Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Mutations
Enviado por
api-2930012170 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
203 visualizações7 páginasTítulo original
mutations
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
203 visualizações7 páginasMutations
Enviado por
api-293001217Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Mutations
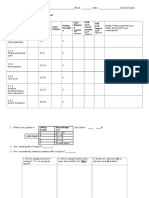
Test Review Packet-Know:
1. The purpose of phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen bases
2. DNA replication makes new DNA from an _____ strand and a
____ strand.
3. What is the transcription?
4. What is translation?
5. How are DNA and RNA similar?
6. How are DNA and RNA different?
7. What are the three types of RNA and their function?
8. how to read a Codon Chart when given both DNA
sequences and RNA sequences
9. the monomer for each major organic molecule
10.the function of each major organic molecule
11.What is the purpose of enzymes and why are they
important?
12.Know difference between aerobic and anaerobic
respiration
13.How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration similar?
different?
14.What are the types of transport and how are they
III. How can DNA be used by the cell to make a
protein?
c.
All of an organisms cells have
the same DNA, but the cells
differ based on the expression
of the genes.
i.
ii.
Multicellular organisms begin as
undifferentiated masses of cells.
Variation in DNA activity
determines cell types.
Different types of cells
expressing different genes leads
to differentiation. Only specific
parts of the DNA are activated in
those cells. Once a cell
differentiates, the process
cannot be reversed. For
example, we have muscle cells,
nerve cells, and others.
III. How can DNA be used by the cell to make a
protein?
iii. Gene regulation is the process
which determines which genes will
be expressed (used to make a
protein). This can be affected by the
cells history and/or environment.
Proteins may be overproduced,
underproduced or produced at
incorrect times. Ex: Injury repair
and cancer
IV. Whth appen swhe nprotei nsynthesi sgoe
swrong?
A.
A mutation is a change in the original DNA
sequence, which may lead to a change
in the amino acid sequence.
B. A mutation occurs when the original DNA
sequence is not copied properly during
replication or protein synthesis.
Mutations can be spontaneous or caused by
radiation and/or chemical exposure.
C. The result of a mutation is a change in the
amino acid sequence. The necessary
protein may not be made or is defective.
This can change the traits of the cell or
organism. Only mutations in sex cells (egg
and sperm) or in the gamete can result in
heritable changes.
IV. Whth appen swhe nprotei nsynthesi sgoe
swrong?
D. There are two types of gene
mutations:
1. Point (or substitution) mutations
occur when a single base is
replaced with a different base.
(For example, A is replaced with
C.)
Ex. GATTACA GAGTACA
a. A point mutation, if it occurs on a
gene, may result in the change of a
single amino acid within the protein.
b. Sickle cell anemia, a disease that
results in misshapen red blood cells,
is caused by a point mutation.
YouTube - Sickle Cell
IV. Whth appen swhe nprotei nsynthesi sgoe
swrong?
2.
Frameshift mutations occur when a single
base is added (addition frameshift) or
deleted (deletion frameshift) within the
sequence. Because DNA and the mRNA copy
are read three bases (a codon) at a time, this
type of mutation shifts the reading frame.
Ex. GAT/TAC/ATT GAT/TAA/CAT/T
a.
b.
The effect of a frameshift depends on the
location of the addition or deletion. The earlier
within the gene sequence the base is added or
deleted, the more amino acids will be changed.
Huntingtons Disease, a disease that results in
the progressive loss of nervous system
function, may be caused by the insertion of
several bases.
YouTube - DNA MUTATION
YouTube - Beneficial Mutations Do Happen
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Nitrogen Cycle ppt-1Documento14 páginasNitrogen Cycle ppt-1api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mutations WorksheetDocumento3 páginasMutations Worksheetapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbon Cycle PPT Notes-1Documento14 páginasCarbon Cycle PPT Notes-1api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1-4 Re-Test Study GuideDocumento3 páginasUnit 1-4 Re-Test Study Guideapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport Webquest 2Documento4 páginasCell Transport Webquest 2api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1-4 ReviewDocumento2 páginasUnit 1-4 Reviewapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- MutationsDocumento7 páginasMutationsapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Meiosis KerlinDocumento1 páginaMeiosis Kerlinapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mitosis and Meiosis Poster Rubric 2Documento1 páginaMitosis and Meiosis Poster Rubric 2api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 4 - Entire ModuleDocumento12 páginasModule 4 - Entire Moduleapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice Questions With AnswersDocumento137 páginasPractice Questions With Answersapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod 3 4 5 Study GuideDocumento1 páginaMod 3 4 5 Study Guideapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Eoc Review PacketDocumento12 páginasEoc Review Packetapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod 3-5 TrackerDocumento2 páginasMod 3-5 Trackerapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod 4Documento10 páginasMod 4api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 10 Day 4Documento8 páginasModule 10 Day 4api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Plant Adaptation Project - RubricsDocumento2 páginasPlant Adaptation Project - Rubricsapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Jeopardy Eoc Bio ReviewDocumento106 páginasJeopardy Eoc Bio Reviewapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Sponge Bob Genetics PracticeDocumento3 páginasSponge Bob Genetics Practiceapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Eoc BiologyDocumento116 páginasEoc Biologyapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod 11 Day 1Documento12 páginasMod 11 Day 1api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Module 5 CombinedDocumento16 páginasUnit 2 Module 5 Combinedapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetics WebquestDocumento3 páginasGenetics Webquestapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 10 Day 5Documento10 páginasModule 10 Day 5api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Evolution Days 2 and 3Documento14 páginasEvolution Days 2 and 3api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Evolutionday 1Documento20 páginasEvolutionday 1api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetis Practice Bunny GeneticsDocumento3 páginasGenetis Practice Bunny Geneticsapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis PracticeDocumento3 páginasMitosis Vs Meiosis Practiceapi-293001217Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 8 Genetics Day 1Documento16 páginasModule 8 Genetics Day 1api-293001217Ainda não há avaliações