Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CHAPTER 2 :the Research Process: A Quick Glance
Enviado por
alia.delareineTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CHAPTER 2 :the Research Process: A Quick Glance
Enviado por
alia.delareineDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CHAPTER 2
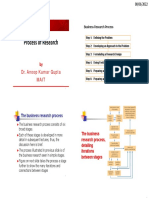
The Research Process: A Quick Glance
The first is to decide what to find out about & to decide how to go about finding their answers.
Phase I: deciding Step I: formulating a research problem most important step in the research process
what to research
what we intend to research
to decide what we want to find out about
Step II: conceptualising a research design Have to use of appropriate methods
to explain how we will find answers to our research questions
should include: the study design per se and the logistical arrangements that we propose
to undertake, the measurement procedures, the sampling strategy, the frame of analysis
and the timeframe
Phase II: planning The selection of an appropriate research design is crucial in enabling us to arrive at valid
a research study findings, comparisons and conclusions
it is important to ensure that it is valid, workable and manageable in selecting r.design
collecting information - ‘research tool’ or a ‘research instrument’. e.g:
Step III: constructing an instrument for observation forms, interview schedules, questionnaires and interview guides.
data collection
to collect data (primary data), we need either to construct a research instrument or to
select one that has already been constructed.
secondary data - (information already collected for other purposes), need to
identify what information is needed and then develop a form to extract the required
data
Field testing (or pre-testing) a research tool is an integral part of instrument
construction
Step IV: selecting a sample basic objective - to minimise, within the limitation of cost, the gap between the values
obtained from our sample and those prevalent in the study population
we should attempt to achieve 2 key aims of sampling the avoidance of bias in the selection of a sample &
the attainment of maximum precision for a given outlay of resources.
Phase II: planning
a research study 3 categories of sampling design : random/probability sampling designs, non-random/non-probability
sampling designs and ‘mixed’ sampling design.
Step V: writing a research It tells about our research problem and how we are planning to investigate
proposal
must have following informations: objectives, hypothesis, study designs, setting, instrument, sample size,
data processing, chapters, problem & limitations and time-frame
Step VI: collecting data collect the data through interviews, mail out a questionnaire, conduct nominal/focus group discussions
or make observations
collecting data through any one of the methods may involve some ethical issues
Phase III: conducting Step VII: processing Analyse the information –depend upon 2 things: the type of information (descriptive, quantitative,
a research study and displaying data qualitative or attitudinal) & the way we want to communicate our findings to readers
Step VIII: writing a 2 categories of reports: quantitative & qualitative
research report
Report should be written in an academic style & be divided into different chapters & sections based
upon the main themes of our study
Você também pode gostar
- Tip Sheet EmdrDocumento2 páginasTip Sheet EmdrVeronica HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 10 :collecting Data Using Attitudinal ScalesDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 10 :collecting Data Using Attitudinal Scalesalia.delareine50% (6)
- Chapter 14 :considering Ethical Issues in Data CollectionDocumento1 páginaChapter 14 :considering Ethical Issues in Data Collectionalia.delareine100% (5)
- CHAPTER 8: Selecting A Study DesignDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER 8: Selecting A Study Designalia.delareine100% (1)
- Social Anxiety Disorder Research PaperDocumento7 páginasSocial Anxiety Disorder Research Paperapi-441382814Ainda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 11: Establishing The Validity and Reliability of A Research InstrumentDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER 11: Establishing The Validity and Reliability of A Research Instrumentalia.delareine100% (3)
- CHAPTER 4: Formulating A Research ProblemDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER 4: Formulating A Research Problemalia.delareine100% (1)
- Armstrong On Reinventing Performance Management Building A Culture of Continuous Improvement (Armstrong, Michael)Documento241 páginasArmstrong On Reinventing Performance Management Building A Culture of Continuous Improvement (Armstrong, Michael)Pia panAinda não há avaliações
- Collecting Data Using Attitudinal Scales: Research MethodologyDocumento12 páginasCollecting Data Using Attitudinal Scales: Research MethodologyEva DanielleAinda não há avaliações
- Research DesignDocumento45 páginasResearch Designsubashik100% (2)
- Phil IRI Action Plan - 2021 2022Documento3 páginasPhil IRI Action Plan - 2021 2022Kimberly Ann Paras100% (4)
- Discipline TheoriesDocumento4 páginasDiscipline TheoriesTeacher Andri100% (2)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Collection of DataDocumento4 páginasA Detailed Lesson Plan in Collection of DataAcire Nonac83% (6)
- Inquiries, Investigations and Immersion: 3 Quarter Week6Documento7 páginasInquiries, Investigations and Immersion: 3 Quarter Week6Pegeeey100% (1)
- CHAPTER 15: Processing DataDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 15: Processing Dataalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 :THE RESEARCH DESIGNDocumento1 páginaChapter 7 :THE RESEARCH DESIGNalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento28 páginasUnit 2Souvagya GangulyAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan MilestonesDocumento26 páginasLesson Plan MilestonesBhawna Pandhu100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 - Research: A Way of ThinkingDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 1 - Research: A Way of Thinkingalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 3: Reviewing The LiteratureDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 3: Reviewing The Literaturealia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9: SELECTING A METHOD OF DATA COLLECTEDDocumento2 páginasChapter 9: SELECTING A METHOD OF DATA COLLECTEDalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- 24SHOBHNAJHA1Documento9 páginas24SHOBHNAJHA1AyanAinda não há avaliações
- Chap002 UpdatedDocumento19 páginasChap002 UpdatedTiến Bùi MinhAinda não há avaliações
- 1online Research Methods Course IntroDocumento11 páginas1online Research Methods Course IntroAus SharjahAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Use in Nursing ResearchDocumento13 páginasComputer Use in Nursing ResearchAhmed MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-I BRMDocumento16 páginasUnit-I BRMTamil piratesAinda não há avaliações
- Session2 - Research Design - SDocumento41 páginasSession2 - Research Design - SLi PerfectAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 The Research Process - An OverviewDocumento16 páginasTopic 2 The Research Process - An OverviewmobanAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Steps in The Research Process - AcqNotesDocumento11 páginas5 Steps in The Research Process - AcqNotesFuad HusenAinda não há avaliações
- C. Marketing ResearchDocumento2 páginasC. Marketing Researchsweet sunshineAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Crit B Graphic Organiser EmpiresDocumento7 páginas01 Crit B Graphic Organiser Empiresayriel.b.maknawiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 The Research Process A Quick Glance PDFDocumento45 páginasChapter 2 The Research Process A Quick Glance PDFkhafid ridlo100% (1)
- The Research Process: A Quick Glance: Chapter 2 - Research Methodology, Ranjit KumarDocumento17 páginasThe Research Process: A Quick Glance: Chapter 2 - Research Methodology, Ranjit Kumarrashmi syraAinda não há avaliações
- Entrepreneurship Week 5Documento5 páginasEntrepreneurship Week 5Miguel CanozaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Scaling TechniqDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Scaling TechniqHabtamu GaromaAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Lecture 04Documento9 páginas03 Lecture 04Sayed Nader Shah MatinAinda não há avaliações
- 3 MBA519A Research MethodologyDocumento3 páginas3 MBA519A Research MethodologyShreelekha NavaleAinda não há avaliações
- PR2 Quarter 2 Reviewer BabyDocumento6 páginasPR2 Quarter 2 Reviewer BabyprcssrhAinda não há avaliações
- MKTG1418 - 2023C - 03 - Research Design - Part 1Documento35 páginasMKTG1418 - 2023C - 03 - Research Design - Part 1maianhnguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Research Process, Phases and 10 Step ModelDocumento5 páginasResearch Process, Phases and 10 Step ModelJ.B ChoAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Research and Research DesignDocumento56 páginasMarketing Research and Research DesignethancfisherAinda não há avaliações
- CH 2Documento20 páginasCH 2Tanvir IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento13 páginasChapter 4delowerAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento18 páginasLecture 1Ayeed AlamAinda não há avaliações
- RM Unit 2 (Research Process)Documento27 páginasRM Unit 2 (Research Process)Yashaswini BangeraAinda não há avaliações
- Mor 1 ReviewerDocumento3 páginasMor 1 ReviewerNicole Deione MorcillaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Skills To Start A Research Education Presentation in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StyleDocumento17 páginasBasic Skills To Start A Research Education Presentation in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StyleondreaysabelleAinda não há avaliações
- Example of MD PMS ActivitiesDocumento6 páginasExample of MD PMS ActivitiesAKSAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Skills To Start A Research Education Presentation in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StyleDocumento17 páginasBasic Skills To Start A Research Education Presentation in Violet Yellow Semi-Realistic Flat Graphic StyleWinshel Peñas AñonuevoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento23 páginasChapter 2aryoooiiiiiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Ii - BRMDocumento22 páginasUnit Ii - BRMTamil piratesAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 3 Business Research Process Marketing Research ProcessDocumento19 páginasModule - 3 Business Research Process Marketing Research ProcessmuneerppAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - Iii BRMDocumento12 páginasUnit - Iii BRMTamil piratesAinda não há avaliações
- Business Research BbaDocumento22 páginasBusiness Research BbashikhavagrawalAinda não há avaliações
- MBA (Professional) Program Faculty of Business AdministrationDocumento4 páginasMBA (Professional) Program Faculty of Business AdministrationTonmoy (123011100)Ainda não há avaliações
- Research MethodologyDocumento270 páginasResearch MethodologyMike Dell100% (2)
- LESSON 4 - Market ResearchDocumento7 páginasLESSON 4 - Market ResearchTriesha GAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Process of ResearchDocumento5 páginas2 Process of ResearchArpana GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Research NewDocumento12 páginasMarketing Research NewupikanchanAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Research ProcessDocumento24 páginasMarketing Research ProcessSohad ElnagarAinda não há avaliações
- (Handout) Introduction To Research MethodologyDocumento6 páginas(Handout) Introduction To Research MethodologyCabdalle KurbeAinda não há avaliações
- Week 6Documento37 páginasWeek 6Carlo TabernaAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Manual For Preface To Marketing Management 13Th Edition Peter Donnelly 0078028841 9780078028847 Full Chapter PDFDocumento29 páginasSolution Manual For Preface To Marketing Management 13Th Edition Peter Donnelly 0078028841 9780078028847 Full Chapter PDFfloyd.hall179100% (13)
- Research Methodology SyllabusDocumento3 páginasResearch Methodology SyllabusPranav choudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Consumer Behaviour Towards Chocolates 1Documento52 páginasConsumer Behaviour Towards Chocolates 1Ashu SinghAinda não há avaliações
- CH - 4 Researech Design (1) - 1Documento29 páginasCH - 4 Researech Design (1) - 1beka negewoAinda não há avaliações
- DesignCriteriaA 1Documento11 páginasDesignCriteriaA 1Vihaan SinghAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORING SESSION KÌ 3 2021 2022 Final Handbook SMA 1Documento127 páginasTUTORING SESSION KÌ 3 2021 2022 Final Handbook SMA 1Chi BongAinda não há avaliações
- BRM Chapter2 - RP SOLUTIONSDocumento48 páginasBRM Chapter2 - RP SOLUTIONSZelalem GashawAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT III Collecting Data July 1Documento13 páginasUNIT III Collecting Data July 1michael sto domingoAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 16: Displaying DataDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 16: Displaying Dataalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 18 :research Methodology and Practice EvaluationDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 18 :research Methodology and Practice Evaluationalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 17 :writing A Research ReportDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 17 :writing A Research Reportalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 13: How To Write A Research ProposalDocumento3 páginasCHAPTER 13: How To Write A Research Proposalalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9: SELECTING A METHOD OF DATA COLLECTEDDocumento2 páginasChapter 9: SELECTING A METHOD OF DATA COLLECTEDalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 6: Constructing HypothesesDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 6: Constructing Hypothesesalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 5: Identifying VariablesDocumento1 páginaCHAPTER 5: Identifying Variablesalia.delareineAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Intelligences in The Classroom Article by Jennifer NolenDocumento3 páginasMultiple Intelligences in The Classroom Article by Jennifer Nolenapi-533624966Ainda não há avaliações
- Based On Concepts Discussed in This ChapterDocumento2 páginasBased On Concepts Discussed in This ChapterJRMSU Finance OfficeAinda não há avaliações
- The Enneagram Personality Test TruityDocumento1 páginaThe Enneagram Personality Test Truitythehumblepotato17.4Ainda não há avaliações
- DLL - English 9 August 5Documento6 páginasDLL - English 9 August 5April Ramos DimayugaAinda não há avaliações
- Command Action PlanDocumento3 páginasCommand Action PlanKalimah PriforceAinda não há avaliações
- Innovative Workspaces Vol 1.1 (HQ) PDFDocumento19 páginasInnovative Workspaces Vol 1.1 (HQ) PDFAmit VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Name: - : English Literature GCSE: An Inspector Calls PLCDocumento11 páginasName: - : English Literature GCSE: An Inspector Calls PLCJamaliAinda não há avaliações
- Yes No NotGivenDocumento7 páginasYes No NotGivenVridhi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Student Activity Evaluation FormDocumento2 páginasStudent Activity Evaluation FormmaddiebaimonAinda não há avaliações
- Writing The Article: Strategy and Preparations: Lesson SummaryDocumento7 páginasWriting The Article: Strategy and Preparations: Lesson SummarySol VirtudazoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation Group 4Documento14 páginasPresentation Group 4Ronit Nadar100% (1)
- Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDocumento18 páginasFoundations of Management and OrganizationsCaroline Rebecca DAinda não há avaliações
- Tawek Johari Window PPT MokodDocumento4 páginasTawek Johari Window PPT Mokodnikos kasiktsisAinda não há avaliações
- 221-2 Autumn 2023Documento11 páginas221-2 Autumn 2023Jawad Saleem BhattiAinda não há avaliações
- Uhv MCQDocumento17 páginasUhv MCQManoj ChallaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write A College Admission Application LetterDocumento24 páginasHow To Write A College Admission Application LetterEms SayAinda não há avaliações
- Tips For A Successful InterviewDocumento24 páginasTips For A Successful InterviewM HuqueAinda não há avaliações
- Introducing Social Psychology: Total Assessment Guide (TAG)Documento62 páginasIntroducing Social Psychology: Total Assessment Guide (TAG)Rubaiya ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Beyond Isolation Senior Housing Competition BriefDocumento24 páginasBeyond Isolation Senior Housing Competition BriefCyan FilmsAinda não há avaliações
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5: C. Learning Competencies / Objectives Write The LC Code For EachDocumento5 páginasDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5: C. Learning Competencies / Objectives Write The LC Code For EachTeacher Lii-Anne MagnoAinda não há avaliações
- SRP Logbook 2020Documento7 páginasSRP Logbook 2020api-436869436Ainda não há avaliações
- Dreamer NotesDocumento17 páginasDreamer NotesDessa Jessica ChristmasAinda não há avaliações
- Yagappa International School: Too Much TV and Chill Could Reduce Brain Power Over TimeDocumento3 páginasYagappa International School: Too Much TV and Chill Could Reduce Brain Power Over TimeNithya NagarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Form 3. LAC Session ReportDocumento3 páginasForm 3. LAC Session ReportRod Aquino89% (9)