Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Treatment Day 1
Enviado por
api-4335321270 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
816 visualizações28 páginasTítulo original
treatment day 1
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
816 visualizações28 páginasTreatment Day 1
Enviado por
api-433532127Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 28
“Actually the bill is part of your
Psychology reality therapy.”
Treatment and Therapy for
Psychological Disorders
Early Theories
Music or singing was
often used to chase
away spirits.
In some cases
trepanning was
used: cutting a hole
in the head of the
afflicted to let out
the evil spirit.
Trepanning
Philippe Pinel
A French doctor
who was one of
the first to take
the chains off
and declare that
these people are
sick and “a cure
must be found.”
Dorothea Dix
American reformer who worked
to get better care for the
mentally ill
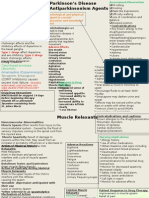
Defining Mental Disorder
Psychosurgery
Surgical procedures, usually directed
at the brain, used to affect
psychological reactions
Split-brain procedure – epilepsy
Small lesions of limbic system – violent
behaviors
Cingulotomy – extreme anxiety and
symptoms of obsessive-compulsive
disorder
Surgical techniques – Parkinson’s
Psychosurgery
Lobotomy – severs the major
neural connections between the
prefrontal lobes and the lower
brain centers
Problem: patients were
calm after the procedure
but also had changed
personality and drive
Creating permanently
lethargic, immature
and uncreative people
Electroconvulsive Therapy–
ECT (hyperlink)
ECT shock treatment) – involves passing
an electric current between 70-150
(usually 100) volts across one of the brain
hemispheres
30 – 60 seconds of electrical current
Anesthesia is given to minimize trauma
Mainly used for profound depression
No one knows exactly why it works
Perhaps because of placebo effects, rebooting
the computer, calming neural centres?
No more than 10-12 treatments
rTMS Repetitive Transcranial
Magnetic Stimulation
Repeated pulses surge through a
magnetic coil held close to the skull
Painless and produces no seizures,
memory loss or other serious side effects
Studies have shown modest benefits
Unclear how it works but possibly because it
energizes the left frontal lobe
Repeated stimulation may cause nerve cells
to form new circuits
Deep Brain Stimulation
For patients whose severe depression
has resisted drugs and ECT
Experimental treatment focusing on a
neural hub that bridges the frontal lobes
to the limbic system (over active in a
depressed brain)
Electrodes are implanted
Excites neurons that inhibit activity
12 / 20 experienced relief for three to six
years of follow up
Drug Therapy
Biomedical therapy may administer
drugs to improve abnormal behavior
Drug classes include:
Antianxiety drugs relieve muscle tension
Antipsychotic drugs improve thought
processes
Can have major adverse side effects
Antidepressant drugs can reverse
depression (hyperlink)
Tricyclics
MAO inhibitors
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Anti-Anxiety Drugs
Help reduce the felt aspect of
anxiety
Majority are benzodiazepines (e.g.,
Valium, and Xanax), which act
directly on CNS
Very effective and most commonly
prescribed of all medications
Dependency and addiction may develop
Muscle relaxants (e.g., Miltown)
Antimanic compounds
Used for bipolar disorder
Lithium carbonate – most effective
at treating the manic phase (once
the mania is eliminated, depression
usually does not follow).
Lithium reduces risk of suicide
Do not fully understand why Lithium
works, but it does…
Lithium side effects
Low level:
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal
pain; tremor, lethargy, impaired
concentration, dizziness; slurred
speech, ataxia, muscle weakness;
memory impairment; weight gain
Long term lithium use:
may enlarge the thyroid, cause skin
rashes, and increase urine output;
impaired motor activity, creativity,
and cognitive activity.
Antipsychotic drugs
The first generation were aimed at the
positive symptoms of schizophrenia -
dopamine receptor blockers
The dopamine hypothesis suggests that
the positive symptoms of schizophrenia
are caused by overactivity of DA
synapses.
Atypical (second generation)
antipsychotics also impact the negative
symptoms
e.g. Clozapine and Risperidone
Anticholinergic side effects
(acetylcholine inhibitors)
Dry mouth
Blurred vision
Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
Urine retention
Constipation
Confusion and memory impairment
Tardive Dyskinesia
• a movement disorder characterized
by involuntary movements of the face
and neck
Drug Therapy
Antidepressant drugs – elevate
the mood of persons who are
feeling depressed, and there are 3
major classes
1. MAO (monoamine oxidase) inhibiters
2. Tricyclics
3. SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake
inhibitors)
Drug Therapy: MAO Inhibiters
Inhibit the enzyme monoamine
oxidase, which normally breaks
down levels of serotonin,
norepinephrine, and dopamine in
the brain
Major drawback is that they can
be toxic and interact with foods
containing tyramine
Foods with high levels of
tyramine
strong or aged cheeses like cheddar, blue cheese, or
gorgonzola
cured or smoked meats or fish, such as sausage or salami
beers on tap or home-brewed
some overripe fruits
soy products like miso soup, bean curd, or tofu
certain beans, such as fava or broad beans
some sauces or gravies like soy sauce, teriyaki sauce, or
bouillon-based sauces
pickled products like sauerkraut
sourdough breads
Drug Therapy: Tricyclics
These drugs generally are safer
and more effective that the older
MAO inhibitors
They mainly affect the operation
of the neurotransmitters
serotonin and norepinephrine
Drug Therapy: SSRIs
These drugs act faster to relieve
symptoms and have fewer side
effects
Work by inhibiting the reuptake
of serotonin, increasing serotonin
levels, which elevates mood
Prozac, Zoloft, Luvox, and Paxil
Antidepressant drugs prolong the activity of the
neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
(a) Ordinarily, after the release of one of the
neurotransmitters, some of the molecules are reabsorbed by
the terminal button, and other molecules are broken down by
the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO). (b) Selective
serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) prevent reabsorption of
serotonin. Tricyclic drugs prevent reabsorption of dopamine,
norepinephrine, and serotonin. (c) MAO inhibitors (MAOIs)
block the enzyme monoamine oxidase and thereby prolong
the effects of the neurotransmitters.
Drug Therapy –
Antidepressants
Drawbacks:
Usually take 2-4 weeks to show
any effect, and may take 6 weeks
to be effective
Unpleasant side effects(hyperlink)
Efficacy
Pharmaceutical vs. Psychotherapy
Depression and Anxiety
Less Effective to just as effective
More effective when combined
Therapeutic lifestyle change show to be
the most effective
Extreme Disorders
More effective/Necessary
More effective when combined
Therapeutic Lifestyle change
Aerobic Exercise
30 mins 3 times a week
Outdoors(nature) more effective
Adequate Sleep
7-8 hours a night
Light Exposure Therapy
30 Minutes each morning
Especially effective for S.A.D
Social Connections
Two meaningful social connections per week
Nutritional Supplements
Specifically omega-3 fatty acids
Você também pode gostar
- Chap 17 Treatment Revised 2018 Pictures RemovedDocumento57 páginasChap 17 Treatment Revised 2018 Pictures Removedapi-391411195Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 - Chap 17 Treatment RGDocumento64 páginas5 - Chap 17 Treatment RGapi-343457547Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap 17 Treatment RevisedDocumento59 páginasChap 17 Treatment Revisedapi-296712028Ainda não há avaliações
- Cns PharmacologyDocumento51 páginasCns PharmacologyAnasAbdelaAinda não há avaliações
- Depression and Antidepressants FinalDocumento37 páginasDepression and Antidepressants FinalKhadija ArshadAinda não há avaliações
- 7.2 Mood Disorders Suicide Part 2Documento11 páginas7.2 Mood Disorders Suicide Part 2ROGELLE FIEHL CONTRERASAinda não há avaliações
- نسخة Antidepressants for Lab. StudentsDocumento64 páginasنسخة Antidepressants for Lab. Studentsنوف الحربي.Ainda não há avaliações
- PharmacologReview File Important (AutoRecovered)Documento29 páginasPharmacologReview File Important (AutoRecovered)sami khanAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Psychotropic DrugsDocumento7 páginasOverview of Psychotropic Drugsnad101Ainda não há avaliações
- 7 - Anxiolytics-Sedatives-HypnoticsDocumento46 páginas7 - Anxiolytics-Sedatives-HypnoticsHadeelAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of UnipolardepressionDocumento14 páginasTreatment of Unipolardepressionapi-358967453Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary Complete Mental Health NursingDocumento20 páginasSummary Complete Mental Health Nursingraquel maniegoAinda não há avaliações
- Psychopharmacology UCEBT Presentation Slides PDFDocumento42 páginasPsychopharmacology UCEBT Presentation Slides PDFjay ar baybayAinda não há avaliações
- Therapeutic Modalities: Therapeutic Modalities, Psychosocial Skills, and Nursing 1 Biophysical/ Somatic InterventionsDocumento15 páginasTherapeutic Modalities: Therapeutic Modalities, Psychosocial Skills, and Nursing 1 Biophysical/ Somatic InterventionsdaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Fitness and Mental HealthDocumento51 páginasFitness and Mental HealthDrSnipes100% (2)
- Anxiety and InsomniaDocumento25 páginasAnxiety and Insomniajheannie02Ainda não há avaliações
- Antidepressant DrugsDocumento15 páginasAntidepressant DrugsDr. Mushfique Imtiaz ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Depressants 2Documento24 páginasAnti Depressants 2Ayesha AyeshaAinda não há avaliações
- 7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersDocumento33 páginas7) 5th Semester - Depression & Affective DisordersFizza ImamAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemsDocumento19 páginasPharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemsShun Reigh SumilangAinda não há avaliações
- Cns DpressantDocumento49 páginasCns DpressantMirza Shaharyar BaigAinda não há avaliações
- The Nervous System: Blood Brain BarrierDocumento17 páginasThe Nervous System: Blood Brain BarrierSuleiman AbdallahAinda não há avaliações
- The Affective DisordersDocumento22 páginasThe Affective DisordersMUHD SUHAILAinda não há avaliações
- Antipsychotic or Neuroleptic DrugsDocumento12 páginasAntipsychotic or Neuroleptic Drugscamile buhanginAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainDocumento9 páginasChapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainciaraAinda não há avaliações
- Antidepressant DrugsDocumento47 páginasAntidepressant DrugsOjambo Flavia75% (4)
- Anti PsychoticsDocumento34 páginasAnti Psychotics88AKKAinda não há avaliações
- PsychopharmacologyDocumento14 páginasPsychopharmacologyMarielie OclimaAinda não há avaliações
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocumento2 páginasParkinson's DiseaseTee WoodAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Treatments: Drug Treatment ChemotherapyDocumento6 páginasBiological Treatments: Drug Treatment ChemotherapyAw AdivaraAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocumento27 páginasPsychiatric Nursing ReviewbiopoolAinda não há avaliações
- Class 1 Antidepressents 2020Documento21 páginasClass 1 Antidepressents 2020Arafat 039Ainda não há avaliações
- DepressionDocumento23 páginasDepressionapi-263913260Ainda não há avaliações
- Psychiatry Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016 PDFDocumento34 páginasPsychiatry Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016 PDFJyothi ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Antidepressants AntidepressantsDocumento38 páginasAntidepressants AntidepressantsjaneAinda não há avaliações
- Antidepressants (ME216) 20 5Documento40 páginasAntidepressants (ME216) 20 5Dineish MurugaiahAinda não há avaliações
- Psychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioDocumento65 páginasPsychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (2)
- PsychopharmacologyDocumento160 páginasPsychopharmacologyInah Sarita100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocumento27 páginasPsychiatric Nursing Reviewgrey26Ainda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocumento32 páginasDrugs Acting On CNSjustin rodrigoAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of Mood Stabilizers: DR - Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapetik Fak - Kedokteran Uhn MedanDocumento51 páginasPharmacology of Mood Stabilizers: DR - Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapetik Fak - Kedokteran Uhn MedanFansisca SiallaganAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in Intro To PsychologyDocumento5 páginasReviewer in Intro To PsychologyCalagos MarianneAinda não há avaliações
- Theracom Final PDFDocumento162 páginasTheracom Final PDFdodong skyroseAinda não há avaliações
- Slides Mood DisordersDocumento15 páginasSlides Mood DisordersEesha TahirAinda não há avaliações
- Null 2Documento46 páginasNull 2Wazeerullah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- DepressionDocumento45 páginasDepressionabdulsemedrihanaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 - TREATMENT OF MENTAL DISEASESDocumento52 páginasTopic 2 - TREATMENT OF MENTAL DISEASESprashant singhAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Neurotransmitters - BioNinjaDocumento2 páginasTypes of Neurotransmitters - BioNinjarebeccaefosa0Ainda não há avaliações
- Psychopharmacology Article StyleDocumento9 páginasPsychopharmacology Article StyleLizethAinda não há avaliações
- CNS Stimulant 2022 - Stu.Documento39 páginasCNS Stimulant 2022 - Stu.Eltaib Mohamad 2427Ainda não há avaliações
- Treatments in PsychiatryDocumento31 páginasTreatments in PsychiatryChro MAAinda não há avaliações
- Depression & Anxiety: What You Need To Know About Treatment with Medications, Herbs & SupplementsNo EverandDepression & Anxiety: What You Need To Know About Treatment with Medications, Herbs & SupplementsAinda não há avaliações
- Exposing the Shameful Face of Drug Addiction: Unveiling the trick behind drug addictionNo EverandExposing the Shameful Face of Drug Addiction: Unveiling the trick behind drug addictionAinda não há avaliações
- The Neuroscience of Meditation: Rewiring Your Brain for Health and HappinessNo EverandThe Neuroscience of Meditation: Rewiring Your Brain for Health and HappinessAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreNo EverandDaily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreAinda não há avaliações
- Overcoming Depression: A guide on how to understand and cure your depressed stateNo EverandOvercoming Depression: A guide on how to understand and cure your depressed stateAinda não há avaliações
- Final Research EssayDocumento2 páginasFinal Research Essayapi-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Day 3 Mood Disorders RV Rushed 2018Documento28 páginasDay 3 Mood Disorders RV Rushed 2018api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Treatment Day 2Documento36 páginasTreatment Day 2api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Road Map To The Senses Unit Project Block 3Documento4 páginasRoad Map To The Senses Unit Project Block 3api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Day 1 Intro RVDocumento34 páginasDay 1 Intro RVapi-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Stress and Health VaessenDocumento25 páginasStress and Health Vaessenapi-391411195Ainda não há avaliações
- Intro To ApaDocumento8 páginasIntro To Apaapi-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning Day 2 - Operant ConditioningDocumento32 páginasLearning Day 2 - Operant Conditioningapi-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning Day 3Documento22 páginasLearning Day 3api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap 12 Motivation Day 1 and 2 Notes RV 2018Documento60 páginasChap 12 Motivation Day 1 and 2 Notes RV 2018api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap 10 ThinkingrvDocumento59 páginasChap 10 Thinkingrvapi-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- Memory Day 1Documento34 páginasMemory Day 1api-433532127Ainda não há avaliações
- MectaDocumento29 páginasMectakinantika nur dewantiAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics Is An ArtDocumento4 páginasStatistics Is An ArtSaurabh ParasharAinda não há avaliações
- Health Law End Sem - QP 1Documento24 páginasHealth Law End Sem - QP 1Vijay Srinivas KukkalaAinda não há avaliações
- Yoga School of Thought and Psychiatry: Therapeutic PotentialDocumento5 páginasYoga School of Thought and Psychiatry: Therapeutic PotentialKersaspNalladaruAinda não há avaliações
- 1770 Question BankDocumento10 páginas1770 Question BankSanal c SabuAinda não há avaliações
- MCQDocumento4 páginasMCQRhey-an Oliveros100% (1)
- Strahlenfolter - Electronic Harassment - Neural Implants - Past, Present & Future PART1Documento11 páginasStrahlenfolter - Electronic Harassment - Neural Implants - Past, Present & Future PART1nwo-mengele-doctorsAinda não há avaliações
- Ketofol Vs Propofol Retrospective StudyDocumento7 páginasKetofol Vs Propofol Retrospective StudyNitasa Miishra RoyAinda não há avaliações
- ECT PharmacologyDocumento29 páginasECT PharmacologySangkaran KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Psychological Outlook of CinemaDocumento10 páginasPsychological Outlook of CinemaDevesh PurbiaAinda não há avaliações
- USMLE Flashcards: Behavioral Science - Side by SideDocumento96 páginasUSMLE Flashcards: Behavioral Science - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffAinda não há avaliações
- Instruction Manual: ECT Unit Paint. No. 57800Documento27 páginasInstruction Manual: ECT Unit Paint. No. 57800ANJANI AULIA DEWI mhsD4TEM2019BAinda não há avaliações
- The History of Psychological TreatmentDocumento16 páginasThe History of Psychological TreatmentNeann Medina De JesusAinda não há avaliações
- Case Types List - 4Documento2 páginasCase Types List - 4Sathish B SathishAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises 3Documento10 páginasExercises 3chinh nguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Foundations of Mental Health Care 6th Edition by Morrison ValfreDocumento36 páginasTest Bank For Foundations of Mental Health Care 6th Edition by Morrison Valfresolutive.zamboowtmcu100% (43)
- Pain Practice - 2023 - YoonDocumento14 páginasPain Practice - 2023 - YoonAbbey WaltzAinda não há avaliações
- Close Study of Text " Cosi" by Louis Nowra Notes by Mark SlocumDocumento6 páginasClose Study of Text " Cosi" by Louis Nowra Notes by Mark SlocumJonathan ZhuAinda não há avaliações
- Mental Health QuizDocumento69 páginasMental Health QuizMelissa martinAinda não há avaliações
- Ava Paravati Paradigm Shift PaperDocumento15 páginasAva Paravati Paradigm Shift Paperapi-607803514Ainda não há avaliações
- Structure Standard ECT PDFDocumento15 páginasStructure Standard ECT PDFMuhammad Riandy Lukman TanjungAinda não há avaliações
- Behavioral Sciences (Qbank Questions)Documento24 páginasBehavioral Sciences (Qbank Questions)aagarwalmdAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 Cosi StudentbookletDocumento43 páginas2018 Cosi Studentbookletapi-3844009950% (2)
- Paranoid SchizophreniaDocumento26 páginasParanoid SchizophreniaCrisha Ann Billones BacutaAinda não há avaliações
- Catatonia Treatment & ManagementDocumento8 páginasCatatonia Treatment & ManagementSanthosh ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Ect MarcDocumento24 páginasEct MarcMarc Andreo MalalaAinda não há avaliações
- All MCQs by DR - RoyalDocumento19 páginasAll MCQs by DR - RoyalVaqasFarooqiAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concepts in Psychiatric NursingDocumento11 páginasBasic Concepts in Psychiatric NursingLorina Lynne Apelacio75% (4)
- Critical Evaluation of Mental Health Acts andDocumento53 páginasCritical Evaluation of Mental Health Acts andSritama Ray100% (1)
- WEEK 3 E.C.T.ppt LEVEL 8Documento23 páginasWEEK 3 E.C.T.ppt LEVEL 8جميل جميلAinda não há avaliações