Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Brain Aneurysm
Enviado por
Lazoi0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
12 visualizações6 páginasBrain Aneurysm
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoBrain Aneurysm
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
12 visualizações6 páginasBrain Aneurysm
Enviado por
LazoiBrain Aneurysm
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 6
Brain Aneurysm
Introduction of Brain Aneurysm
A brain aneurysm is an abnormal bulging or protruding of one of the arteries
inside the brain. It is a medical condition that is characterised by abnormal
widening or ballooning of a blood vessel in the brain, which has weakened over
time. It mainly develops at the junctions of the large arteries present at the base
of the brain, in a region called the Circle of Willis. When the blood vessel gets
ruptured, it causes bleeding into the brain or the space closely surrounding it
(called the subarachnoid space), thereby, leading to a subarachnoid haemorrhage.
It can be life-threatening and one should seekimmediate medical attention.
However, most of them remain small and never become an issue and usually get
detected during tests for other conditions.
Casue of Brain Aneurysm
A brain aneurysm is an acquired problem i.e., it is not present from birth but
develops over time. However, some of the probable causes are:
Neurofibromatosis:Neurofibromatosis is agenetic disorderof the
nervous system that dominantly affects the growth and development of neural
or nerve cell tissues that causes tumours to grow on the nerve.
Tobacco Consumption:Chewing tobacco or smoking is another factor that
primarily increases the risk of this disorder. In fact, studies show that nonsmokers have nearly 10 times more potential to sustain a rupture than a
smoker.
High Blood Pressure:The risk of subarachnoid haemorrhage or rupture is
more in people with a history ofhigh blood pressure(hypertension).
High Cholesterol:Although the effect ofhigh cholesterolremains unclear,
some studies show that it can also lead to the rupturing of the aneurysm.
Alcohol Abuse:Moderate to high level ofalcoholabuse is another factor
contributing to a rupture.
Symptom of Brain Aneurysm
Usually there are no symptoms however, some of the probable ones are given
below:
Severeheadaches
Peripheral vision deficits
Perceptual problems
Thinking or processing problems
Speech complications
Short-termmemory difficulty
Sudden changes in behaviour
Decreased concentration
Loss of balance and coordination
Fatigue
Diagnosis of Brain Aneurysm
The diagnosis generally includes the following tests:
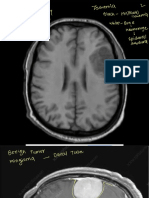
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:To detect bleeding in the brain.
Computed Tomography Angiogram (CTA) scan:To locate the actual site of the
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA):To obtain images or pictures of blood
Cerebral Angiogram:It is an X-ray test, employed to locate small (less than 5 mm
Treatment of Brain Aneurysm
The treatment involves repairing the affected blood vessels. Coil embolisation and
surgical clipping are the two main surgeries used to cure this disorder. Coil embolisation
is a procedure in which a small tube is inserted into the affected artery. Tiny metal coils
are then moved through the tube into the aneurysm, thereby easing pressure and
reducing its probability to rupture. This procedure is less invasive and more effective
than surgical clipping. Surgical clipping is another method, where a tiny metal clip is
placed around the base of the aneurysm to isolate it from normal blood circulation. It
also relieves the pressure and keeps it from rupturing.
A brain aneurysm can be life-threatening, if left untreated for long. The main dangers
are suffering from astrokeor in extreme cases, death, especially if it ruptures and
bleeds. However, its survival rates can increase by immediate hospitalisation and early
detection. Potential blood vessel spasms need to be controlled with medications as
soon as possible.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Topmost Cancers That Affect WomenDocumento6 páginasTopmost Cancers That Affect WomenLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- The Thyroid Gland Metabolism RegulatorDocumento4 páginasThe Thyroid Gland Metabolism RegulatorLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Epilepsy AwarenessDocumento3 páginasEpilepsy AwarenessLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Daily ExerciseDocumento4 páginasDaily ExerciseLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Crohn's DiseaseDocumento7 páginasCrohn's DiseaseLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Rise of Autism in IndiaDocumento4 páginasRise of Autism in IndiaLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Trichotillomania (Hair Pulling Disorder)Documento10 páginasTrichotillomania (Hair Pulling Disorder)LazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Low Back PainDocumento10 páginasLow Back PainLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Sago or TapiocaDocumento4 páginasSago or TapiocaLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Hemifacial Spasm (HFS)Documento5 páginasHemifacial Spasm (HFS)LazoiAinda não há avaliações
- GastroenterologyDocumento7 páginasGastroenterologyLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Ketotic HypoglycaemiaDocumento6 páginasKetotic HypoglycaemiaLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Peptic Ulcer SurgeryDocumento7 páginasPeptic Ulcer SurgeryLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- DystoniaDocumento6 páginasDystoniaLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Ptosis or Drooping EyelidDocumento7 páginasPtosis or Drooping EyelidLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- EpilepsyDocumento5 páginasEpilepsyLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Brain HaemorrhageDocumento6 páginasBrain HaemorrhageLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocumento7 páginasParkinson's DiseaseLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia)Documento9 páginasLow Sperm Count (Oligospermia)LazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Brachial Plexus Neuropathy SyndromeDocumento6 páginasBrachial Plexus Neuropathy SyndromeLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Crohn's DiseaseDocumento7 páginasCrohn's DiseaseLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Mandibulofacial DysostosisDocumento5 páginasMandibulofacial DysostosisLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- UrethritisDocumento6 páginasUrethritisLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Tuberous SclerosisDocumento5 páginasTuberous SclerosisLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Scoliosis (Curved Spine)Documento8 páginasScoliosis (Curved Spine)Lazoi100% (1)
- KwashiorkorDocumento6 páginasKwashiorkorLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Kyphosis (Curved Thoracic Spine)Documento6 páginasKyphosis (Curved Thoracic Spine)LazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerular DiseasesDocumento6 páginasGlomerular DiseasesLazoiAinda não há avaliações
- Abruptio Placentae (Placental Abruption)Documento6 páginasAbruptio Placentae (Placental Abruption)LazoiAinda não há avaliações
- MMDS PDFDocumento1.241 páginasMMDS PDFyusnitaAinda não há avaliações
- Cns PathologyDocumento18 páginasCns Pathologysunnyorange8Ainda não há avaliações
- CNS (102 Questions) : Form More Slowly and Insidiously ThanDocumento38 páginasCNS (102 Questions) : Form More Slowly and Insidiously Thanclark146Ainda não há avaliações
- ANEURYSMDocumento39 páginasANEURYSMIvan Roque100% (1)
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With AneurysymDocumento30 páginasSubarachnoid Hemorrhage With AneurysymmunaAinda não há avaliações
- Neuroasia 2017 22 (3) 185Documento7 páginasNeuroasia 2017 22 (3) 185Ray ParikesitAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Tourism Magazine - Issue6Documento76 páginasMedical Tourism Magazine - Issue6El ComandanteAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Pustaka - Aneurisma IntrakranialDocumento2 páginasDaftar Pustaka - Aneurisma IntrakranialTheofilus AswadiAinda não há avaliações
- Multimodal Tretment of Intracranial Aneurysm: A. Chiriac, I. Poeata, J. Baldauf, H.W. SchroederDocumento10 páginasMultimodal Tretment of Intracranial Aneurysm: A. Chiriac, I. Poeata, J. Baldauf, H.W. SchroederApryana Damayanti ARAinda não há avaliações
- Aphasia AssessmentDocumento6 páginasAphasia Assessment蔡季霖Ainda não há avaliações
- Seminar: Jan Claassen, Soojin ParkDocumento17 páginasSeminar: Jan Claassen, Soojin ParkRaul DoctoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Brain Aneurysm?Documento2 páginasWhat Is A Brain Aneurysm?shinAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Reading: Imaging of Intracranial HemorrhageDocumento27 páginasJournal Reading: Imaging of Intracranial HemorrhagehasrilAinda não há avaliações
- Neurología: Clinical Management Guidelines For Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento18 páginasNeurología: Clinical Management Guidelines For Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Diagnosis and TreatmentJonathan Mindiola SantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Disease and Neurology (2017)Documento22 páginasRenal Disease and Neurology (2017)mysticmdAinda não há avaliações
- Neurosurgery ImagesDocumento51 páginasNeurosurgery ImagesAhmad SobihAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral AneurysmDocumento24 páginasCerebral Aneurysmcaptain_rafeAinda não há avaliações
- Intracranial Aneurysms and SAH: Philippe Younes MD Neurosurgeon Head of Neuroscience Department BMCDocumento37 páginasIntracranial Aneurysms and SAH: Philippe Younes MD Neurosurgeon Head of Neuroscience Department BMCHussein TarhiniAinda não há avaliações
- DynaMed Plus - Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento56 páginasDynaMed Plus - Subarachnoid HemorrhageSarah Shafa MarwadhaniAinda não há avaliações
- PhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 8 List of Medical Conditions Allowed For Referral PackageDocumento7 páginasPhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 8 List of Medical Conditions Allowed For Referral PackageChrysanthus HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Subarachno Id Hemorrhag E: DONE BY: Rawan AlebousDocumento54 páginasSubarachno Id Hemorrhag E: DONE BY: Rawan AlebousHiba AliAinda não há avaliações
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento31 páginasHemorrhagic StrokeKaren Mae Dacoco MamuyacAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Aneurysm Thesis StatementDocumento7 páginasBrain Aneurysm Thesis Statementchristinewhitebillings100% (2)
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocumento29 páginasCerebrovascular DiseaseKamsha UyAinda não há avaliações
- Aneurysm: Symptoms of An AneurysmDocumento3 páginasAneurysm: Symptoms of An AneurysmArun MuralidharanAinda não há avaliações
- Stroke and Its Imaging EvaluationDocumento21 páginasStroke and Its Imaging EvaluationLisa VebrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines SAH AHADocumento71 páginasGuidelines SAH AHAAnselmo CaricatoAinda não há avaliações
- Ischemic StrokeDocumento7 páginasIschemic StrokeAlly Juaneza100% (1)
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Continuumaudio Interview Available OnlineDocumento35 páginasSubarachnoid Hemorrhage: Continuumaudio Interview Available OnlineJose DavidAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento25 páginasDiagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid HemorrhageMisael ClintonAinda não há avaliações