Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Industrial Training Report
Enviado por
vhuust0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
40 visualizações14 páginasreport
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoreport
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
40 visualizações14 páginasIndustrial Training Report
Enviado por
vhuustreport
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 14
INDUSTRIAL TRAINING REPORT
Gyan Ganga Institute Of
Technology & Sciences
Submitted by : Vishal Kumar Dubey
0206EC141182
Submitted To : Head of Department
Electronics & Communication Engineering
CONTENTS
Introduction to Indian Railways
RAILNET
PRS & UTS
IVRS
Networking & Interconnection
Indian Railways
Indian Railways is owned and operated by the Government
of India through the Ministry of Railways.
It is the fourth largest railway network in the world
comprising 119,630 km of total track and 92,081 km of
running track over a route of 66,687 km with 7,216 stations
at the end of 2015-16.
IR is the world's eighth biggest employer and had 1.331
million employees at the end of 2015-16. In 2015-16, IR
carried around 8.107 billion passengers annually.
RAILNET
RAILNET is the name of the Corporate Wide Information
System (CWIS) of Indian Railways, aimed to provide
computer connectivity between Railway Board, Zonal
Railways, Production Units, Training Institutes, CORE,
etc.
RAILNET was commissioned by IRCOT (Indian Railways
Central Organization of Telecom) through a contract
agreement with Tata – Infotech.
INTRA-NET: It is a digitized internal network allowing
the railway officers and staff to communicate.
INTER-NET: Allows user to get into global comm.
Through world wide web (www) , in a secured manner.
Passenger Reservation Service
PRS started in 1985 as a pilot project in New Delhi. The
objective was to provide ticketing system for reserved
accommodation on any train from any counter,
preparation of train charting and keeping a proper
record of the money received. This was implemented all
over Indian Railway later on.
With this implementation any passenger can get a
reserved ticket from one destination to another station
of India Railway from any Passenger Reservation
Systems counter of Indian Railways.
Unreserved Ticketing System
More than 1.2 crore Rail
passengers travel in
unreserved coaches and
trains every day and thus
form the bulk of rail
users. For this category
of passengers Railways
have introduced the
facility of Computerised
Unreserved Ticketing
System.
Interactive Voice Response System
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) is a software
application that accepts a combination of voice
telephone input and touch-tone keypad selection and
provides appropriate responses in the form of voice, fax,
callback, e-mail and perhaps other media.
An IVR application provides pre-recorded voice
responses for appropriate situations, keypad signal logic,
and access to relevant data, and potentially the ability
to record voice input for later handling.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems allow callers to
get access to information without human intervention. Thus
callers hear a pleasant and cheerful voice 24-hours a day, 7
days a year without any attendant human fatigue.
Since even the cost of the call is borne by the caller, apart
from the one-time installation cost, there is no running
expense for the company who deploys the IVR systems.
Another advantage to the company is that it would
otherwise be impossible to handle high loads of callers, both
in terms of time, and the cost of the large number of
individuals that it would require.
Network Devices & Topologies
UTP : Short for unshielded twisted pair, a
popular type of cable that consists of
two unshielded wires twisted around each
other. Due to its low cost, UTP cabling is
used extensively for local-area networks
(LANs) and telephone connections.
UTP cabling does not offer as high
bandwidth or as good protection from
interference as coaxial or fiber optic
cables, but it is less expensive and easier
to work with.
A repeater is a physical layer device used to
interconnect the media segments of an extended
network. Repeaters receive signals from one network
segment and amplify, retime, and retransmit those
signals to another network segment.
Bridges connect two LAN segments of similar or
dissimilar types, such as Ethernet and Token Ring. This
allows two Ethernet segments to behave like a single
Ethernet.
A router is a device that forwards data packets along
networks, and determines which way to send each data
packet based on its current understanding of the state
of its connected networks.
Conclusion
Practical training is very important for each and every
student along with the theoretical knowledge.
Thank you.
Você também pode gostar
- Industrial TrainingDocumento17 páginasIndustrial TrainingAKSHAT TIWARIAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Rail Signaling and Telecom ReportDocumento33 páginasIndian Rail Signaling and Telecom ReportGunjan GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- PresentationDocumento16 páginasPresentationMudir TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- SaurabhDocumento19 páginasSaurabhSaurabh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and Telecommunicaton Engineering Divisional Railway Manager Office, JhansiDocumento43 páginasSignal and Telecommunicaton Engineering Divisional Railway Manager Office, JhansiMudir TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Summer Training Project Presentation OnDocumento18 páginasSummer Training Project Presentation OnJaisa Ram Patel JPAinda não há avaliações
- Railway DhruvDocumento41 páginasRailway DhruvKartikAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Signal & Telecom in Ensuring Safety and ConnectivityDocumento11 páginasRole of Signal & Telecom in Ensuring Safety and ConnectivityNitesh Kumar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Railway Systems OverviewDocumento26 páginasRailway Systems OverviewHimanshu Nainpuriya100% (1)
- A Project Report On: Submitted By: Manish Gupta Manish ChauhanDocumento72 páginasA Project Report On: Submitted By: Manish Gupta Manish Chauhanlove_amyAinda não há avaliações
- Indian RailwayDocumento19 páginasIndian RailwayDaksh AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Create: Case Study Exploit New Opportunities For BroadbandDocumento9 páginasCreate: Case Study Exploit New Opportunities For BroadbandHozefa bohraAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Railways: Practical Training Seminar OnDocumento18 páginasIndian Railways: Practical Training Seminar OnMohammad Shakeer HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Railway TrainingDocumento25 páginasIndian Railway TrainingJayant Soni57% (7)
- Optical Transmission and SDH Training ReportDocumento23 páginasOptical Transmission and SDH Training ReportAvissh MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- MTRC TRAIN COMMUNICATION REPORTDocumento53 páginasMTRC TRAIN COMMUNICATION REPORTMayank Krishnan75% (4)
- Signal and Telecom: SignallingDocumento3 páginasSignal and Telecom: SignallingRahul SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Network Management System: Submitted by Guru Vashist 0830531011 E.C. Vii SemDocumento46 páginasNetwork Management System: Submitted by Guru Vashist 0830531011 E.C. Vii SemGuru VashistAinda não há avaliações
- Project ReportDocumento16 páginasProject ReportMukesh BishtAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Ad Hoc NetworkingDocumento11 páginasMobile Ad Hoc NetworkingSana JavedAinda não há avaliações
- An Intelligent Transportation System UsiDocumento8 páginasAn Intelligent Transportation System Usiluiseduardoaraujo91Ainda não há avaliações
- Next Generation Train Control and Management SystemDocumento3 páginasNext Generation Train Control and Management SystemJay PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Iptv in Vanet'S With Wimax Access NetworkDocumento6 páginasIptv in Vanet'S With Wimax Access NetworkAditya WijayantoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Indian Railway: Submitted by Himanshu Mahendru 1003331816Documento18 páginasPresentation On Indian Railway: Submitted by Himanshu Mahendru 1003331816Sudhanshu RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Cordect TechnologyDocumento22 páginasReport On Cordect TechnologyAnkush JamthikarAinda não há avaliações
- Networking in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANET) For Accident PreventionDocumento9 páginasNetworking in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANET) For Accident PreventionIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Automation and Robotics Week 03 Theory Notes 20ME51IDocumento23 páginasAutomation and Robotics Week 03 Theory Notes 20ME51IThanmay JSAinda não há avaliações
- DMRC ReportDocumento15 páginasDMRC ReportShreya ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Traffic Signal Preemption For Emergency PDFDocumento6 páginasTraffic Signal Preemption For Emergency PDFSimona NicoletaAinda não há avaliações
- Telecommunications NetworkDocumento3 páginasTelecommunications NetworkVíctor Alfonso Medina LugoAinda não há avaliações
- Study On 4G Communication Architecture Components For Social NetworksDocumento5 páginasStudy On 4G Communication Architecture Components For Social NetworksNithya GopikrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Internship ReportDocumento12 páginasInternship ReportnosherwanAinda não há avaliações
- v64 23Documento4 páginasv64 23srikandiujungAinda não há avaliações
- Final INTERNSHIP Report-AshishDocumento66 páginasFinal INTERNSHIP Report-AshishAshish PantAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6 - Reading3 - TelecommunicationNetworkDocumento5 páginasModule 6 - Reading3 - TelecommunicationNetworkChristopher AdvinculaAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Training at AirtelDocumento65 páginasIndustrial Training at AirtelShiv Kumar Chauhan100% (1)
- 14457Documento3 páginas14457SafirinaFebryantiAinda não há avaliações
- corDECT Wireless Access System OverviewDocumento48 páginascorDECT Wireless Access System Overview14_swapnil_14Ainda não há avaliações
- An Efficient Mobile Gateway Selection and Discovery Based-Routing Protocol in Heterogeneous Lte-Vanet NetworksDocumento23 páginasAn Efficient Mobile Gateway Selection and Discovery Based-Routing Protocol in Heterogeneous Lte-Vanet NetworksAIRCC - IJCNCAinda não há avaliações
- Railways Communication System: A Report OnDocumento16 páginasRailways Communication System: A Report Onpurvakhanna915851Ainda não há avaliações
- Telecommunication AbstractDocumento15 páginasTelecommunication AbstractAman SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- IJSRD - Performance of OLSR Routing Protocol in MANETDocumento5 páginasIJSRD - Performance of OLSR Routing Protocol in MANETFatima Zahra LeAinda não há avaliações
- Network AssignmentDocumento8 páginasNetwork Assignmentmohammed BiratuAinda não há avaliações
- DMRC CSDocumento5 páginasDMRC CSJencyAinda não há avaliações
- Comp 103 MauDocumento9 páginasComp 103 MauMiaca MishaAinda não há avaliações
- Intelligent NetworksDocumento5 páginasIntelligent Networksdilush ranathunge RanathungeAinda não há avaliações
- Passenger Reservation System OverviewDocumento22 páginasPassenger Reservation System OverviewlvsaruAinda não há avaliações
- Compusoft, 3 (6), 985-993 PDFDocumento9 páginasCompusoft, 3 (6), 985-993 PDFIjact EditorAinda não há avaliações
- Maharishi Arvind College of Engineering & Technology, Kota Railway ProjectDocumento21 páginasMaharishi Arvind College of Engineering & Technology, Kota Railway ProjectNilesh Kumar ParjapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Monthly Report 2Documento22 páginasMonthly Report 2khalid hussenAinda não há avaliações
- Incredible India - Presentation on the History and Growth of the Internet in IndiaDocumento3 páginasIncredible India - Presentation on the History and Growth of the Internet in IndiaSurajit RoyAinda não há avaliações
- ISGF White Paper On Next Generation Smart Metering - IP MeteringDocumento10 páginasISGF White Paper On Next Generation Smart Metering - IP MeteringDipankar GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- 1 102 1 PBDocumento7 páginas1 102 1 PBThành Nguyễn BáAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and Telecommunication Workshop-2Documento13 páginasSignal and Telecommunication Workshop-2Sarath Kumar100% (1)
- Inplant Training AT BSNL, Chennai: Aswinkumar.R Ece 3Rd YearDocumento33 páginasInplant Training AT BSNL, Chennai: Aswinkumar.R Ece 3Rd YearAshaAinda não há avaliações
- Design of SCS Protocol and Analysis of Quality of Service in Wireless Sensor NetworksDocumento5 páginasDesign of SCS Protocol and Analysis of Quality of Service in Wireless Sensor NetworksChitra RAinda não há avaliações
- A Step of Mobile Ad-Hoc On-Demand Routing Protocols Towards 4G Cellular NetworksDocumento5 páginasA Step of Mobile Ad-Hoc On-Demand Routing Protocols Towards 4G Cellular Networksghabr2000Ainda não há avaliações
- The Evolution of Computer NetworksDocumento6 páginasThe Evolution of Computer NetworksTiffany PriceAinda não há avaliações
- Implementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkNo EverandImplementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Kavach: Cab Signalling & Automatic Train Protection System for Digital RailwaysNo EverandKavach: Cab Signalling & Automatic Train Protection System for Digital RailwaysAinda não há avaliações
- ConclusionDocumento1 páginaConclusionvhuustAinda não há avaliações
- Control Communication, Railnet, Power Supply System & ExchangeDocumento3 páginasControl Communication, Railnet, Power Supply System & ExchangevhuustAinda não há avaliações
- Positive DifferentialDocumento3 páginasPositive DifferentialvhuustAinda não há avaliações
- PercentagesDocumento12 páginasPercentagesvhuustAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Railways ReportDocumento57 páginasIndian Railways ReportRitesh MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Manoj KR Das Tata-HwhDocumento3 páginasManoj KR Das Tata-HwhManoj DasAinda não há avaliações
- Project On EMPLOYEES WELFARE MEASURESDocumento77 páginasProject On EMPLOYEES WELFARE MEASURESLenin Nd82% (187)
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service (Agent) Electronic Reservation SlipDocumento2 páginasIrctcs E-Ticketing Service (Agent) Electronic Reservation SlipaltafskAinda não há avaliações
- Railway Engineering PDFDocumento6 páginasRailway Engineering PDFMadhu Kumar100% (1)
- Railway Budget 2015-16 Key HighlightsDocumento16 páginasRailway Budget 2015-16 Key HighlightsSheeba Singh RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Whitemanual 2013Documento305 páginasRevised Whitemanual 2013neelesh2k5Ainda não há avaliações
- Vocational Training Report 2018Documento38 páginasVocational Training Report 2018Sameer Bara50% (2)
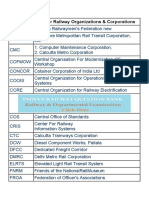
- Abbreviations For Railway Organizations & CorporationsDocumento39 páginasAbbreviations For Railway Organizations & Corporationsshiv kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-1 State of Finances: 1.1 Summary of Current Year's Fiscal TransactionsDocumento26 páginasChapter-1 State of Finances: 1.1 Summary of Current Year's Fiscal TransactionsANURAJM44Ainda não há avaliações
- Irctc Ar 2019-20Documento244 páginasIrctc Ar 2019-20Nikhil AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Transport and Communication: Presented by Akshay Lajpal Class VII B'Documento19 páginasTransport and Communication: Presented by Akshay Lajpal Class VII B'bharatAinda não há avaliações
- Loco Diesel Shed PuleraDocumento23 páginasLoco Diesel Shed PuleraAnupamAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Rail Reservation Database Systemit ProjectDocumento24 páginasIndian Rail Reservation Database Systemit ProjectAvinash85% (40)
- Indian Railways-The Backbone of Service SectorDocumento10 páginasIndian Railways-The Backbone of Service SectorRadhakrishnan KrishnamoorthyAinda não há avaliações
- IRSTE Emerging Trends in Indian Railway Signalling Seminar BookDocumento325 páginasIRSTE Emerging Trends in Indian Railway Signalling Seminar BookRuve Baba91% (11)
- Foundation of RaceDocumento7 páginasFoundation of RacetilakdhariAinda não há avaliações
- JMRC Vacancy Circular For DeputationDocumento20 páginasJMRC Vacancy Circular For DeputationSumit AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome To Indian Railway Passenger Reservation EnquiryDocumento1 páginaWelcome To Indian Railway Passenger Reservation Enquiryrakhikishore143Ainda não há avaliações
- Indian Railways: Circular Journey Tickets FARE TABLE (Distance-Wise)Documento5 páginasIndian Railways: Circular Journey Tickets FARE TABLE (Distance-Wise)Abhijit Tulsankar100% (1)
- RDSO 2008 CG-04 (Rev.-5) - Final Draft - Final PDFDocumento31 páginasRDSO 2008 CG-04 (Rev.-5) - Final Draft - Final PDFNeeraj Bansal100% (1)
- SEM III ElectiveDocumento9 páginasSEM III ElectivePrashant GaradAinda não há avaliações
- Consumer BehaviourDocumento16 páginasConsumer BehaviourAbhishekGuptaAinda não há avaliações
- R3i Policy Indian RailwaysDocumento8 páginasR3i Policy Indian RailwayssatishanushaAinda não há avaliações
- Train 18Documento18 páginasTrain 18Diptanu DasAinda não há avaliações
- Signal & Telecom Systems OverviewDocumento5 páginasSignal & Telecom Systems OverviewMonuAinda não há avaliações
- IRS Specification For Composite GRSP (6.2mm Thick) With Amendment 2 of 2017Documento27 páginasIRS Specification For Composite GRSP (6.2mm Thick) With Amendment 2 of 2017RAJKUMARIAinda não há avaliações
- Economics For 2nd PUC - ToPIC 6Documento22 páginasEconomics For 2nd PUC - ToPIC 6Vipin Mandyam KadubiAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On Consumer Satisfaction With Regards To Service Quality of Indian RailwaysDocumento97 páginasA Study On Consumer Satisfaction With Regards To Service Quality of Indian RailwaysNeeraj BaghelAinda não há avaliações
- Jhajha Railway StationDocumento1 páginaJhajha Railway StationatewarigrAinda não há avaliações