Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Post-Op Oliguria
Enviado por
Nigel SparksTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Post-Op Oliguria
Enviado por
Nigel SparksDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
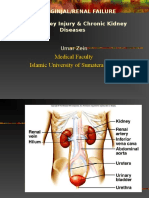
Post Operative Oliguria
Post-Operative Oliguria
Post-Operative Oliguria
Definitions
Oliguria - <0.5 cc/kg per hr in adult
About 30-70 cc/hr
Children less than 10kg: <1 cc/kg per hr
Anuria - <100cc/24hrs
Acute renal dysfunction oliguria and
increase in Creatinine (>1 mg/dl from
baseline)
Post-Operative Oliguria
Case Presentation
65y M w PVD, POD#0 s/p RLE bypass
Called by the ICU for UOP 20mL over 2hrs
Post-Operative Oliguria
General Approach
Go see patient, talk with nursing staff, get flowsheet
ABC (evaluate mental status)
Resuscitate - does pt have adequate IV access, does the pt
need Foley, NGT, continuous monitoring?
H&P
Physical examination
Order appropriate labs/tests
Diagnose and treat
Communicate plan with team and patient
Post-Operative Oliguria
Case: Assessment & Resuscitation
AAOx3, afebrile, P 105, BP 100/60, O2 sat 96% RA
Tachycardic, oliguric = hypovolemia
Ensure adequate IV access
Fluid bolus
While pt is receiving bolus, continue the evaluation
What are potential causes? What exam findings/tests
will help you make a diagnosis?
Post-Operative Oliguria
DDx
Pre-renal (2/2 renal perfusion)
Dehydration, bleeding
Shock 2/2 sepsis, cardiogenic
Abdominal compartment syndrome
Renal artery stenosis
Post-renal (obstructive)
Obstructed Foley catheter
Extrinsic compression on ureter, bladder, urethra (BPH, CA, hematoma)
Stone
Intrinsic renal
ATN (contrast, prolonged pre-renal, toxins, rhabdomyolysis)
AIN (drugs i.e. antibiotics)
Less common in surgical population:
Vascular (Wegeners, HUS, TTP, embolism)
Glomerular
Nephritic (red cells, red cell casts)
Nephrotic (proteinuria, edema, HTN)
Post-Operative Oliguria
H&P
Focused history: time since surgery, surgical
complications, anesthesia history (any periods of
hypotension during surgery?), recent medications,
recent h/o contrast, check fluid balance (include
operative period and even pre-operative period)
Physical: signs of bleeding, signs of dehydration,
look at urine
Tip: Flush the Foley (catheter obstruction)
Post-Operative Oliguria
Labs
Initial labs:
CBC - ?bleeding?
BMP, urine Na & Cr, U/A
Note: if pt has been on diuretics, send for urea
instead of Cr
Additional studies: Urine Eos, CPK, Urine myoglobin,
Renal U/S
As suspected: septic workup, MI workup
Interpretation of FeNa:
Pre-renal:
UNa<20, FeNa<1%, BUN/Cr >20
ATN:
UNa>40, FeNa>1%
Post-Operative Oliguria
FeNa Calculation
FENa = UNa * PCr / PNa * UCr x 100
Online calculators
Post-Operative Oliguria
Studies
Renal Ultrasound evaluate renal blood
flow
Central catheter to evaluate CVP,
Swan-Ganz catheter
Bladder pressures (for Abd
Compartment Syndrome)
Via foley, >20 abd HTN, >40 requires
intervention
Bladder US or IV pyelogram
Post-Operative Oliguria
Post-Op Oliguria: Treatment
Pre-renal: resuscitation, improve CO
Post-renal: fix the obstruction
New foley, suprapubic tube, nephrostomy tube
Sepsis: resuscitate & broad-spectrum abx
Contrast-induced nephropathy: IVF, Nacetylcysteine, +/- bicarbonate
Nephrotoxin or AIN: stop the agent
Post-Operative Oliguria
Indications for Hemodialysis
Acidosis (pH < 7.10)
Electrolytes (for example, hyperkalemia)
Ingestion (toxins)
Overload (fluid overload)
Uremia
Post-Operative Oliguria
Take Home Points
What to do when youre called with low UOP
Go see the patient
Always start with your ABCs
Resuscitate
Oliguria ddx: pre-renal, post-renal, intrinsic
Look for bleeding
FeNa can help
Você também pode gostar
- Daftar Isi Bridwell SpineDocumento38 páginasDaftar Isi Bridwell Spineronny0% (1)
- Surgical Intern Survival GuideDocumento85 páginasSurgical Intern Survival Guidesgod34100% (1)
- Arellano University: Andres Bonifacio Campus College of Arts and Sciences Psychology DepartmentDocumento97 páginasArellano University: Andres Bonifacio Campus College of Arts and Sciences Psychology DepartmentJohn Michael MortidoAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Nursing - HandoutDocumento16 páginasRenal Nursing - HandoutJoms Kim Mina100% (3)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingAinda não há avaliações
- CRRT in The ICU - Getting It RightDocumento45 páginasCRRT in The ICU - Getting It RightSweetcharmed Go100% (2)
- Food Worksheet Go Grow and Glow Foods Worksheet Grade 1 WAKDocumento2 páginasFood Worksheet Go Grow and Glow Foods Worksheet Grade 1 WAKdawn100% (4)
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocumento1 páginaSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Genitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDocumento35 páginasGenitourinary System: Billy Ray A. Marcelo, RNDarell M. BookAinda não há avaliações
- Manpower Planning FinalDocumento108 páginasManpower Planning FinalDevi PrasannaAinda não há avaliações
- CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Nurse CareDocumento32 páginasCORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Nurse CareCharisma Bailey Doody100% (1)
- PolyuriaDocumento49 páginasPolyuriasky rainAinda não há avaliações
- Meal Plan MenDocumento35 páginasMeal Plan Menoddo_mneAinda não há avaliações
- Genito Urinary TractDocumento199 páginasGenito Urinary TractKim GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Op Assessment: Dr. Ayesha Ehsan House Surgeon S-IIDocumento25 páginasPre-Op Assessment: Dr. Ayesha Ehsan House Surgeon S-IIFatima MAinda não há avaliações
- Paediatric Thesis Topics Risk Factors & OutcomesDocumento4 páginasPaediatric Thesis Topics Risk Factors & OutcomesSaumilAinda não há avaliações
- A Step-By-step Guide Before Doing Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy1Documento34 páginasA Step-By-step Guide Before Doing Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy1vincent malonzoAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodialysis Adequacy AssessmentDocumento81 páginasHemodialysis Adequacy AssessmentEvi PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Care For Hemodialysis Patients: Pre, During, Post Dialysis CareDocumento18 páginasCare For Hemodialysis Patients: Pre, During, Post Dialysis CareHemanth PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Initial Assessment and Management of the Multiply Injured PatientDocumento48 páginasInitial Assessment and Management of the Multiply Injured PatientDeep Katyan DeepAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed NFPA 1851 Decision TreeDocumento2 páginasProposed NFPA 1851 Decision Treeepraetorian100% (1)
- Expanding Designed Exercise Awareness and Produced by Gregory Petrovich GrabovoiDocumento5 páginasExpanding Designed Exercise Awareness and Produced by Gregory Petrovich GrabovoiManojkumar NairAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Failure: A Guide to Acute and Chronic ConditionsDocumento52 páginasRenal Failure: A Guide to Acute and Chronic Conditionsmgopigio5Ainda não há avaliações
- Course in The WardDocumento8 páginasCourse in The WardMalshika JayatissaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Common Medical Surgical EmergenciesDocumento99 páginasFinal Common Medical Surgical Emergenciesapi-195799092Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal Failure SymptomsDocumento10 páginasAcute Renal Failure SymptomsEdwin Delos Reyes AbuAinda não há avaliações
- LDLT V 3.0Documento49 páginasLDLT V 3.0anna67890Ainda não há avaliações
- Defining-Critically Ill-Icu SummaryDocumento33 páginasDefining-Critically Ill-Icu SummaryNetAinda não há avaliações
- Scans: Dr. Padmesh. VDocumento40 páginasScans: Dr. Padmesh. Vakheel ahammedAinda não há avaliações
- Surgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Documento49 páginasSurgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Muhammad ArsalAinda não há avaliações
- Surgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Documento49 páginasSurgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Muhammad ArsalAinda não há avaliações
- PREOPERATIF EVALUASI & PERSIAPAN ANESTESI (Autosaved)Documento42 páginasPREOPERATIF EVALUASI & PERSIAPAN ANESTESI (Autosaved)Siq Febri SmnjtkAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid & Electrolytes in SurgeryDocumento64 páginasFluid & Electrolytes in SurgeryakunmereclarkAinda não há avaliações
- Advice Admission - Diet: Npo Until Further Order - Monitor Vs Q1H and Record. Refer For BP 90Mmhg. Monitor Input and Output Q ShiftDocumento4 páginasAdvice Admission - Diet: Npo Until Further Order - Monitor Vs Q1H and Record. Refer For BP 90Mmhg. Monitor Input and Output Q ShiftAlcntara AllenAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 6 NotesDocumento17 páginasExam 6 NotesWhitney WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Surgery and Post OpDocumento96 páginasSurgery and Post OpNguyễn Nhật HoàngAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal Failure: The Kidney Is Your Friend (Under 40 CharactersDocumento31 páginasAcute Renal Failure: The Kidney Is Your Friend (Under 40 CharactersAlina BoiangiuAinda não há avaliações
- Preop Conference AnesthesiaDocumento33 páginasPreop Conference AnesthesiaBhi-An BatobalonosAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Operative AssessmentDocumento33 páginasPre Operative AssessmentShimmering MoonAinda não há avaliações
- 02 CystotomyDocumento28 páginas02 CystotomyM Amriyan NurrakhmanAinda não há avaliações
- Genito-Urinary Tract Disorders By: Mtespiriturnmd: NephronDocumento10 páginasGenito-Urinary Tract Disorders By: Mtespiriturnmd: NephronCristybaby MunozAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Scintigraphy Procedures and IndicationsDocumento18 páginasRenal Scintigraphy Procedures and IndicationsViorelVelenciucAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal Failure Chronic Renal FailureDocumento48 páginasAcute Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failurekimchi girlAinda não há avaliações
- Approach To A Patient With Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento70 páginasApproach To A Patient With Acute Kidney InjuryShivamAinda não há avaliações
- MED2 2022 (Autosaved)Documento33 páginasMED2 2022 (Autosaved)Adakun SamuelAinda não há avaliações
- Bloody ReportDocumento60 páginasBloody Reporttrinamajam_md809Ainda não há avaliações
- Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence: Daniel Rapoport UBC Urology Nov 14, 2007Documento44 páginasPost-Prostatectomy Incontinence: Daniel Rapoport UBC Urology Nov 14, 2007Sucipto HartonoAinda não há avaliações
- Management Guidelines PancreatitisDocumento18 páginasManagement Guidelines Pancreatitisfahadrock2002Ainda não há avaliações
- Manage Chronic Kidney Injury in ChildrenDocumento29 páginasManage Chronic Kidney Injury in ChildrenPriya GKAinda não há avaliações
- Urodynamics: Daniel Simanjuntak Samuel Aji Enrico SautDocumento54 páginasUrodynamics: Daniel Simanjuntak Samuel Aji Enrico SautDipo Mas SuyudiAinda não há avaliações
- Upper GI BleedDocumento50 páginasUpper GI BleedNiladri BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Yetti, CAP Hipoxia, Duty HannaDocumento18 páginasYetti, CAP Hipoxia, Duty HannaHanna GustinAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal Hypertension No PhotosDocumento33 páginasAbdominal Hypertension No Photosimma_drAinda não há avaliações
- Anesthesia for Liver TransplantationDocumento54 páginasAnesthesia for Liver TransplantationPeeyoosh RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Electrolytes 2Documento22 páginasFluid Electrolytes 2QueenClerk VillarteAinda não há avaliações
- 3- Bacterial Sepsis - Case 1Documento36 páginas3- Bacterial Sepsis - Case 1koteshwara raoAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Aging On The HeartDocumento56 páginasEffects of Aging On The HeartJustin Ahorro-DionisioAinda não há avaliações
- Pre and Post Op Management of Surgical PatientsDocumento36 páginasPre and Post Op Management of Surgical PatientsPrabhakar KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Preoperative and Postoperative Care of Surgical Patient ModifiedDocumento68 páginasPreoperative and Postoperative Care of Surgical Patient ModifiedJohn Wesley OmbogoAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Acute Abdominal PainDocumento77 páginasManaging Acute Abdominal PainFeatric AnjuAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment of Digestive and GI FunctionDocumento23 páginasAssessment of Digestive and GI FunctionSandeepAinda não há avaliações
- APH Case PresentationDocumento14 páginasAPH Case Presentationdrjaikrish100% (1)
- Abdominal Hypertension No PhotosDocumento33 páginasAbdominal Hypertension No PhotospratiwiAinda não há avaliações
- Funda 2Documento59 páginasFunda 2nucahersheyskatAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Tests&procedures.Documento5 páginasDiagnostic Tests&procedures.Nursidar Pascual MukattilAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Failure: DR Uzma BanoDocumento29 páginasRenal Failure: DR Uzma BanoUzma BanoAinda não há avaliações
- Gagal GinjalDocumento75 páginasGagal GinjalAndi HeriantoAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 Renal DisorderDocumento74 páginasWeek 3 Renal DisorderManal jAinda não há avaliações
- Packed Red Cells: Administration of Blood ProductsDocumento36 páginasPacked Red Cells: Administration of Blood ProductsRj SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Adolescent Romantic Relationships (Article) Author Sarah SorensenDocumento4 páginasAdolescent Romantic Relationships (Article) Author Sarah SorensenDavidAinda não há avaliações
- Bentonite MSDSDocumento3 páginasBentonite MSDSMohammed Ahmed NasherAinda não há avaliações
- Tsca Toxic Substanteces Control ActDocumento1 páginaTsca Toxic Substanteces Control ActAlbert Casanova FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Philips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensDocumento3 páginasPhilips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensChris SilerAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Sample Psychology Cover LettersDocumento2 páginas2013 Sample Psychology Cover LettersLavander Meggie100% (1)
- HFGHHJV DocumentDocumento7 páginasHFGHHJV DocumentYosi PramelisaAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Pre-Proof: American Journal of Kidney DiseasesDocumento27 páginasJournal Pre-Proof: American Journal of Kidney DiseasesGabriel Felipe CGAinda não há avaliações
- Total XVDocumento8 páginasTotal XVMohammed HaiderAinda não há avaliações
- NEBOSH IGC1 Past Exam Paper March 2012Documento3 páginasNEBOSH IGC1 Past Exam Paper March 2012Seleni100% (1)
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDocumento140 páginasPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingAinda não há avaliações
- Aorn Laser SafetyDocumento16 páginasAorn Laser SafetyAmanda RapaAinda não há avaliações
- 2010 - 3 Idsp Detail Information BKDocumento73 páginas2010 - 3 Idsp Detail Information BKPankaj ModhAinda não há avaliações
- HypotrophyDocumento3 páginasHypotrophyopeyemi daramolaAinda não há avaliações
- Code of Ethics For PharmacistsDocumento6 páginasCode of Ethics For PharmacistsYalc LapidAinda não há avaliações
- Parenteral FeedingDocumento7 páginasParenteral Feeding4gen_7Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment - EugenicsDocumento11 páginasAssignment - EugenicsNavneet GillAinda não há avaliações
- Levels of Professionalism Among Physical Therapists in India A National Cross Sectional Survey 2161 0673.1000123Documento6 páginasLevels of Professionalism Among Physical Therapists in India A National Cross Sectional Survey 2161 0673.1000123riddhiAinda não há avaliações
- Talkshow #5Documento11 páginasTalkshow #540Thiên TrangB2Ainda não há avaliações
- Psychotherapy Definition, Goals and Stages of PsychotherapyDocumento5 páginasPsychotherapy Definition, Goals and Stages of PsychotherapycynthiasenAinda não há avaliações
- Lower Back PainDocumento4 páginasLower Back PainAizaz ul HaqAinda não há avaliações
- ICU nurse with 8 years experience seeks new opportunitiesDocumento2 páginasICU nurse with 8 years experience seeks new opportunitiesClara R HarrisAinda não há avaliações