Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Laring Faring Final
Enviado por
Iustitia Septuaginta Samben0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
61 visualizações32 páginasThis document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the pharynx and larynx. It describes the structures and functions of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx. It details the muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and roles in swallowing and phonation of these areas. The pharynx acts as a passageway for food and air and protects the airway, while the larynx contains vocal cords and openings that regulate breathing and swallowing.
Descrição original:
tht
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the pharynx and larynx. It describes the structures and functions of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx. It details the muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and roles in swallowing and phonation of these areas. The pharynx acts as a passageway for food and air and protects the airway, while the larynx contains vocal cords and openings that regulate breathing and swallowing.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
61 visualizações32 páginasLaring Faring Final
Enviado por
Iustitia Septuaginta SambenThis document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the pharynx and larynx. It describes the structures and functions of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx. It details the muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and roles in swallowing and phonation of these areas. The pharynx acts as a passageway for food and air and protects the airway, while the larynx contains vocal cords and openings that regulate breathing and swallowing.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 32
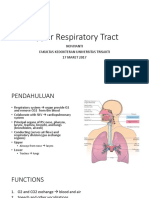
Pharnyx and Larynx
Anatomy and Physiology
Pharnyx
Tubular,
fibromuscular space
extending from the
skull base to upper
esophagus
Function
Swallowing
Immune response
Resonance chamber
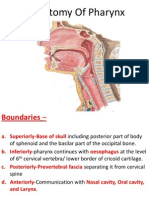
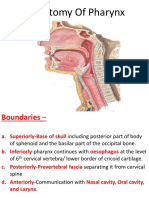
Nasopharnyx
Oropharnyx
Hypopharnyx
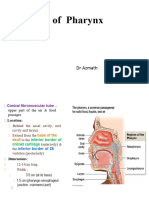
Nasopharnyx
Posterior
apaerature -Soft
palate
Pharngeal
isthmus
Soft palate
contraction:men
utup jalan.
(palatopharngea
l spinchter)
Pharngeal tonsil:
membesar
Nasophanyx
Pharngygotymoanic tube:
menghubughan phanyx denga
middle ear.
Salpingipharngeal muscle
Oropharnyx
Batas inferior
of soft palate-
upper epglotis.
Palatoglossal
arch
Palatine tonsil
1/3 posterior
lidah: lingual
tonsil
Hypopharnyx
Laryngopharnyx:
batasnya dari
superior larnyx-
esophagus level
c7
Muscle
Constrictor muscle
Longituidnal muscle
Constrictor Muscle
Longitudinal Muscle
Vessels of pharnyx
Ascending phrangeal
artery
Facial artery: the
ascending and
tonsillar branches
Branches of maxilaary
artery and linguinal
artery
Origins from external
carotid artery
Veins and lymphatic
Vessels of phranyx
Lower part of phranyx supplied by
inferior thyroid artery, origin from
thyrocervical trunk of subclavian
artery
Veins: drains into prethygroid plexus
in infratemporal fossa and inferiorly
into the facial and internal jugalar
veins
Lymphatic: Retropharngeal ,
parathracheal and infrahyoid nodes
Nerves
Vagus nerveL: Pharngeal
branch of the vagus
nerve X all muscle
except stylopharyngeus
that innervated
glossopharngeal nerve IX
Sensory:Nasopharnyx
(maxilarry nerve V2),
Oropharnyx IX(gag
reflex), laryngopharnyx X
Tonsils
Physiology of phanyx
Swallowing
Oral phase: food is broken down and moistened to
form a bolus, moved to oropharnyx. Pressing the food
agains hard palate with the toounge
Pharyngeal phase: bolus comes contact with receptor
in the thorat, eliciting an involutary swallowing
reflex. Afferent impules travel through
glossopharngeal and vagus nerve. So involuntary
swallowing reflex is triggered.
Velum close of the nasophanyx.
Larnyx is also sealed of by elevation of the epilgotis.
Physiology of phanyx
Esophangeal: food swallowing by
peristaltic wave. Within 7-10 second
Larnyx
Function
Respiration
Phonation
Effort closure
Swallowing
larnyx
Three large unpaired
cartilages(cricoid,
thyroid and epiglottis)
Smaller cartilage
(arytenoid, corniculate
and cuneiform
Fibroelastic membrane
and numerous intrinsic
muscle
Innervation motory and
sensory of nerve x
Ligaments of Larnyx
Extrinsic ligament(thyrohyoid
membrane,hypoepiglotic membrane
and cricotracheal ligament
Intrinsic ligament (Fibro-elastic
membrane, cricothyroid ligmanent,
quadrogranular membrane)
Cavity of larnyx
Vestibule:larngeal
inlet and vestibular
folds
Middle larngeal :
vestibalr folds and
vocal folds
Infraglotis: vocal
folds and inferior
the opening of the
larynx
Cavity of Larnyx
Ventricles: mucus gland. Menuju
saccule untuk lubrikasi vocal folds
Intrinsic Muscle
Adjust the vocal ligament
Open and close the roma glottidis
Control the inner dimesnion of the
vestibule
closing larngeal inlet
Cricothyroid muscle
Forward and
downward
rotation of the
thyroid
cartilage or
cricothyroid
joint
Posterior crico artyneoid
muscle, primary abductor of
the vocal folds. The primary
openers of the rima glottida
Lateraltcrico arytenoid
muscles: adduction vocal
folds
Transverve arytenoid
muscle adduction of
arytenoid cartilage
Obelique arytenoid muscles:
spincther of laryngeal inlet
Thyro-arytenoid: spinchter
of vestibule and of laryngeal
inlet
Vocalis muscle: laryngeal
inlet
Intrinsic muscle
Tightening of the vocal cords:
posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
closing the glottis:lateral crico
arytedoid ,transverve and obelique
intrarytenoid muscle,thyroarytenoid
muscle
opening glottis: cricothyroid muscle,
thyroarytenoid muscle, vocalis
muscle
Vessels
Superior laryngeal
artery
Inferior laryngeal
artery
Veins
Superior
larngeal
vein,drain into
jugular vein
Inferio larngeal
vein, left
brachiocephalic
vein
Nerve
Superior larngeal nerve
Inferor laryngeal nerve:
sensory laringeal avity
down to the level of
the vocal folds
Reccurent larengal
nerve:Sensory below
the vocal cords, motor:
all the intrinsic muslce
expect for cricothyroid.
Physiology larnyx
Protective mechanism:Reflex closure
of the vocal cords in response
phrangeal swallowing.
Contraction of suprahyoid and
infrayoid muscle elevates larnyngeal
skeleton 2-3cm.
While tongue bulges and press
epilgotis downward, direct the food
bolus pas and behind the larnyx io
esophangeal inlet.
Physiology larnyx
Cough reflex: protect the lower
airway. Glottis closes tightly, allowing
a rise intrathoraic pressure. Rapidly
to allow forceful explusion of the
aspirated material.
Reference
Grays anatomy anatomy for students
thrid edition
Basic otolaryngology: a step by step
learning guide: Thieme
Você também pode gostar
- Parts of The Guitar QuizDocumento2 páginasParts of The Guitar Quizapi-293063423100% (1)
- Prayer Points 7 Day Prayer Fasting PerfectionDocumento4 páginasPrayer Points 7 Day Prayer Fasting PerfectionBenjamin Adelwini Bugri100% (6)
- Partnership Liquidation May 13 C PDFDocumento3 páginasPartnership Liquidation May 13 C PDFElla AlmazanAinda não há avaliações
- Laring Faring FinalDocumento32 páginasLaring Faring FinalJohn ThunderAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture PharynxDocumento28 páginasLecture PharynxHoor AlnabhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Pharyanx IDocumento38 páginasPharyanx Iwaqar khanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusDocumento52 páginasAnatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusYashoda Amarasekera100% (1)
- Throat AnatomyDocumento70 páginasThroat AnatomyMegan ShanzuAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Hypopharynx and LarynxDocumento39 páginasAnatomy of Hypopharynx and LarynxArjun NambiarAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento115 páginasUntitledİpek OMURAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento84 páginasUntitledWardah AliAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of PharynxDocumento27 páginasAnatomy of PharynxParul Gupta100% (2)
- Phraynx FinalDocumento54 páginasPhraynx FinalAbdullah NayyarAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Throat DR Oscar PresentasiDocumento53 páginasAnatomy of The Throat DR Oscar Presentasiharyo wiryantoAinda não há avaliações
- 14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalDocumento50 páginas14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalSudeep DhakalAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology of Pharynx-1Documento44 páginasAnatomy & Physiology of Pharynx-1Emaan NoorAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Respiratory System: Moderator: Dr. Aruna Speaker:Dr - Vipin KR - SinghDocumento69 páginasAnatomy of Respiratory System: Moderator: Dr. Aruna Speaker:Dr - Vipin KR - SinghAnshul JainAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Cranial Nerve Ix and XDocumento12 páginas8 Cranial Nerve Ix and Xwidya tirtaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SystemDocumento54 páginasRespiratory SystemEndin Nokik StujannaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of PharynxDocumento34 páginasAnatomy of PharynxNasr HudaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Nasopharynx: Shajahan.C 51 Batch Medical College CalicutDocumento26 páginasAnatomy of Nasopharynx: Shajahan.C 51 Batch Medical College CalicutRukman Mecca67% (3)
- Anatomy of PharynxDocumento27 páginasAnatomy of PharynxmichelleAinda não há avaliações
- Pharyanx IDocumento28 páginasPharyanx Ij8bhfmc6s9Ainda não há avaliações
- Pharyanx IDocumento13 páginasPharyanx IDaniyar MyrzabekovAinda não há avaliações
- Laryngology, General & Emeregency ORLDocumento96 páginasLaryngology, General & Emeregency ORLalmazmulu76Ainda não há avaliações
- 12 Pharynx DR GosaiDocumento9 páginas12 Pharynx DR GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiAinda não há avaliações
- LarynxDocumento28 páginasLarynxwfvtdpngdtAinda não há avaliações
- (Ent) - Lec5 Anatomy of The Pharynx & Esophagus - GonzalesDocumento25 páginas(Ent) - Lec5 Anatomy of The Pharynx & Esophagus - GonzalesMark Loid Lucero AnlapAinda não há avaliações
- Modul DL MP 4Documento28 páginasModul DL MP 4Mahasiswa StrugleAinda não há avaliações
- PharynxDocumento47 páginasPharynxAchraf RabadiAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Cavity585689409Documento37 páginasOral Cavity585689409mittal.shubham0007Ainda não há avaliações
- BevyDocumento33 páginasBevySaneem AnwerAinda não há avaliações
- Azmath - Anat of PharynxDocumento36 páginasAzmath - Anat of Pharynxjeswanthyelavarthi2Ainda não há avaliações
- Abdomen Engl PDFDocumento51 páginasAbdomen Engl PDFShuler0071Ainda não há avaliações
- Head - Neck Anatomy LectureDocumento91 páginasHead - Neck Anatomy Lecturen42.nayanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of PharynxDocumento31 páginasAnatomy of PharynxMuhammad KamilAinda não há avaliações
- The Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaDocumento22 páginasThe Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaNAND KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Surgery Board NotesDocumento69 páginasPlastic Surgery Board Notesseandarcy600100% (1)
- PHARYNXDocumento75 páginasPHARYNXDr. Janarthanan VAinda não há avaliações
- Alimentary System Till EsophagusDocumento64 páginasAlimentary System Till EsophagusYashfa YasinAinda não há avaliações
- Hard & Soft Palate + InnervationDocumento7 páginasHard & Soft Palate + InnervationSahrish IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderDocumento25 páginasAnatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderFarhan Fader100% (1)
- Anatomy of ESophagusDocumento28 páginasAnatomy of ESophagusAbdur RaqibAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 29 Palate NewDocumento53 páginasChapter 29 Palate NewMohan PalanimalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Pharynx IiDocumento21 páginasPharynx IiHompreetha RajamanickamAinda não há avaliações
- Larynx and TracheaDocumento23 páginasLarynx and Tracheaoreoluwa emmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Anatomy PharynxDocumento35 páginasSurgical Anatomy PharynxDian NivaanAinda não há avaliações
- Ace Achievers: LarynxDocumento5 páginasAce Achievers: LarynxaditryjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of EarDocumento43 páginasAnatomy of Earulfah febyAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract ReseaarchDocumento31 páginasAnatomy of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract ReseaarchOmar Ali AyoubkhanAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System - Kelompok A4Documento102 páginasDigestive System - Kelompok A4Fathoni akbarAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SystemDocumento49 páginasRespiratory SystemVishal SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar 1 Rhinorrhoea Nasal Airway ObstructionDocumento399 páginasSeminar 1 Rhinorrhoea Nasal Airway ObstructionKasey ChaseAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Huma Fatima AliDocumento24 páginasDr. Huma Fatima AliNouman Umar100% (1)
- 5 The Perineum DiyaDocumento35 páginas5 The Perineum DiyaOmotosho DavidAinda não há avaliações
- Nasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEDocumento4 páginasNasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEAnna AyumAinda não há avaliações
- Dev of Hard & Soft PalateDocumento94 páginasDev of Hard & Soft PalatepriyaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharynx Esophagus StomachDocumento18 páginasPharynx Esophagus StomachTakshikaAinda não há avaliações
- (9-2) THT - KL Anatomi 2020Documento88 páginas(9-2) THT - KL Anatomi 2020ayurhrdiniAinda não há avaliações
- Head Neck Face-13 (Larynx and Deep Neck Structures)Documento47 páginasHead Neck Face-13 (Larynx and Deep Neck Structures)spitzmark2030Ainda não há avaliações
- Salivary Glands & PharynxDocumento8 páginasSalivary Glands & Pharynxزين العابدين محمد عويشAinda não há avaliações
- LG 1 (Half - The Salivary Glands)Documento31 páginasLG 1 (Half - The Salivary Glands)allanAinda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to The Laryngitis and Vocal Cord DiseasesNo EverandA Simple Guide to The Laryngitis and Vocal Cord DiseasesAinda não há avaliações
- Orbita: (Malar) Bone, and Maxilla Form A Sturdy Approximately Circular Bony Aperture That IsDocumento1 páginaOrbita: (Malar) Bone, and Maxilla Form A Sturdy Approximately Circular Bony Aperture That IsIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 257: Head Trauma: Introduction and EpidemiologyDocumento35 páginasChapter 257: Head Trauma: Introduction and EpidemiologyIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Neuro Exam - Clinical NeurologyDocumento38 páginasNeuro Exam - Clinical NeurologyIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Komplikasi Kehamilan Awal Dan Definisi Baru Tentang KeguguranDocumento2 páginasKomplikasi Kehamilan Awal Dan Definisi Baru Tentang KeguguranIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- A Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine-NeurologyDocumento40 páginasA Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine-NeurologyIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- A Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine-NeurologyDocumento40 páginasA Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine-NeurologyIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Intra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsDocumento10 páginasIntra Arterial Thrombo Lys IsIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Diskusi Topik EdemaDocumento1 páginaDiskusi Topik EdemaIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism of OedemaDocumento9 páginasMechanism of OedemaIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Thermoregulation PresentationDocumento11 páginasThermoregulation PresentationIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- EdemaDocumento9 páginasEdemaIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism of EdemaDocumento9 páginasMechanism of EdemaIustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous System 4 Feb 2013Documento55 páginasNervous System 4 Feb 2013Iustitia Septuaginta SambenAinda não há avaliações
- FS0008 Toolangi State Forest Walking TrailsDocumento2 páginasFS0008 Toolangi State Forest Walking TrailsMichael ConosAinda não há avaliações
- Tumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneDocumento61 páginasTumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneKartthik ShanmugamAinda não há avaliações
- 06 - Wreak Bodily HavokDocumento40 páginas06 - Wreak Bodily HavokJivoAinda não há avaliações
- Principle of ManagementsDocumento77 páginasPrinciple of ManagementsJayson LucenaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade12 Rigel Group4 Assesing The Solid Waste Management Off Small Foos Store in Gingoog CityDocumento31 páginasGrade12 Rigel Group4 Assesing The Solid Waste Management Off Small Foos Store in Gingoog CityMa. Joan ApolinarAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Mechanical Engineering Si Edition 4Th Edition Wickert Lewis 1305635752 9781305635753 Solution Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasIntroduction To Mechanical Engineering Si Edition 4Th Edition Wickert Lewis 1305635752 9781305635753 Solution Manual Full Chapter PDFwilliam.munoz276100% (13)
- BI410 Plant Developmental BiologyDocumento41 páginasBI410 Plant Developmental BiologyLaisla CagliariAinda não há avaliações
- WeeblyDocumento6 páginasWeeblyapi-302258377Ainda não há avaliações
- Soal Inggris PrintDocumento3 páginasSoal Inggris Printmtsn1okus ptspAinda não há avaliações
- Essay On Stamp CollectionDocumento5 páginasEssay On Stamp Collectionezmt6r5c100% (2)
- Revised Poea Rules and Regulations Governing RecruitmentDocumento8 páginasRevised Poea Rules and Regulations Governing RecruitmenthansAinda não há avaliações
- Intensive Care Fundamentals: František Duška Mo Al-Haddad Maurizio Cecconi EditorsDocumento278 páginasIntensive Care Fundamentals: František Duška Mo Al-Haddad Maurizio Cecconi EditorsthegridfanAinda não há avaliações
- The Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920Documento5 páginasThe Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920Shahid HussainAinda não há avaliações
- RAW TM & HM Users Manual V 11Documento8 páginasRAW TM & HM Users Manual V 11arcangelus22Ainda não há avaliações
- Communique Supply Teacher (Oriental Languages) (Primary) 2021-2022Documento4 páginasCommunique Supply Teacher (Oriental Languages) (Primary) 2021-2022nishiAinda não há avaliações
- Balochistan Civil Servants (Appointment, Promotion and Transfer) Rules 2009 (22222)Documento42 páginasBalochistan Civil Servants (Appointment, Promotion and Transfer) Rules 2009 (22222)Zarak KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Personal FinanceDocumento15 páginasIntroduction To Personal FinanceMa'am Katrina Marie MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Critical LengthDocumento3 páginasCritical LengthRamiro RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 Price ListDocumento17 páginas2014 Price ListMartin J.Ainda não há avaliações
- Contoh DVDocumento5 páginasContoh DVHiruma YoishiAinda não há avaliações
- DRTA-directed Reading Thinking Activity: M. Truscott Staff Development 9-24-10Documento13 páginasDRTA-directed Reading Thinking Activity: M. Truscott Staff Development 9-24-10ehaines24Ainda não há avaliações
- DAA R19 - All UnitsDocumento219 páginasDAA R19 - All Unitspujitha akumallaAinda não há avaliações
- New Tally 3Documento3 páginasNew Tally 3Yashaswini JettyAinda não há avaliações
- Nail DisordersDocumento123 páginasNail DisordersyaraamadoAinda não há avaliações
- CWTS Narrative ReportDocumento10 páginasCWTS Narrative ReportJa Rich100% (1)
- GRP 15 Property Law Final DDocumento15 páginasGRP 15 Property Law Final DBruno OsananAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Analysis CourseDocumento51 páginasTechnical Analysis CourseAkshay Chordiya100% (1)