Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Indian Oil Corporation Limited Mathura PPT - PPTX Ashu 11
Enviado por
iampiyushsahu0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
383 visualizações20 páginasiocl ppt
Título original
Indian Oil Corporation Limited Mathura Ppt.pptx Ashu 11
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoiocl ppt
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
383 visualizações20 páginasIndian Oil Corporation Limited Mathura PPT - PPTX Ashu 11
Enviado por
iampiyushsahuiocl ppt
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 20
Submitted BY: Submitted TO:
VINEET KUMAR GUPTA Mr.VK DWIVEDI
B.Tech. 4th Year Mr.KUWAR MAUSAM
PROJECT STUDY REPORT
On
VARIOUS MECHANICAL DEVICES
CONTENTS
Introduction -- Mathura Refinery Unit Profile
Energy Consumption
Products of Mathura Refinery
Units of Mathura refinery
Mechanical Workshop
Machine Shop
Pumps
Pressure Relief Devices
Heat Exchanger Shop
Contd.
Thermal Power Station (T.P.S)
Demineralization Plant
Boiler
Steam Turbine
Gas Turbine Generator
Cooling Towers
UNIT PROFILE
Indian Oil Corporation Limited (Indian Oil) is the largest commercial
enterprise in India with a sales turnover of Rs.150, 677 crores and profit of
Rs.4, 891 crores for the fiscal year 2004.
Indian Oil is Indias number one company in Fortunes prestigious listing
of the worlds 500 largest corporations, ranked 170 based on fiscal 2004
performance. It is also the 18
th
largest petroleum company in the world and
adjudged number one in petroleum trading among the 15 national oil
companies in the Asia-Pacific region.
Contd.
Mathura Refinery, commissioned in 1982, current rated capacity of
8.0 MMTPA crude processing, is meeting the product demand of
Northwest region of the country including the National Capital
Delhi. The Refinery processes low sulphur crude from Bombay
High, imported low sulphur crude from Nigeria, and high sulphur
crude from Middle East Countries. In the original refinery
configuration, there was one primary Atmospheric Vacuum unit
coupled with Vis-breaker Unit, Fluidized Catalytic Cracking Unit,
Bitumen unit and Sulphur Recovery unit as secondary units.
ENERGY CONSUMPTION
Mathura Refinery consumes various types of fuels viz. Natural gas, R-LNG,
refinery fuel gas and low Sulphur internal fuel oil (IFO) in furnaces /
boilers. Natural gas, which is about 50% of total fuel consumed at MR is
supplied by M/s GAIL whereas all others fuels are generated in the refinery
itself. The IFO is fired as alternate fuel in old furnaces only.
PRODUCTS
Liquefied Petroleum Gas for domestic use
Naphtha for fertilizer as feed
Aviation Turbine Fuel For Civil and Defense aviation purposes
Superior Kerosene Oil For domestic purposes
High Speed Diesel Oil - For Transportation
Furnace Oil and Heavy Petroleum Stock
Petroleum
Light Diesel Oil For agro equipments
Bitumen For road paving
Propylene For high polymers
Sulphur For chemical industries
UNITS
OLD UNIT-
Old unit is further divided into various subunits:
AVU(Atmospheric Vacuum Unit):
The ADU (Atmospheric Distillation Unit) separates most of the lighter end
products such as gas, gasoline, naphtha, kerosene, and gas oil from the
crude oil. The bottoms of the ADU are then sent to the VDU (Vacuum
Distillation Unit).
Crude oil is preheated by the bottoms feed exchanger, further preheated and
partially vaporized in the feed furnace and passed into the atmospheric towe
This tower contains 20 fractionation trays, is equipped with one top pump
around, an overhead reflux system, and three side strippers (for naphtha,
kerosene, and gas oil products).
CONTD.
The VDU (Vacuum Distillation Unit) takes the residual from the ADU
(Atmospheric Distillation Unit) and separates the heavier end products such
as vacuum gas oil, vacuum distillate, slop wax, and residue.
VBU(Viscosity Breaker Unit):
A visbreaker is a processing unit in oil refinery whose purpose is to
reduce the quantity of residual oil produced in the distillation of crude
oil and to increase the yield of more valuable middle distillates by the
refinery. A visbreaker thermally cracks large hydrocarbon molecules in
the oil by heating in a furnace to reduce its viscosity and to produce
small quantities of light hydrocarbons (LPG and gasoline). The process
name of "visbreaker" refers to the fact that the process reduces the
viscosity of the residual oil.
CCRU(Controlled Catalytic Regeneration Unit):
Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery
naphthas, typically having low octane ratings, into high-octane liquid
products called reformates which are components of high-octane gasoline
(also known as petrol).
FCC(Fluidized Catalytic Cracking):
It is the most important conversion process used in petroleum
refineries. It is widely used to convert the high-boiling, high-molecular
weight hydrocarbon fractions of petroleum crude oils to more valuable
gasoline, olefin gases and other products.
NEW UNITS
The New Unit includes:
OHCU(Once Through Hydrocracker Unit):
DHDT
DHDS
HGU(Hydrogen Generation Unit)
NHGU(New Hydrogen Generation Unit)
PRIME-G (This unit is recently installed in Mathura refinery plant to
provide Euro4 products. It removes Sulphur from 300 ppm to 50 ppm
MECHANICAL WORKSHOP
In mechanical workshop we saw the following sections
Machine Shop
Pump and Valve Section
Gaskets and Grease
Machine Shop
In machine section we saw the various types of machines on which
operations like threading, turning, facing, boring, drilling, etc. were being
performed by using these machines. In machine shop all the lathes were
centre lathes. Various machines in workshop were
Machines Name Quantity
Lathe 8
Boring Machine 1
Shaper 1
Milling 1
Drill 3
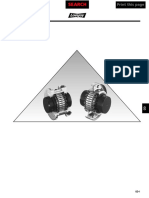
Pumps
The function of pump is to convert mechanical energy in to hydraulic
energy. So they are used to transfer fluid from one place to another. In
Mathura Refinery mainly two types of pumps are used
Centrifugal Pump
Reciprocating Pump
Centrifugal Pumps are of two types
Vertical
Horizontal
Centrifugal Pumps - Centrifugal Pumps are used where higher head and low
discharge is required. Centrifugal pump works on the principle of centrifugal
force acting on the liquid. Head (pressure) is controlled is controlled by RPM,
impeller diameter and flow rate.
Multistage Pumps - If a larger head is required more no. of impellers
are to be fitted in series so that the discharge from first impeller is
guided to the inlet of second impeller. This is repeated with third
impeller and so on until the required head is reached. Each impeller will
increase the pressure by the same amount; a pump of this type is called a
multistage pump.
A typical boiler feed may have six to eight stages
All the impellers are keyed to the same shaft and usually all the impellers
and diffusers of the one pump are identical.
This has the advantage of reducing the labour in manufacturing and
stocking spares of maintenance.
Main parts of circumferential pump are
Impeller
Suction Pipe
Delivery pipe
Casing
Mechanical Seal
Oil Seal
Shaft
Bearing
Bearing house
Impeller It is rotating part of centrifugal pump. It consists of series of
backward curved vanes. I is mounted on shaft which is connected to the shaft
of an electric motor.
Mechanical Seal Mechanical seal is used to prevent the leakage of product.
IT has two parts.
a ) Rotary part Which rotates with the shaft.
b) Stationary part Which does not rotate with the shaft.
Oil Seal Oil seal is used to prevent the leakage of lube oil.
Bearing Two types of bearings are used
Axial Bearing Which take the load along the axis of the shaft.
Radial Bearing Which take the load acting perpendicular to the
load of the shaft.
Suction Pipe Its one end connected to outlet of pump and
other end delivers the water at required height.
Generally following types of faults are found out after the certain
working hours of pump
Bearing Damage
Damage of mechanical seal
Damage of oil seal
THERMAL POWER PLANT
Mathura Refinery has its own captive thermal power station supplied and
erected by M/s BHEL (Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited) to meet the
electricity requirements of Mathura Refinery as well as the township.
There are three Boilers, three Steam Turbine Generators (S.T.G.) as well
as three Gas Turbine Generators (G.T.G.) and three Heat Recovery
Steam Generators (H.R.S.G.) set as T.P.S. Normally one Steam Turbine
Generator and three Gas Turbine Generator are in service with one
boiler out of three to provide steam to them. Rest of the remaining unit
stays on standby. Each boiler is capable of generating steam at a rate of
150 TPH (Tonnes Per Hour) at a pressure of 64 kg/cm and temperature
of 450. Each STG is capable of generating a electric power of 12.5 MW
with regulated steam of 0 to 105 TPH to meet
the process requirement in the refinery. Each GTG is capable of
generating an electric power of 20 MW. Nowadays not only the
boilers but the HRGS also used to generate the steam with the help
of Gas turbine exhaust as heat source and supplementary firing (If
needed).
Objectives of the Thermal Power Station
Uninterrupted power, steam, feed water & DM water to units.
Optimization of resources & efficiency improvement.
Ensure reliability and quality of services.
Safe practice of operations.
Environmental safety.
COOLING TOWER
The steam in the LP Side of the Turbine is collected in the condenser
and has to be condensed and is re-used as a feed in the boiler. The
cooling media used for exchange of heat is water and to economize on
the use of water, water is re-circulated through a cooling tower.
There are many types of cooling towers, the more common being the
one with the induced draft cross- flow method. The scheme of
operation is that hot water from the condenser is sprayed across the
latticed work in a rectangular cell and an induced draft fan is mounted
at top of each Call. The draft fan induces a draft current from the cell
towards the atmosphere and in the process carried away the water
vapors. The cooled water collects in the sump and is again pumped into
the condenser to cool the steam in the condenser.
These types of cooling towers are more efficient, economic in operation
and occupy minimum space.
THANKYOU
Você também pode gostar
- For Indian Oil HaldiaDocumento42 páginasFor Indian Oil Haldiamohit0% (1)
- A Seminar On Bharat Pumps & Compressors LTD: Presented by Amit Singh Roll - No. 1110440006Documento17 páginasA Seminar On Bharat Pumps & Compressors LTD: Presented by Amit Singh Roll - No. 1110440006madhurauto100% (3)
- Industrial Training Report at i.O.C.L.Documento24 páginasIndustrial Training Report at i.O.C.L.mihir301171% (7)
- Project Study Report: "Centrifugal Pump, Gas Turbine & Mechanical Seal"Documento28 páginasProject Study Report: "Centrifugal Pump, Gas Turbine & Mechanical Seal"Shivam AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Untitled DocumentDocumento87 páginasUntitled DocumentLakshya GothwalAinda não há avaliações
- Mirch Masala-GurbaniDocumento5 páginasMirch Masala-GurbanigbAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Summer Vocational Training: Indian Oil Corporation LimitedDocumento22 páginasReport On Summer Vocational Training: Indian Oil Corporation LimitedAditya SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Changing Scenario of Petroleum Business and Need for Improved Customer ServiceDocumento35 páginasChanging Scenario of Petroleum Business and Need for Improved Customer ServiceRAJ NIDHIAinda não há avaliações
- Abhishek ProjectDocumento50 páginasAbhishek ProjectDeep GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Iocl Training ReportDocumento10 páginasIocl Training ReportAbhishek GautamAinda não há avaliações
- IOCL Summer Training Presentation on Barauni RefineryDocumento16 páginasIOCL Summer Training Presentation on Barauni Refineryamish umar0% (1)
- Final - Financial Performance - IOCLDocumento79 páginasFinal - Financial Performance - IOCLPramod ShawAinda não há avaliações
- Project On Indain Oil Corporation LimitedDocumento93 páginasProject On Indain Oil Corporation LimitedKavisha singhAinda não há avaliações
- Niharika Final......... Report........ IoclDocumento62 páginasNiharika Final......... Report........ IoclNiharika Satyadev JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Oil ReportDocumento51 páginasIndian Oil ReportAshish Rajak100% (1)
- Summer TrainingDocumento15 páginasSummer Trainingpulkit agarwalAinda não há avaliações
- IOCL, Mathura Refinery Training ReportDocumento26 páginasIOCL, Mathura Refinery Training ReportNamishaAgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Trainning Report Iocl MathuraDocumento19 páginasTrainning Report Iocl MathuraDheeraj ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of The Cash Management & Banking System With A Financial Analysis of Indian Oil Corporation LTDDocumento78 páginasEvaluation of The Cash Management & Banking System With A Financial Analysis of Indian Oil Corporation LTDgain.moumitaAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling The Prediction of Product Life CycleDocumento12 páginasModeling The Prediction of Product Life CycleViwanou AloumonAinda não há avaliações
- Kanhaiya IoclDocumento82 páginasKanhaiya IoclRahul Anand100% (1)
- Non Fuel Retailing - Report - Arvind DwivediDocumento87 páginasNon Fuel Retailing - Report - Arvind Dwivediarvind_dwivedi100% (4)
- Oil Accounting and Excise Duties at IOCL Mathura RefineryDocumento127 páginasOil Accounting and Excise Duties at IOCL Mathura RefineryMohit Agarwal0% (1)
- BYCO Report Highlights Oil CompanyDocumento17 páginasBYCO Report Highlights Oil CompanyAliRashidAinda não há avaliações
- Triveni EggDocumento321 páginasTriveni EggSahith MallampatiAinda não há avaliações
- Sachin IoclDocumento22 páginasSachin IoclSweekrati GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Iocl 1Documento80 páginasIocl 1Rishi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- NFL Summer Internship ReportDocumento54 páginasNFL Summer Internship ReportIsha Chhabra100% (1)
- Reliance petroleum internship reportDocumento32 páginasReliance petroleum internship reportNeeraj BajoliyaAinda não há avaliações
- MISs Mis in IoclDocumento68 páginasMISs Mis in IoclMahima MohanAinda não há avaliações
- A Project Report On On Indian Oil Out Lets and Bazzar Traders On Servo Lubricants at IOCLDocumento56 páginasA Project Report On On Indian Oil Out Lets and Bazzar Traders On Servo Lubricants at IOCLNitinAgnihotriAinda não há avaliações
- Summer Internship/Vocational Training Report: - Mr. Bardan LamaDocumento40 páginasSummer Internship/Vocational Training Report: - Mr. Bardan Lamachemical todiAinda não há avaliações
- Iocl Project AnjuDocumento93 páginasIocl Project AnjuKain Anjali100% (4)
- Report SubmissionDocumento65 páginasReport Submissionvidit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Case Analysis On IOCLDocumento12 páginasCase Analysis On IOCLRaoul Savio GomesAinda não há avaliações
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber Production PlantDocumento6 páginasStyrene Butadiene Rubber Production PlantHarold AldayAinda não há avaliações
- Bhel Haridwar Summer Training Report Electronic & CommunicationDocumento22 páginasBhel Haridwar Summer Training Report Electronic & Communicationritika_arora19067% (3)
- Survey On Various Lubricant Companies in India: Synopsis ofDocumento14 páginasSurvey On Various Lubricant Companies in India: Synopsis ofRupesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Oil Gas 210708Documento28 páginasOil Gas 210708gauravvirendraAinda não há avaliações
- Report On NFLDocumento38 páginasReport On NFLanand DoliaAinda não há avaliações
- Fertilizer Mangalore India New Mangalore Port NH-17 Urea DAPDocumento39 páginasFertilizer Mangalore India New Mangalore Port NH-17 Urea DAPJagadeesha MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Ongc - IntroDocumento34 páginasOngc - IntroAnshul AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- ONGC's Welfare Policies & Industrial RelationsDocumento127 páginasONGC's Welfare Policies & Industrial Relationsvpceb22enAinda não há avaliações
- a.BULL (ITR) REPORTDocumento11 páginasa.BULL (ITR) REPORTaathira rameshAinda não há avaliações
- Table of Contents For Industry Focus-Lubricants & Engine OilsDocumento4 páginasTable of Contents For Industry Focus-Lubricants & Engine OilsJinalSAinda não há avaliações
- Project On Indian OilDocumento102 páginasProject On Indian Oiljignas cyberAinda não há avaliações
- Reliance Industrial Report)Documento48 páginasReliance Industrial Report)Piyush AbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited, Haldia Refinery Vocational TrainingDocumento33 páginasIndian Oil Corporation Limited, Haldia Refinery Vocational TrainingSandeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Morarjee ReportDocumento26 páginasMorarjee ReportAjay YadavAinda não há avaliações
- A Project Report On The Work Done During Summer Training: DCM Shriram Consolidated Limited (DSCL)Documento44 páginasA Project Report On The Work Done During Summer Training: DCM Shriram Consolidated Limited (DSCL)asifstarAinda não há avaliações
- Reliance PetroleumDocumento15 páginasReliance Petroleummadhav75% (4)
- Customer Perception For Purchasing Petrol DieselDocumento74 páginasCustomer Perception For Purchasing Petrol DieselManjeet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited Mathura PPT PPTX Ashu 11Documento20 páginasIndian Oil Corporation Limited Mathura PPT PPTX Ashu 11Pradeep UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- A Power Point Presentation of BHELDocumento24 páginasA Power Point Presentation of BHELSiddharth SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Power Systems in HPCLDocumento16 páginasPower Systems in HPCLSarat ChandraAinda não há avaliações
- Tank Vessel HandbookDocumento57 páginasTank Vessel HandbookRahulAinda não há avaliações
- CFMTTI DudhniDocumento35 páginasCFMTTI DudhniVISHAL SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Bhel ReportDocumento44 páginasBhel ReportRoyalAryansAinda não há avaliações
- Report on Vocation Training at Barauni RefineryDocumento23 páginasReport on Vocation Training at Barauni RefineryImtiaz AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 CADDocumento45 páginasUnit 4 CADiampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- Multi Valve SynopsisDocumento11 páginasMulti Valve SynopsisiampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- AUDIDocumento18 páginasAUDIiampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- Cad Module 1Documento126 páginasCad Module 1iampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- AUDIDocumento18 páginasAUDIiampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- Rrbchennai Employment News Cen 02 2014Documento19 páginasRrbchennai Employment News Cen 02 2014mithun46Ainda não há avaliações
- Multi Valve EngineDocumento14 páginasMulti Valve EngineiampiyushsahuAinda não há avaliações
- The Introduction of Sterilization PouchesDocumento3 páginasThe Introduction of Sterilization PouchesjarzloniezAinda não há avaliações
- Covalent Bonding in ElementsDocumento31 páginasCovalent Bonding in ElementsOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Chapter 11-Refrigeration CyclesDocumento24 páginasChapter 11-Refrigeration CyclesAbas S. AcmadAinda não há avaliações
- Estacion Manual Direccionable 52013 PDFDocumento2 páginasEstacion Manual Direccionable 52013 PDFLuis Ivan Moreno ParraAinda não há avaliações
- ZAK Expo 2023 InviteDocumento6 páginasZAK Expo 2023 Inviteprajapatimanish806100% (1)
- 1kz-Te Cooling System PDFDocumento14 páginas1kz-Te Cooling System PDFwill meridith100% (2)
- Cement Properties and Testing MethodsDocumento22 páginasCement Properties and Testing Methodsankit kasanaAinda não há avaliações
- BOP-231 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IIIDocumento14 páginasBOP-231 Pharmaceutical Chemistry-IIINiraj GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- STD 146Documento18 páginasSTD 146nirajbnb8417Ainda não há avaliações
- User Manual RCU Universal Rev01Documento48 páginasUser Manual RCU Universal Rev01Anonymous FGY7goAinda não há avaliações
- An Accelerator Free Peroxide Vulcanization TechniqueDocumento17 páginasAn Accelerator Free Peroxide Vulcanization TechniqueClinton ThomsonAinda não há avaliações
- Samsung Refrigeretor - RS265TD Fast Track R2Documento6 páginasSamsung Refrigeretor - RS265TD Fast Track R2Dan DrambareanuAinda não há avaliações
- Bioreactor and SterilizationDocumento22 páginasBioreactor and SterilizationMuhd Shukri100% (2)
- Flexible grid coupling selection guideDocumento18 páginasFlexible grid coupling selection guidechavico113Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecoflam BurnersDocumento40 páginasEcoflam Burnerseuroused100% (1)
- Different Approaches in Modeling of RC Shear Wall: A ReviewDocumento15 páginasDifferent Approaches in Modeling of RC Shear Wall: A Reviewrahimmulla100% (2)
- Transporte IntermodalDocumento8 páginasTransporte IntermodalDavid LatorreAinda não há avaliações
- The Rheology Degradation Processing and Characterization of ReDocumento261 páginasThe Rheology Degradation Processing and Characterization of ReDeidra CadeAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Procedure For ASTM D 698Documento2 páginasSummary of Procedure For ASTM D 698Miller De Leon Cutora100% (1)
- Lec-2 Structural Steel PropertiesDocumento10 páginasLec-2 Structural Steel PropertiesRifat HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Bullet Valve Series GuideDocumento2 páginasBullet Valve Series GuideAnthony PecorinoAinda não há avaliações
- On The Nanofluids Application in The Automotive RaDocumento21 páginasOn The Nanofluids Application in The Automotive RaJayant YadavAinda não há avaliações
- JKR Mech DRWG PDFDocumento117 páginasJKR Mech DRWG PDFFelix Semion100% (1)
- 2 - SEPARATION TECHNIQUES-Introduction PDFDocumento11 páginas2 - SEPARATION TECHNIQUES-Introduction PDFSitti Alwiyah maulani desiAinda não há avaliações
- General Question Related To Coiled Tubing UnitDocumento4 páginasGeneral Question Related To Coiled Tubing UnitBOy GeologErAinda não há avaliações
- EdDocumento1 páginaEdpandirajaAinda não há avaliações
- Sealbond Etl-100: Epoxy Tank Lining (100% Solids) Solvent Free System Food GradeDocumento2 páginasSealbond Etl-100: Epoxy Tank Lining (100% Solids) Solvent Free System Food GradegregAinda não há avaliações
- Aama 501.2-83Documento3 páginasAama 501.2-83Abdul Raqeeb67% (3)
- Vitrified CBN Crankshaft Grinding WheelDocumento18 páginasVitrified CBN Crankshaft Grinding WheelJulkar Nain ShakibAinda não há avaliações
- Intl Warranty PDF t65 HeatersDocumento1 páginaIntl Warranty PDF t65 HeatersMVPlanzaroteAinda não há avaliações