Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
PSUBSsols
Enviado por
Carrion HumbertoDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PSUBSsols
Enviado por
Carrion HumbertoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
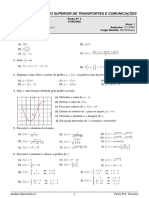
IQ Prova Subs. de MAT-2110 prova?
Nome completo:
Nro. USP: 16/07/2023
IME-USP Professor: Humberto D. Carrion V
Responda cada item a) se vc vai susbstituir a 1ra prova, os items b) se vc vai substituir a 2da prova e os item c) se vc
vai substituir a 3ra prova. Marcar em dois ou mais, anula a quest~
ao. Deixar sem resposta indica N.A.
1 2x
1. Seja f (x) = ln 3+2x
(a) Se para todo x 2 dom (f ) temos jxj < c, ent~ao vc pode a rmar que
i)c > 2 ii) c 1 iii)c 1=2 iv) c 3=2.
1 2x 3 1
SOL.- 3+2x > 0, Solution is: 2; 2 , resposta: c 3=2
d
(b) A derivada dx f (1=x) e
8 8 4 5
i) 3x3 +4x2 +4 ii) 3x2 +4x+4 iii) 4x2 +4x 3 iv) x2 +4x+4 .
d 1 2x 8 d d
SOL.- dx ln 3+2x = 4x2 +4x 3 )si (u = 1=x), dx f (1=x) = dx f (u) du
dx =
8
4u2 +4u 3
1
x2 =
8 1 8
4(1=x)2 +4(1=x) 3 x2 = 3x2 +4x+4 ,
R0
(c) A integral 1
f (x) dx e
i) ln 2 ii) 1=2 iii) ln 2 iv) 0
R0 1 2x
SOL.- 1
ln 3+2x dx = 0, mudancas u = 1 2x e v = 3 + 2x.
2x
2. Seja f (x) = 1+3x2 .
p i
1 3 1
(a) Se f e a inversa de f , em 1; 3 entonces f ( 1=2) e
p
3
i) 1=2, ii) 3 iii) 1 iv) 1=3.
p i
1 2x 1 3
SOL.- f ( 1=2) = x , f (x) = 1=2 , 1+3x2 = 1=2, Solution is: 1; 3, e 12 1; 3
(b) O valor maximo absoluto de f em [ 1; 2] e.
p p p
i) 13 3 ii) 134
iii) 23 iv) 3.
d 2x 3x2 1
p 2 1 4
SOL.- dx 1+3x2 = 2 (3x 2 +1)2 . x = 3=3. f ( 1) = 4 = 2, f (2) = 13 = 0:307 69,
p
p 2( 3=3) 1
p
f 3=3 = p 2 = 3 3 = 0:577 35
1+3( 3=3)
R1
(c) A integral 0 f (x) dx e
3
i)ln 3 ii) 23 ln 2 iii) 23 ln 2
2 iv) 2 ln 2.
R 1 2x 2
SOL.- 0 1+3x 2 dx = 3 ln 2
p
3. Seja f (x) = 1 x2 e g (x) = x2
(a) O valor de f (g (1=2)) g (f (1=2)) e
p p p p
i) 14 15 34 ii) 41 15 + 34 iii) 12 15 12 iv) 12 15 32 .
p p
SOL.- g (1=2) = 14 , f (1=2) = 21 3. f (g (1=2)) = 41 15, g (f (1=2)) = 34 , ) f (g (1=2)) g (f (1=2)) =
1
p 3
4 15 4
f (x) g(1)
(b) O limite limx!0 g(x) e
2 1 1 1
i) 3 ii) 3 iii) 4 iv) 2
p
f (x) g(1) 1 x2 1 1
SOL.-limx!0 g(x) = limx!0 x2 = 2
3g(x)
(c) A area limitada por F (x) = xf (x) e G (x) = 5x
98 37 24 52
i) 475 ii)
iii) 275 iv) 375
375
p p
SOL.- F (x) = x 1 x2 , G (x) = 35 x. G (x) = F (x) , 53 x = x 1 x2 , Solution is: 4 4
5 ; 5 ; 0,
Z 4=5 p 3x
A=2 x 1 x2 dx
0 5
R 4=5 p 98
R 4=5 3x 24
0
x 1 x2 = 375 , 0 5 dx = 125 .
98 24 52
A=2 =
375 125 375
4. Seja f (x) = 2x 2 x
(a) A soluc~ ao da equac~
ao f (x) = 3 e
p p p p
log( 13 1) ln 3 13 4 log( 13+3) ln 2 13+3
i) 5 ii) log2 2 iii) 10 iv) log2 2
p
3 1
p p p ln( 12 13+ 32 )
SOL.- 2x 2 x
= 3, t t 1
= 3, Solution is: 2 2 13; 21 13 + 32 , 2x = 12 13 + 32 , x = ln 2 =
p
13+3
log2 2
f (x)
(b) O limx!0 x e
ln 2 3 ln 2
i) 2 ln 2 ii) 3 ln 2 iii) 2 iv) 2
2x 2 x
2x ln 2+2 x
ln 2
SOL.- limx!0 x = limx!0 1 = 2 ln 2. (Lhospital)
(c) A primitiva de f (x) e
4x +1 2x +1 4x +1 4x +1
i) 2x ln 4 ii) ln 2 iii) 4x ln 2 iv) 2x ln 2
R R 1 1 2x 22x +1
SOL.- (2x 2 x
) dx = ex ln 2 e x ln 2
dx = 2x ln 2 22x + 1 = 2x ln 2 + ln 2 = 2x ln 2
2
5. Seja f (x) = xex e g (x) = xex
(a) A soma das raices de f (x) = g (x) e,
i) 2 ii) 1 iii) 0 iv) 1
2
SOL.- xex = xex ) x = x2 ) x = 0; x = 1. Rpta 1.
(b) O maximo absoluto de h (x) = f (2x) g ( x) em [ 2; 4] e atingido no ponto:
i) 1 ii) 0 iii) e iv) 1
2 2 2
d d
SOL.- h (x) = f (2x) g ( x) = 2xe2x xex = 2x2 ex +2x
. dx h = dx 2x2 ex +2x =
2 ( 2)2 +2( 2)
4xex(x+2) x2 + x + 1 . Unica raiz x = 0. h (0) = 0, h ( 2) = 2 ( 2) e = 8,
2 (4)2 +2(4) 24
h (4) = 2 (4) e = 32e . O maximo e 0, atingido em x = 0.
(c) O volume gerado pela regi~
ao R limitada por f e h (x) = ex em torno do eixo Y e
2 4 1 2
i) 3 (5 e) ii) 3 (3 e) iii) 3 (3 e) iv) 3 (2 e).
SOL.- Z 1
4
2 x (ex xex ) dx = (3 e)
0 3
R1
(intregrar por partes 0
x2 ex dx = e 2)
x
6. Seja f (x) = x2 x 2 , x 2 ( 1; 2).
1
(a) f (1 + f (1=2)) e igual a
7 9
p p p p
i) 5 5 2 ii) 37 43 2 iii) 8
7
9
7 2 iv) 8
3 + 5
3 2
p
SOL.- f (1=2) = 29 , 1 + f (1=2) = 79 . Si f 1
(7=9) = x, ent~ao x
x2 x 2 = 7=9, ) x = 8
7
9
7 2 ou
p p
x = 79 2 + 87 . Assim x = 87 79 2X
(b) Uma ass ntota oblicua de g (x) = x2 f (x) e
i)y = 2x 1 ii) y = x 1 iii) y = 1 2x iv) y = x + 1
3
x
SOL.-g (x) = x2 f (x) = x2 x 2
g (x) x3
m = lim
= lim 2 =x
x!+1 x x!+1 x x 2
2
x
= lim =1
x!+1 x2 x 2
b = lim (g (x) mx)
x!+1
x+2
= lim x
x!+1 (x + 1) (x 2)
= 1
Assim y = mx + b = x + 1 e uma ass ntota ( a mesma assintota e no 1)
(c) O volume gerado pela regi~
ao limitada por f (x) e a reta y = x=2 ao girar em torno do eixo Y e
i) 31 ( 10 ln 2 + 7) ii) 15 ( 9 ln 2 + 6) iii) 1
4 ( 8 ln 2 + 5) iv) 1
2 ( 5 ln 2 + 6)
x
SOL.- x2 x 2 = x=2, Solution is: 1; 0
Z 1
x
2 x + x=2 dx
0 x2 x 2
R1 x 5 7 7 10 1
2 0
x x2 x 2 + x=2 dx = 2 3 ln 2 6 = 3 3 ln 2 = 3 ( 10 ln 2 + 7)
x 4 1
(por frac~
oes parciais: x x2 x 2 = 3(x 2) 3(x+1) + 1:)
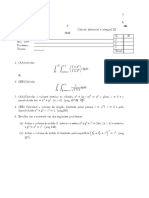
1 2 3 4 5 6
i
ii
iii
iv
1
10 6 = 1: 666 7
2
10 6 = 3: 333 3
3
10 6 = 5:0
4
10 6 = 6: 666 7
5
10 6 = 8: 333 3
Você também pode gostar
- Lista 2 Integral Definida AplicaçõesDocumento2 páginasLista 2 Integral Definida AplicaçõesguiviniciusAinda não há avaliações
- Texto Rex RexDocumento60 páginasTexto Rex RexThiago Dantas100% (1)
- Lista de Casa 2 - DerivadaDocumento7 páginasLista de Casa 2 - DerivadaPaulo RobertoAinda não há avaliações
- 0ee17171-4a93-4417-a976-f1d5eb42a1a0Documento196 páginas0ee17171-4a93-4417-a976-f1d5eb42a1a0Lorena Santos Novaes75% (4)
- Plano de Aula - Educação FísicaDocumento3 páginasPlano de Aula - Educação FísicaAiala Priscila Nunes100% (1)
- Crônicas RPG - Livro BásicoDocumento309 páginasCrônicas RPG - Livro Básicoiurimalkavyano67% (9)
- Calculo1 Lista2 PDFDocumento3 páginasCalculo1 Lista2 PDFPedroAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 7Documento1 páginaLista 7Samuel PulciniAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 7 - Clculo II - BSIDocumento3 páginasLista 7 - Clculo II - BSIRayane AlvesAinda não há avaliações
- Roteiro de Trabalho - Cálculo III (Regime Especial)Documento8 páginasRoteiro de Trabalho - Cálculo III (Regime Especial)Manuely SousaAinda não há avaliações
- Lista de Exercícios de Matemática IntegralDocumento2 páginasLista de Exercícios de Matemática IntegralJunior LemosAinda não há avaliações
- LISTA 5 DERIVADAS IntroduçãoDocumento3 páginasLISTA 5 DERIVADAS IntroduçãoDavi Granzotto OteroAinda não há avaliações
- K 6 X 1 K X 1: Acadêmico (A) : - Curso: EngenhariaDocumento2 páginasK 6 X 1 K X 1: Acadêmico (A) : - Curso: EngenhariaKarineAndressaAssmannAinda não há avaliações
- AL Lista2Documento5 páginasAL Lista2MikaellyAinda não há avaliações
- Aula 04 - Engenharia Civil - Calculo I - Derivada 2016Documento6 páginasAula 04 - Engenharia Civil - Calculo I - Derivada 2016willmpaivaAinda não há avaliações
- List7 2023 UspDocumento7 páginasList7 2023 UspAnderson AquilesAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 11 de Exercícios - Calculo IDocumento2 páginasLista 11 de Exercícios - Calculo IRoan Souza Dos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- PRIMITIVAS - Lista 1 - Integrais - 20231Documento2 páginasPRIMITIVAS - Lista 1 - Integrais - 20231Bruno LuzAinda não há avaliações
- Listade Integral Definidae Aplicaesde IntegralDocumento2 páginasListade Integral Definidae Aplicaesde IntegralSayonara KarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercícios Analise3Documento10 páginasExercícios Analise3Clara OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 3Documento1 páginaLista 3Gabrielly MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- Lista2 CalculoIIDocumento2 páginasLista2 CalculoIICompras VendasAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 4 PDFDocumento7 páginasLista 4 PDFGabi VeigaAinda não há avaliações
- Lista de Matemática FunçõesDocumento1 páginaLista de Matemática FunçõesFv PauloAinda não há avaliações
- Lista de Exercícios 4 de Cálculo IDocumento2 páginasLista de Exercícios 4 de Cálculo IGabriel Gomes CardosoAinda não há avaliações
- Lista0 CalculoA 2020-2Documento3 páginasLista0 CalculoA 2020-2Yasmin SeloisAinda não há avaliações
- 333Documento4 páginas333Carrion HumbertoAinda não há avaliações
- Lista Exercicios 2Documento3 páginasLista Exercicios 2Nadyne DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 8Documento14 páginasLista 8Luis Felipe Figueiredo OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- ListaS5 CalculoA 2020-2Documento2 páginasListaS5 CalculoA 2020-2Yasmin SeloisAinda não há avaliações
- CalculoDocumento7 páginasCalculoBiancaBeloAinda não há avaliações
- Lista Derivadas AplicacoesDocumento7 páginasLista Derivadas AplicacoesSayonara KarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercicios DerivadaDocumento4 páginasExercicios DerivadaLeandro SerraAinda não há avaliações
- Ficha Exercicios Nº4 FuncoesDocumento3 páginasFicha Exercicios Nº4 FuncoesEneas NaieneAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 1 de EDODocumento2 páginasLista 1 de EDOronaldo lopesAinda não há avaliações
- Atividade Diagnóstica (C4-T01)Documento2 páginasAtividade Diagnóstica (C4-T01)lucas santanaAinda não há avaliações
- AnaliseReal I M1011 2122teste2resDocumento3 páginasAnaliseReal I M1011 2122teste2resAntonio AntaoAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 4 MapDocumento2 páginasLista 4 MapVictor SosaAinda não há avaliações
- Func ºo Âes - AulaDocumento6 páginasFunc ºo Âes - AulaJuliana AdamateAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Lista - de - C - Lculo - 2022 - 1 (1Documento2 páginas2 - Lista - de - C - Lculo - 2022 - 1 (1Savio LAinda não há avaliações
- Lista de 22.12.22Documento3 páginasLista de 22.12.22viniciusAinda não há avaliações
- Lista IntegralDocumento4 páginasLista IntegralLUCIANO MeloAinda não há avaliações
- Solução Exercicios Funções de Varias Variaveis - Calculo James StewartDocumento3 páginasSolução Exercicios Funções de Varias Variaveis - Calculo James StewartHugo MottaAinda não há avaliações
- Exer Revisao PDFDocumento1 páginaExer Revisao PDFValquíriaAinda não há avaliações
- Teste2a CDI 1s 17 18 SolDocumento4 páginasTeste2a CDI 1s 17 18 SoljuniorAinda não há avaliações
- Ap2 Calculo Com RespostaDocumento3 páginasAp2 Calculo Com RespostaGlaudestony Aragão FerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 8Documento3 páginasLista 8José PaivaAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 3Documento6 páginasLista 3rafaelwylke200Ainda não há avaliações
- Lista Edo Primeira Ordem Calculo 3Documento14 páginasLista Edo Primeira Ordem Calculo 3Reginaldo NetoAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 01Documento4 páginasLista 01Carmen MathiasAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 6Documento3 páginasLista 6José PaivaAinda não há avaliações
- 2021.1 - Gab - Apx1 - CiDocumento5 páginas2021.1 - Gab - Apx1 - CiVitorAinda não há avaliações
- Integral IDocumento10 páginasIntegral IRaimundo Renato RabeloAinda não há avaliações
- AP1 C2 2017 2 GabaritoDocumento3 páginasAP1 C2 2017 2 GabaritoGiancarlo Medeiros de AlmeidaAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 3 SedoDocumento3 páginasLista 3 SedoIzabel FerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 4Documento4 páginasLista 4Oliver SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Lista I Com RespostasDocumento4 páginasLista I Com RespostasangelodelamareAinda não há avaliações
- Lista 5 - C1 PDFDocumento4 páginasLista 5 - C1 PDFRafaella OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Calculo1 ECA Lista4 15 2 PDFDocumento2 páginasCalculo1 ECA Lista4 15 2 PDFVenilson SenaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.4 Regra Da Cadeia ExercíciosDocumento1 página3.4 Regra Da Cadeia ExercíciospolyengquimicaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Lista Ex Regras DerivadaDocumento2 páginas2 Lista Ex Regras DerivadaErick HenriqueAinda não há avaliações
- Lista Edo Primeira Ordem C3 2020.1Documento14 páginasLista Edo Primeira Ordem C3 2020.1Joao HenriqueAinda não há avaliações
- ExCalc3TB3 2B-SolDocumento5 páginasExCalc3TB3 2B-SolMaurer UFMGAinda não há avaliações
- Exerres 1Documento1 páginaExerres 1Carrion HumbertoAinda não há avaliações
- ListaDocumento1 páginaListaCarrion HumbertoAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Da Prova CALIII2006 PosteriorDocumento1 página2 Da Prova CALIII2006 PosteriorCarrion HumbertoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Ra Prova Cal Economia SOLUÇÃODocumento3 páginas1 Ra Prova Cal Economia SOLUÇÃOCarrion HumbertoAinda não há avaliações
- Regras Da Casa by LeviDocumento13 páginasRegras Da Casa by LeviEmerson RodriguesAinda não há avaliações
- MetaStock TemplatesDocumento7 páginasMetaStock TemplatesNLimaFAinda não há avaliações
- Bengalelê MotumboDocumento7 páginasBengalelê MotumboLucas LineageAinda não há avaliações
- Tragoedia Ficha de HeroiDocumento2 páginasTragoedia Ficha de HeroiFelipe MorlóAinda não há avaliações
- Mundo Tentacular Queimando Tudo! - Regras para Utilizar Lança-Chamas em Call of CthulhuDocumento8 páginasMundo Tentacular Queimando Tudo! - Regras para Utilizar Lança-Chamas em Call of CthulhuEduardo GomesAinda não há avaliações
- Arlequim - LadinoDocumento3 páginasArlequim - LadinoFabiano ViegasAinda não há avaliações
- Jogador Número UmDocumento550 páginasJogador Número UmClara NodaAinda não há avaliações
- Naipe de Paus No Tarô MitológicoDocumento4 páginasNaipe de Paus No Tarô Mitológicokrislena100% (1)
- Ficha OPRPG - Gina LinettiDocumento2 páginasFicha OPRPG - Gina LinettiNicolas MaiaAinda não há avaliações
- Jetion 16 Abril 2013Documento107 páginasJetion 16 Abril 2013ggiovanniviAinda não há avaliações
- Live Action (RPG)Documento5 páginasLive Action (RPG)Thiago MedeirosAinda não há avaliações
- História Do VoleiDocumento2 páginasHistória Do VoleiRogério MeloAinda não há avaliações
- Relatório Destino de Amyri - Gustavo Cerino PaulinoDocumento84 páginasRelatório Destino de Amyri - Gustavo Cerino PaulinoNaiane MarconAinda não há avaliações
- Detonado de Pokemon Black e WhiteDocumento173 páginasDetonado de Pokemon Black e WhiteJorge Luiz VionattoAinda não há avaliações
- MapaDocumento1 páginaMapaPaulo GenaroAinda não há avaliações
- O PROBLEMA DE PAUL MORPHY Por Ernest JonesDocumento10 páginasO PROBLEMA DE PAUL MORPHY Por Ernest JonesValéria Luíza GonçalvesAinda não há avaliações
- Agenda Da Atividade - Fé em DeusDocumento3 páginasAgenda Da Atividade - Fé em DeusNayara ValoisAinda não há avaliações
- CPR Corebook Cyberpunk Red v121pdf PDF Free (1) 408 458.en - PTDocumento51 páginasCPR Corebook Cyberpunk Red v121pdf PDF Free (1) 408 458.en - PTAndré LuísAinda não há avaliações
- Como Purificar Seu Baralho de TarôDocumento3 páginasComo Purificar Seu Baralho de TarôLuana NatanAinda não há avaliações
- Bingo Das Palavras SimplesDocumento16 páginasBingo Das Palavras SimplesLIVIA MARIANE BARBUTIAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Fifa 18Documento80 páginasEbook Fifa 18Simon BartholomewAinda não há avaliações
- Histograma de Mobilizaçao Da ObraDocumento9 páginasHistograma de Mobilizaçao Da ObraRoger CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- Screenshot 2023-10-15 at 2.46.13 PMDocumento2 páginasScreenshot 2023-10-15 at 2.46.13 PMNaresh AnkamAinda não há avaliações
- QUANDO AS MAQUINAS PARAM - Primeiro QuadroDocumento8 páginasQUANDO AS MAQUINAS PARAM - Primeiro QuadroraulAinda não há avaliações
- Ficha de ShadowrunDocumento2 páginasFicha de ShadowrunEmerson Cardoso VieiraAinda não há avaliações
- Ebulicao RPG 1.1Documento26 páginasEbulicao RPG 1.1IZANAGI YTAinda não há avaliações