Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Hpa Hptaxeschart
Enviado por
dikadika_tansDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Hpa Hptaxeschart
Enviado por
dikadika_tansDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
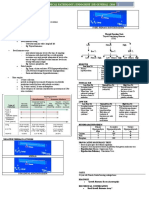
HPA HPT Axes
HPA axis HPT axis
negative
feedback loop
STRESS:
psychological Hypothalamus
traumatic
eltromagnetic
Hypo1 Hyper ecinfectious
allergic TRH
dysbiotic
Hypothalamus enobiotic Pituitary
x
SNS
CRH CRH inhibition
inhibition TSH
Pituitary Thyroid
T4
ACTH ACTH rT3
(competitive inhibition
inhibitor of 5' - deiodinase enzyme
T3) (primarily in liver and
Adrenal kidneys)
cortex T3
medulla (active form
inhibition of the
hormone)
glucocorticoids gluco orticoids
(cortisol) c rtisol)
(co
catecholamines catecholamines
(epinephrine,norepinephrine), (epinephrine,norepinephrine),
aldosterone aldosterone 2003 BioHealth Diagnostics
Given the direct influence of the HPA axis on the HPT axis, adrenal function should always be evaluated when assessing
thyroid function.
Major points:
- Excess CRH inhibits TSH.
- Excess glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) inhibit conversion of the less active T4 to the more active T3.
- Excess high cortisol can result in high output of rT3 which inhibits T3.
Common Acronyms:
HPA Axis = Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis HPT Axis: Hypothalamic Pituitary Thyroid Axis
CRH = Corticotrophic Releasing Hormone ACTH = Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
TRH = Thyroid Releasing Hormone TSH = Thyroid Stimulating Hormone rT3 = Reverse T3
2004 - BioHealth Diagnostics - 2929 Canon St, San Diego, CA 92106
www.biodia.com Phone 800-570-2000 Fax 800-720-7239 Page 1 of 1
Você também pode gostar
- Endocrine PathologyDocumento13 páginasEndocrine Pathologysarguss14100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocumento93 páginasPharmacologyPh SamerAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocumento43 páginasDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Mnemonics For Biochemistry PDFDocumento162 páginasVisual Mnemonics For Biochemistry PDFMahin Rahman100% (2)
- Clinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSDocumento7 páginasClinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleAinda não há avaliações
- The Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkDocumento23 páginasThe Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkMylz MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Hpa HptaxeschartDocumento2 páginasHpa Hptaxeschartdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- 19 Lecture PresentationDocumento65 páginas19 Lecture PresentationLeilaAinda não há avaliações
- Gland of Endocrine System_AVCN2Documento3 páginasGland of Endocrine System_AVCN2Nguyễn Thành DanhAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry of Hypertension: Etiology and TreatmentDocumento44 páginasBiochemistry of Hypertension: Etiology and TreatmentAlberto MayorgaAinda não há avaliações
- Chart of HormonesDocumento2 páginasChart of HormonesspringdingAinda não há avaliações
- Graves' Disease OverviewDocumento1 páginaGraves' Disease OverviewMichael PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhDocumento2 páginasGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhshirleyAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid Dse - SupersummaryDocumento3 páginasThyroid Dse - SupersummaryMissDyYournurseAinda não há avaliações
- Amended Endocrine System SummerDocumento41 páginasAmended Endocrine System SummerKatherineVoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 20 OutlineDocumento54 páginasChapter 20 OutlineIván Cruz DávalosAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento11 páginasEndocrine Systemshannon c. lewisAinda não há avaliações
- 11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - NotesDocumento7 páginas11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - Notesdisha shuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Name: - Date: - Score: - /190 - LevelDocumento2 páginasName: - Date: - Score: - /190 - LevelJielle SantarinAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones 2Documento4 páginasHormones 2den mAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs affecting the Endocrine SystemDocumento4 páginasDrugs affecting the Endocrine SystemJoanna BakAinda não há avaliações
- Control and CoordinationDocumento2 páginasControl and Coordinationcoolsk2580Ainda não há avaliações
- ANS DrugsDocumento68 páginasANS DrugsROSEMARIE ONGAinda não há avaliações
- EAU Pocket On Sexual and Reproductive Health 2023Documento65 páginasEAU Pocket On Sexual and Reproductive Health 2023Alexander Joel Guzmán CórdovaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 24 HormonesDocumento3 páginasLab Report 24 HormonesLyka ElenaAinda não há avaliações
- Anticholinergics: Larissa I. Velez and Sing-Yi FengDocumento5 páginasAnticholinergics: Larissa I. Velez and Sing-Yi FengSAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperthyroidism: Modifiable and Non-Modifiable FactorsDocumento1 páginaHyperthyroidism: Modifiable and Non-Modifiable FactorsAmber BlodduweddAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento5 páginasEndocrine Systemwardahafif00Ainda não há avaliações
- 9 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Endocrinology PDFDocumento56 páginas9 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Endocrinology PDFLalaAinda não há avaliações
- Low Free T4 Normal Free T4 High Free T4Documento3 páginasLow Free T4 Normal Free T4 High Free T4Joseph De JoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Autonomic DrugsDocumento9 páginasAutonomic DrugscrayonAinda não há avaliações
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocumento2 páginasPa Tho PhysiologyArnel Luces BeatoAinda não há avaliações
- TABLE 134 - Antipsychotic MedicationsDocumento2 páginasTABLE 134 - Antipsychotic MedicationsDragutin PetrićAinda não há avaliações
- Bcetal - Psychedelic DrugsDocumento6 páginasBcetal - Psychedelic DrugsMumuji BirbAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Apr 08, 2021Documento7 páginasAdobe Scan Apr 08, 2021Kuldeep YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones Synthesized and Secreted by The Anterior Pituitary and Their EffectsDocumento15 páginasHormones Synthesized and Secreted by The Anterior Pituitary and Their EffectsAaron James RuedasAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases of the Pituitary GlandDocumento8 páginasDiseases of the Pituitary GlandSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioAinda não há avaliações
- The Pituitary Gland and its HormonesDocumento1 páginaThe Pituitary Gland and its HormonesAnonymous wRiKUO07DHAinda não há avaliações
- The Pituitary - Adrenal Axis and Pa Tho Physiology of HyperadrenocorticismDocumento7 páginasThe Pituitary - Adrenal Axis and Pa Tho Physiology of Hyperadrenocorticismtaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- Hypothalamus and The Pituitary LectureDocumento51 páginasHypothalamus and The Pituitary LecturealkalicharanAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocumento32 páginasEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanAinda não há avaliações
- PHYL2001 - Tony's Final Tutorial Questions - 2021 FinalDocumento32 páginasPHYL2001 - Tony's Final Tutorial Questions - 2021 FinalAlisha Rodrigo100% (1)
- Endo PhysioDocumento177 páginasEndo PhysioPahw BaluisAinda não há avaliações
- Manejo Del VómitoDocumento4 páginasManejo Del VómitoDennis J RiosAinda não há avaliações
- Autacoids A4 56Documento2 páginasAutacoids A4 56ahmedsalah565vvvAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrinology ROAMSDocumento12 páginasEndocrinology ROAMSvkAinda não há avaliações
- Pcol Lec Book FinalsDocumento61 páginasPcol Lec Book FinalsMarco Sta AnaAinda não há avaliações
- Endro ReproDocumento55 páginasEndro Reproa.muhsinAinda não há avaliações
- 7. Endocrine GM Eng 2020Documento32 páginas7. Endocrine GM Eng 2020snowrose2609Ainda não há avaliações
- Endocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemDocumento34 páginasEndocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemRezaul RazibAinda não há avaliações
- Coordination: GlandsDocumento11 páginasCoordination: Glandskashish joshiAinda não há avaliações
- Cc1 Pituitary Bookbased SummaryDocumento6 páginasCc1 Pituitary Bookbased SummaryPrecious EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Pituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Documento17 páginasPituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Kiprono Keitany TimothyAinda não há avaliações
- Hipotalamus dan HipofisisDocumento1 páginaHipotalamus dan HipofisisLiana DaniellaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 7 - Drugs Acting On ANSDocumento13 páginasLec 7 - Drugs Acting On ANSمحمد الاسوانيAinda não há avaliações
- SNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Documento5 páginasSNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Whitney Krabbenhoft100% (1)
- Autonomic_nervous_system_07_Class_Notes_MBBS_Prof_2nd_YearDocumento24 páginasAutonomic_nervous_system_07_Class_Notes_MBBS_Prof_2nd_YeardevAinda não há avaliações
- Pendahuluan Mata Kuliah FitoterapiDocumento16 páginasPendahuluan Mata Kuliah FitoterapiQhoissul Saufus salfwaAinda não há avaliações
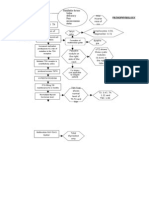
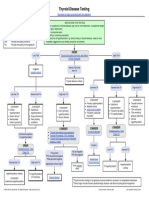
- Thyroid Disease Testing AlgorithmDocumento1 páginaThyroid Disease Testing AlgorithmAnte SalečićAinda não há avaliações
- O26 Ampe O70 KetikanDocumento12 páginasO26 Ampe O70 Ketikandikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- O70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan RevisiDocumento6 páginasO70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisidikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- PEMFIGUS VULGARISDocumento21 páginasPEMFIGUS VULGARISWahyudinAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Pneumonia Kak YunDocumento8 páginasJurnal Pneumonia Kak Yundikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- ICD TanDocumento12 páginasICD Tandikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- 9pomgt PDFDocumento8 páginas9pomgt PDFdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Pre EclampsiaDocumento7 páginasPre Eclampsiadikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- O70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisi AwDocumento6 páginasO70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisi Awdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- N94 Ampe O25 KetikanDocumento6 páginasN94 Ampe O25 Ketikandikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Compromised Patient (Klasifikasi Asa) : Surya Triharsa Andina Novita Sari Lisna Mirna Kuntari Muhamad SyafriDocumento17 páginasCompromised Patient (Klasifikasi Asa) : Surya Triharsa Andina Novita Sari Lisna Mirna Kuntari Muhamad Syafridikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas VATER DKKDocumento33 páginasTugas VATER DKKdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- 234 60 PDFDocumento9 páginas234 60 PDFdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Therapeutic Applications of Punica GranatumDocumento17 páginasTherapeutic Applications of Punica GranatumyigalbyAinda não há avaliações
- 02 5102 PDFDocumento5 páginas02 5102 PDFdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Asli - Kelainan Refraksi - Willy Hartanto - 25-30Documento6 páginas05 Asli - Kelainan Refraksi - Willy Hartanto - 25-30Dinka RoselyAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento6 páginasPDFdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- 18 1312355856 PDFDocumento7 páginas18 1312355856 PDFdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Bab IIDocumento18 páginasBab IIdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- University of California: PostprintsDocumento17 páginasUniversity of California: Postprintsdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Pomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565Documento11 páginasPomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565dikadika_tans0% (1)
- Article1380880456 - Sepulveda Et AlDocumento6 páginasArticle1380880456 - Sepulveda Et Aldikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- PDF 40 Aguilera-Carbo 2008Documento5 páginasPDF 40 Aguilera-Carbo 2008dikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- AC Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid Rich Pomegranate Extract 0n Ultraviolet Pigmentation in The Human SkinDocumento6 páginasAC Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid Rich Pomegranate Extract 0n Ultraviolet Pigmentation in The Human Skindikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Molecules 19 18923Documento13 páginasMolecules 19 18923dikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Junior Mine Environment Engineer - External LocalDocumento1 páginaJunior Mine Environment Engineer - External Localdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Fibroadenoma PDFDocumento2 páginasFibroadenoma PDFAthika Dwi Sofiana100% (1)
- What Is HPA-Axis DysregulationDocumento3 páginasWhat Is HPA-Axis Dysregulationdikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Linear Regression: Definition of TermsDocumento13 páginasSimple Linear Regression: Definition of TermscesardakoAinda não há avaliações
- Ipi 16359Documento9 páginasIpi 16359dikadika_tansAinda não há avaliações