Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia, Ventricular System
Enviado por
Justine Nyangaresi0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações21 páginasThis document provides an overview of several brain structures including the ventricles, diencephalon, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and limbic system. It describes the location and components of each structure, their connections, functions, and related clinical disorders.
Descrição original:
cerebellar anatomy
Título original
Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia, Ventricular System,
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document provides an overview of several brain structures including the ventricles, diencephalon, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and limbic system. It describes the location and components of each structure, their connections, functions, and related clinical disorders.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações21 páginasCerebellum, Basal Ganglia, Ventricular System
Enviado por
Justine NyangaresiThis document provides an overview of several brain structures including the ventricles, diencephalon, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and limbic system. It describes the location and components of each structure, their connections, functions, and related clinical disorders.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 21
Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia,
Ventricular System, Limbic
System, Diencephalon
An Overview
Ventricles
origin
• Derived from the canal of the neural tube
• Telencephalon – lateral ventricle
- rosral part of 3rd ventricle
. Diencephalon – caudal part of the 3rd
. Mesencephalon – aqueduct
. Metencephalon – rostral 4TH ventricle
. Myelencephalon _ caudal 4th
Lateral ventricles
• Paired
• Parts (4)- anterior horn, body, trigone
(antrum), inferior horn, posterior horn
• Choroid plexus
Relations
• Anterior Horn- roof – corpus callosum
• medial – septum pellucidum
• lateral, floor – caudate nucleus,thalamus
• anterior_ rostrum and genu
• Posterior horn _roof ,lateral_ tapetum of corpus
• medial_ calcar avis?,forceps major
• floor_ occipital lobe
• Inferior horn roof ,medial– tapetum,
caudate(tail),stria
terminalis
• floor – hippocampus ,caudate
eminence
•
•
third ventricle
• Lateral wall – thalamus and hypothalamus ,
subthalamus
• Roof _ fornix, tela choroidea
• Posterior_ post commisure, pineal, recess
• Floor_ tuber cinerium, mammilary bodies
• Rostral _ anterior commisure, lamina terminalis
• Interthalamic adhesion (Massa intermedia)
• Recesses- optic, infundibulum, pineal,
suprapineal
Fourth ventricle
• Ventral(rhomboid fossa) _ pons, medulla
• Dorsal _ cerebellum
• Lateral _ peduncles
• Superior and inferior limit – vela, obex
Connections
Interventricular foramen of monroe
Cerebral aqueduct of sylvus
Medial foramen?CM
Lateral foramen of?(cisterns)CP
Cental canal
Csf
• Formation (3sources-)cp, metabolic water,
capillary ultrafiltrate
• Circulation
• Absorption- ARACHNOID GRANULATIONS
• Functions
blood brain barrier
Components and functions.
Clinical_ hydrocephalus(ext,int)
Diencephalon
• Components – 4
• Thalamus- nucleus, and functions , clinical
correlation, thalamic radiation
• Hypothalamus- nucleus and fx, clinical
Functional Divisions of Thalamic
Nuclei.
• Sensory_ Lateral geniculate .Medial geniculate
Ventral posterolateral(body) .Ventral
posteromedial (face)
• Motor _Ventral anterior ,Ventral lateral
• Limbic_ Anterior Dorsomedial
• Multimodal _Pulvinar ,Lateral posterior
(posterolateral) Lateral dorsal (dorsolateral)
• Intralaminar_ Reticular ,Centrum medianum
,Intralaminar
functions
• Sensory integration _ except?
• Motor integration_receive from striatum and
cerebellum, and project to the cortex
• Regulate alertness, consciousness, and sleep
• Emotion correlation of various sensory stimuli,
via its connection to limbic
Hypothalamus
• Location and relations
• Connections_ humoral, neural.
• Supraoptic, paraventricular, posterior, anterior,
dorsomedial , ventromedial
• Functions_ eating behavior(feeding and satiety
centre)
• Temperature control
• Water balance
• Circadian rhythm
Secretion of ant pituitary hormones , GRH,TRH,CRH
Emotions, via limbic sys connections
Basal Ganglia
• Components
• Neostriatum(striatum), palaeostriatum(gp 1,2),
archistriatum(amygdala)
• Connections- direct loop, indirect loop
• Excitatory pathways(NT?)_ corticostriate,
thalamocortical
• Inhibitory-
• Fx – modulation of motor activity, occurs during all
stages of mvts, and will control patterns of muscle
contractions
• disorders
disorders
• Parkinsonism (antipsychotics)inability to
initiate wanted movements
• Athetosis-
• Huntington’s chorea(inability to prevent
unwanted movement)_striatopallidal fibres
• Hemiballismus_SN
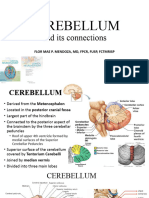
Cerebellum
• Position- p.c.f
• Parts and fissures
• Phyllogenetic divisions and functions
• Histology_ 3 layers and 5 cell types
• Deep cerebellar nuclei (roof nuclei)
• Connections
• Blood supply and lesions_ ataxia, intention
tremors, hypotonia, rebound phenomenon
Limbic system
• Components
• Cortical areas _ parahippocampus, uncus,
cingulum, amygdala, subcallosal gyrus
• Hippocampal formation_ hippocampus, dentate
• Diencephalon_ septal nuclei, septum pellucidum,
nucleus accumbens, ventral striatum, substantia
nigra, thalamus(anterior, dorsal,intralaminar)
• Brain stem regions_ mammillary bodies,
hypothalamus, habenular nuclei, reticular
formation?
Functions
• 5 Fs
• Control of autonomic functions.
• Modulation of homeostatic mechanism
• Modulation of conditioned reflexes
• Thirst drive and body fluid regulation
• Modulating eating behaviour
• Control of adrenocortical activity
• Control of emotions
• Learning and memory
• lesions
Você também pode gostar
- Anatomy of CNS and PNSDocumento72 páginasAnatomy of CNS and PNSTony Hermawan100% (1)
- Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia: Presented byDocumento68 páginasCerebellum and Basal Ganglia: Presented byDivya AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Arterial Blood Supply of The Brain: - Brain Supplied by Branches of Two Major ArteriesDocumento31 páginasArterial Blood Supply of The Brain: - Brain Supplied by Branches of Two Major Arteriesahmed mahamedAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem CranialnervesDocumento93 páginasBrainstem CranialnervesmarykristiroseAinda não há avaliações
- CerebellumDocumento49 páginasCerebellumsjs6r8wwv9Ainda não há avaliações
- Diencephalon: Consist of Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus and SubthalamusDocumento32 páginasDiencephalon: Consist of Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus and SubthalamusueumanaAinda não há avaliações
- Zodiac Academy: Hari Krishna G L Academic CoordinatorDocumento94 páginasZodiac Academy: Hari Krishna G L Academic CoordinatorHARI KRISHNA G LAinda não há avaliações
- The Limbic System: Juan Enrique Toro Perez UWO Fellow Neurology Residents Neurosciences Review Tutor: Jorge BurneoDocumento54 páginasThe Limbic System: Juan Enrique Toro Perez UWO Fellow Neurology Residents Neurosciences Review Tutor: Jorge BurneoJuan Enrique Toro PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Brain AnatomyDocumento57 páginasBrain AnatomyCarlo BelazaAinda não há avaliações
- 14 The Central Nervous SystemDocumento61 páginas14 The Central Nervous SystemvanderphysAinda não há avaliações
- DR MartinDocumento42 páginasDR MartindeycallmebudAinda não há avaliações
- Central Nervous System: - BrainDocumento26 páginasCentral Nervous System: - BrainMonaAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem EnglDocumento28 páginasBrainstem EnglNasrudin EfendiAinda não há avaliações
- Ne Znam Ni Ja StaDocumento103 páginasNe Znam Ni Ja StaHarunKarovićAinda não há avaliações
- The Nervous SystemDocumento48 páginasThe Nervous SystemBinal MorabiaAinda não há avaliações
- HypothalamusDocumento37 páginasHypothalamusMalka LiaqatAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of The Nervous System: Lecture No. 7Documento106 páginasPhysiology of The Nervous System: Lecture No. 7Nawghty AbbasiAinda não há avaliações
- Neuro Anatomy of BrainDocumento79 páginasNeuro Anatomy of BrainSruthi SruthiAinda não há avaliações
- Charity Kapenda Muselema: Term 3 - NeurophysiologyDocumento50 páginasCharity Kapenda Muselema: Term 3 - NeurophysiologyHomeground entertainmentAinda não há avaliações
- Head - Neck Anatomy LectureDocumento91 páginasHead - Neck Anatomy Lecturen42.nayanAinda não há avaliações
- Wawa - Sistem Saraf PusatDocumento38 páginasWawa - Sistem Saraf PusatnuhaAinda não há avaliações
- Brain and Cranial NervesDocumento111 páginasBrain and Cranial NervesAnonymous m9wRhxF4d100% (2)
- BRAINSTEM Anatom - in .Ua 04.04.2015Documento101 páginasBRAINSTEM Anatom - in .Ua 04.04.2015Sevval OzcelikAinda não há avaliações
- Brain AnatomyDocumento56 páginasBrain AnatomymirelahanganuAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanDocumento37 páginasAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanAnonymous xfBKTQfAinda não há avaliações
- Diencephalon 2018Documento87 páginasDiencephalon 2018EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- LIMBIC SYSTEM PPT by AmulyaDocumento54 páginasLIMBIC SYSTEM PPT by AmulyaSid KolgeAinda não há avaliações
- Diencephalon 2Documento38 páginasDiencephalon 2Coskar MethodAinda não há avaliações
- Limbic System NeuroscienceDocumento82 páginasLimbic System Neuroscience250187155Ainda não há avaliações
- AHD Jan 26 11 - Cerebellum - Presentaton - McDowellDocumento36 páginasAHD Jan 26 11 - Cerebellum - Presentaton - McDowelllion2chAinda não há avaliações
- HypothalamusDocumento38 páginasHypothalamuscmabdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Central Nervous System: Brain & Spinal CordDocumento36 páginasCentral Nervous System: Brain & Spinal Cordthe_jokosAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysioDocumento4 páginasAnatomy and PhysioRhiza PagdangananAinda não há avaliações
- HypothalamusDocumento39 páginasHypothalamusAfsaneh Javanmard100% (1)
- Hypothalamus 2019Documento71 páginasHypothalamus 2019b.bethel2003Ainda não há avaliações
- The Nervous System IDocumento44 páginasThe Nervous System IayeshaAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocumento71 páginasCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Lecture 4 - ThalamusDocumento49 páginasAnatomy Lecture 4 - ThalamusBISMARCK BANAHENE BOAHENEAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebrum: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Documento111 páginasCerebrum: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Hephzibah JaporAinda não há avaliações
- Brainstem - Pons MidbrainDocumento24 páginasBrainstem - Pons MidbrainjabirAinda não há avaliações
- Endo All MergeDocumento586 páginasEndo All MergeShivani DurgeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Brain: Prof. Ashraf HusainDocumento58 páginasIntroduction To Brain: Prof. Ashraf Husainraanja2Ainda não há avaliações
- Cerebellardisordersppt 200731144621Documento108 páginasCerebellardisordersppt 200731144621Dr.Aman SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 - BrainstemDocumento33 páginas4 - Brainstemb.ozyurek84Ainda não há avaliações
- Brain Anatomy in BriefDocumento12 páginasBrain Anatomy in BriefSatinder BhallaAinda não há avaliações
- PPT2Documento47 páginasPPT2CBM UBJOM KALTIMAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebellum, Thalamus, and HypothalamusDocumento40 páginasCerebellum, Thalamus, and Hypothalamusasep100% (1)
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocumento37 páginasBrain Structure and FunctionVijay Shanthi100% (1)
- Brainstem (Yuni)Documento34 páginasBrainstem (Yuni)Ayi Abdul Basith100% (2)
- Hypothalamus: By: Ma. Athena C. Del Rosario-Rebulado MD September 10, 2021Documento45 páginasHypothalamus: By: Ma. Athena C. Del Rosario-Rebulado MD September 10, 2021AthenaAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of The BrainDocumento106 páginasParts of The BrainbechichemelissaAinda não há avaliações
- BRAINDocumento114 páginasBRAINJaravuy JaravuyAinda não há avaliações
- Hypophysis CerebriDocumento21 páginasHypophysis CerebriAli Akand AsifAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word - Rangkuman Anatomi Blok I.5Documento23 páginasMicrosoft Word - Rangkuman Anatomi Blok I.5Ferica Christinawati PutriAinda não há avaliações
- The Central Nervous System - Part ADocumento6 páginasThe Central Nervous System - Part AKhamron BridgewaterAinda não há avaliações
- Limbic Sys - ArchDocumento85 páginasLimbic Sys - Archdrkadiyala2Ainda não há avaliações
- Total Reflexology: The Reflex Points for Physical, Emotional, and Psychological HealingNo EverandTotal Reflexology: The Reflex Points for Physical, Emotional, and Psychological HealingNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- The Colleges of Medicine of South Africa: FCORL (SA) FinalDocumento6 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South Africa: FCORL (SA) FinalJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento6 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento3 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento4 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- FCORL (SA) Final Past Papers - 2010 Sept 26 4 2012Documento6 páginasFCORL (SA) Final Past Papers - 2010 Sept 26 4 2012Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento7 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento4 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocumento4 páginasThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- NEUROANATOMYDocumento25 páginasNEUROANATOMYsayed34Ainda não há avaliações
- MCQs in Cardiovascular MedicineDocumento144 páginasMCQs in Cardiovascular MedicineRiham Mohye Eldeen MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Presidential Address - State Interventions To Cushion Kenyans Against Economic Effects of Covid 19 Pandemic - 25th March, 2020Documento31 páginasPresidential Address - State Interventions To Cushion Kenyans Against Economic Effects of Covid 19 Pandemic - 25th March, 2020Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrology CritiquesDocumento18 páginasNephrology CritiquesYelle QuilatanAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital and Acquired Hemolytic AnemiasDocumento32 páginasCongenital and Acquired Hemolytic AnemiasAatekaAinda não há avaliações
- Pedi AcuteOE Slides 101122Documento32 páginasPedi AcuteOE Slides 101122Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- HIV Head Neck Pic 1010 10Documento25 páginasHIV Head Neck Pic 1010 10Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Otology Revision.Documento3 páginasOtology Revision.Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- NEUROANATOMYDocumento25 páginasNEUROANATOMYsayed34Ainda não há avaliações
- NEUROANATOMYDocumento25 páginasNEUROANATOMYsayed34Ainda não há avaliações
- Laryng Reflux Slides 090825Documento47 páginasLaryng Reflux Slides 090825Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Ent MCQSDocumento18 páginasEnt MCQSJustine Nyangaresi100% (1)
- Superior Canal Pic 2010 09Documento19 páginasSuperior Canal Pic 2010 09Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Ulceration Slides 090331Documento62 páginasUlceration Slides 090331mumutdwsAinda não há avaliações
- DiverticulumZenk Slides 100428Documento30 páginasDiverticulumZenk Slides 100428Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in AdultsDocumento30 páginasSurgical Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in AdultsJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in AdultsDocumento30 páginasSurgical Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in AdultsJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Laryng Reflux Slides 090825Documento47 páginasLaryng Reflux Slides 090825Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Ped Onc For ENT 091216Documento28 páginasPed Onc For ENT 091216Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Pedi Lymphnode Slides 090924Documento56 páginasPedi Lymphnode Slides 090924Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- FB Aspir Slides 090225Documento53 páginasFB Aspir Slides 090225Justine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Otology: Balasubramanian ThiagarajanDocumento58 páginasClinical Otology: Balasubramanian ThiagarajanJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Characteristics of SoilDocumento26 páginasPhysical Characteristics of SoillfpachecoAinda não há avaliações
- DGKCC Internship ReportDocumento17 páginasDGKCC Internship ReportMuhammad AtharAinda não há avaliações
- Splash25 Winner InstructionsDocumento8 páginasSplash25 Winner InstructionsRamkrishna PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Tasks: Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction To 20Documento2 páginasLesson Tasks: Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction To 20Марина СтанојевићAinda não há avaliações
- Course 3 Mathematics Common Core Workbook AnswersDocumento4 páginasCourse 3 Mathematics Common Core Workbook Answerspqdgddifg100% (1)
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDocumento19 páginasModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- 555 TimerDocumento25 páginas555 TimerDr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Documento75 páginasIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiAinda não há avaliações
- Vishakha BroadbandDocumento6 páginasVishakha Broadbandvishakha sonawaneAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersDocumento26 páginasA Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersJohn DoeAinda não há avaliações
- Prevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCDocumento6 páginasPrevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCMuhammad FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Topic - Temperature SensorDocumento9 páginasTopic - Temperature SensorSaloni ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Norm ANSI PDFDocumento1 páginaNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment On Porters Generic StrategiesDocumento12 páginasAssignment On Porters Generic StrategiesGeetinder Singh78% (9)
- Viking 062293Documento8 páginasViking 062293Lukman ZakariyahAinda não há avaliações
- JurnalDocumento12 páginasJurnalSandy Ronny PurbaAinda não há avaliações
- Emulsion LectureDocumento30 páginasEmulsion LectureRay YangAinda não há avaliações
- Opentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDocumento38 páginasOpentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDoond adminAinda não há avaliações
- The Eye WorksheetDocumento3 páginasThe Eye WorksheetCally ChewAinda não há avaliações
- Reaction Paper GattacaDocumento1 páginaReaction Paper GattacaJoasan PutongAinda não há avaliações
- Reaffirmed 1998Documento13 páginasReaffirmed 1998builconsAinda não há avaliações
- Luxi User's GuideDocumento14 páginasLuxi User's GuidephilsouthAinda não há avaliações
- Hasan Bin Ekram: Career ObjectiveDocumento3 páginasHasan Bin Ekram: Career ObjectiveHasan SarikAinda não há avaliações
- IBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Documento80 páginasIBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Abubakar SidikAinda não há avaliações
- STIHL TS410, TS420 Spare PartsDocumento11 páginasSTIHL TS410, TS420 Spare PartsMarinko PetrovićAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebDocumento4 páginasActivity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebMohamidin MamalapatAinda não há avaliações
- Review Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5Documento4 páginasReview Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5XeniaAinda não há avaliações
- You'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyDocumento2 páginasYou'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyTommy Juliansyah MarsenoAinda não há avaliações
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belgavi-590018, Karnataka, INDIADocumento7 páginasVisvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belgavi-590018, Karnataka, INDIAShashi KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Method Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)Documento72 páginasMethod Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)NP Dien100% (1)