Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Fall 16 Optoelectronics Lecture 1,2,3,4
Enviado por
sohaibTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fall 16 Optoelectronics Lecture 1,2,3,4
Enviado por
sohaibDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
@ McGraw-Hill Education
The Path to Optical Networks
1- Morse Code Telegraph system,1837
2- Maximum speed 120 bits/s
3- Voice Communication, 1874
4- Z-12 F (12 channels)
5- Carrier, Modulation
6- Coaxial System
7- Microwave
8- Optical Fiber
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Optical History
LASER, 1960, 770-1675 nm.
Optical Fiber by Corning, 1970.
First Optical Fiber Link,1970, 6 Mbits/s, 10
Km.
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Advantages of Optical Fiber
1- Long Distance Transmission
2- Large Information Capacity
3- Small Size and Low weight
4- Immunity to Electrical Interference
5- Enhanced Safety.
6- Increased Signal Security
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
10
@ McGraw-Hill Education
11
@ McGraw-Hill Education
12
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
13
Optical Spectral Bands
Wavelength
Photon Energy or Optical Power
Relationship of Speed of light with
wavelength and frequency.
Frequency
Planks Law.
14
@ McGraw-Hill Education
15
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
16
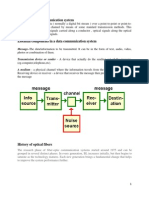
Fundamental Data
Communication Concept
Elementary Communication Link
Source
Destination
Transmitter
Transmission Channel
Encoding
Receiver
Decoding
17
@ McGraw-Hill Education
18
@ McGraw-Hill Education
19
@ McGraw-Hill Education
20
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
21
Digital Signal
Discrete Symbol
Binary Waveform
Bit Interval
Bit Rate Or Data Rate
22
@ McGraw-Hill Education
23
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
24
Digitization of Analogue Signals
Sampling
Quantization
Nyquist Theorem
25
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
26
Channel Capcity
Shanon Capcity Formula
C=B log2 (1+S/N)
Log x = (log x)/(log 2) = (log x)/0.3
SNR = 10 log (Signal Power/ Noise
Power) = 10 log S/N
2
10
dB
10
10
@ McGraw-Hill Education
27
Decibel Units
Power Ratio in dB = 10 log (P2 / P1 )
28
@ McGraw-Hill Education
29
@ McGraw-Hill Education
30
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
31
Network Information Rates
Telecom Signal multiplexing
1- Time Division Multiplexing
2- PDH
@ McGraw-Hill Education
32
SONET / SDH Multiplexing
Hierarchy
SONET
SDH
STS
STM-1,STM-4, STM-16, STM-64, STM256
33
@ McGraw-Hill Education
@ McGraw-Hill Education
34
BW demands in communication systems
Type &
applications
Format
Uncompressed
Compressed
Voice, digital
telegraphy
4 kHz voice
64 kbps
16-32 kbps
Audio
16-24 kHz
512-748 kbps
32-384 kbps
(MPEG, MP3)
Video conferencing
176
144 or 352
288 frames @ 1030 frames/s
2-35.6 Mbps
64 kbps-1.544
Mbps (H.261
coding)
Data transfer, Ecommerce,Video
entertainment
1-10 Mbps
Full-motion
broadcast video
720480frames @
30 frames/s
249 Mbps
2-6Mbps (MPEG-2)
HDTV
1920 1080
frames@ 30
frames /s
1.6 Gbps
19-38 Mbps
(MPEG-2)
@ McGraw-Hill Education
35
Early application of fiber optic communication
Digital link consisting of time-division-multiplexing (TDM) of 64 kbps
voice channels (early 1980).
Optical Fiber communications, 3rd ed.,G.Keiser,McGrawHill, 2000
@ McGraw-Hill Education
36
SONET & SDH Standards
SONET (Synchronous Optical NETwork) is the network standard used in
north America & SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) is used in other
parts of the world. These define a synchronous frame structure for sending
multiplexed digital traffic over fiber optic trunk lines.
The basic building block of SONET is called STS-1 (Synchronous
Transport Signal) with 51.84 Mbps data rate. Higher-rate SONET signals
are obtained by byte-interleaving N STS-1 frames, which are scramble &
converted to an Optical Carrier Level N (OC-N) signal.
The basic building block of SDH is called STM-1 (Synchronous Transport
Module) with 155.52 Mbps data rate. Higher-rate SDH signals are
achieved by synchronously multiplexing N different STM-1 to form STMN signal.
@ McGraw-Hill Education
37
SONET & SDH transmission rates
SONET level
Electrical level
Line rate (Mb/s)
SDH equivalent
OC-1
STS-1
51.84
OC-3
STS-3
155.52
STM-1
OC-12
STS-12
622.08
STM-4
OC-24
STS-24
1244.16
STM-8
OC-48
STS-48
2488.32
STM-16
OC-96
STS-96
4976.64
STM-32
OC-192
STS-192
9953.28
STM-64
Optical Fiber communications, 3rd ed.,G.Keiser,McGrawHill, 2000
@ McGraw-Hill Education
38
WDM Concept
FDM
WDM
39
@ McGraw-Hill Education
40
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Key Elements of Optical Fiber System
41
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Fig. 1-3: Operating ranges of components
42
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Fig. 1-5: Major elements of an optical fiber link
43
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Fig. 1-6: Optical fiber cable installations
@ McGraw-Hill Education
44
Fig. 1-7: History of attenuation
@ McGraw-Hill Education
45
Fig. 1-8: Optical multiplexing
46
Window and Spectral Bands
@ McGraw-Hill Education
Você também pode gostar
- HCIA-Access V2.5 Training MaterialDocumento933 páginasHCIA-Access V2.5 Training MaterialSergio ZaletaAinda não há avaliações
- Optical NetworksDocumento14 páginasOptical Networksrahulvema_11Ainda não há avaliações
- IEC 60811-100 General-Electric and Optical Fibre Cables - Test Methods For Non-Metallic MaterialsDocumento26 páginasIEC 60811-100 General-Electric and Optical Fibre Cables - Test Methods For Non-Metallic Materialssohaib100% (1)
- Inputing Data in Other WaysDocumento9 páginasInputing Data in Other WaysFai ShAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Amplifiers and NetworksDocumento45 páginasOptical Amplifiers and NetworksDr Ravi Kumar A VAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Communications Optical CommunicationsDocumento30 páginasOptical Communications Optical CommunicationsNung NingAinda não há avaliações
- Unit1 Evolution of Optical CommunicationDocumento51 páginasUnit1 Evolution of Optical CommunicationDeepak KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Lecture 1 NUDocumento96 páginasOptical Lecture 1 NUPhon PhannaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec4 ES475 2023 UploadDocumento29 páginasLec4 ES475 2023 UploadEmad RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Fallsem2016-17 Ece401 Eth 1566 18-Aug-2016 RM001 2Documento89 páginasFallsem2016-17 Ece401 Eth 1566 18-Aug-2016 RM001 2murthyAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Devices and CommunicationDocumento50 páginasOptical Devices and CommunicationSyed Haider AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Unit1 Evolution of Optical CommunicationDocumento47 páginasUnit1 Evolution of Optical CommunicationTisha KhatriAinda não há avaliações
- A. Lecture - Introduction Optical Fiber Communication.Documento57 páginasA. Lecture - Introduction Optical Fiber Communication.gauravnitin123Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento19 páginasChapter 1Alene tesfawAinda não há avaliações
- Vikash: REG. No.-11410993Documento46 páginasVikash: REG. No.-11410993ChaitanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-1 IntroductionDocumento19 páginasChapter-1 IntroductionAlene tesfawAinda não há avaliações
- Historical Perspective: Savera Tanwir - Title: Fiber Optics Communication Systems - Credit Hours: 3+0 - Text BookDocumento12 páginasHistorical Perspective: Savera Tanwir - Title: Fiber Optics Communication Systems - Credit Hours: 3+0 - Text BookBasel DalatiAinda não há avaliações
- Training On Optical Fiber NetworkDocumento96 páginasTraining On Optical Fiber Networkpriyasingh1682100% (1)
- EN554 Photonic Networks: Professor Z GhassemlooyDocumento29 páginasEN554 Photonic Networks: Professor Z GhassemlooyNigel CharlesAinda não há avaliações
- Ex.: Sending Alarms, Calls For Help, Announcement of Certain EventsDocumento30 páginasEx.: Sending Alarms, Calls For Help, Announcement of Certain EventsramAinda não há avaliações
- GSM System Overview: Wireless Mobile CommunicationDocumento18 páginasGSM System Overview: Wireless Mobile CommunicationMohamedSalahAinda não há avaliações
- UMTS Material (LT)Documento215 páginasUMTS Material (LT)Matthew JejeloyeAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optics Telecommunications: Dr. Muhammad Hassan SayyadDocumento111 páginasFiber Optics Telecommunications: Dr. Muhammad Hassan SayyadAtifAinda não há avaliações
- Lec3 ES475 2023 UploadDocumento32 páginasLec3 ES475 2023 UploadEmad RazaAinda não há avaliações
- 6-3emerging Network TechnologiesDocumento24 páginas6-3emerging Network TechnologiesBijay PoudelAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Communications, 3e - Gerd KeiserDocumento289 páginasOptical Fiber Communications, 3e - Gerd Keiserअमित सचान100% (5)
- BiniyamDocumento8 páginasBiniyamnafntitesfayeAinda não há avaliações
- Satyaspeak Everything Over IP (EOIP) - All You Wanted To Know About NGNDocumento31 páginasSatyaspeak Everything Over IP (EOIP) - All You Wanted To Know About NGNThắng Phạm ĐứcAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Books:: ICT 6612: Advanced Optical CommunicationsDocumento12 páginasReference Books:: ICT 6612: Advanced Optical CommunicationsRashed IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Telecom For Rural Areas: U. B. DesaiDocumento30 páginasTelecom For Rural Areas: U. B. DesaiAlessandro Defilippi EliasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: Network Access: ObjectivesDocumento10 páginasChapter 4: Network Access: Objectivesovidiu0702Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11Documento45 páginasChapter 11Jitendra YadavAinda não há avaliações
- 1xEV DO TechnologyDocumento220 páginas1xEV DO TechnologyYu LeAinda não há avaliações
- Transmission of Data by by Rajesh ChhetryDocumento21 páginasTransmission of Data by by Rajesh ChhetryBhegz EscalonaAinda não há avaliações
- Instructor: Dr. S.M.Sajid,: SM - Sajid@nu - Edu.pkDocumento29 páginasInstructor: Dr. S.M.Sajid,: SM - Sajid@nu - Edu.pkkami2121Ainda não há avaliações
- Fiber-Optic Communication Systems An Introduction: Xavier Fernando Ryerson UniversityDocumento36 páginasFiber-Optic Communication Systems An Introduction: Xavier Fernando Ryerson UniversityBiswarup MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Cabling and ConnectorsDocumento11 páginasCabling and ConnectorsPushpinder Singh KhalsaAinda não há avaliações
- Standards For Broadband AccessDocumento21 páginasStandards For Broadband AccessShaikh Muhammad NomanAinda não há avaliações
- Enhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewDocumento72 páginasEnhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewPrashant SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Local Area Networks: Lans Are Designed ToDocumento73 páginasLocal Area Networks: Lans Are Designed ToVivek DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Optical Wireless Network For Next Generation Wireless SystemsDocumento13 páginasIntegrated Optical Wireless Network For Next Generation Wireless SystemsRKSethiAinda não há avaliações
- SC2004M6Documento385 páginasSC2004M6Ankita Tarun DhariwalAinda não há avaliações
- Sir Syed PTCL ReportDocumento22 páginasSir Syed PTCL Reportashar565Ainda não há avaliações
- GSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced DataDocumento17 páginasGSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced Datashikhar15Ainda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optic TDocumento87 páginasFiber Optic TMunimbkr100% (2)
- Optical FiberDocumento38 páginasOptical FiberHarnish DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Y. Anil Kumar V. Sateesh KumarDocumento15 páginasY. Anil Kumar V. Sateesh KumarAnil Kumar YernintiAinda não há avaliações
- OC PartDocumento34 páginasOC PartEmad MassoodAinda não há avaliações
- Ethernet 102 The Physical Layer of EthernetDocumento30 páginasEthernet 102 The Physical Layer of EthernetPhátTrầnAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Communications: Chapter 1: IntroductionDocumento17 páginasOptical Communications: Chapter 1: IntroductionDang KhueAinda não há avaliações
- Telecom: U. B. DesaiDocumento30 páginasTelecom: U. B. DesaiNitin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Communication SystemkirankumarikanchanAinda não há avaliações
- Fallsem2016-17 Ece401 Eth 1593 11-Jul-2016 Rm001 Introduction-Session-1Documento27 páginasFallsem2016-17 Ece401 Eth 1593 11-Jul-2016 Rm001 Introduction-Session-1murthyAinda não há avaliações
- PSTN and ISDNDocumento29 páginasPSTN and ISDNleangsimAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber-Optic Communication: Conte NtsDocumento17 páginasFiber-Optic Communication: Conte NtsVicky DhimanAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Communications & Networking - An OverviewDocumento20 páginasOptical Communications & Networking - An OverviewAima sridiAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber-Optic Communication Systems An Introduction: Xavier Fernando Ryerson UniversityDocumento33 páginasFiber-Optic Communication Systems An Introduction: Xavier Fernando Ryerson UniversityDila ZFAinda não há avaliações
- Telecommunications and Network Security: CISSP Guide To Security EssentialsDocumento102 páginasTelecommunications and Network Security: CISSP Guide To Security EssentialsMuhammad Nauman AkramAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsNo EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- OQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsNo EverandOQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Optically Amplified WDM NetworksNo EverandOptically Amplified WDM NetworksJohn ZyskindAinda não há avaliações
- Bsen50525 2-11-2011 Cables For General ApplicationsDocumento22 páginasBsen50525 2-11-2011 Cables For General ApplicationssohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Cqap Six SigmaDocumento39 páginasCqap Six SigmasohaibAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 CqapDocumento1 página2021 CqapsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Lean Management: Learning ObjectivesDocumento20 páginasLean Management: Learning ObjectivessohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Instructor's Introduction: Dr. Kamran MoosaDocumento1 páginaInstructor's Introduction: Dr. Kamran MoosasohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Part # Total Sorted Total RejectsDocumento9 páginasPart # Total Sorted Total RejectssohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Bsen50525 2-11-2011 Cables For General ApplicationsDocumento22 páginasBsen50525 2-11-2011 Cables For General ApplicationssohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Relationship Management: Learning ObjectivesDocumento19 páginasCustomer Relationship Management: Learning ObjectivessohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Pmbok Guide (Ch-7)Documento9 páginasPmbok Guide (Ch-7)sohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Pmbok Guide (Ch-1)Documento10 páginasPmbok Guide (Ch-1)sohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Relationship Management: Learning ObjectivesDocumento21 páginasCustomer Relationship Management: Learning ObjectivessohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Work Breakdown StructureDocumento6 páginasWork Breakdown StructuresohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Pmbok Guide (Ch-3)Documento7 páginasPmbok Guide (Ch-3)sohaibAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 CqapDocumento1 página2021 CqapsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Technology of MoldingDocumento12 páginasTechnology of MoldingsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Maintenance Records Laboratory 2015Documento3 páginasMaintenance Records Laboratory 2015sohaibAinda não há avaliações
- ILO - Fundamental Principles of OHSDocumento221 páginasILO - Fundamental Principles of OHSGustavo AlcântaraAinda não há avaliações
- Global Occupational Safety and Health Management HandbookDocumento359 páginasGlobal Occupational Safety and Health Management HandbookKay AayAinda não há avaliações
- Solidification: Freeze Wave Mechanism, Solidification TimeDocumento3 páginasSolidification: Freeze Wave Mechanism, Solidification TimesohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Conductors ClassesDocumento3 páginasConductors ClassessohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Technology of MoldingDocumento12 páginasTechnology of MoldingsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- 8nptel CastingDocumento11 páginas8nptel CastingmayilsvhecAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 1Documento4 páginasLec 1venkatachalapathy.thAinda não há avaliações
- Solidification: Problem Solving On SolidificationDocumento5 páginasSolidification: Problem Solving On SolidificationsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 1Documento4 páginasLec 1venkatachalapathy.thAinda não há avaliações
- IEC 60811-406 Resistance To Stress Cracking of Polyethylene and Polypropylene CompoundsDocumento36 páginasIEC 60811-406 Resistance To Stress Cracking of Polyethylene and Polypropylene CompoundssohaibAinda não há avaliações
- Solidification: Cooling Curves, Concept of Nucleation and GrowthDocumento5 páginasSolidification: Cooling Curves, Concept of Nucleation and Growthvenkatachalapathy.thAinda não há avaliações
- Solidification: Solidification of Pure Metals and AlloysDocumento5 páginasSolidification: Solidification of Pure Metals and AlloyssohaibAinda não há avaliações
- IEC 62230 Electric Cables-Spark-test MethodDocumento82 páginasIEC 62230 Electric Cables-Spark-test MethodsohaibAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Megger?: Definition: A Megger Is A Device That Is Used To Measure The Resistance of InsulatorsDocumento4 páginasWhat Is Megger?: Definition: A Megger Is A Device That Is Used To Measure The Resistance of InsulatorsTarun VarshneyAinda não há avaliações
- CM108AH Datasheet v1.90Documento27 páginasCM108AH Datasheet v1.90getfiredupAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Document-Obstacle Detection System Final ReportDocumento17 páginasReference Document-Obstacle Detection System Final ReportNabeel KhanAinda não há avaliações
- EDC ManualDocumento43 páginasEDC Manualprasanth ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Lenovo Ideapad 320: User GuideDocumento41 páginasLenovo Ideapad 320: User GuideuuulisaAinda não há avaliações
- Tic 300 Pro Tic TracerDocumento2 páginasTic 300 Pro Tic Traceredwin-cuchieyesAinda não há avaliações
- Power System Protection Lecture NotesDocumento47 páginasPower System Protection Lecture NotesMoiz khan100% (1)
- Implementation of Information Technology in RedFox Internet CafeDocumento13 páginasImplementation of Information Technology in RedFox Internet CafeMuhamad Adji YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Soldier Tracking and Health Monitoring SystemDocumento18 páginasSoldier Tracking and Health Monitoring SystemKavana K GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Ginkosynthese Grains Building Manual v2-6 Not PRGMDDocumento1 páginaGinkosynthese Grains Building Manual v2-6 Not PRGMDinformagicAinda não há avaliações
- Instructions 5Documento55 páginasInstructions 5Razvan KalavrezosAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: CD ReceiverDocumento73 páginasService Manual: CD ReceiverAnonymous jPETS5DA6NAinda não há avaliações
- X 7 Proh 0808Documento12 páginasX 7 Proh 0808MIGUELAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced ElectronicsDocumento19 páginasAdvanced ElectronicsKevin G. TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Easy UPS On-Line - SRV1KI-EDocumento3 páginasEasy UPS On-Line - SRV1KI-EAnh nguyen tran minh namAinda não há avaliações
- Final - Sum SmallDocumento72 páginasFinal - Sum Smalledna sisayAinda não há avaliações
- D-Link DIR 842Documento6 páginasD-Link DIR 842Henry EsquivelAinda não há avaliações
- Bringing Deep Learning To Embedded Systems: Mark NadeskiDocumento7 páginasBringing Deep Learning To Embedded Systems: Mark NadeskiMarlessonSantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Datasheet Vega Cc12 HPDocumento1 páginaDatasheet Vega Cc12 HPOscar CanonAinda não há avaliações
- Shindengen F072-15Documento47 páginasShindengen F072-15Nikko PaguioAinda não há avaliações
- Satellite TVDocumento4 páginasSatellite TVproluvieslacusAinda não há avaliações
- COMPUTER KNOWLEDGE - 2000 MCQs PDFDocumento83 páginasCOMPUTER KNOWLEDGE - 2000 MCQs PDFVickraman SAinda não há avaliações
- MB Manual Ga-H55m-S2v eDocumento80 páginasMB Manual Ga-H55m-S2v eAnildo Eldivar De Oliveira SarmentoAinda não há avaliações
- Sylabus of BCS ExamDocumento162 páginasSylabus of BCS ExamMd. Adilur RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- DSPPA POE170 DatasheetDocumento3 páginasDSPPA POE170 DatasheetAleksandar FilipovićAinda não há avaliações
- Baykon BX11 UserManual-rfsDocumento40 páginasBaykon BX11 UserManual-rfsMohamed NasrAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Modulation Techniques PDFDocumento34 páginasDigital Modulation Techniques PDFParas RastogiAinda não há avaliações
- Asus P5L 1394Documento4 páginasAsus P5L 1394Alexandr SyomchenkoAinda não há avaliações
- PowerPack 2600 User ManualDocumento2 páginasPowerPack 2600 User Manualslide1931Ainda não há avaliações