Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
08 Alaúde
Enviado por
David De Jesus Cassimiro0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
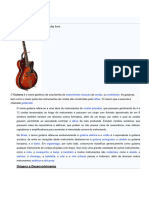
18 visualizações1 páginaO alaúde é um instrumento musical de cordas com uma caixa em forma de meia pêra ou gota. Sua origem vem da palavra árabe al'ud ou da palavra persa rud, significando corda ou instrumento de cordas. O ʿūd é um tipo de alaúde proeminente na música islâmica medieval e moderna, com uma caixa profunda e um braço ligeiramente mais curto do que o alaúde europeu.
Descrição original:
Título original
08.Alaúde
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoO alaúde é um instrumento musical de cordas com uma caixa em forma de meia pêra ou gota. Sua origem vem da palavra árabe al'ud ou da palavra persa rud, significando corda ou instrumento de cordas. O ʿūd é um tipo de alaúde proeminente na música islâmica medieval e moderna, com uma caixa profunda e um braço ligeiramente mais curto do que o alaúde europeu.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
18 visualizações1 página08 Alaúde
Enviado por
David De Jesus CassimiroO alaúde é um instrumento musical de cordas com uma caixa em forma de meia pêra ou gota. Sua origem vem da palavra árabe al'ud ou da palavra persa rud, significando corda ou instrumento de cordas. O ʿūd é um tipo de alaúde proeminente na música islâmica medieval e moderna, com uma caixa profunda e um braço ligeiramente mais curto do que o alaúde europeu.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
O alaúde é um instrumento musical da família dos cordofones.
Este instrumento é de
corda palhetada ou dedilhada, com braço trastejado e com a sua característica caixa em
forma de meia pêra ou gota.
A origem das palavras alaúde e oud possivelmente remontam da palavra árabe al'ud, "a
madeira"; alguns investigadores sugerem também que seja uma simplificação da palavra
persa rud, que significa corda, instrumento de cordas ou alaúde. Sitar é um tipo de
alaúde de braço longo originário da Índia.
ʿūd, also spelled Oud, stringed musical instrument prominent in medieval
and modern Islāmic music. It was the parent of the European lute. The ʿūdhas a deep,
pear-shaped body; a fretless fingerboard; and a relatively shorter neck and somewhat less
acutely bent-back pegbox than the European lute. The tuning pegs are set in the sides of
the pegbox. The gut strings, plucked with a plectrum, are fastened to a tension (guitar-type)
bridge on the instrument’s belly.
The ʿūd is not completely standardized in size or number of strings. Four pairs of strings
(the classical number) are common, although five and
Você também pode gostar
- Apostila de Cordas CCB Viola - Corrigida Finalizada RevisadaDocumento38 páginasApostila de Cordas CCB Viola - Corrigida Finalizada Revisadas4mukz100% (1)
- Etimologias das palavras do Português corrente. Palavras portuguesas vindas do Inglês, Francês, Alemão....; de línguas africanas, americanas e asiáticas.No EverandEtimologias das palavras do Português corrente. Palavras portuguesas vindas do Inglês, Francês, Alemão....; de línguas africanas, americanas e asiáticas.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Historia Violino - O Início de TudoDocumento13 páginasHistoria Violino - O Início de TudoLucasSilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Apostila Guitarra CompletaDocumento172 páginasApostila Guitarra CompletaWagner TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Dicionario Iorubá PortuguesDocumento75 páginasDicionario Iorubá PortuguesJonatas Jose Silva50% (2)
- Dicionario YorubáDocumento56 páginasDicionario YorubáTrdfara Pdeaa75% (8)
- Dicionario YorubaDocumento56 páginasDicionario YorubaDi CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- Dicionário de Instrumentos MusicaisDocumento33 páginasDicionário de Instrumentos MusicaisMarco GuimaraesAinda não há avaliações
- GuitarraDocumento21 páginasGuitarraJoão Diogo Leitão100% (4)
- História Do PandeiroDocumento2 páginasHistória Do Pandeirojunior_lopes9100% (1)
- Guitarra e Alaúde - Uma História de Evoluções e EstagnaçõesDocumento11 páginasGuitarra e Alaúde - Uma História de Evoluções e EstagnaçõesLuan MatosAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentos MusicaisDocumento7 páginasInstrumentos MusicaisNando GaleanoAinda não há avaliações
- História Do PandeiroDocumento5 páginasHistória Do PandeiroMarcelo Borba100% (2)
- A Viola de Arame Origem e Introdução No Brasil PDFDocumento20 páginasA Viola de Arame Origem e Introdução No Brasil PDFAulusRodrigues100% (1)
- História Concisa Da Guitarra ClássicaDocumento17 páginasHistória Concisa Da Guitarra ClássicafunxoAinda não há avaliações
- A História Do ViolãoDocumento25 páginasA História Do ViolãoFrancisco CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- A Dança Dos 5 ElementosDocumento8 páginasA Dança Dos 5 Elementosrosapires26Ainda não há avaliações
- Árabe Instrumento de Cordas Pêra Classificação de Instrumentos de Hornbostel-Sachs CursosDocumento9 páginasÁrabe Instrumento de Cordas Pêra Classificação de Instrumentos de Hornbostel-Sachs CursosraissaAinda não há avaliações
- Alaúde RenascentistaDocumento4 páginasAlaúde RenascentistaKleyton FreitasAinda não há avaliações
- Documento 10Documento13 páginasDocumento 10Maria RibeiroAinda não há avaliações
- Apostila Curso de Guitarra CompletaDocumento101 páginasApostila Curso de Guitarra CompletaRafael AlmeidaAinda não há avaliações
- História Da GuitarraDocumento29 páginasHistória Da GuitarraPedro MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- História Da GuitarraDocumento10 páginasHistória Da GuitarrainstrumentosmozartAinda não há avaliações
- Teoria Do Mini-Curso de ViolinoDocumento7 páginasTeoria Do Mini-Curso de ViolinoVando Da Silva OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Trabalho AlaudeDocumento6 páginasTrabalho AlaudeMarcos FaustinoAinda não há avaliações
- Oud - Wikipédia, A Enciclopédia LivreDocumento3 páginasOud - Wikipédia, A Enciclopédia LivreraissaAinda não há avaliações
- Música CarnáticaDocumento12 páginasMúsica CarnáticaGuilherme Battistella Frigini PintoAinda não há avaliações
- Historia e Surgimento Dos Instrumentos MusicaisDocumento2 páginasHistoria e Surgimento Dos Instrumentos Musicaiszybegy8Ainda não há avaliações
- A História Do ViolãoDocumento4 páginasA História Do ViolãoAndré Neves0% (1)
- Historia Do Violao PDFDocumento1 páginaHistoria Do Violao PDFRildo SansAinda não há avaliações
- Viola de Arame Indrodução No BrasilDocumento20 páginasViola de Arame Indrodução No BrasilFelipe BarãoAinda não há avaliações
- 6.5-Instrumentos Musicais MedievaisDocumento3 páginas6.5-Instrumentos Musicais Medievaiseduardo vasconcelosAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentos Musicais de PortugalDocumento5 páginasInstrumentos Musicais de PortugalElisa VanessaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Instrumentos Musicais MedievaisDocumento16 páginas5 Instrumentos Musicais MedievaisAfonso GomesAinda não há avaliações
- FlautaDocumento7 páginasFlautaIgor CostaAinda não há avaliações
- Métododo de Violão PopularDocumento75 páginasMétododo de Violão PopularEdson CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- OrganologiaDocumento4 páginasOrganologiaSofia de Azevedo SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Introdução Ao Instrumento e A TécnicaDocumento10 páginasIntrodução Ao Instrumento e A TécnicapaganininicolaAinda não há avaliações
- AULA Historia Do Instrumento AcusticoDocumento7 páginasAULA Historia Do Instrumento AcusticoAnonymous Dv5Yf4JAinda não há avaliações
- A RabecaDocumento1 páginaA RabecaIsaque CIprianoAinda não há avaliações
- Musica e Dança MedievalDocumento16 páginasMusica e Dança MedievalAfonso Gomes100% (1)
- Violin oDocumento9 páginasViolin oBreno PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentos Da Grécia AntigaDocumento5 páginasInstrumentos Da Grécia AntigaZecca Joe CarreiroAinda não há avaliações
- Música Celta2 - FinalDocumento19 páginasMúsica Celta2 - FinalEugenio Rocha100% (2)
- Instrumentos Tradicionais IndianosDocumento2 páginasInstrumentos Tradicionais IndianosAna Paula CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Dic Yor Port1Documento99 páginasDic Yor Port1joauraAinda não há avaliações
- Texto PandeiroDocumento2 páginasTexto Pandeiroahle.rjAinda não há avaliações
- SitarDocumento1 páginaSitarCátia PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Trabalho de Música - Harpa - Gabriela BorgesDocumento6 páginasTrabalho de Música - Harpa - Gabriela BorgesGermano BorgesAinda não há avaliações
- Os Instrumentos Musicais Na Grécia AntigaDocumento13 páginasOs Instrumentos Musicais Na Grécia AntigaRafaela MoreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentos GregosDocumento4 páginasInstrumentos GregostharcisoAinda não há avaliações
- Apostila Violão Básico IDocumento46 páginasApostila Violão Básico IMarcio ManfrinAinda não há avaliações
- Alfabeto MusicalDocumento12 páginasAlfabeto MusicalcatboomboxAinda não há avaliações