Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
High Strength Steel Plate - Production, Properties and Use
Enviado por
lazaroccsDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
High Strength Steel Plate - Production, Properties and Use
Enviado por
lazaroccsDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
BLOG
STRUCTURAL
HIGHSTRENGTH
OFFSHORE
PRESSUREVESSEL
SHIPBUILDING
ABOUT
WEARRESISTANT
CONTACTUS
THICKPLATES
HomeHighStrengthSteelPlate
HIGHSTRENGTHSTEELPLATE
JULY16,2014BYDENISOAKLEY
WHYCHOOSEOAKLEYSTEEL?
LEAVEACOMMENT
Sincethefirstapplicationofsteelinsteelstructuresinthe19thcenturythedevelopmentofsteel
constructionhasbeencloselylinkedtothedevelopmentinmaterialpropertiesandproduction
methods.Significantachievementsconcerningstrength,economy,designversatility,fabrication
anderectiontechniquesandserviceperformancewouldnothavebeenpossiblewithoutthe
substantialimprovementsofhighstrengthsteelplate.Especiallywiththeapplicationofnew
productionprocessesforcarbonsteelssuchasthethermomechanicalrollingandthequenching
andtemperingprocess,highstrengthsteelplatewithgoodfabricationpropertiessuchas
weldabilitywasintroducedintotheconstructionmarket.
1.AwesomeService
2.ThickestPlates
3.BestAvailability
4.BestQualitySteel
5.SuperDelivery
2,884
BENEFITSOFHIGHSTRENGTHSTEELPLATE
Today,theapplicationofhighstrengthsteelplateisdrivenbythefollowingmajorreasons:
Economy:Byincreasingthestrengthofsteel,thestructuralsectioncanbereduced
dependingonthestructuralproblem.Thismayreducefabricationanderectioncostsan
importanttaskinhighwageeconomies.
Architecture:Thesizeofstructuralelementscanbereduced,enablingspecialaestheticand
elegantstructures,whichembedintheenvironmentinanoutstandingmanner.
Environment:Constructionwithlesssteelmeansalsoareducedconsumptionofour
worldsscarceresources.
Safety:Modernhighstrengthsteelgradesexhibitnotonlyhighstrengthvalues.Special
gradescombinethisstrengthwithexcellenttoughnesssothatahighsafetybothin
fabricationandapplicationofthestructuresisensured.Inparticular,modernoffshoresteel
gradesperformingatsomeofthelowestservicetemperaturesareagoodexample.
Itshouldnotbeneglectedthatseveralotherbranchesstartedwiththeapplicationofhighstrength
steelplateearlier.Mobilecraneconstructionusestodaysteelgradesuptoayieldstressof1100
MPaintheoffshoreindustrythermomechanicallyrolledsteelsinhigherstrengthclassesare
likelytobethesteelgroupthemostoftenusedforcoldwaterapplications.
AncoferWaldramisoneofEuropes
leadingsteelstockholders.With40,000
metrictonnesofheavycarbonsteel
platesinstockAncoferisabletosupply
largequantitiesofheavyplateto
projectsthatneedfastdelivery.
AncoferisfullyownedbyDillinger
Hutte.OakleySteelisAncofer'sagent
inAsia
Eventheshipbuildingindustryhasstartedtodesignwithhighstrengthsteel.Nevertheless,this
articlefocusesonthehighstrengthsteelplategradeswhicharetodayusedinsteelconstruction
(bridges,buildings,hydraulicsteelwork)inEuropealthoughweknowthatengineersinthisfield
canprofitalotfromthegoodexperiencemadeinotherbranches.
THEPRODUCTIONPROCESSESFORHIGHSTRENGTHSTEELPLATE
Thedevelopmentofnewgradesofhighstrengthsteelplatewasalwaysdrivenbythedemandof
theuserswantingmaterialsexhibitinggoodmechanicalcharacteristicssuchasyieldstrengthand
toughnessaswellasexcellentfabricationpropertiesensuringanefficientfabricationtechnologyin
theworkshopandduringtheerectionofasteelstructure.Amongotherstherearetwomajorways
ofincreasingtheyieldstrengthofsteel:
DillingerHutteistheworld'sleading
heavyplatemill.AGermansteelmill
Dillingerspecialisesinproducing
heavycarbonsteelplatefor
construction,offshoreandprocess
equipment.
Alloying:Byalloyingelementssuchascarbonandmanganesethestrengthofsteel
productscanbeeasilyincreased.Butitisknownthatanadditionofalloyingelementsin
mostcasesalsoworsensthefabricationpropertiesofsteelproducts,inparticularthe
weldability.
Heattreatment:Heattreatmenthasaneffectonmicrostructureandgrainsize.Themain
advantageofthisprocessconsistsintheachievementofafinegrainedstructureresulting
inhigherstrengthaswellasbettertoughnessofthematerialcomparedtoacoarsegrained
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
1/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
structure(HallPetchrelationship).
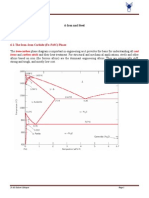
Forthisreasontheheattreatmentisofmajorimportanceinthedevelopmentofnewsteelgrades
andthehistoricalcontextisshowninFig.1.Until1950thesteelwhichistodayknownasS355J2
accordingtotheEuropeanstandardEN10025wasregardedashightensilesteel.
Asaplatethisgradeisusuallyproducedbyconventionalhotrolling(seeFig.2,processA)
followedbyanormalizingheattreatmentaheatingslightlyabovetheAotemperature
(temperaturewheretheferriticperliticstructurehastotallychangedtoaustenite)followedbya
slowcoolingresultinginafineandhomogeneousgrainstructure(seeFig.2,processB).This
processcanbereplacedbyanormalizingrollingwheresimplyexpressedthisheat
treatmentisincludedintherollingbutleadstoasimilarresult.
Duringthe1960stheapplicationofthe
quenchingandtemperingprocessfor
structuralsteelgradesbegan(processC).
Thisprocessconsistsofarollingfollowedby
heatingabovetheAotemperatureanda
rapidcooling,normallyinwater,plusa
subsequenttemperingbelowAr1
(temperaturewhereaustenitebeginsto
form.SeeFig.2processC).
Fig1:HistoricalDevelopmentofProductionProcessesfor
RolledSteelProducts
Roughlyspeakingduringthefirststepa
strongmartensiticorbaintiticgrain
structureisobtainedwhosetoughness
propertiesaresignificantlyimprovedduringthetemperingprocess.SeeFig.3.Besidesthisheat
treatmentthegoodbalancebetweenstrengthandtoughnessisbasedonthefactthatthese
steelsarealloyedbyaddingmicroalloyingelements(niobium,vanadium,titanium)precipitating
asfinelydistributedcarbonitrides.
Todaythisprocessgiveshighstrengthsteelplategradeswithyieldstrengthupto1100MPa,
althoughonlygradesupto960MPayieldstressarestandardised:Furthermore,classical
Europeansteelconstruction,i.e.buildingsandbridges,profitsonlyveryrarelyfromthisultra
highstrengthsteelandismostlylimitedtosteelgradesuptoS690.
TMCPROLLINGOFHIGHSTRENGTH
STEELPLATE
Fig2:Differenttypesofheattreatmentandrollingprocesses.
Temperatureontheverticalaxis.yrecrdenotesrecrystallized
austenite,ynotrecrdenotesnonrecrystallizedaustenite,a+y
thetemperaturerangeforaustenite+ferriteandathe
temperatureregionforferriteandpearliteinconventionalsteels.
MLEshowstheincreaseinthetemperatureforrecrystallization
duetomicroalloying.TNisthenormalizationtemperature.
CONTACTUSAT:
sales@oakleysteel.co.uk
+60123357743
+60193357743
Inthe1970sthermomechanicalrolling
processwasdevelopedandfirstappliedfor
linepipeplates,butthenquicklyfoundits
wayintothefieldsofshipbuildingandthe
constructionofoffshoreplatforms,bothfor
platesandforrolledsections.
TMrollingisdefinedasaprocessinwhich
finaldeformationiscarriedoutinacertain
temperaturerangeleadingtomaterial
propertieswhichcannotbeachievedbyheat
treatmentalone.Theresultingsteelgrade
hashighstrengthaswellashightoughnessandatthesametimeaminimumalloyingcontent
resultinginbestweldability.
Alsohereitisusualtoaddtothesteelsomemicroalloyingelementssuchasniobium,vanadium
or/andtitaniuminaverysmallamountinordertoachieveanadditionalstrengtheningeffectby
theformationoffinecarbonitridesandtoincreasetherecrystallisationtemperature.
Firstrollingpassesarecarriedoutattraditionalrollingtemperature.Furtherrollingpassesare
accuratelydefinedatatemperaturebelowtherecrystallisationtemperature(processD)and
sometimeseveninthetemperaturerangeofcoexistingausteniteandferrite/pearlite(process
E).Theprocessmaybefinishedbyanacceleratedcoolingespeciallyforthickerplates(process
F).
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
2/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
AllthesevarietiesoftheTMprocessproduceaveryfinegrainedmicrostructureofferriteand
pearliteorpartlyalsobainiteasshowninFig.3,avoidinghighalloyingcontentand
thereforeprovidingverygoodtoughnesspropertiesandanexcellentweldability.Furthermore,
highyieldstrengthgradescanbeproducedbythesetechniques.Plateswithguaranteed
minimumyieldstrengthvalueupto500MPaareavailableinthicknessesupto80mmandare
alreadyusedinshipbuildingandoffshoreconstruction.Forconstructionalsteelworkevenplatesof
120mmhavebeenproducedandappliedsuccessfullyinparticularinbridges.
ProcessGshowsTMrollingfollowedbydirectquenchingandselftempering.Hereanouterlayer
ofthematerialisquenched.Theinterior,beingwarmer,subsequentlygivesatemperingofthe
quenchedmaterial.
Intheremainderofthisarticlequenchedand
temperedsteelswillbereferredtoasQT
andthermomechanicallyrolledsteelsasTM
sinceQandM(formaldeliveryconditions)
arealsoqualitydesignationsforimpact
toughness.
STANDARDSFORHIGHSTRENGTH
STEELPLATE
InNovember2004thenewstandardforhot
rolledsteelproductsforusageinsteel
constructionEN10025waspublished.This
standardhassixpartsanddefinesthemost
Fig3:Grainmicrostructureofquenchedandtemperedand
commonstructuralsteelgradeswhichwere
thermomechanicallyrolledsteelcomparedtonormalizedsteel
formerlytreatedintheindependent
standardsEN40113andEN10137.With
referencetothehigherstrengthgrades,whichareunderdiscussioninthisdocument,foreach
stateofdeliveryexplainedinchapter4.1.2,onepartofEN10025(2004)isnowreserved.
However,asfaraschemicalandmechanicalpropertiesofthedefinedsteelgradesare
concerned,thesepartsdonotshowbigchangesincomparisontotheformerstandardsEN
10113and10137.
RegardingHighPerformanceSteelsEN10025Part4(replacingEN101133)describesTM
steelswithminimumyieldstressof420and460MPaatthelowestproductthickness.Foreach
yieldstressgrade,twoqualitiesexistwithdifferentguaranteedtoughnesslevelsmeasuredbythe
CharpyVtestwiththespecimeninthelongitudinaldirection:anMqualitywith40Jat20Cand
anMLqualitywith27Jat50C.QTsteelgradesarenowstandardisedinEN10025Part6
(replacingEN101372)withyieldstressgradesfrom460MPaupto960MPa,whereas
constructionalsteelworkinEuropetodayislimitedtosteelgradesuptoS690.
Higherstrengthsteelplategradesarestillthedomainoftheconstructionequipmentindustry.
Here,foreachyieldstressgradeexceptS960threedifferentqualitiesexistCharpyVtestedinthe
longitudinaldirection:aQqualitywith30Jat20C,aQLqualitywith30Jat40CandaQL1
qualitywith30Jat60C.
Tables1,2and3summarisethemechanicalpropertiesofthesesteelgradesaccordingtothe
standard.Nevertheless,itmustberecognisedthatproductsfromactualproductionmostlyexceed
theseminimumvaluesbyfar.
Table1:StrengthrequirementsforstructuralsteelsEN100254,TMsteels
Grade
Nominalthickness(mm)
16
>1640
>4063
>6380
>80100
>100120
MinimumyieldstrengthReH,MPa
S420M
420
400
390
380
370
365
S460M
460
440
430
410
400
385
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
3/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
TensilestrengthRm.MPa
S420M
520680
500660
480650
470630
460620
S460M
540720
530710
510690
500680
490660
Table2:StrengthrequirementsforstructuralsteelsEN100256,QTsteels
Grade
NominalThicknesst(mm)
3t50
50<t100
100<t150
MinimumyieldstrengthReH,MPa
S460Q
460
440
400
S500Q
500
480
440
S550Q
550
530
490
S620Q
620
580
560
S690Q
690
650
630
S890Q
890
830
S960Q
960
TensilestrengthRm,MPa
S460Q
550720
500670
S500Q
590770
540720
S550Q
640820
590770
S620Q
700890
650830
S690Q
770940
760930
S890Q
9401100
8801100
S960Q
9801150
710900
Table3:Minimumenergyvaluesforimpacttestsonlongitudinalspecimens.TMandQT
steels
Quality
TestTemperatureC
20
40
60
40J
ML
Q
50
27J
30J
QL
30J
QL1
30J
Energyrequirementsatthelowesttesttemperaturearegivenforeachquality.Transverseimpact
testingcanbeorderedasanoption.Forfurtherdetailsrefertotherelevantstandard
CHEMICALPROPERTIESOFHIGHSTRENGTHSTEELPLATE
Themaximumalloyingcontentsforhighstrengthsteelsasgiveninthestandardsareoften
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
4/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
consideredtogiveveryconservativeupperlimits.Actualvaluesfortheproductsareusuallymuch
lower.Furthermore,itshouldbetakenintoaccountthatnotonlythesteelgradehasaninfluence
onthealloyingcontentinadditionthechemicalcompositionmayvarywiththethicknessrange.
Itisobviousthatdifferencesbetweenproductsofdifferentproducersarequitenormal.
Table4givesexamplesofthechemicalcompositionsofS460ML,S460QL,andS690QLin
comparisontothecommonEuropeanconstructionalsteelS355J2.Itcanbeseenthatforgrades
uptoS460TMrolledgradesshowaverycleanchemicalcompositionresultinginexcellent
weldability.Butalsothealloyingconceptsofthehigherstrengthgrade,inparticularS690,allow
forefficientfabricationprocesses,asdescribedbelow.
Table4:Chemicalcompositionsofhighstrengthsteel,50mmthick(weight%).S355J2is
givenforcomparison.Excerptfromthestandardrequirementsandexamplesofactual
values.
S355J2
S460ML
S460QL
S690QL
EN
10025
Part2
Typical
Analysis
EN
10025
Part4
Typical
Analysis
EN
10025
Part6
Typical
Analysis
EN
10025
Part6
Typical
Analysis
0.22
0.17
0.16
0.08
0.20
0.15
0.16
Si
0.55
0.45
0.60
0.45
0.80
0.45
0.80
0.30
Mn
1.60
1.50
1.70
1.65
1.70
1.50
1.70
1.30
0.025
0.015
0.025
0.011
0.020
0.012
0.020
0.012
0.025
0.015
0.020
0.002
0.010
0.005
0.010
0.005
Nb
0.05
<0.04
0.06
0.017
0.06
<0.04
0.12
0.12
0.12
Ti
0.05
0.05
0.05
Mo
0.20
0.70
Ni
0.80
0.19
0.55
0.17
Cu
0.55
Cr
0.30
B
CE
0.47
0.42
0.47
0.39
0.70
0.37
2.0
2.0
0.15
0.50
0.50
0.08
1.50
1.50
0.40
0.0050
0.0050
0.003
0.65
0.65
0.47
0.115
0.39
Pcm
0.26
0.19
0.19
0.29
CET
0.32
0.26
0.26
0.35
Widevariationofthecompositionispossibleduetoavarietyofpossibleproductionroutes.
Carbonequivalents:
CE=C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15
Pcm=C+Si/30+(Mn+Cu+Cr)/20+Ni/60+Mo/15+V/10+5B
CET=C+(Mn+Mo)/10+(Cr+Cu)/20+Ni/40
MECHANICALPROPERTIESOFHIGHSTRENGTHSTEELPLATE
Ithastobeclearlystatedthatthevaluesguaranteedbythestandardsareminimumvalues.The
usercannormallyexpectconsiderablybettervalues,inparticularfortoughness.Fig.4showsas
anexampletypicaltransitioncurvesfortheCharpyVenergyagainstthetesttemperatureforan
S460MLandanS690QLsteelandcomparesthemtoaconventionalsteel,S355J2.
ItcanbeseenthatthesehighstrengthsteelsshowsignificantlyhigherCharpyVvaluesatthe
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
5/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
testingtemperaturethangiveninthestandard(27Jat50Cand30Jat40Crespectively).
EvenatroomtemperaturethetoughnessbehaviourisbetterthanforaconventionalS355J2.
Thesehightoughnessvaluesalsoresultingoodweldingpropertiesasdescribedbelow.
FABRICATIONPROPERTIESOFHIGH
STRENGTHSTEELPLATE
Welding
GeneralrecommendationsforweldingofTM
andQTsteelsaregiveninEN10112,
WeldingRecommendationsforweldingof
metallicmaterialsPart2Arcweldingof
ferriticsteels.
Moststeelproducersgivedetailed
informationonweldingonrequest.Such
informationmayalsobefoundonthe
respectiveInternetwebsitesofthesteel
producers.Itisrecommendedtocontactthe
steelproducerfordetailedinformationsincethealloyingconceptsmaydifferbetweendifferent
producers.
Fig4:CharpyVtemperaturetransitioncurvesforS460MLand
S690QLwithS355J2forcomparison
Thesteelstreatedherehavelowcontentsofalloyingelementsandlowcarbonequivalents.They
canbeeasilyweldedtoallordinarystructuralsteelsusinganyconventionalarcweldingmethod.
ThisisespeciallytruefortheTMsteelssinceanS460Msteelhasalowercarbonequivalentthan
anordinarystructuralsteel.TheTMsteelshaveawiderwindowforheatinputandpreheating
thanQTsteels.EvenforthickerplatesofS460Mpreheatingcanbeomittedandthuswelding
costsreduced.
Themainpointstoavoidcoldcrackingare:
Preheatingtheparentmaterialwhenrecommended.Thisisalsomostimportantfortack
weldingandtherootpass.
Thejointsurfacesshouldbeperfectlycleananddry.
Minimisetheshrinkagestressbyensuringagoodfitandawellplannedsequenceofweld
runs.
Useafillermaterialwithlowhydrogencontent.
AnexampleofpreheatingrecommendationsfromoneproducerisgiveninTable5
SteelGrade
Maximumcombinedplatethickness,mm
30 40
50
60
S460M,S460ML
RoomTemperature,RT
S690Q,S690QL,
S690QL1
RT
75C
75C
70
80
90 100 110
120 130
75C
75C
75C
100C
150C
Combinedplatethicknessisthesumofthethicknessesoftheplatesjoined.Maximumhydrogen
contentofweldmetal5mg/100g.Heatinputapproximately1.7kJ/mm.
Theheatinputdeterminesthepropertiesoftheweld.Lowheatinputincreasesthemaximum
hardnessandtheriskforcoldcracking,whereashighheatinputdecreasesthetoughness.
Examplesofrecommendationsare:ForS420M,S460Mupto5.3kJ/mmforS690Qupto3.5
kJ/mm,dependinginbothcasesonthecombinedplatethickness.Forthinnercombined
thicknesses,below60to80mm,theheatinputmustbereduced.
Onthechoiceoffillermaterial:Chooseafillermaterialgivingahydrogencontent10ml/100g.
ForanS690platethickerthan20mm,5m1/100gisrecommended.RegardingS460Msteels
matchingorovermatchingmaterialcanbechosen,whileforS690Qmatchingorundermatchingis
appropriate.ForS690Qsteelitisadvisabletouseanundermatchingmaterialfortherootrun.
Forfilletweldsitisalwaysadvisabletoselectanundermatchingfillermaterial.Themajorbenefits
ofselectinglowerstrengthfillermaterialforQTsteelwithyieldstrength>500MPaare:higher
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
6/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
toughnessoftheweldmetal,improvedductilityofthejoint,reducedsensitivitytocracking.
Onstressrelieving:EN100251hasthefollowinginformation.Stressrelievingatmorethan
580Cformorethan1hmayleadtoadeteriorationofthemechanicalpropertiesofthesteel
gradesasdefinedinparts2to5.(Comment:thiscorrespondstotheoldstandardsEN
10025+A1,EN101132,EN101133,EN10155).
FornormalizedornormalizedrolledgradeswithminimumRef460MPathemaximumstress
relieftemperatureshouldbe560C.FortheQTsteelgradesofEN100256(correspondingtoEN
101372)themaximumstressrelieftemperatureshouldbe30Kbelowthetempering
temperature.ForQTsteelsthepurchaserisrecommendedtocontactthesteelproducer.The
maximumtemperatureisnormallyintherange550Cto580C.
Ourgeneralpracticalexperienceisthatpostweldheattreatmentisnotnecessary.Thetoughness
andhardnessoftheweldmentnormallymeettherequirementsandisnotsubstantiallyimproved
bystressrelieving.Itshouldonlybecarriedoutifareductionoftheresidualstressesisneeded
forsomespecialpurposeorifspecifiedinthedesigncodes.
FlameStraighteningofHighStrengthSteelPlate
TMandQTsteelscanbeflamestraightened,butthisrequiresmorecarethanforconventional
normalizedorhotrolledsteels.Gasheatingand/orinductionheatingarerecommended.Theskill
oftheoperatorisessential.Thetemperatureshouldbemeasuredusingthermocouples.
Temperaturesnotexceeding600Cformorethantenminutesdonotaffectthematerial
propertiesdetrimentallyforQTsteelofthetypeS690QLandS960QL.
ForTMmaterialuptoS460Mitwasshownthatasuperficialheatingupto950Cdoesnot
influencethemechanicalpropertiessignificantly,whereasformoresevereheatingconditionsup
tothemiddleoftheplatesamaximumof700Cshouldbeobserved.Thematerialmanufacturer
shouldbecontactedifmoredetailedinformationisneeded.
ColdFormingofHighStrengthSteelPlate
Thematerialstandards(EN100254,6)haveaNote:Coldformingingeneralleadstoa
reductionoftheductility.Furthermoreitisnecessarytodrawattentiontotheriskofbrittlefracture
inconnectionwithhotdipzinccoating.
ForTMsteelsEN100254hasoptionsregardingflangeabilityformaterialwithanominal
thicknesst512mmandrollformingformaterialwitht5.8mm.ForthesteelgradesS420and
S460theminimumbendradiusis4timestwiththeaxisofthebendinthetransversedirection
and5timestinthelongitudinaldirection.
ForQTsteelsEN100256hasanoptionregardingflangeabilityformaterialwithanominal
thicknesst16mm.Forthe5690gradetheminimumbendradiusis3.0timestwiththeaxisofthe
bendinthetransversedirectionand4.0timestinthelongitudinaldirection.Transverseand
longitudinalrefertotherollingdirection.
However,alsointhisrespectthesteelsoftenhavefarbetterpropertiesthanspecifiedinthe
standards.AnexamplefromonemanufacturerisgiveninTable6.
Table6:Exampleofbendingrecommendationsfromonemanufacturer.Theyreferto
shotblastandshopprimedplate.Asdeliveredplatemaybebentsomewhatnarrower.
Grade
Thickness
(mm)
Transverse
R/t
Longitudinal
R/t
Springback
degrees
1.0
1.5
36
t<8
1.5
2.0
610
8t<20
2.0
3.0
t>20
3.0
4.0
S420M,MLS460M,
ML
S690Q,QL,QL1
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
7/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
Rdenotesthepunchradiusandttheactualthickness
Mostmanufacturersgiverecommendationsforbendingandcanbecontactedformoredetailed
informationsuchasestimatesofthebendingforceneeded.
HotFormingofHighStrengthSteel
AccordingtoEN100254TMsteelsshallnotbehotformed.Ifdeemednecessarythe
manufacturershallbeconsulted.Oftenformingatamaximumtemperatureof580Cforshort
timesisallowed.QTsteelscanbehotformed.EN100256permitshotformingup,tothestress
reliefannealingtemperature,normallyintherange550Cto580C.Thisagreeswiththe
recommendationsofthesteelmanufacturers.Inpracticehotformingisrarelyusedduetothe
goodcoldformabilityofthesesteels.
HeatTreatmentofHighStrengthSteelPlate
Highstrengthsteelplategradesarenotintendedforheattreatmentafterdelivery.Theonly
exceptionisstressreliefannealingasdescribedabove.TMsteelsobtaintheirpropertiesduring
rolling,i.e.controlleddeformationatprecisetemperatures.Thiscannotberepeatedbyheat
treatment.QTsteelsareheattreated.However,thesteelmanufacturernormallyhasmuchmore
efficientquenchingequipmentthancanbefoundelsewhere.
Thesteelmanufactureradjuststhesteelcompositiontomatchthepropertiesofthequenching
andtemperingequipmenttoobtaintheintendedproperties.Thereforearenewedquenching
treatmentmaynotrestorethematerialpropertiesandmakestheinspectiondocumentsinvalid.In
rarecases,ifheattreatmentisdeemednecessarythesteelmanufacturermustbeconsulted.
ZincCoatingofHighStrengthSteelPlate
AllofthesteelsinEN10025exceptthoseofpart5haveoptionsfororderinggradessuitablefor
hotdipzinccoating.ReferenceismadetoENISO1461andENISO14713ortospecial
chemicalrequirementsinthestandards,seeTable7.Theselimitsconcernthethicknessand
appearanceofthezinclayer.
Table7:Classesforthesuitabilityforhotdipzinccoating(ladleanalysis)
Classes
Compositionwt%
Si
Si+2.5P
Class1
0.030
0.090
Class2
0.35
Class3
0.14Si.25
0.035
Class2appliesonlyforspecialzincalloys
Forclass2themaximumcarbonequivalentCEshallbeincreasedby0.02,forclass3by
0.01.Forthesteelstreatedhereclass2isthemostrelevantone.Galvanizingisacomplexissue
andonlygeneraladvicewillbegiven.Fordetailedinformationthesteelmanufactureror
companiesperforminggalvanizingortheirnationalassociationsshouldbeconsulted.The
outcomeforthehigheststrengthsteelsisgreatlyinfluencedbydetailsofthegalvanizingprocess
andtheapplication.Itisimportantthatthegalvanizingcompanyisinformedaboutthesteeltype.
Themainproblemforhighstrengthsteelsishydrogencrackingorzincpenetrationintothegrain
boundariesoftheparentmaterial.Localstressconcentrationsorresidualstressesfromwelding,
gascuttingorcoldformingwillincreasetherisk.Theseproblemsmayoccurevenforsteelsofthe
S355J2type.Stressrelievingandanabrasivewaterjetinsteadofflamecuttingmayreducethe
problem.
ThisarticleoriginallyappearedinHighPerformanceSteelsinEuropeandwaswrittenbyAnders
SamuelssonandFalkoSchroter,HeadofMarketingatDillingerHutte.Allimagesandtext
copyrightofDillingerHutte.
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
8/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
SHARETHIS:
More
RELATED
HeavySteelPlatesinCivil
Engineering
In"Blog"
HeavySteelPlatesforEconomic
ConstructionandOffshore
Structures
In"Blog"
HighStrengthSteelTMCPand
QTPlatesforHeavyStructures
In"Blog"
HeavySteelPlatesinCivil
Engineering
In"Blog"
HeavySteelPlatesforEconomic
ConstructionandOffshore
Structures
In"Blog"
HighStrengthSteelTMCPand
QTPlatesforHeavyStructures
In"Blog"
FILEDUNDER:BLOG,DILLINGERHUTTETECHNICALPAPERS
SPEAKYOURMIND
Name*
Email*
Website
PostComment
Notifymeoffollowupcommentsbyemail.
Notifymeofnewpostsbyemail.
AnIntroductiontoSteelMaking
TheRealCostofChineseSteel
DuriansorLemons?GettingaGoodPrice
forSteel
10TipsforGettingBetterSteelQuotations
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
9/10
21/03/2016
HighStrengthSteelPlateProduction,PropertiesandUse
WhenSteelPlateisLikeaBabysNappy!
SteelShippingRatesfromAntwerpto
SoutheastAsia
TestsforSteelPlates
TheTruthAboutBuyingSmallPiecesof
Steel
WillPuttingaCarinaDishEndHelpyouto
WinMoreOrders?
Returntotopofpage
http://www.oakleysteel.co.uk/highstrengthsteelplate
2016OakleySteelLimited|ContactUs|TermsofUse|ConditionsofSale|PrivacyPolicy|Sitemap
10/10
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Moving Average SimplifiedDocumento136 páginasMoving Average Simplifiedimmachoboy100% (13)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Aws D10.10Documento107 páginasAws D10.10praveentien91% (11)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- TWM - Total Welding Management - Barckhoff 2005Documento197 páginasTWM - Total Welding Management - Barckhoff 2005lazaroccs100% (5)
- Corrosion Technology Types of Metallic CorrosionDocumento44 páginasCorrosion Technology Types of Metallic CorrosionTariq100% (1)
- Comparison Between Smaw and Gmaw-Stt Plus Fcaw-G Welding of Api 5L X80 Tubes For Pipeline FabricationDocumento8 páginasComparison Between Smaw and Gmaw-Stt Plus Fcaw-G Welding of Api 5L X80 Tubes For Pipeline FabricationJaimeCasanova Junior100% (1)
- WeldingofStainlesssSteelandotherJoiningMethods 9002Documento0 páginaWeldingofStainlesssSteelandotherJoiningMethods 9002jvs11021102Ainda não há avaliações
- Aws d1.1 WPQR GuidesDocumento3 páginasAws d1.1 WPQR GuidesDo XuanAinda não há avaliações
- Offshor Mooring SystemDocumento6 páginasOffshor Mooring SystemcudalbgeoAinda não há avaliações
- Offshor Mooring SystemDocumento6 páginasOffshor Mooring SystemcudalbgeoAinda não há avaliações
- Welding Low Alloy SteelsDocumento14 páginasWelding Low Alloy SteelsNanda Al Alif100% (1)
- High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel: Standard Specification ForDocumento4 páginasHigh-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel: Standard Specification ForislamakthamAinda não há avaliações
- Bokaro Steel PlantDocumento3 páginasBokaro Steel PlantSayan ChatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- SAE J343-2001 Test and Test Procedures For SAE 100R Series Hydraulic Hose and Hose AssembliesDocumento9 páginasSAE J343-2001 Test and Test Procedures For SAE 100R Series Hydraulic Hose and Hose AssembliesMiguel GalindoAinda não há avaliações
- Fracture and Crack Propagation in Weldments: Prepared By: DSC Dževad Hadžihafizović (Deng) Sarajevo 2023Documento48 páginasFracture and Crack Propagation in Weldments: Prepared By: DSC Dževad Hadžihafizović (Deng) Sarajevo 2023lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Training MaterialDocumento15 páginasTraining MateriallazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Stellite-6 Surface Layers Reinforced With Hard andDocumento7 páginasStellite-6 Surface Layers Reinforced With Hard andlazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue Failure of Notched Specimen-A Strain-LifeDocumento12 páginasFatigue Failure of Notched Specimen-A Strain-LifelazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Welding Defects With Radiographic Images: Prepared By: DSC PHD Dževad Hadžihafizović (Deng)Documento7 páginasWelding Defects With Radiographic Images: Prepared By: DSC PHD Dževad Hadžihafizović (Deng)lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- BrochureWeldability EN PDFDocumento39 páginasBrochureWeldability EN PDFAl0611981Ainda não há avaliações
- WJ 2015 08 s250Documento7 páginasWJ 2015 08 s250lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 Analises TermicosDocumento12 páginas1.2 Analises Termicosandreslatino27Ainda não há avaliações
- 26-Hardox 600 The - Ultimate Wear Plate PDFDocumento4 páginas26-Hardox 600 The - Ultimate Wear Plate PDFlazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- WJ 2015 08 s250Documento7 páginasWJ 2015 08 s250lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Astm A36-A36m-2004 PDFDocumento4 páginasAstm A36-A36m-2004 PDFmsalinasaguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Welding of Ferritic - Martensitic Stainless Steels - Job Knowledge 101Documento3 páginasWelding of Ferritic - Martensitic Stainless Steels - Job Knowledge 101lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Drawings CancellationsDocumento1 páginaDrawings CancellationslazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- 098 2017 en GL WireFluxCombinations WEBDocumento24 páginas098 2017 en GL WireFluxCombinations WEBlazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Cored Wires BÖHLER HL 46 MC BÖHLER HL 51-FD (EN)Documento4 páginasMetal Cored Wires BÖHLER HL 46 MC BÖHLER HL 51-FD (EN)lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Amp 16303 P 043Documento3 páginasAmp 16303 P 043lazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Track 2 - CardenasDocumento23 páginasTrack 2 - CardenaslazaroccsAinda não há avaliações
- Summary ISO TR 15608 Metallic Materials Grouping SystemDocumento4 páginasSummary ISO TR 15608 Metallic Materials Grouping SystemV SwamiAinda não há avaliações
- Aplication SDocumento12 páginasAplication SRubia ReisAinda não há avaliações
- TimkenSteel Metallurgy - 6thgrade PDFDocumento27 páginasTimkenSteel Metallurgy - 6thgrade PDFSilverio AcuñaAinda não há avaliações
- Damage MechaismDocumento11 páginasDamage Mechaismsoheilkhosh3311Ainda não há avaliações
- Effect of Various Heat Treatment Process On Tensile Strength and Elongation of Stainless SteelDocumento5 páginasEffect of Various Heat Treatment Process On Tensile Strength and Elongation of Stainless SteelehsanAinda não há avaliações
- Brazilian Green Pig Iron IndustryDocumento18 páginasBrazilian Green Pig Iron IndustryJorge MadiasAinda não há avaliações
- Austempered Ductile Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocumento8 páginasAustempered Ductile Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForJosé Ramón GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Coating Treatments of Steel For Reducing The Risk of Hydrogen EmbrittlementDocumento3 páginasPost-Coating Treatments of Steel For Reducing The Risk of Hydrogen EmbrittlementLeo CostaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 Phase TransformationDocumento20 páginasChapter 10 Phase TransformationVinicius SudrajatAinda não há avaliações
- An 11.2 Abrasion Resistance of Hot Dip Galvanized CoatingsDocumento4 páginasAn 11.2 Abrasion Resistance of Hot Dip Galvanized CoatingsnarmathaAinda não há avaliações
- Pakistan Steel MillDocumento24 páginasPakistan Steel MillMuhammad OsafAinda não há avaliações
- Metallurgical AnalysisDocumento4 páginasMetallurgical AnalysisIrah Antonniette SagutAinda não há avaliações
- Specification For Forged or Rolled Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts For High-Temperature ServiceDocumento19 páginasSpecification For Forged or Rolled Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts For High-Temperature Servicekranthi kumarAinda não há avaliações
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocumento25 páginasWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book Publishermhd efriyansyahAinda não há avaliações
- DFM Module 1Documento51 páginasDFM Module 1Orville SutariAinda não há avaliações
- CIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 1Documento18 páginasCIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 1Anthony TangAinda não há avaliações
- Saej1562 99Documento9 páginasSaej1562 99Tomás jesus De Paz LópezAinda não há avaliações
- Gasnitriding - Plasmanitriding - SaltbathnitridingDocumento4 páginasGasnitriding - Plasmanitriding - SaltbathnitridingKevin ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Science CO PO Mapping With JustificationDocumento4 páginasApplied Science CO PO Mapping With JustificationChemistryGAinda não há avaliações
- The Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) PhaseDocumento8 páginasThe Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) PhaseRecep VatanseverAinda não há avaliações
- Material Groups: ISCAR Catalog DirectoryDocumento14 páginasMaterial Groups: ISCAR Catalog DirectorygielAinda não há avaliações
- C10C - 1.0214 - SteelNumber - Chemical Composition, Equivalent, PropertiesDocumento2 páginasC10C - 1.0214 - SteelNumber - Chemical Composition, Equivalent, PropertiesSergiAinda não há avaliações
- F 2229 - 12Documento6 páginasF 2229 - 12jose floresAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Corrosion - Dr. Govind VagadiyaDocumento14 páginasFundamentals of Corrosion - Dr. Govind VagadiyaDr. Govind VagadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Genesis of Spalling in Tandem Mill Work-RollsDocumento9 páginasGenesis of Spalling in Tandem Mill Work-Rolls54321qazAinda não há avaliações
- Euro PM 2012Documento59 páginasEuro PM 2012Michelle HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- AIRCRAFT STRUCTURE MATERIAL METAL Pictures OnlyDocumento27 páginasAIRCRAFT STRUCTURE MATERIAL METAL Pictures OnlyYasser ZubaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Metallurgy of Inconel Alloys For Corrosive EnvironmentDocumento12 páginasPhysical Metallurgy of Inconel Alloys For Corrosive EnvironmentSyavash EnshaAinda não há avaliações
- Shape Memory AlloysDocumento40 páginasShape Memory Alloysudit kumarAinda não há avaliações
- 6-Surface Hardening PDFDocumento11 páginas6-Surface Hardening PDFSohanur RahmanAinda não há avaliações