Yitbarek100% (1)
- CyberSecurity Short Course - Week 3Documento46 páginasCyberSecurity Short Course - Week 3tapera_mangeziAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Security NetworkDocumento21 páginasIntroduction To Security NetworkQistina AbdulAinda não há avaliações
- Domain 6 - Security Assessment and TestingDocumento35 páginasDomain 6 - Security Assessment and TestingNgoc Do100% (1)
- Enterprise IT Security: The Ultimate GuideDocumento44 páginasEnterprise IT Security: The Ultimate GuideVlad VikernesAinda não há avaliações
- Domain 8 Software Development SecurityDocumento19 páginasDomain 8 Software Development Securitysrivatsan_eceAinda não há avaliações
- Arbor DdosDocumento13 páginasArbor DdosLuca Mattia FerrariAinda não há avaliações
- Ddos AttacksDocumento3 páginasDdos AttacksJames Ryan Pascua VillalonAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud SecurityDocumento70 páginasCloud SecurityIbtissem Ch75% (4)
- Tounsi - Threat IntelligenceDocumento22 páginasTounsi - Threat IntelligenceRafael PaimAinda não há avaliações
- Network Security MonitoringDocumento0 páginaNetwork Security MonitoringUmakanth V SherkhaneAinda não há avaliações
- Top 100+ Cyber Security Interview Questions and AnswersDocumento27 páginasTop 100+ Cyber Security Interview Questions and AnswersDwayne PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Running Head: The Incident Response PlanDocumento14 páginasRunning Head: The Incident Response Plankevin obwoyereAinda não há avaliações
- How To Make Sense of Cybersecurity Frameworks: Frank KimDocumento38 páginasHow To Make Sense of Cybersecurity Frameworks: Frank Kimivans2009100% (1)
- Network Security by M.Vineeth KumarDocumento72 páginasNetwork Security by M.Vineeth KumarPranavAinda não há avaliações
- Email SecurityDocumento11 páginasEmail Securitysush93Ainda não há avaliações
- 1.3-Basic Packet Analysis WiresharkDocumento43 páginas1.3-Basic Packet Analysis Wiresharknbadung100% (1)
- An Overview of Penetration TestingDocumento20 páginasAn Overview of Penetration TestingAIRCC - IJNSAAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Sec 02Documento36 páginasCCNA Sec 02Aissa ChaabiAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Security - Defense in DepthDocumento150 páginasCyber Security - Defense in DepthsivextienAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Network Cyber SecurityDocumento25 páginasIntroduction To Network Cyber SecuritySivaKumarReddyAtlaAinda não há avaliações
- Enterprise Cyber Security Fundamentals: Presented by Matt ConstableDocumento47 páginasEnterprise Cyber Security Fundamentals: Presented by Matt Constabletapera_mangeziAinda não há avaliações
- Wireshark Display FiltersDocumento2 páginasWireshark Display FiltersAnovar_ebooks100% (1)
- Cybersecurity Fundamentals: Threat.Documento17 páginasCybersecurity Fundamentals: Threat.Ahmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- File Trajectory Device Trajectory: To Start A Free TrialDocumento14 páginasFile Trajectory Device Trajectory: To Start A Free TrialAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Wireshark User's GuideDocumento334 páginasWireshark User's GuideAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Diff Rence RoutingDocumento3 páginasDiff Rence RoutingAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna NotesDocumento2 páginasCcna NotesAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- 200 Networking Interview QuestionsDocumento50 páginas200 Networking Interview QuestionsAngel Simo MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Carey Williamson Icore Chair and Professor Department of Computer Science University of CalgaryDocumento8 páginasCarey Williamson Icore Chair and Professor Department of Computer Science University of CalgaryAhmad Ali100% (1)
- CCNDocumento1 páginaCCNAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Syn Flood Attack With Hping3Documento1 páginaSyn Flood Attack With Hping3Ahmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Common ErrorsDocumento1 páginaCommon ErrorsAhmad AliAinda não há avaliações
- MindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapDocumento1 páginaMindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapgarbett294Ainda não há avaliações
- Aindumps 312-50 v2016-08-09 by Worm 260qDocumento101 páginasAindumps 312-50 v2016-08-09 by Worm 260qbob johnAinda não há avaliações
- CFS 105 Digital Security Chapter 1 IntroductionDocumento17 páginasCFS 105 Digital Security Chapter 1 IntroductionKatherineAinda não há avaliações
- Sync Install LogDocumento5 páginasSync Install LogAzeem bhaiAinda não há avaliações
- SV2800 SV3800 Admin-Guide. 3.7Documento146 páginasSV2800 SV3800 Admin-Guide. 3.7jnaAinda não há avaliações
- Aix EfsDocumento6 páginasAix EfsEllen WuAinda não há avaliações
- Social EngineeringDocumento36 páginasSocial EngineeringVîñàý Pãtêl100% (1)
- Key ManagementDocumento14 páginasKey Managementmanju287Ainda não há avaliações
- SAP ASE Security Administration Guide enDocumento384 páginasSAP ASE Security Administration Guide enKreethi VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter8 Connecting To Network-Defined Users and GroupsDocumento2 páginasChapter8 Connecting To Network-Defined Users and GroupsBrent Michel FarmerAinda não há avaliações
- Extracting Encryption Keys From RAMDocumento10 páginasExtracting Encryption Keys From RAMChris100% (2)
- Ethical Hacking My Seminar ReportDocumento22 páginasEthical Hacking My Seminar ReportDhyana Swain50% (2)
- OWASP Mobile AppSec VerificationDocumento37 páginasOWASP Mobile AppSec VerificationnandaanujAinda não há avaliações
- Isc2 CCSP Student Guide 3rdedition 2017 First 50 Pages 428415Documento70 páginasIsc2 CCSP Student Guide 3rdedition 2017 First 50 Pages 428415justforfun2009100% (4)
- History of CryptographyDocumento7 páginasHistory of CryptographyrestlesskidAinda não há avaliações
- Rapid7 PDFDocumento15 páginasRapid7 PDFSimon KohAinda não há avaliações
- Executive Ju32nioDocumento11 páginasExecutive Ju32nioexxgineAinda não há avaliações
- Database and Application Security, Nov 2006 1Documento50 páginasDatabase and Application Security, Nov 2006 1Chya QadrAinda não há avaliações
- Information Security Policy TemplateDocumento4 páginasInformation Security Policy TemplateAnonymous ZWDQ57TAinda não há avaliações
- Network SecurityDocumento17 páginasNetwork SecurityMimranB67% (3)
- Seminar Report On HackingDocumento20 páginasSeminar Report On HackingJamesCarter100% (2)
- Essay On Cyber SecurityDocumento3 páginasEssay On Cyber SecurityBalseng Chezang M Marak100% (1)
- Nombre de Usuario Contraseña Vence: ESET Smart Security (ESS) 4-8Documento4 páginasNombre de Usuario Contraseña Vence: ESET Smart Security (ESS) 4-8Bruno TelloAinda não há avaliações
- Write A Program To Implement Monoalphabetic Cipher AlgorithmDocumento6 páginasWrite A Program To Implement Monoalphabetic Cipher AlgorithmPalak BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Result of AntiVirusDocumento7 páginasResult of AntiVirusFalanaD'iekoloreoluwaAinda não há avaliações
- A Review Paper On Cryptographic Hash FunctionDocumento11 páginasA Review Paper On Cryptographic Hash Functionhamid khanAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Crime FullDocumento24 páginasCyber Crime FullDevendra Ponia100% (1)
- Basic KerberosDocumento8 páginasBasic KerberosvycentyAinda não há avaliações
- Bpsu-Rof-042 Edrielle L. Valdez1Documento1 páginaBpsu-Rof-042 Edrielle L. Valdez1Edrielle ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- 200 IT Security Job Interview QuestionsDocumento6 páginas200 IT Security Job Interview QuestionsRizwan KhanAinda não há avaliações