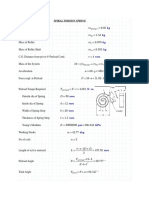
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Presentation Fatigue
Enviado por
Ravi Kiran Meesala0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
81 visualizações22 páginaspistons fatigue
Título original
Presentation fatigue
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentopistons fatigue
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
81 visualizações22 páginasPresentation Fatigue
Enviado por
Ravi Kiran Meesalapistons fatigue
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 22
SEMINAR PRESENTATION ON
Fatigue on engine pistons
A compendium of case
studies
by
M.V.RAVI KIRAN
Abstract
Engine pistons are one of the most complex components among all
automotive or other industry field components. The engine can be
called the heart of a car and the piston may be considered the most
important part of an engine.
There are lots of research works proposing, for engine pistons but
there are huge number of damaged pistons.
Damage mechanisms have different origins and are mainly wear,
temperature, and fatigue related. Among the fatigue damages,
thermal fatigue and mechanical fatigue, either at room or at high
temperature , play a prominent role.
This work is concerned only with the analysis of fatigue-damaged
pistons.
Pistons from petrol and diesel engines,from automobiles, motorcycles
and trains will be analyzed.
A compendium of case studies of fatigue-damaged pistons is
presented.
A fractographic study is carried out in order to confirm crack initiation
sites.
Introduction
Piston may be considered the heart of an engine. piston is one of the most
stressed components of an entire vehicle.
As one of the major moving parts in the power transmitting assembly ,
the piston must be so designed that it can withstand the extreme heat and
pressure of combustion.
Piston also aids in sealing the cylinder to prevent the escape of combustion
gases.
As it is the main components in an engine, pistons technological evolution
is expected to continue and they are expected to be more and more
stronger , lighter, thinner and durable.
The pistons form the bottom half of the combustion chamber and
transmits the force of combustion through the wrist pin and connecting
rod to the crankshaft.
There are many significant number of damaged pistons.
Damages may have different origins: mechanical stresses , thermal
stresses , wear mechanisms , temperature degradation etc.
Fatigue is a source of piston damages.
Cyclic stresses have mainly two origins : load and temperature.
Traditional mechanical fatigue may be the main damaging mechanism
in different parts of a piston depending on different factors.
High temperature fatigue is also present in some damaged pistons.
In this work, different pistons, from different kinds of engines: train
engines; motorcycle engines; and automotive engines will be
presented.
FATIGUE DAMAGED PISTONS
Mechanical and high
temperature
mechanical damaged
pistons.
Thermal and thermal
mechanical damaged
pistons.
EXPERIMENTAL WORK
Mechanical and high temperature
mechanical fatigue
Damaged areas
Piston head and
piston pin holes
Piston
compression
Ring grooves
Piston skirt
Piston head and piston pin hole
Typical engine piston
Typical stress distribution on an engine piston
Fractographic analysis
Petrol engine piston with a crack from one side of the pin hole
to the head
Diesel engine piston (with cooling gallery) with a crack from
one side of the pin hole to the head
Diesel engine piston with a crack from one side of the pin hole
to the other pin hole going through the head of the piston
Linear static stress distribution of piston
Piston compression grooves
The striations clearly show the propagation of the crack
Typical stress distribution on stress radius on the grooves
piston skirt
Engine piston with damaged skirt
Typical stress distribution on engine skirt with a big clearance
Thermal/thermal mechanical fatigue
Thermal fatigue is related to the stresses in the material induced by
thermal gradients in the component.
In a piston thermal stresses are due to
(a) The vertical distribution of the temperature along the piston high
temperatures at the top and lower temperatures at the bottom.
(b) the different temperatures at the head of the piston due to the flow
of the hot gases or to fuel impingement.
(a) Thermal stresses due to the vertical distribution
(b) Thermal stresses due to the different temperatures at
the head
of the piston
Examinations and discussion
Mechanical fatigue:
Piston head and piston pin hole
Static stresses concentrate mainly at pin holes. But piston starts their
cracks at head.
Reason for the crack to initiate at that point may be due to two different
aspects:
Mechanical fatigue:
Crack always initiate at the same points at the same vertical plane that
contains pin holes.
Thermal fatigue does not seem to be the reason for these cracks because
thermal fatigue produces more than one visible cracks.
High temperature mechanical fatigue:
Piston head is always hotter than the bottom and pin hole area.
If we combine effect of temperature with static stresses, there are
two critical areas.
This is the biggest of all fatigue damaged pistons.
Piston compression grooves:
Compression ring is the one has the function of not allowing the
pressure to be lost between piston and cylinder wall.
When clearance between piston and cylinder wall becomes high,
there is an increase of pressure acting on the ring and a stress
increase on compression groove.
Piston skirt:
Piston skirt may break by fatigue and reason are the stresses act on
the curvature radius of some skirt geometries.
Damage may be related to clearance between piston and cylinder
wall.
Thermal/thermal-mechanical fatigue:
Thermal fatigue cracks are easy to identify because they usually show
a particular feature.
If they were high temperature mechanical fatigue cracks it would be
only one crack and the crack would be located at the vertical plane
that contains the pin hole.
Proposals and in course solutions
This analysis will be divided into five aspects:
Materials
Local reinforcements
Surface coatings
Design
Piston cooling
conclusions
The first main conclusion that could be drawn from this work is that
although fatigue is not the responsible for biggest slice of damaged
pistons, it remains a problem on engine pistons and its solution
remains a goal for piston manufacturers and it will last a problem for
long because efforts on fuel consumption reduction and power
increase will push to the limit weight reduction, that means thinner
walls and higher stresses.
To satisfy all the requirements with regard to successful application of
pistons, in particular mechanical and high temperature mechanical
fatigue and thermal/thermalmechanical fatigue there are several
concepts available that can be used to improve its use, such as
design, materials, processing technologies, etc.
Você também pode gostar
- Structural Health MonitoringNo EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of Mechatronics: V. ThulasikanthDocumento46 páginasElements of Mechatronics: V. ThulasikanthNeela MuraliAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsNo EverandVibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- SKF GreaseDocumento3 páginasSKF GreaseKumar SwamiAinda não há avaliações
- Productivity and Reliability-Based Maintenance Management, Second EditionNo EverandProductivity and Reliability-Based Maintenance Management, Second EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Mechatronics Application and System DesignDocumento10 páginasMechatronics Application and System Designswap1983Ainda não há avaliações
- Soot Blower Lance Tube CorrosionDocumento11 páginasSoot Blower Lance Tube CorrosionKECS_kck100% (1)
- System DescriptionDocumento28 páginasSystem DescriptionGloria HamiltonAinda não há avaliações
- Let's Talk About How They Compress AirDocumento6 páginasLet's Talk About How They Compress AirrahulAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling TowerDocumento11 páginasCooling TowertusherAinda não há avaliações
- PE 4030chapter 1 Mechatronics 9 23 2013 Rev 1.0Documento76 páginasPE 4030chapter 1 Mechatronics 9 23 2013 Rev 1.0Charlton S.InaoAinda não há avaliações
- Fracture - Material TechnologyDocumento18 páginasFracture - Material TechnologyayushdbcAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Mechanisms and Machines (Amitabha Ghosh and Asok Kumar Mallik)Documento640 páginasTheory of Mechanisms and Machines (Amitabha Ghosh and Asok Kumar Mallik)Manoj SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Oil System ReportingDocumento39 páginasOil System ReportingArgelCorderoUy100% (1)
- MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS RAO 4th EDITION Solution ManualDocumento4 páginasMECHANICAL VIBRATIONS RAO 4th EDITION Solution ManualOwombi0% (3)
- Moment of InertiaDocumento33 páginasMoment of InertiaHasanur Rahman MishuAinda não há avaliações
- TB015-The Eight Step Preventive Maintenance ProgramDocumento5 páginasTB015-The Eight Step Preventive Maintenance Programapi-3732848100% (5)
- Turbine Engine Lubrication SystemDocumento55 páginasTurbine Engine Lubrication SystemAkmal FitriAinda não há avaliações
- Voith Hydro BulbDocumento12 páginasVoith Hydro Bulbkamil_canadaAinda não há avaliações
- History of MechatronicsDocumento20 páginasHistory of MechatronicsManoj DhageAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Hydraulic Control Oil TroubleshootingDocumento6 páginasLesson Hydraulic Control Oil Troubleshootingmister pogiAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Control SystemDocumento33 páginasBoiler Control SystemYusufroni SitompulAinda não há avaliações
- Gland Seal SystemDocumento12 páginasGland Seal SystemFahad KhalilAinda não há avaliações
- Turbine Supervisory InstrumentationDocumento3 páginasTurbine Supervisory InstrumentationMAS98Ainda não há avaliações
- Asme, Ansi, Astm, Aga, Api, Awwa, BS, Iso, DinDocumento3 páginasAsme, Ansi, Astm, Aga, Api, Awwa, BS, Iso, DinmustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Grease Quantity, FrequencyDocumento5 páginasCalculating Grease Quantity, Frequencymans2014Ainda não há avaliações
- Ondition Onitoring: P - H N.SDocumento39 páginasOndition Onitoring: P - H N.Sकृष्णकुमार दत्तात्रेय जोशीAinda não há avaliações
- Hot Isotactic Processing (Hip) : Mehmet Can HATİBOĞLUDocumento18 páginasHot Isotactic Processing (Hip) : Mehmet Can HATİBOĞLUthesecretgardenscatAinda não há avaliações
- Analisa Getaran BerlebihDocumento5 páginasAnalisa Getaran BerlebihMatsaid ReksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Journal BearingDocumento7 páginasJournal BearingFarhan TalibAinda não há avaliações
- Research and Innovations For Continuous Miner's Cutting Head, For Efficient Cutting Process of Rock/CoalDocumento12 páginasResearch and Innovations For Continuous Miner's Cutting Head, For Efficient Cutting Process of Rock/CoalKarthii Aju100% (1)
- Systematic Approach To Solving Vibration ProblemsDocumento24 páginasSystematic Approach To Solving Vibration Problemsantok09Ainda não há avaliações
- 250+ TOP MCQs On Types of Valves and AnswersDocumento6 páginas250+ TOP MCQs On Types of Valves and Answersahmadreza777Ainda não há avaliações
- LubeCoach Volume and Frequency Recommendations PDFDocumento13 páginasLubeCoach Volume and Frequency Recommendations PDFEstebanRiveraAinda não há avaliações
- T30Documento4 páginasT30V P Singh0% (1)
- Advanced Troubleshooting of Rotating EquipmentDocumento3 páginasAdvanced Troubleshooting of Rotating EquipmentJose Luis RattiaAinda não há avaliações
- Animated Soot BlowerDocumento2 páginasAnimated Soot BlowerSoumya Ranjan Sethy0% (2)
- Guy - Time and Spectrum Analysis Paper - Part IDocumento25 páginasGuy - Time and Spectrum Analysis Paper - Part Ikeepmoshing100% (1)
- Turbine AccessoriesDocumento22 páginasTurbine Accessoriessrikanth9555Ainda não há avaliações
- Reduction of High Maintenance Costs by Noah Olela Abong'oDocumento20 páginasReduction of High Maintenance Costs by Noah Olela Abong'oNABONGO2Ainda não há avaliações
- Belt and Chain VcetDocumento56 páginasBelt and Chain VcetgowthamkuttiAinda não há avaliações
- Meas Ins1Documento148 páginasMeas Ins1HilalAldemir0% (1)
- Mechanical Interview Questions and AnswersDocumento7 páginasMechanical Interview Questions and AnswersAkesh KakarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Screw Compressor Packages Grasso Ssp1 Smart Screwpack Operating InstructionsDocumento72 páginasScrew Compressor Packages Grasso Ssp1 Smart Screwpack Operating InstructionsMarcu TeodorAinda não há avaliações
- Bearing Life TimeDocumento83 páginasBearing Life TimeFadoooll100% (1)
- Vibrations in A Francis Turbine A Case StudyDocumento4 páginasVibrations in A Francis Turbine A Case Studybukit_guestAinda não há avaliações
- Gridco PresentationDocumento97 páginasGridco PresentationJanmejaya Mishra100% (1)
- Material HandlingDocumento52 páginasMaterial HandlingMuan TullohAinda não há avaliações
- Steering System and TyresDocumento32 páginasSteering System and TyresFraolAinda não há avaliações
- Turbine Trouble Shooting: S.N Trouble Possible CauseDocumento6 páginasTurbine Trouble Shooting: S.N Trouble Possible Causekumarmm1234Ainda não há avaliações
- LAC - Air Oil Cooler With AC Motor For Industrial Use - HY10-6001 UKDocumento12 páginasLAC - Air Oil Cooler With AC Motor For Industrial Use - HY10-6001 UKMorgan PalmaAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Turbo MachineryDocumento2 páginasAdvanced Turbo Machineryjvinod2025Ainda não há avaliações
- Bearing BasicsDocumento69 páginasBearing BasicsHashem Mohamed HashemAinda não há avaliações
- Tech Data 1500 GPM - For Power Island System Rev.01Documento101 páginasTech Data 1500 GPM - For Power Island System Rev.01spazzbgt100% (1)
- DPG Coal FeederDocumento11 páginasDPG Coal FeederPanimanPalengaiAinda não há avaliações
- Condition Based Maintenance of Pumps PDFDocumento22 páginasCondition Based Maintenance of Pumps PDFumair saleemAinda não há avaliações
- TPMDocumento32 páginasTPMmanolo6490Ainda não há avaliações
- PumpsDocumento45 páginasPumpsMehmood Ul Hassan100% (1)
- Tutorial Diagnostics Randall PDFDocumento84 páginasTutorial Diagnostics Randall PDFkfathi55Ainda não há avaliações
- Study On Fatigue Failure Analysis On Ic Engine PistonDocumento35 páginasStudy On Fatigue Failure Analysis On Ic Engine PistonRavi Parkhe100% (1)
- Index PDFDocumento167 páginasIndex PDFRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Corrigendum To Advertisement No.01/2021Documento14 páginasCorrigendum To Advertisement No.01/2021Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Tires Altair Auc02 Altair PDFDocumento10 páginasTires Altair Auc02 Altair PDFRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Statically Indeterminate Structures: P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. ZavatskyDocumento28 páginasStatically Indeterminate Structures: P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. ZavatskySarah SullivanAinda não há avaliações
- WIL-Result-30 06 2020Documento4 páginasWIL-Result-30 06 2020Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 202001211704026212defence Corridor MapDocumento1 página202001211704026212defence Corridor MapRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 41Documento5 páginas41Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- A Proud Moment - Double SpreadDocumento3 páginasA Proud Moment - Double SpreadRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Placement Office, Nizam College, Ou Notice R&D Openings With HyderabadDocumento1 páginaPlacement Office, Nizam College, Ou Notice R&D Openings With HyderabadRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- WILSON ARUYVEDIC BEACH RESORT (Kovalam, Kerala) - Hotel Reviews, Photos, Rate Comparison - TripAdvisor PDFDocumento1 páginaWILSON ARUYVEDIC BEACH RESORT (Kovalam, Kerala) - Hotel Reviews, Photos, Rate Comparison - TripAdvisor PDFRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Screenshot 2019-11-26 at 12.21.06 PMDocumento2 páginasScreenshot 2019-11-26 at 12.21.06 PMRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- A Numerical Study On Effects of Friction-Induced Thermal Load For Rail Under Varied Wheel Slip ConditionsDocumento12 páginasA Numerical Study On Effects of Friction-Induced Thermal Load For Rail Under Varied Wheel Slip ConditionsRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- ABSLI Guaranteed Milestone Plan BrochureDocumento8 páginasABSLI Guaranteed Milestone Plan BrochureRavi Kiran Meesala100% (1)
- Lnmmoniva EngDocumento1 páginaLnmmoniva EngRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Limit State DesignDocumento4 páginas1 Limit State DesignKartik MathurAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Limit State DesignDocumento4 páginas1 Limit State DesignKartik MathurAinda não há avaliações
- EwldDocumento4 páginasEwldRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Fea Capabilities 1 IsDocumento1 página18 Fea Capabilities 1 IsRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Spiral Torsion Spring: M M M M R M M M M M A F MaDocumento3 páginasSpiral Torsion Spring: M M M M R M M M M M A F MaRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 6Documento7 páginas6Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 2300rpm Max Output TorqueDocumento8 páginas2300rpm Max Output TorqueRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- A Numerical Study On Effects of Friction-Induced Thermal Load For Rail Under Varied Wheel Slip ConditionsDocumento12 páginasA Numerical Study On Effects of Friction-Induced Thermal Load For Rail Under Varied Wheel Slip ConditionsRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- 2300rpm Max Output TorqueDocumento8 páginas2300rpm Max Output TorqueRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Fabrication of Pneumatic Arm For Pick and Place of Cylindrical ObjectsDocumento6 páginasDesign and Fabrication of Pneumatic Arm For Pick and Place of Cylindrical ObjectsAjitAinda não há avaliações
- KotDocumento2 páginasKotRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- I S En13157-2004+a1-2009Documento8 páginasI S En13157-2004+a1-2009Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Worm DriveDocumento6 páginasWorm DriveRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme and Syllabus For Recruitment To The Post of Port Officers in Port ServiceDocumento1 páginaScheme and Syllabus For Recruitment To The Post of Port Officers in Port ServiceRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Offshore Knuckle Boom Crane - Part OneDocumento18 páginasAnalysis of Offshore Knuckle Boom Crane - Part OneRavi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Test Review: Section Title: One Mark Questions Total Questions: 10 Max Marks: 1 Ve Marks:0.33Documento24 páginasTest Review: Section Title: One Mark Questions Total Questions: 10 Max Marks: 1 Ve Marks:0.33Ravi Kiran MeesalaAinda não há avaliações
- Serafin Spark 2010 Taxi PDFDocumento2 páginasSerafin Spark 2010 Taxi PDFoliver lealAinda não há avaliações
- FG8111 PDFDocumento1 páginaFG8111 PDFPier GreppiAinda não há avaliações
- Toyota TSB For Error Code P0012Documento6 páginasToyota TSB For Error Code P0012Rick McGuireAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ReportDocumento41 páginasLab Reportharoon100% (1)
- D-260 Engine - SpecificationsDocumento13 páginasD-260 Engine - SpecificationsGurpreet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Sebp7236 01 00 All PDFDocumento920 páginasSebp7236 01 00 All PDFmahmudiAinda não há avaliações
- Saito Gas Engines-ManualDocumento36 páginasSaito Gas Engines-ManualPERSONAL arlojiAinda não há avaliações
- Dv15Tis: Mechanical System Fuel SystemDocumento2 páginasDv15Tis: Mechanical System Fuel SystemBùi Xuân ĐứcAinda não há avaliações
- Tulsa Triplex Tt-600Documento2 páginasTulsa Triplex Tt-600miguelgarciamartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Kawasaki Parts LISTING V15 6Documento40 páginasKawasaki Parts LISTING V15 6Kudanthai Senthilkumar100% (1)
- Jet Propulsion: Pramod Kumar Yadav Aeronautical Engineering 16/206Documento18 páginasJet Propulsion: Pramod Kumar Yadav Aeronautical Engineering 16/206pramod kumar yadavAinda não há avaliações
- Regarding The Spark Plug Replacement TimingDocumento1 páginaRegarding The Spark Plug Replacement Timingmotley crewzAinda não há avaliações
- Cylinder Pressure Closed Loop ControlDocumento11 páginasCylinder Pressure Closed Loop ControlkhalihneAinda não há avaliações
- PT6-6 and - 20 Maint ManualsDocumento782 páginasPT6-6 and - 20 Maint ManualsMathew Brown89% (19)
- Partes Motor CD2RDocumento3 páginasPartes Motor CD2Rdany riversAinda não há avaliações
- DAB. Prays Zapchasti 01.11.2021Documento616 páginasDAB. Prays Zapchasti 01.11.2021Belgacem ArramiAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual Musso Engine (OM 600)Documento187 páginasService Manual Musso Engine (OM 600)Dennis Cezar Mendes100% (1)
- Yesa-3102 (3.0) EngDocumento52 páginasYesa-3102 (3.0) EngChristopher Jesus Reàtegui OlivaresAinda não há avaliações
- Fe120 Fe170 Fe250 Fe290 Fe350 Fe400 Kawasaki Service Repair ManualDocumento101 páginasFe120 Fe170 Fe250 Fe290 Fe350 Fe400 Kawasaki Service Repair ManualOmar Andres Rodriguez100% (2)
- ISX Fault Codes List - Cummins ECMDocumento3 páginasISX Fault Codes List - Cummins ECMBassie100% (1)
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-4 STEAM TURBINE: October 2014Documento42 páginasPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-4 STEAM TURBINE: October 2014Akhilesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Combustion Brayton Cycle ReviewerDocumento3 páginasCombustion Brayton Cycle ReviewerOwel CabugawanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iv - Jet Propulsion PDFDocumento4 páginasUnit Iv - Jet Propulsion PDFKeerthi Varman33% (3)
- Product Sheet - TDI T30Documento2 páginasProduct Sheet - TDI T30klashincoviskyAinda não há avaliações
- 1979 Garelli Engine ManualDocumento57 páginas1979 Garelli Engine ManualRicardo Cesar Bueno BertichevicAinda não há avaliações
- SPN Fault Codes Man TgsDocumento7 páginasSPN Fault Codes Man Tgssamuel0% (3)
- Engine MechanicalDocumento117 páginasEngine MechanicalВіталій ЛенівAinda não há avaliações
- Cubex Machine RogerDocumento18 páginasCubex Machine Rogerseoanemercado0% (1)
- P300 2Documento4 páginasP300 2Kevin LoayzaAinda não há avaliações
- Diesel Fuel System Service3Documento71 páginasDiesel Fuel System Service3kemal sultiAinda não há avaliações