Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1 Introduction
Enviado por
Kenneth ChawDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1 Introduction
Enviado por
Kenneth ChawDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Inside of Digital Image
1
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Example of Digital Image
2
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Example of Digital Image
B
R
G
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Features of Digital Image
Processing
Big data
- One 640 x 480 gray-scale picture contains
640 x 480 x 8bit = 307 Kbyte information.
And, if the camera catches the image 20 frame per second,
we need 6 Mbyte for 1 second consecutive pictures
- Since there is 307,200 pixels in an image,
we need 307 second if the processing speed for 1pixel is 1ms.
+
4
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Application for DIP
Image Processing for OA
Medical application
Satellite Image Processing
Factory Automation
Broadcasting, Movie, Game
Image Indexing
Compression and Communication
+
5
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Application for DIP
6
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Application for DIP
7
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Application for DIP
8
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Important Definitions
of
+
Linear Algebra: Review
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Definition
10
An mn (read "m by n") matrix, denoted by A, is a rectangular array of
entries or elements (numbers, or symbols representing numbers)
enclosed typically by square brackets, where m is the number of rows
and n the number of columns.
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Definition
A is square if m= n.
A is diagonal if all off-diagonal elements are 0, and not all diagonal
elements are 0.
A is the identity matrix ( I ) if it is diagonal and all diagonal elements
are 1.
A is the zero or null matrix ( 0 )+if all its elements are 0.
The trace of A equals the sum of the elements along its main diagonal.
Two matrices A and B are equal iff the have the same number of rows
and columns, and aij = bij .
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
11
Definition
The transpose AT of an mn matrix A is an nm matrix obtained by
interchanging the rows and columns of A.
A square matrix for which AT=A is said to be symmetric.
Any matrix X for which XA=I and AX=I is called the inverse of A.
Let c be a real or complex number
+ (called a scalar). The scalar
multiple of c and matrix A, denoted cA, is obtained by multiplying
every elements of A by c. If c = 1, the scalar multiple is called the
negative of A.
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
12
Definition
13
A column vector is an m 1 matrix:
A row vector is a 1 n matrix:
A column vector can be expressed as a row vector by using
the transpose:
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Definition
The sum of two matrices A and B (of equal dimension), denoted A + B, is
the matrix with elements aij + bij.
The difference of two matrices, A B, has elements aij bij.
The product, AB, of mn matrix A and pq matrix B, is an mq matrix C
whose (i,j)-th element is formed by multiplying
the entries across the ith
+
row of A times the entries down the jth column of B; that is,
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
14
Definition
15
The inner product (also called dot product) of two vectors
is defined as
Note that the inner product is a scalar.
HRI lab, Dongguk University, Korea
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Strategy Tester PDFDocumento20 páginasStrategy Tester PDFKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Strategy Tester PDFDocumento20 páginasStrategy Tester PDFKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
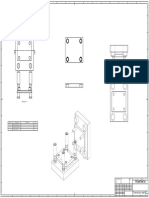
- Cylinder Sheet Metal DimensionsDocumento1 páginaCylinder Sheet Metal DimensionsKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- SolidWorks For Sheet MetalDocumento15 páginasSolidWorks For Sheet MetalCodreanu Petru100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Create 3D Solid Primitives in AutoCADDocumento4 páginasCreate 3D Solid Primitives in AutoCADKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- 19-08-2018Documento1 página19-08-2018Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- 1 B Roll No 2Documento1 página1 B Roll No 2himanshugarg979Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- 06-Mydin DoneDocumento12 páginas06-Mydin DoneKenneth Chaw100% (1)
- Hello PDFDocumento3 páginasHello PDFKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Orientation Test-01 - IndexDocumento1 páginaOrientation Test-01 - IndexKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Lock Box Bottom - InCH - Sheet1Documento1 páginaLock Box Bottom - InCH - Sheet1Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Power Supply Box Chassis - SheeDocumento1 páginaPower Supply Box Chassis - SheeKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Sheet Metal BoxDocumento1 páginaSheet Metal BoxKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Toy Box2 - SolidworksDocumento1 páginaToy Box2 - SolidworksKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Identifying Customer Needs SweetwaterDocumento26 páginasIdentifying Customer Needs SweetwaterKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHDocumento1 páginaSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- cls17 DMD Forcst PDFDocumento32 páginascls17 DMD Forcst PDFamenstoAinda não há avaliações
- Part 2Documento1 páginaPart 2Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHDocumento1 páginaSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Cs WP Sample Exam Question Part 1Documento2 páginasCs WP Sample Exam Question Part 1Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHDocumento1 páginaSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Practical Paper Model PDFDocumento2 páginasPractical Paper Model PDFKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Revision 1Documento1 páginaRevision 1Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Fluent Tut Mixing ElbowDocumento58 páginasFluent Tut Mixing Elbowgp1707Ainda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Examples BoilerDocumento5 páginasExamples BoilerKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking Course OutlineDocumento4 páginasCritical Thinking Course OutlineKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Academy Award: Current Special CategoriesDocumento1 páginaAcademy Award: Current Special CategoriesKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Fuel of Give Out of Calorific Ofoxygen, ofDocumento17 páginasFuel of Give Out of Calorific Ofoxygen, ofKenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Sources of Energy - Malaysian Scenario Part 1Documento11 páginasSources of Energy - Malaysian Scenario Part 1Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- Limit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Documento1 páginaLimit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Kenneth ChawAinda não há avaliações
- (Single Correct Choice Type) (6 × 3 18) Class:XII Time: Min. M.M.: Dpp. No.Documento4 páginas(Single Correct Choice Type) (6 × 3 18) Class:XII Time: Min. M.M.: Dpp. No.Purushottam KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 6400 Lecture SpreadsheetsDocumento351 páginas6400 Lecture SpreadsheetsPhuong HoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)Documento22 páginasIntroduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)goldencomet100% (1)
- Elliptical Trammel Mechanism FinalDocumento4 páginasElliptical Trammel Mechanism FinalAbdel Hamied Ebrahem100% (1)
- Water Rocket ProjectDocumento5 páginasWater Rocket Projectjwinfield12Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 4 - Impulse Response in LTIC Systems (Textbook: Ch. 3.2 - 3.4)Documento21 páginasWeek 4 - Impulse Response in LTIC Systems (Textbook: Ch. 3.2 - 3.4)siarwafaAinda não há avaliações
- Unacademy Straight LineDocumento32 páginasUnacademy Straight LineSahil PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real NumbersDocumento11 páginasNCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real NumbersSANCHIT UPADHYAYAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 10 Polynomials & WorksheetDocumento10 páginasCBSE Class 10 Polynomials & WorksheetVINOTHKANNA DEVAAinda não há avaliações
- Annex1 Module Handbook-PEDocumento128 páginasAnnex1 Module Handbook-PEAmelSiljo2Ainda não há avaliações
- Floyd Warshall AlgorithmDocumento19 páginasFloyd Warshall AlgorithmSamaksh JhalaniAinda não há avaliações
- Bu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsDocumento119 páginasBu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsPhạm Gia DũngAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 09Documento75 páginasChapter 09osoreneg100% (1)
- GenmathDocumento2 páginasGenmathJosafatAinda não há avaliações
- International Mathematics Olympiad: Sample PaperDocumento4 páginasInternational Mathematics Olympiad: Sample PaperEmil Lewin LukoseAinda não há avaliações
- Integral Calculus Activity Sheet ReviewDocumento12 páginasIntegral Calculus Activity Sheet ReviewFrankie GamboaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two (LPM)Documento18 páginasChapter Two (LPM)Yohannes BelaynehAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3, Numerical Based On Population ForecastingDocumento26 páginasLecture 3, Numerical Based On Population ForecastingShivam SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Book R Master PisaDocumento101 páginasBook R Master Pisaboris djiongoAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Genius Srinivasa Ramanujan, FRS: Dr.S.Sridhar, Ph.D. (JNUD)Documento14 páginasMathematics Genius Srinivasa Ramanujan, FRS: Dr.S.Sridhar, Ph.D. (JNUD)Vedant SinghAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Unit I-1Documento26 páginasMCQ Unit I-1Naughty PAPAAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures NOTESDocumento178 páginasLectures NOTESÉTUDES KAAinda não há avaliações
- Orca Share Media1579045614947Documento4 páginasOrca Share Media1579045614947Teresa Marie Yap CorderoAinda não há avaliações
- Algorithms - ProblemsDocumento98 páginasAlgorithms - ProblemsAmir RamiAinda não há avaliações
- Arithmetic Dynamical Systems - Joseph SilvermanDocumento518 páginasArithmetic Dynamical Systems - Joseph Silvermansmangerel100% (4)
- M Thamban Nair - Measure and Integration - A First Course (2019, Chapman and Hall - CRC) PDFDocumento216 páginasM Thamban Nair - Measure and Integration - A First Course (2019, Chapman and Hall - CRC) PDFlucas100% (1)
- Lect 6 - Asymptotic Notation-1Documento24 páginasLect 6 - Asymptotic Notation-1kaushik.grAinda não há avaliações
- (Maa 5.20) Integration by Parts - SolutionsDocumento6 páginas(Maa 5.20) Integration by Parts - Solutionsdhruvkhera2Ainda não há avaliações
- Pil Unit Review2015 KeyDocumento6 páginasPil Unit Review2015 Keyapi-296347043Ainda não há avaliações