Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
276735
Enviado por
ajmain0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações30 páginasTítulo original
1111128618_276735.ppt
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações30 páginas276735
Enviado por
ajmainDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 30
Engine Sealing, Gaskets, and
Fastener Torque
Chapter 51
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Objectives
Order the correct gaskets for a variety of engine
repair jobs
Explain the theory related to torque and
clamping force
Understand the role that friction plays when
tightening parts
Describe the differences between types of head
gaskets
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Objectives (cont'd.)
Understand the theory behind torque-to-yield
fasteners
Select the correct sealer for use in a variety of
applications
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Introduction
This chapter deals with a very important area
Sealing lubricants and coolants within the engine
Leaks
Unprofessional
Lead to serious mechanical part failures
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Clamping Force
Avoid leaks by applying clamping force on two
parts that are held together
Clamping force results from:
Tension or stretch on bolts securing two pieces
Springiness of a gasket between parts
Clamping force will change if threads are not
clean and undamaged
Cleanliness is very important when assembling
parts
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Torque and Friction
Torque
Measurement of twisting effort required to tighten
a fastener
Amount of fastener clamping force changes with
use of lubricants
90% of torque applied in tightening a fastener is
used to overcome friction
Final 10% provides clamping force
Fastener threads must be sealed and lightly oiled
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Torque Wrenches
Torque is measured with a torque wrench
Types
Beam wrench
Click (spring) wrench
Dial torque wrench
Torque measured in foot-pounds or inch-pounds
Metric measurement is Newton-meter
Digital torque wrenches
More expensive
Purported to be as accurate as dial torque
wrenches
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Torque-to-Yield
Normal head bolt torque values
Calculated safety factor 25% less than maximum
Clamping force is 75% of potential for size
Head bolts
Produce clamping force of 200%
Torque-to-yield
Tighten bolts to within 2% of yield point
Consistent clamping force and fatigue resistant
Work well with aluminum heads
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Torque by Degrees
Torque turn (i.e., torque angle)
Ensures equal tightness of fasteners
Method
Tighten the bolt to specified torque
Turn it additional 35 to 180 degrees
Torque angle gauge
Measures how far a fastener is turned
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Fastener Clamping Load
Preload
Clamping load on a fastener
Ways to measure preload
Torque wrench
Torque angle gauge
Measure bolt stretch
Both ends must be accessible
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Gaskets and Seals
Gaskets: installed between two surfaces to
prevent leaks
Can be purchased individually or in sets
Modern head gaskets: difficult to seal
Non-retorque composite gasket: has facing,
coating, and core
Graphite-faced gaskets: premium
Teflon, moly, or silicone-based antifriction
coating: seals minor surface imperfections
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Gaskets and Seals (contd.)
Metallic head gasket: single and multilayer
Multilayer steel gaskets more common as
cylinder head gaskets
Gasket should be appropriate for surface texture
Surface texture: measured by roughness average
Copper head gaskets
Used for corrosive and high-vibration uses
No-retorque gaskets
Resistant to compression
Bolt stretch does not diminish clamping force
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Cleaning the Head
Clean before assembly
Use sharp scraper to clean iron head and block
Clean aluminum heads with plastic scraper
Abrasive bristle discs can damage engine
Never use with a die grinder
Do not use them on aluminum head with
multilayer steel gasket
Do not use too coarse a grit
Do not clean ghost marks
Do not to clean in one area longer than another
Remove material thrown about by the discs
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Head Gasket Installation
Head gaskets perform most difficult sealing job
Sealing of combustion is very critical
Clamping pressure on bolts greater than
combustion pressure
75% of clamping load on head bolts used to seal
combustion
Match new gasket to old one or to block and
head
Cooling and oil holes do not match up: serious
problems result
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Other Engine Gaskets
Other gaskets are used at several locations in
the engine
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Valve Cover, Timing Cover,
and Oil Pan Service
Valve cover gaskets: molded to shape of cover
Oil pan gaskets: made of several pieces
Sheet metal parts: often become distorted when
tightening bolts
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Valve Cover, Timing Cover,
and Oil Pan Service (cont'd.)
Cork used in vintage applications
Shrinks in the presence of air
Rubberized cork
Does not shrink
Silicone and neoprene gaskets are the best
Expensive, but sometimes reusable
Paper gaskets
Require sealer
Intake manifold gaskets
Must be resistant to air and water leaks
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Valve Cover, Timing Cover,
and Oil Pan Service (cont'd.)
Exhaust manifold gaskets
Not usually found on new cast iron heads
Gaskets used once parts are separated for
service
Bottom of exhaust manifold uses O-ring gasket
Chemical gaskets
Silicone or chemical sealers
Not used for head gasket or fuel systems gasket
Anaerobic sealers cure without air
Used only on precision machine parts
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Gasket Sealers
Gasket sealers purposes
Help gaskets seal
Hold gaskets in place
Substitute for gaskets
hardening gasket cements
Do not use as sealers in automotive applications
Anaerobic adhesive sealers (i.e., threadlockers)
Blue: parts may need disassembly
Red: parts not intended to be disassembled
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Silicone-RTV Sealant
Room temperature vulcanizing (RTV) (i.e.,
silicone rubber)
Cures when exposed to air
Many gaskets can be eliminated by using a bead
of RTV applied by a robot
Sets faster in warm temperatures and high
humidity
Develops skin in 15 minutes
Sets completely in a day
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Silicone-RTV Sealant (cont'd.)
Low-volatile RTV
Used on vehicles equipped with oxygen sensors
High-temperature RTV
Adding iron oxides to RTV increases its
temperature rating by 50-100F
Teflon tape or liquid thread sealer
Threads can be sealed with Teflon tape
Rubber cement sealers
Popular and easy to use
Thicken with exposure to air
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Seals
Dynamic seals (i.e., chevron seals)
Seal moving parts
Seal installation
Several items of concern
Front seals
Usually lip-type seals with a garter spring
Camshaft seals on OHC heads
Located behind camshaft sprocket(s)
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Rear Main Seals
Leaking rear seal
Can destroy a clutch
Newer engines use neoprene lip seal
Be sure crankshaft rear sealing surface is clean
and smooth
Sealer must be applied to flywheel bolts to
prevent oil leakage from interior of oil pan
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Transmission Front Pump Seal
Keeps transmission oil from leaking between
torque converter and transmission oil pump
Becomes brittle with age
If seal fails: transmission fluid leaks from
between engine and transmission
Often replaced as preventative when engine
overhauled
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Você também pode gostar
- 85Documento1 página85ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- SD 08Documento1 páginaSD 08ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- SD.24 Handrial PDFDocumento1 páginaSD.24 Handrial PDFajmainAinda não há avaliações
- SD.20 Structural Concrete Standards Anchor Bolt DetailsDocumento1 páginaSD.20 Structural Concrete Standards Anchor Bolt DetailsajmainAinda não há avaliações
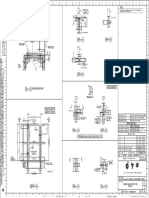
- L L L L: Section Section SectionDocumento1 páginaL L L L: Section Section SectionajmainAinda não há avaliações
- 86Documento1 página86ajmainAinda não há avaliações
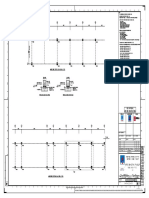
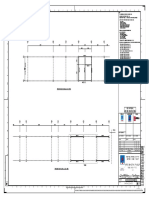
- Steel Supports ListDocumento4 páginasSteel Supports ListajmainAinda não há avaliações
- SD.23 Standard Ladder (Safety Gate)Documento1 páginaSD.23 Standard Ladder (Safety Gate)ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- Method of MeasurmentDocumento3 páginasMethod of MeasurmentajmainAinda não há avaliações
- (B.O.Q) Supply & Install 2Documento2 páginas(B.O.Q) Supply & Install 2ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- STDocumento23 páginasSTajmainAinda não há avaliações
- Free Issue MaterialDocumento1 páginaFree Issue MaterialajmainAinda não há avaliações
- SPEDocumento15 páginasSPEajmainAinda não há avaliações
- S-00-1390-001 Rev 0 (Hot Insulation Specifications For BOP)Documento20 páginasS-00-1390-001 Rev 0 (Hot Insulation Specifications For BOP)ajmain100% (1)
- D 90 1331 203 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 203 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- Piping General Arrangement Cooling Tower Water System AreaDocumento1 páginaPiping General Arrangement Cooling Tower Water System AreaajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 202 RevA PDFDocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 202 RevA PDFajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 211 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 211 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 200 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 200 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- For Construction: Bio-Fuel Ethanol Plant in Northern Region ProjectDocumento24 páginasFor Construction: Bio-Fuel Ethanol Plant in Northern Region ProjectajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 208 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 208 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 202 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 202 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 205 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 205 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D 90 1331 201 RevADocumento1 páginaD 90 1331 201 RevAajmainAinda não há avaliações
- C-90-1323-011 - Rev 0Documento20 páginasC-90-1323-011 - Rev 0ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- C-90-1323-009 - Rev 0Documento21 páginasC-90-1323-009 - Rev 0ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- C-90-1331-200 - Rev 0Documento114 páginasC-90-1331-200 - Rev 0ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- D-90-1331-210 - Rev 0 - Sheet 1 of 2Documento1 páginaD-90-1331-210 - Rev 0 - Sheet 1 of 2ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- C-90-1323-010 - Rev 0Documento46 páginasC-90-1323-010 - Rev 0ajmain100% (1)
- C-90-1323-008 - Rev 0Documento25 páginasC-90-1323-008 - Rev 0ajmainAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Pulse GerminationDocumento21 páginasPulse GerminationChetan KambojAinda não há avaliações
- Refrigeration Cycle, HVAC System Basics and Refrigerant Charging PDFDocumento13 páginasRefrigeration Cycle, HVAC System Basics and Refrigerant Charging PDFMurillo MendesAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Different Ways To Use Hair Oils Curly Hair Care The Wild CurlDocumento1 página4 Different Ways To Use Hair Oils Curly Hair Care The Wild CurlMaria jose MondragonAinda não há avaliações
- Publication PDFDocumento80 páginasPublication PDFakshatjain3001Ainda não há avaliações
- Ok Kadar Abu KencurDocumento7 páginasOk Kadar Abu KencurMuhamad IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- 409 Data BulletinDocumento12 páginas409 Data BulletinWilliam PaivaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 6 12 Microbial Enumeration Tests PDFDocumento5 páginas2 6 12 Microbial Enumeration Tests PDFThao TrangAinda não há avaliações
- G10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekDocumento4 páginasG10 - Handout - Organic - Makeup Handout - First WeekSheela BatterywalaAinda não há avaliações
- Chromatography NotesDocumento25 páginasChromatography NotesGeetha AnjaliAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Corrosion in StructuresDocumento32 páginasEffect of Corrosion in StructuresasvihariAinda não há avaliações
- Installation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyDocumento28 páginasInstallation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyRenārs BērtiņšAinda não há avaliações
- Superalloys - A Primer and HistoryDocumento4 páginasSuperalloys - A Primer and Historyhemakumars100% (1)
- Extraccion 4 PDFDocumento9 páginasExtraccion 4 PDFsergioenriquerozoperAinda não há avaliações
- Culligan MedallistDocumento58 páginasCulligan MedallistskballAinda não há avaliações
- Density MethodDocumento5 páginasDensity MethodMajed DawaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology - Chromatography Lab ReportDocumento7 páginasBiology - Chromatography Lab ReportJuana TestAinda não há avaliações
- Gravimetric Analysis Laboratory ReportDocumento9 páginasGravimetric Analysis Laboratory ReportShawn RizalAinda não há avaliações
- InternshipDocumento16 páginasInternshipSarthak SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Lecture NotesDocumento51 páginasChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Lecture NotesEdith EatonAinda não há avaliações
- 01-0019-01 Flame Methods Manual For AADocumento117 páginas01-0019-01 Flame Methods Manual For AARobert Larry Cordova DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Sarcosine MsdsDocumento41 páginasSarcosine MsdsAnonymous ZVvGjtUGAinda não há avaliações
- Enviromental Toxicity and EvaluationDocumento25 páginasEnviromental Toxicity and EvaluationSalma ShadAinda não há avaliações
- Spesifikasi Material Finishing Unit ApartemenDocumento34 páginasSpesifikasi Material Finishing Unit ApartemenArif GumelarAinda não há avaliações
- DELTA-FC 1022 Tds - EngDocumento2 páginasDELTA-FC 1022 Tds - EngAhmed HassanAinda não há avaliações
- TM 10-4930-220-13PDocumento133 páginasTM 10-4930-220-13PAdvocateAinda não há avaliações
- Structure Based Drug DesignDocumento91 páginasStructure Based Drug DesignMariamAinda não há avaliações
- Bioburden Recovery Method Using Swabbing TechniqueDocumento8 páginasBioburden Recovery Method Using Swabbing TechniquePiruzi MaghlakelidzeAinda não há avaliações
- Sedimentation by David GavinDocumento7 páginasSedimentation by David GavinDavid GavinAinda não há avaliações
- Hofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsDocumento11 páginasHofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsRajeshwari SridharanAinda não há avaliações