Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Erosion - Corrosion
Enviado por
Lakshman Tumpati0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações18 páginascorrosion mechanisms
Título original
Corrosion
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentocorrosion mechanisms
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações18 páginasErosion - Corrosion
Enviado por
Lakshman Tumpaticorrosion mechanisms
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 18
Erosion - corrosion
• Damage that occurs when corrosion contributes
to erosion by removing protective films/scales or
by exposing metal surface to further corrosion
under combined action of erosion and corrosion.
• Metals,alloys,refractories
• Metal loss rates depend on velocity and
concentration of impacting medium, impacting
articles size and hardness, angle of impact,
hardness and corrosion resistant of material
subject to corrosion.
• Softer alloys of CU,AL subject to metal loss under
high velocity conditions
• For each environment and metal condition,
threshold velocity above which impacting
medium produce metal loss
• Metal loss depends on
size,shape,density,hardness of impacting medium
• Metal removed from surface as dissolved ions or
solid corrosion products which are swept away
from metal surface
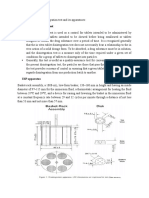
Affected Equipment
• Equipment exposed to moving fluids/catalyst
• Piping particularly at bends,elbows,pumps,blowers,heat
exchanger tubing,propellers,impellers,turbine blades,nozzles
• erosion by particles carried by liquid (slurry) like catalyst
movement in FCC,coke handling equipment in fluidized bed
cokers
• Crude unit piping exposed to naphthenic acids,sulfur content
Appearance
• Erosion-corrosion seen by loss in thickness in
form of pits,groove,rounded holes and valleys
prevention
• Increase pipe diameter to decrease velocity,
streamlining bends to reduce
impingement,increase wall thickness
• increase substrate thickness (hard alloys),surface
hardening treatments
• Alter process environment to reduce corrosivity
(deaeration)
• Heat exchangers use impingement plates to
minimize erosion
• High Mo contain alloys to improve resistant to
naphthenic acid corrosion
Inspection
• Visual examination,UT checks
• IR scans to detect refractory loss on stream
Erosion-corrosion: Mechanism
• Cavitation,liquid impingemen erosion,fretting
Corrosion under insulation (CUI)
• Steel pipe-protective coating-insulation-
weather barrier
• Corrosion of piping,pressure vessels,structural
components from water trapped under
insulation
• Carbon steel,low alloy steel,300 ss,duplex
stainless steel
• Affects- -12 c to 175 c for carbon and low alloy
steel; 60c to 205c stainless steel
• CUI increases with increase metal
temperature, severe at 100 c 120 c where
water vaporize and insulation stays wet longer
• Insulation material which hold water not used
• Equipment operates below water dewpoint
condense water increase cui
• Environments contain air contaminants as
chlorides,so2 inc cui
appearance
• Carbon and low alloy steels – local
pitting,localised loss in thickness
• 300 SS subject to stress corrosion cracking,if
chlorides are present, duplex ss less
susceptible
prevention
• Use paints/coatings, maintain insulation
barriers to prevent moisture enter
• Flame sprayed Al coatings use on carbon
steels- coating corrodes preferentially by
gakvanic action and protects base metal
• Al foil wrapped in SS pipes
Chloride stress corrosion cracking
(SCC)
• Surface initiated cracks caused by envionmental
cracking of 300 SS, Ni based alloy due to tensile
stress,temperature,aqueous chloride environment.
• Dissolved oxygen presence inc cracking
• 300 SS – suspectible, duplex ss – more resistant
• Inc temp,inc chloride – inc cracking
• SCC occurs at pH above 2
• Ni based alloys- highly resistant but not immune
Affected eqipment
• 300 ss piping,pressure vessel components,
• Drains in hydro processing units,bellows and
instrument tubing with hydrogen recycle
streams affected
• Cracking in boiler drain lines
appearance
• Cracks appear on surface
• Fracture surface have brittle appearance
prevention
• Use resistant material for construction
• When hydrotesting use low cl content water
• Design should not allow stagnant regionwhere
chloride can depoist
Hydrochloric acid corrosion
• Vapors containing water and hcl condense from
overhead stream of distillation,fractionation
tower,first water condense is highly acidic and
promote high corrosion rates
• Hcl concentration inc ,temp inc , inc
corrosion,alloy composition
• HCl is normally not corrosive but very corrosive
where water is available to hcl acid
• Carbon steel,low alloy steels excess corrosive
when ph below 4.5
• 300 ss not resistant to any hcl level
Affected equipment
• Crude unit,hydro processing units,catalytic
reforming units
Wet h2s damage (blistering)
• Hydrogen blistering
Form as surface bulges on ID,OD of
pipe/pressure vessel,
• Hydrogen induced cracking
• Stress oriented hydrogen induced cracking
• Sulfide stress cracking
Você também pode gostar
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler tube failures causes and solutionsDocumento43 páginasBoiler tube failures causes and solutionsProsenjit Ghosh100% (3)
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelAinda não há avaliações
- MCE328 - Pipeline CorrosionDocumento74 páginasMCE328 - Pipeline CorrosionM PAinda não há avaliações
- Sexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicNo EverandSexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicAinda não há avaliações
- CorrosionDocumento42 páginasCorrosionhector vansAinda não há avaliações
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesAinda não há avaliações
- Failur of Boiler TubesDocumento71 páginasFailur of Boiler TubesHari100% (1)
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonAinda não há avaliações
- The Forms of Corrosion-Part2Documento71 páginasThe Forms of Corrosion-Part2quiron2010100% (1)
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion Protection Methods for Steel Reinforced ConcreteDocumento23 páginasCorrosion Protection Methods for Steel Reinforced ConcreteMohammad AL HaririAinda não há avaliações
- Blacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithNo EverandBlacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3. Corrosion of MetalsDocumento48 páginasChapter 3. Corrosion of MetalsEjaj Siddiqui100% (2)
- Boiler (Steam Generation) KSDocumento25 páginasBoiler (Steam Generation) KSBangun WijayantoAinda não há avaliações
- Bab 5 - Corrosion by WaterDocumento22 páginasBab 5 - Corrosion by WaterFachry Hafidz AhmadiAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroprocessing Units CorrosionDocumento49 páginasHydroprocessing Units CorrosionAvinawAinda não há avaliações
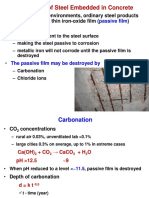
- Corrosion of Steel Embedded in Concrete: Are Covered by A Thin Iron-Oxide FilmDocumento10 páginasCorrosion of Steel Embedded in Concrete: Are Covered by A Thin Iron-Oxide FilmSteven KuaAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion in Oil GasDocumento108 páginasCorrosion in Oil Gaslaz_k100% (1)
- Corrosion and Its TypesDocumento68 páginasCorrosion and Its TypesBilal AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion and Its TypesDocumento68 páginasCorrosion and Its Typeshafiz ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Tube Failures: Pradip PatelDocumento69 páginasBoiler Tube Failures: Pradip PatelVishnu ParvandaAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosive Damage in Metals and Its PreventionDocumento36 páginasCorrosive Damage in Metals and Its Preventionsamurai7_7783% (6)
- Lecture 2Documento49 páginasLecture 2Meshack NyitiAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion Under Insulation in Process IndustryDocumento30 páginasCorrosion Under Insulation in Process IndustryWILLIAM100% (1)
- Material SelectionDocumento44 páginasMaterial SelectionFebbyOktaviaAinda não há avaliações
- Steve Mcintyre, Boiler Tube Failures-Nace 2006 Read-OnlyDocumento83 páginasSteve Mcintyre, Boiler Tube Failures-Nace 2006 Read-OnlyLeire MeigaAinda não há avaliações
- Casting 119 - EndDocumento39 páginasCasting 119 - EndVarun AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Degradation: Understanding Corrosion and its FormsDocumento18 páginasMaterials Degradation: Understanding Corrosion and its FormsAustin Okoth OmondiAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrogen PresentationDocumento57 páginasHydrogen Presentationkamal615Ainda não há avaliações
- Galvanic, Concentration and Pitting CorrosionDocumento42 páginasGalvanic, Concentration and Pitting CorrosionLeeMayYanAinda não há avaliações
- CY-008 Lecture - Corrosion - Cy008 - April2014Documento31 páginasCY-008 Lecture - Corrosion - Cy008 - April2014akashAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion Protection Methods for SteelDocumento21 páginasCorrosion Protection Methods for SteelShruti SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Api 571 NotesDocumento22 páginasApi 571 NotesAMN zd100% (9)
- Metal Casting ProcessesDocumento55 páginasMetal Casting ProcessesSajailslhuti JilluAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Casting Processes ExplainedDocumento55 páginasMetal Casting Processes ExplainedMuhammad MajidAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion - Erossion: Ulhas ThakurDocumento14 páginasCorrosion - Erossion: Ulhas ThakurmkkamarajAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Protective Measures Against CorrosionDocumento38 páginasUnit 3 Protective Measures Against CorrosionmohamadkamarudeenAinda não há avaliações
- Scaling in BoilersDocumento12 páginasScaling in BoilersVikneswaran BalakrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler MaintenanceDocumento42 páginasBoiler MaintenanceJose Manuel FreitasAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Corrosion Cracking in Refunery Pipework and VesselsDocumento34 páginasStress Corrosion Cracking in Refunery Pipework and VesselsBOB100% (2)
- Corrosion: IntroducingDocumento29 páginasCorrosion: Introducingkeval patelAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Water Treatment and TestDocumento56 páginasBoiler Water Treatment and TestRayhaan Ahmed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion Testing D Rossi CathodicDocumento63 páginasCorrosion Testing D Rossi CathodicRahmat MohsinAinda não há avaliações
- Ladle Refining Melting ProcessDocumento14 páginasLadle Refining Melting ProcessSudeepAinda não há avaliações
- Alloy & Special SteelsDocumento33 páginasAlloy & Special Steelstanishka narayanAinda não há avaliações
- Rusting of Reinforcemen T Bars: A Challenge To OvercomeDocumento13 páginasRusting of Reinforcemen T Bars: A Challenge To OvercomeOchini ChandrasenaAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Tube Failures Causes and ControlsDocumento20 páginasBoiler Tube Failures Causes and ControlsParmeshwar Nath Tripathi100% (1)
- Metal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material ScienceDocumento49 páginasMetal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material Sciencedr nfAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion Prevention Materials SelectionDocumento106 páginasCorrosion Prevention Materials SelectionFachry Hafidz AhmadiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Corrosion Assessment and ManagementDocumento27 páginasIntroduction To Corrosion Assessment and ManagementMohamad Faeze100% (1)
- Chapter 15 - Coatings-1Documento32 páginasChapter 15 - Coatings-1Sumit Ghosh KabboAinda não há avaliações
- Detecting Susceptibility To Intergranular Corrosion: Seminar ONDocumento12 páginasDetecting Susceptibility To Intergranular Corrosion: Seminar ONDevashish JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Tube FailuresDocumento83 páginasBoiler Tube Failuressen_subhasis_5867% (3)
- Corrosion and Tuberculation in Iron PipesDocumento3 páginasCorrosion and Tuberculation in Iron PipesAsad100% (1)
- Study Material - CorrosionDocumento10 páginasStudy Material - CorrosionIScourse materialAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 3 Lec 8Documento16 páginasMod 3 Lec 8The Layman TheoryAinda não há avaliações
- Final Corrosion Science Trimester-IDocumento60 páginasFinal Corrosion Science Trimester-IKISHAN SHUKLAAinda não há avaliações
- Forms of Corrosion: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotDocumento17 páginasForms of Corrosion: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotAnonymous NxpnI6jCAinda não há avaliações
- OISD-118: Layouts For Oil and Gas InstallationsDocumento21 páginasOISD-118: Layouts For Oil and Gas InstallationsLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- SOP BioreaktorDocumento17 páginasSOP BioreaktorElma PuspaningtyasAinda não há avaliações
- New Figo BrochureDocumento12 páginasNew Figo BrochureLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Brio BrochureDocumento2 páginasBrio BrochureLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Boiling Condensation and Two Phase FlowDocumento4 páginasBoiling Condensation and Two Phase FlowLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- 31 Screw Threads and Gear Manufacturing MethodsDocumento17 páginas31 Screw Threads and Gear Manufacturing MethodsPRASAD326100% (8)
- Capability PDFDocumento34 páginasCapability PDFLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About Fired HeatersDocumento9 páginasEverything You Need to Know About Fired HeatersLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Application Engineer WorkDocumento1 páginaApplication Engineer WorkLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- 60 Sudokus Pattern DifficultDocumento10 páginas60 Sudokus Pattern DifficultYogi GustriansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Bme059unit 1Documento20 páginasBme059unit 1Mukesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- No Dues Report FormDocumento1 páginaNo Dues Report FormLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- 32 Screw Threads and Gear Manufacturing MethodsDocumento21 páginas32 Screw Threads and Gear Manufacturing MethodsquockhanhspktAinda não há avaliações
- AnswersDocumento1 páginaAnswersLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Keys, Couplings & Gear DesignDocumento3 páginasKeys, Couplings & Gear DesignLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- AnsysDocumento18 páginasAnsysmechanical engineering100% (12)
- No Dues Report FormDocumento1 páginaNo Dues Report FormLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Workbench Tutorial AirfoilDocumento10 páginasWorkbench Tutorial Airfoilfab1991Ainda não há avaliações
- Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) Bangalore, India: Application FormDocumento2 páginasIndian Space Research Organisation (Isro) Bangalore, India: Application FormLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Calender Jan - May 2014 Semester26.12.2013Documento2 páginasAcademic Calender Jan - May 2014 Semester26.12.2013Krishnan ChockalingamAinda não há avaliações
- Insti FeesDocumento1 páginaInsti FeesLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- A122 Z89 Admit CardDocumento1 páginaA122 Z89 Admit CardLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Boiling Condensation and Two Phase FlowDocumento4 páginasBoiling Condensation and Two Phase FlowLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Resume TemplateDocumento3 páginasStandard Resume TemplateLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Timetable - Indian Institute of Technology MadrasDocumento3 páginasTimetable - Indian Institute of Technology MadrasLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- Cost of GI Pipe Vs Diameter: Diameter in In. Diameter in MM Cost in INRDocumento1 páginaCost of GI Pipe Vs Diameter: Diameter in In. Diameter in MM Cost in INRLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- CAD Drawing of Proposeddb DesignDocumento1 páginaCAD Drawing of Proposeddb DesignLakshman TumpatiAinda não há avaliações
- ảnh hưởng của stress mặn đối với lúaDocumento18 páginasảnh hưởng của stress mặn đối với lúa20.Nguyễn Hà MyAinda não há avaliações
- 03 - 120803 Hot Melt Extrusion With BASF Pharma PolymersDocumento201 páginas03 - 120803 Hot Melt Extrusion With BASF Pharma PolymersMoeen Khan Risaldar100% (1)
- Biomass EnergyDocumento12 páginasBiomass Energydgagan22Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia UniversityDocumento38 páginasChapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia Universitybeyond1241Ainda não há avaliações
- Test Certificate: Ferro Steel SolutionDocumento1 páginaTest Certificate: Ferro Steel SolutionNeeraj Singh100% (4)
- CPCB SOPs Utilization Spent Alkali Bromide Manufacturing Recovery BromineDocumento11 páginasCPCB SOPs Utilization Spent Alkali Bromide Manufacturing Recovery Brominekrunal soniAinda não há avaliações
- Environment Impact AssessmentDocumento11 páginasEnvironment Impact AssessmentBimal AntonyAinda não há avaliações
- MentholsDocumento296 páginasMentholsrachelsantoso5259Ainda não há avaliações
- Reliance Water Controls Hoseguard Bib Tap WRAS 1999 HTAP218001 520-041-0003Documento2 páginasReliance Water Controls Hoseguard Bib Tap WRAS 1999 HTAP218001 520-041-0003AdvancedWaterCompanyAinda não há avaliações
- LWAASHJSPLANGULDocumento5 páginasLWAASHJSPLANGULAmiy SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Fosroc Structuro W435: Constructive SolutionsDocumento2 páginasFosroc Structuro W435: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateAinda não há avaliações
- 07 Circulating Systems-1Documento19 páginas07 Circulating Systems-1ScarduelliAinda não há avaliações
- Section 5 - Concrete PavementDocumento18 páginasSection 5 - Concrete PavementLipSingCheong100% (2)
- Everest Fibre Cement Boards: Durable Building MaterialDocumento2 páginasEverest Fibre Cement Boards: Durable Building MaterialSTRUCTURAL ENGG DEPT TDLCCSAinda não há avaliações
- 3300 XL Ceramic Capped Probe 172932Documento9 páginas3300 XL Ceramic Capped Probe 172932Cecep AtmegaAinda não há avaliações
- GroupIV WSDocumento14 páginasGroupIV WSMaryam RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Balance For A MultiDocumento12 páginasEnergy Balance For A MultiAwoluyi TolaAinda não há avaliações
- Investigating Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Levels in Inhaled and Exhaled AirDocumento2 páginasInvestigating Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Levels in Inhaled and Exhaled AirAdy Phanterz100% (1)
- Battery Basics: Cell Chemistry and DesignDocumento40 páginasBattery Basics: Cell Chemistry and DesignAliAinda não há avaliações
- Cemtec AL PU CoatingDocumento2 páginasCemtec AL PU CoatingAhmad ElghazolyAinda não há avaliações
- FCC Wash Water SystemsDocumento16 páginasFCC Wash Water SystemsBehnam RahzaniAinda não há avaliações
- Tablet Disintegration Test and Basket Rack AssemblyDocumento2 páginasTablet Disintegration Test and Basket Rack AssemblyPhoenix100% (1)
- NJ DEP Guidance on Process Hazard Analysis and Risk AssessmentDocumento17 páginasNJ DEP Guidance on Process Hazard Analysis and Risk AssessmentaakashtrivediAinda não há avaliações
- Autoclaved Aerated Concrete - WikipediaDocumento4 páginasAutoclaved Aerated Concrete - WikipediaNagarjun ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Tos Notes 3rd YrDocumento4 páginasTos Notes 3rd YrDEEPAK SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Establishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFDocumento11 páginasEstablishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFRicardo MendesAinda não há avaliações
- TRC - Lesson Plan Plant and Animal Cell 2Documento10 páginasTRC - Lesson Plan Plant and Animal Cell 2Armaan0% (1)
- Production of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionDocumento11 páginasProduction of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionAsim RafiqueAinda não há avaliações
- Characterization and Reuse of Kiln Rollers Waste in The Manufacture of Ceramic Floor TilesDocumento7 páginasCharacterization and Reuse of Kiln Rollers Waste in The Manufacture of Ceramic Floor Tilesmap vitcoAinda não há avaliações
- Hosmane2017 Point Group BookDocumento12 páginasHosmane2017 Point Group BookRenato EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações