Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CHAP17
Enviado por
MISS_ARORADireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CHAP17
Enviado por
MISS_ARORADireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 17
Managing Multinational Cash
Flows
Order
Order
Placed
Placed
Order
Order
Received
Received
Sale
Sale
Payment
PaymentSent
Sent Cash
Cash
Received
Received
Accounts
Collection
Accounts
Collection
<<Inventory
Inventory>> << Receivable
Receivable >> << Float
Float >>
Accounts
Accounts
<< Payable
Payable >>
Disbursement
Disbursement
<< Float
>>
Float
Invoice
InvoiceReceived
Received
Payment
PaymentSent
Sent
Copyright
Time
Time==>
==>
Cash
CashDisbursed
Disbursed
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Learning Objectives
Have an appreciation of the development of the
current exchange rate system.
Understand the basic driving forces causing
exchange rates to fluctuate.
Gain a basic understanding of the various means
by which firms create internal structures to
manage exchange rate fluctuations.
Have an appreciation for the differences between
the U.S. and foreign banking systems.
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Exchange Rates
Fixed versus floating
Spot rates
Forward rates
Futures rates
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Foreign Exchange Quotes
Spot and forward rate quotes
US $ equiv
British (Pound)
1.8486
30-Day Forward
1.8443
90-Day Forward
1.8355
180-Day Forward
1.8219
Japan (Yen)
30-Day Forward
90-Day Forward
180-Day Forward
.009401
.009411
.009428
.009455
Switzerland (Franc)
30-Day Forward
60-Day Forward
180-Day Forward
.8195
.8202
.8213
.8230
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates
Relative level of interest rates in one country
compared to another
Relative rate of inflation in one country compared
to another
Governments central bank reaction to changes in
exchange rates caused by economic circumstances
Economic and political factors
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Foreign Exchange Exposure
Economic exposure
the possibility that the long-term net present value of a firms
expected cash flows will change due to unexpected changes in
exchange rates
Transaction exposure
the gains or losses associated with the settlement of business
transactions denominated in different currencies
Translation exposure
results when the balance sheet and income statement of a
foreign subsidiary are translated into the parent companys
domestic currency for consolidated financial reporting
purposes
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Corporate Structure for Global
Liquidity Management
Centralize or not? The evidence is that financial
executives are
building global liquidity pyramids that consolidate net cash
positions at the national level, then the broad regional level, and
finally at the enterprise level,
leveraging capacity of their ERP systems and treasury work
stations to get timely cash balance reports system wide, and
reducing number of banks in their system.
Survey results of U.S.-based firms have centralized
their treasury structures with 30% fully
centralized and 62% centrally coordinating
treasury functions from HQ.
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Managing Foreign Exchange
Exposure
Avoidance
Leading and Lagging
Netting
Re-invoicing
Hedging
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
A Typical Multilateral Netting
System
Subsidiary
A
Net amount owe
Subsidiary
A
Netting
Agent
Net amount
Subsidiary
B
Subsidiary
C
Subsidiary
B
Payment Flows Without Netting
Subsidiary
C
Net Payment Flows W
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Features of Non-US Banking
Systems
Check clearing
Interest on demand deposits
Pooling
Governmental policies and restrictions
Cash management services
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Summary
The chapter began with a brief history of exchange rate
system.
Different forms of currency quotations were described
including: spot, forward, and futures.
Three types of foreign exchange exposure were
introduced including: economic, transaction, and
translation exposure.
The chapter discussed a variety of techniques for
managing foreign currency exposure.
Complicating factors of managing international cash
flows including: different regulations, value dating, and
fluctuating currency values.
Copyright
2005 by Thomson Learning, Inc.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
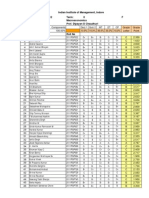
- CISCO ERP CaseDocumento8 páginasCISCO ERP CaseMISS_ARORA0% (3)
- FIN 370 Final Exam 30 Questions With AnswersDocumento11 páginasFIN 370 Final Exam 30 Questions With Answersassignmentsehelp0% (1)
- Audit of Cash PDFDocumento3 páginasAudit of Cash PDFVincent SampianoAinda não há avaliações
- PGP1 SecA Grp03 CiscoDocumento6 páginasPGP1 SecA Grp03 CiscoMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- TLP V 2014 PDFDocumento5 páginasTLP V 2014 PDFMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- ME Sec F PDFDocumento2 páginasME Sec F PDFMISS_ARORA0% (1)
- Post Graduate Programme in Management 2014-15 Term: V Title of The Course: Option, Futures and Other DerivativesDocumento6 páginasPost Graduate Programme in Management 2014-15 Term: V Title of The Course: Option, Futures and Other DerivativesMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- SopDocumento2 páginasSopMISS_ARORA100% (1)
- Data BricsDocumento18 páginasData BricsMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Executive Summary MSDocumento1 páginaExecutive Summary MSMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 3Documento1 páginaAssignment 3MISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Elite 4 ReferencesDocumento4 páginasElite 4 ReferencesMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Test Grade Average 90 Ram 40 KM/HR 11:00 AM B 78 Shyam 100 KM/HR 1:00 PM C 89 2 D 91 80 E 102 1.3333333 0 Average 90Documento2 páginasTest Grade Average 90 Ram 40 KM/HR 11:00 AM B 78 Shyam 100 KM/HR 1:00 PM C 89 2 D 91 80 E 102 1.3333333 0 Average 90MISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Data ServerDocumento1 páginaData ServerMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Name Original Value Final ValueDocumento4 páginasCell Name Original Value Final ValueMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Qlikview, Data Analyst JDDocumento2 páginasQlikview, Data Analyst JDMISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- qt2 Class 1-3Documento6 páginasqt2 Class 1-3MISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- The Fashion Channel - 10Documento5 páginasThe Fashion Channel - 10MISS_ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Total Gadha List of Confusing WordsDocumento0 páginaTotal Gadha List of Confusing WordsDhiwakar SbAinda não há avaliações
- Small Funds: Don't Count Them OutDocumento3 páginasSmall Funds: Don't Count Them OutMoiz SaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Core - 6 - Cash & Liquidity ManagementDocumento55 páginasCore - 6 - Cash & Liquidity ManagementShailjaAinda não há avaliações
- AAPub Auc 063015 NCRDocumento22 páginasAAPub Auc 063015 NCRCedric Recato DyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17 Capital StructureDocumento27 páginasChapter 17 Capital StructureJaveria asimAinda não há avaliações
- (Revised) Officer of Bank Financial Institution AffidavitDocumento1 página(Revised) Officer of Bank Financial Institution Affidavitin1or100% (8)
- AEC 103 - Intermediate Accounting: Assignment 3 Accounts Receivable and Estimation of Doubtful AccountDocumento4 páginasAEC 103 - Intermediate Accounting: Assignment 3 Accounts Receivable and Estimation of Doubtful Accountjames bryan angklaAinda não há avaliações
- HDFC ProjectDocumento31 páginasHDFC ProjectSakshi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- TISS BronchureDocumento1 páginaTISS BronchureMwaiya TwahaAinda não há avaliações
- Ap103 ReceivablesDocumento5 páginasAp103 Receivablesbright SpotifyAinda não há avaliações
- Class 03Documento3 páginasClass 03Aasim Bin BakrAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Analisis Kelayakan Investasi Pertambangan NikelDocumento7 páginasJurnal Analisis Kelayakan Investasi Pertambangan NikelSitiHasnaFathimahAinda não há avaliações
- Bitcoin - Review of LiteratureDocumento27 páginasBitcoin - Review of LiteratureNeha ChhabdaAinda não há avaliações
- A2 Level Essential Vocabulary: The Global Economy (Economics)Documento10 páginasA2 Level Essential Vocabulary: The Global Economy (Economics)A Grade EssaysAinda não há avaliações
- MFE Lesson 1 SlidesDocumento38 páginasMFE Lesson 1 SlidesRudy Martin Bada AlayoAinda não há avaliações
- Diners Privilege One PagerDocumento2 páginasDiners Privilege One PagernboAinda não há avaliações
- Tender Document GSM1Documento78 páginasTender Document GSM1Varsha Vaishali KotharyAinda não há avaliações
- Barron 39 S - Aug 16 2021Documento72 páginasBarron 39 S - Aug 16 2021Hud DentAinda não há avaliações
- Delivery Advice - 20181017 - 182441 PDFDocumento2 páginasDelivery Advice - 20181017 - 182441 PDFAR-Jay ARAinda não há avaliações
- Money TransmittersDocumento18 páginasMoney TransmittersCoin FireAinda não há avaliações
- Accounts Question and AnswerDocumento47 páginasAccounts Question and AnswerVinod Kumar PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Information Technology (It) On Banking Sector: Madhushree L. M., Revathi Radhakrishnan, & P. S. AithalDocumento8 páginasImpact of Information Technology (It) On Banking Sector: Madhushree L. M., Revathi Radhakrishnan, & P. S. Aithaltushar vatsAinda não há avaliações
- DisinvestmentDocumento15 páginasDisinvestmentjeevithajeevuAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation: Samir K MahajanDocumento9 páginasInflation: Samir K MahajanKeval VoraAinda não há avaliações
- True or FalseDocumento27 páginasTrue or FalseMary DenizeAinda não há avaliações
- Entrepreneurship - Quarter 2 Week 9Documento8 páginasEntrepreneurship - Quarter 2 Week 9SHEEN ALUBAAinda não há avaliações
- Ulep - Uneven Cash PaymentsDocumento4 páginasUlep - Uneven Cash PaymentsNoel BajadaAinda não há avaliações
- Relic Spotter Inc. CaseDocumento9 páginasRelic Spotter Inc. CaseC DonisAinda não há avaliações
- Credit Enhancement Research-99Documento106 páginasCredit Enhancement Research-99carmo-netoAinda não há avaliações