Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Elements of Design
Enviado por
Nikhil GuptaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Elements of Design
Enviado por
Nikhil GuptaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The elements of design are the building blocks of all designs chosen to convey a message.
The basic components used as part of any composition. The elements of design build upon one another, the former element helping to create the latter.
Point and Lines Form and Shapes Direction Sizes Textures Value Colors
POINT
Point refers to a mark on the blank page. It is an initiator of any line or form of structure.
Number of dots or continuous marks placed consecutively forms a line. An element of art used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. Lines can be combined with other lines to create textures and patterns.
LINE
o o o
Width, Length, Direction and Feeling are amongst the few characteristics. Lines can be classified further as three : Vertical Horizontal Oblique
Vertical Lines
Horizontal lines
Contour lines
VERTICAL is associated with BALANCE, FORMALITY and ALERTNESS and is used FORMAL OUTFITS
HORIZONTAL is associated with CALMNESS and is used CASUAL OUTFITS.
OBLIQUE is associated with MOVEMENT or ACTION and is used for SPORTS AND GYM WEAR.
Vertical representing formality, alertness and balance
Representing casual, more relaxed and an informal way
Oblique represents movement and motion resulting in activity
Shape is one of the basic elements of design When a line crosses itself or intersects with other lines to enclose a space it creates a shape. Shape is twodimensional it has heights and width but no depth. Form is the threedimensionality of an object.
Geometric shapes are structured, often symmetrical shapes. Ex: Squares, triangles Natural shapes are found in nature or they can be manmade shapes. Ex: Leaves, stones. Abstract shapes are stylized or simplified versions of natural shapes. Ex: Symbols.
Texture is the feeling and visual feel of the fabrics, colours, and room accessories. Texture is the roughness of the surface of a material.
Real Texture and Implied Texture. Texture is both a visual delight and a sensual phenomenon meant for the senses to experience via feel and for the eyes through the mode of vision.
Color is the perceived character of a surface according to the wavelength of light reflected from it. Color comes form light They are wavelengths of such radiations which human beings can visually perceive
HUES
VALUE
SATURATION
Where
the color is positioned on the color wheel. Terms such as red, bluegreen, and mauve all define the hue of a given color.
Value refers to the density of the color i.e. the lightness or the darkness of the color. It refers to the White Black balance
The intensity, or level of chroma, of a color. The more gray a color has in it, the less chroma it has.
PRIMARY COLOR. Example : Red, Blue, Yellow. SECONDARY COLOR. Example : Orange, Green, Violet TERTIARY/INTERMEDIATE COLOR. Example : Yellow Green, Red Orange, Blue Violet. COMPLEMENTARY COLORS. Example : Yellow and Violet
A subtractive color space is the traditional color is pigment-based color, as in the mixing of paint. The absence of any pigment produces white, and all pigments blended together produces black. Primary colors: Red, yellow, blue Secondary colors: Orange, green, violet
SUBSTRACTIVE COLOR SPACE
Additive color space is an electronic color space. It is light-based color, as in the mixing of color on the computer Light is added to the screen in differing amounts to produce color Absence of any light is black, the presence of all light, or light at full intensity, is white.
Primary colors: Red, green, blue Secondary colors: Yellow, magenta, cyan
ADDITIVE COLOR SPACE
Design implies a conscious effort to create something that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing and the principles of design represent the basic assumptions of the world that guide the design practice.
Created by :
Nikhil Gupta,
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Light: 1.1 Light Travels in Straight LinesDocumento11 páginasLight: 1.1 Light Travels in Straight Linesching_jyoAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Introduction To XAFSDocumento270 páginasIntroduction To XAFSEric William CochranAinda não há avaliações
- Cas RF Engineering Basic ConceptsDocumento49 páginasCas RF Engineering Basic Conceptsraghu438Ainda não há avaliações
- In Uence of Light Intensity, Spectrum and Orientation On Sea Bass Plasma and Ocular MelatoninDocumento7 páginasIn Uence of Light Intensity, Spectrum and Orientation On Sea Bass Plasma and Ocular MelatoninMarko PotočnikAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Cluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)Documento33 páginasCluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)manpreetsingh3458417Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 - Color Image ProcessingDocumento98 páginasChapter 6 - Color Image ProcessingReza Mazlooman100% (1)
- Structure of Atom MAster Explanation PRESS4Documento105 páginasStructure of Atom MAster Explanation PRESS4Chad Ashley VandenbergAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- DC Pandey Optics and Modern Physics (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFDocumento559 páginasDC Pandey Optics and Modern Physics (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFYASH PRANESH75% (4)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
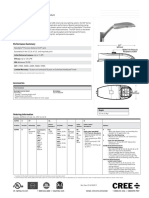
- XSP Street - Area Spec Sheet - Medium (1) Ficha Poste Av.Documento8 páginasXSP Street - Area Spec Sheet - Medium (1) Ficha Poste Av.Flor cortezAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Documento6 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Danish XainAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Radioactive Pollution ProjectDocumento19 páginasRadioactive Pollution ProjectMega No01Ainda não há avaliações
- Materials and DesignDocumento13 páginasMaterials and DesignbobAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Pinoy Bix TomasiDocumento22 páginasPinoy Bix TomasiRegine B. BactatAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge Organisers Gcse PhotographyDocumento5 páginasKnowledge Organisers Gcse Photographyapi-565375679Ainda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Microscope pp1Documento11 páginasMicroscope pp1api-217912133Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Crime Scene PhotographyDocumento107 páginasCrime Scene PhotographyTrickDaddy112Ainda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic Waves (Emw)Documento12 páginasElectromagnetic Waves (Emw)Divyansh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- BS en 167 Eye Ppe Optical TestDocumento23 páginasBS en 167 Eye Ppe Optical TestMAGNUMECAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- V 1200 Mapada EspecificacionesDocumento1 páginaV 1200 Mapada EspecificacionesVanessa Dominguez100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Project Guide: Dr. Karamjit Singh Lecturer Department of Applied Sciences, C.I.E.TDocumento17 páginasProject Guide: Dr. Karamjit Singh Lecturer Department of Applied Sciences, C.I.E.TtinuAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- PE175BF Lampara XenonDocumento2 páginasPE175BF Lampara Xenonfrancheska bacaAinda não há avaliações
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocumento42 páginasLight-Reflection and Refractionapi-24735088292% (25)
- Physics MicroprojectDocumento12 páginasPhysics Microproject134 Bilolikar AdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocumento33 páginasAtomic and Nuclear PhysicsKavita RajaramAinda não há avaliações
- 13 - Large Scale Path Loss - Practical Link Budget Design PDFDocumento7 páginas13 - Large Scale Path Loss - Practical Link Budget Design PDFWaqas AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Series 9000 Photoelectric Sensors: Technical DataDocumento10 páginasSeries 9000 Photoelectric Sensors: Technical DataRafael IbarraAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan What Is LightDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan What Is LightManjula MprkAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.Documento9 páginasWorksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.John WickAinda não há avaliações
- A Level Physic 2 2017 PDFDocumento324 páginasA Level Physic 2 2017 PDFAref DahabrahAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Telescope Book HistoryDocumento24 páginasTelescope Book HistoryMd Chand AsiqueAinda não há avaliações