Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
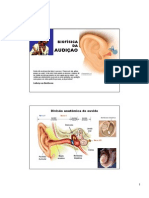
Órgãos Dos Sentidos Humanos Ouvido
Enviado por
DarleneDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Órgãos Dos Sentidos Humanos Ouvido
Enviado por
DarleneDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name Date Class Score
HUMAN SENSE
Human hearing is remarkable as it allows us
to hear sounds in our environment, such as
ORGANS: HEARING
birds singing or cars honking. Sound waves
are picked up by our ears and then sent to
our brain, which interprets the sound.
LABEL
FUN FACT: The human ear can distinguish up to 10,000 different sounds.
ARRANGE THE STEPS OF HEARING PROCESS IN SEQUENTIAL ORDER (1-7)
The small bones transmit vibrations to The eardrum vibrates from the
the cochlea, an organ in the inner ear. sound waves and sends a signal to
the tiny bones in the middle ear.
The brain recognizes the signals as
sound and we can hear! The sound waves travel through the
Sound waves travel through the air and ear canal and reach the eardrum.
enter our ears.
The cochlea is filled with fluid and
The hair cells then send electrical signals tiny hair cells that move when the
to the brain through the auditory nerve. sound waves reach them.
Nome Data Aula Pontuação
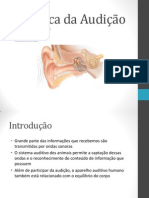
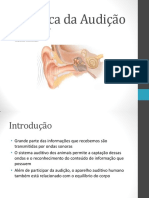
ÓRGÃOS DOS SENTIDOS A audição humana é notável porque nos permite ouvir
sons do nosso ambiente, como o canto dos pássaros ou
HUMANOS: AUDIÇÃO a buzina dos carros. As ondas sonoras são captadas
pelos nossos ouvidos e depois enviadas ao nosso
cérebro, que interpreta o som.
RÓTULO
FATO ENGRAÇADO: O ouvido humano pode distinguir até 10.000 sons diferentes.
ORGANIZE AS ETAPAS DO PROCESSO AUDITIVO EM ORDEM SEQUENCIAL (1-7)
Os pequenos ossos transmitem vibrações à O tímpano vibra com as ondas sonoras
cóclea, um órgão do ouvido interno. e envia um sinal aos minúsculos ossos
do ouvido médio.
O cérebro reconhece os sinais como som e
podemos ouvir!
As ondas sonoras viajam pelo canal
auditivo e chegam ao tímpano.
As ondas sonoras viajam pelo ar e entram
em nossos ouvidos.
A cóclea é preenchida com fluido e
As células ciliadas então enviam sinais elétricos ao pequenas células ciliadas que se movem
cérebro através do nervo auditivo. quando as ondas sonoras as atingem.
Name Date Class Score
HUMAN SENSE
Human hearing is remarkable as it allows us
to hear sounds in our environment, such as
ORGANS: HEARING
birds singing or cars honking. Sound waves
are picked up by our ears and then sent to
our brain, which interprets the sound.
LABEL
outer ear auditory canal hammer stirrup
eardrum anvil cochlea auditory nerve
FUN FACT: The human ear can distinguish up to 10,000 different sounds.
ARRANGE THE STEPS OF HEARING PROCESS IN SEQUENTIAL ORDER (1-7)
The small bones transmit vibrations to The eardrum vibrates from the
4 3
the cochlea, an organ in the inner ear. sound waves and sends a signal to
the tiny bones in the middle ear.
The brain recognizes the signals as
7
sound and we can hear! The sound waves travel through the
2
Sound waves travel through the air and ear canal and reach the eardrum.
1
enter our ears.
5 The cochlea is filled with fluid and
6 The hair cells then send electrical signals tiny hair cells that move when the
to the brain through the auditory nerve. sound waves reach them.
Nome Data Aula Pontuação
ÓRGÃOS DOS SENTIDOS A audição humana é notável porque nos permite ouvir
sons do nosso ambiente, como o canto dos pássaros ou
HUMANOS: AUDIÇÃO a buzina dos carros. As ondas sonoras são captadas
pelos nossos ouvidos e depois enviadas ao nosso
cérebro, que interpreta o som.
RÓTULO
ouvido
canal auditivo martelo estribo
externo
tímpano bigorna cóclea nervo auditivo
FATO ENGRAÇADO: O ouvido humano pode distinguir até 10.000 sons diferentes.
ORGANIZE AS ETAPAS DO PROCESSO AUDITIVO EM ORDEM SEQUENCIAL (1-7)
Os pequenos ossos transmitem vibrações à O tímpano vibra com as ondas sonoras
4 3
cóclea, um órgão do ouvido interno. e envia um sinal aos minúsculos ossos
do ouvido médio.
O cérebro reconhece os sinais como som e
7
podemos ouvir!
2 As ondas sonoras viajam pelo canal
auditivo e chegam ao tímpano.
As ondas sonoras viajam pelo ar e entram
1
em nossos ouvidos.
A cóclea é preenchida com fluido e
5
As células ciliadas então enviam sinais elétricos ao pequenas células ciliadas que se movem
6 quando as ondas sonoras as atingem.
cérebro através do nervo auditivo.
Você também pode gostar
- A Fisiologia AuditivaDocumento7 páginasA Fisiologia Auditivaesqueci o nomeAinda não há avaliações
- Professora: Ana Carvalho Disciplina: Física Módulo 6: Realizado Por: Rita Vieira P47Documento16 páginasProfessora: Ana Carvalho Disciplina: Física Módulo 6: Realizado Por: Rita Vieira P47Rita VieiraAinda não há avaliações
- ACUSTICADocumento9 páginasACUSTICAHermenegildo PascoalAinda não há avaliações
- AULA Sistema SensorialDocumento39 páginasAULA Sistema SensorialBryan VargasAinda não há avaliações
- O Ouvido HumanoDocumento5 páginasO Ouvido HumanoKARINE DOS SANTOS SERNAJOTTO100% (1)
- Processos Psicológicos Básicos (PPB) - AUDIÇÃODocumento17 páginasProcessos Psicológicos Básicos (PPB) - AUDIÇÃOsephiroth1208Ainda não há avaliações
- Bases Fà - Sicas Da Audià à o - FonoDocumento1 páginaBases Fà - Sicas Da Audià à o - Fonocspmyyrq6tAinda não há avaliações
- Aula 02 - Audicao 01 Correto 2020Documento56 páginasAula 02 - Audicao 01 Correto 2020Bio AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- AudiçãoDocumento3 páginasAudiçãoAlexAinda não há avaliações
- Cartaz AudiçãoDocumento6 páginasCartaz Audiçãollllllll1234llll123Ainda não há avaliações
- AUDIÇÃODocumento2 páginasAUDIÇÃOFernanda SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Biofisica Dos SistemasDocumento6 páginasBiofisica Dos SistemasCédrick CunhaAinda não há avaliações
- O Ouvido e o Canto1Documento9 páginasO Ouvido e o Canto1joaoAinda não há avaliações
- Artigo PsicoacusticaDocumento5 páginasArtigo PsicoacusticaAndré Dos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Sentidos Do Corpo HumanoDocumento6 páginas5 Sentidos Do Corpo Humanokvenon179Ainda não há avaliações
- Resumo (Sistema Da Audição)Documento4 páginasResumo (Sistema Da Audição)Yasmim SylvaAinda não há avaliações
- Resumo - Biofisica Na AudiçãoDocumento6 páginasResumo - Biofisica Na AudiçãoAnna Lidia Brito RiosAinda não há avaliações
- O SomDocumento6 páginasO SomInêsAinda não há avaliações
- Biofísica Da AudiçãoDocumento24 páginasBiofísica Da AudiçãoPaulo Henrique Queiroz Brito100% (1)
- Os Principais Sentidos Do Corpo HumanoDocumento6 páginasOs Principais Sentidos Do Corpo Humanokvenon179Ainda não há avaliações
- Ouvido HumanoDocumento6 páginasOuvido HumanolinieAinda não há avaliações
- Biofisica Da AudiçãoDocumento55 páginasBiofisica Da AudiçãoBio AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- Tabanho de Julia 4bDocumento4 páginasTabanho de Julia 4bprimusservicosemsaudeAinda não há avaliações
- Ouvido PDFDocumento4 páginasOuvido PDFMaria Papoila CrisAinda não há avaliações
- Os Sons Do MundoDocumento24 páginasOs Sons Do MundoSantosAinda não há avaliações
- Resumo Da Fisiologia Da AudiçãoDocumento2 páginasResumo Da Fisiologia Da AudiçãoCamila CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- Biologia PPT - Órgãos Dos SentidosDocumento59 páginasBiologia PPT - Órgãos Dos SentidosBiologia ppt89% (9)
- Guia para EducadoresDocumento76 páginasGuia para EducadoresTamiris AlvesAinda não há avaliações
- Biofisica Da AudicaoDocumento12 páginasBiofisica Da AudicaoMarcus WiniciusAinda não há avaliações
- AudiçãoDocumento2 páginasAudiçãoDuda ArandibaAinda não há avaliações
- Terminologia para ExamesDocumento18 páginasTerminologia para ExamesÁdylla SayúriAinda não há avaliações
- A Audição e Os Outros SentidosDocumento4 páginasA Audição e Os Outros SentidosAna Luiza RodriguesAinda não há avaliações
- Audicao 3Documento301 páginasAudicao 3Alice FerminoAinda não há avaliações
- Trabalho OuvidoDocumento4 páginasTrabalho OuvidoMatheus SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Você Já Reparou Quantas Coisas Diferentes Nosso Corpo É Capaz de FazerDocumento7 páginasVocê Já Reparou Quantas Coisas Diferentes Nosso Corpo É Capaz de FazerRosane HaasAinda não há avaliações
- Biofisica Da AudiçãoDocumento23 páginasBiofisica Da AudiçãoNicole CameloAinda não há avaliações
- Avaliação e Reabilitação Do Processamento Auditivo CentralDocumento8 páginasAvaliação e Reabilitação Do Processamento Auditivo Centralheloisa pincinato100% (1)
- Gabarito Exercícios Sistema SensorialDocumento5 páginasGabarito Exercícios Sistema SensorialikazueAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - Sistemas VibrantesDocumento6 páginas7 - Sistemas VibrantesAzeitona Raphael GomesAinda não há avaliações
- Atributos Do Som e Sua Deteção Pelo Ser HumanoDocumento3 páginasAtributos Do Som e Sua Deteção Pelo Ser HumanoDaniel Neves DiasAinda não há avaliações
- Física Acústica para FonoaudiologiaDocumento8 páginasFísica Acústica para FonoaudiologiafilipecwaAinda não há avaliações
- Biofísica Da AudiçãoDocumento28 páginasBiofísica Da AudiçãoLuciano SabinoAinda não há avaliações
- Sistema Nervoso Sensorial Audição & EquilíbrioDocumento78 páginasSistema Nervoso Sensorial Audição & EquilíbrioRodrigo de Oliveira ReisAinda não há avaliações
- AUDIÇÃODocumento20 páginasAUDIÇÃOHospital Chagas BarretoAinda não há avaliações
- Tutoria 2.2 Revisão NeuroDocumento6 páginasTutoria 2.2 Revisão Neuro5qq8vs45xjAinda não há avaliações
- Aula Pratica - Sistema Auditivo e Vestibular - 2024Documento4 páginasAula Pratica - Sistema Auditivo e Vestibular - 2024vivisaggiomoAinda não há avaliações
- 1568920804-1552968663-Fisio Neuro Sistema Auditivo PDFDocumento9 páginas1568920804-1552968663-Fisio Neuro Sistema Auditivo PDFANA MARGARIDA MARGARIDAAinda não há avaliações
- Fechamento Problema 1Documento10 páginasFechamento Problema 1Wellington SouzaAinda não há avaliações
- Biofisica Da Audicao PDFDocumento28 páginasBiofisica Da Audicao PDFAndréa GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- 77988d90-de39-11ea-b706-0fc8bf1e2202Documento6 páginas77988d90-de39-11ea-b706-0fc8bf1e2202eng civil Paulo Vitor MedeirosAinda não há avaliações
- Aula AudiçãoDocumento26 páginasAula AudiçãoFisioterapia XXVIIAinda não há avaliações
- A AudiçãoDocumento2 páginasA AudiçãoFlavio AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- Audição e VisãoDocumento27 páginasAudição e VisãoMayara CarolyneAinda não há avaliações
- BIOFISICA Da AudiçãoDocumento13 páginasBIOFISICA Da AudiçãoandressafgaAinda não há avaliações
- Biofísica Da AudiçãoDocumento66 páginasBiofísica Da AudiçãoGuilherme P AraujoAinda não há avaliações
- Apresentação Biofísica OkDocumento21 páginasApresentação Biofísica OkTony NogueiraAinda não há avaliações
- Orgãos de SentidoDocumento8 páginasOrgãos de SentidoRosario João JoséAinda não há avaliações
- A Nossa AudiçãoDocumento24 páginasA Nossa AudiçãoDiego MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- Resumo - Bases Físicas Da Fonação, Audição e PsicoacústicaDocumento8 páginasResumo - Bases Físicas Da Fonação, Audição e PsicoacústicaLeonardo Brum100% (1)
- Tour Otorrinolaringologia FechadoDocumento12 páginasTour Otorrinolaringologia FechadoMpn ForteAinda não há avaliações
- Audiçao e Equilibrio - CavDocumento80 páginasAudiçao e Equilibrio - CavMillena ConollyAinda não há avaliações
- Ressonância Magnética de HipófiseDocumento32 páginasRessonância Magnética de HipófiseIsannara Fernandes100% (3)
- Estudos de NeuropsicofisiologiaDocumento7 páginasEstudos de NeuropsicofisiologiaisadorasauthierAinda não há avaliações
- Sebenta de Anatomia Humana Versão Final PDFDocumento214 páginasSebenta de Anatomia Humana Versão Final PDFDiogoFevereiro100% (1)
- Bulbo - SNCDocumento5 páginasBulbo - SNCLeyson FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- Laudo Ultrassom Músculo Esquelético Das Funçõe FonoaudiológicasDocumento3 páginasLaudo Ultrassom Músculo Esquelético Das Funçõe FonoaudiológicascarlosAinda não há avaliações
- Buracos e Canais Da Base Do Cr+ónioDocumento2 páginasBuracos e Canais Da Base Do Cr+ónioMiguel FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia Do Aparelho RespiratórioDocumento43 páginasAnatomia Do Aparelho RespiratórioItamersonMacellAinda não há avaliações
- Livro OtitesDocumento219 páginasLivro OtitesNuno CavaleiroAinda não há avaliações
- Resumo NeuroDocumento10 páginasResumo Neuromalumorais368Ainda não há avaliações
- Tumores CerebraisDocumento6 páginasTumores CerebraisAlfredo Altuzarra100% (4)
- FT Anatomia-para-Colorir Musculos MastigDocumento2 páginasFT Anatomia-para-Colorir Musculos Mastigcarina M cardosoAinda não há avaliações
- Ossos Do NeurocrânioDocumento8 páginasOssos Do NeurocrânioBrenda Prado GondimAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia e Fisiologia Do Sistema EstomatognaticoDocumento264 páginasAnatomia e Fisiologia Do Sistema EstomatognaticoRaquel EmillyAinda não há avaliações
- PDF Apostila Anatomia ColorirDocumento39 páginasPDF Apostila Anatomia ColorirLuíza CabralAinda não há avaliações
- Aula NeuroanatomiaDocumento32 páginasAula NeuroanatomiaNavegantes Silva de OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Portfolio de Neuroanatomia Ciclo 2 Claretiano, 2020Documento11 páginasPortfolio de Neuroanatomia Ciclo 2 Claretiano, 2020Janaina Felix100% (1)
- Estudo Dirigido 1Documento5 páginasEstudo Dirigido 1Marllon Barro'sAinda não há avaliações
- Livro Patologia Naso-SinusalDocumento204 páginasLivro Patologia Naso-SinusalEleseElasAinda não há avaliações
- Semiologia Cabeça e Pescoço - Roteiro Exame FísicoDocumento2 páginasSemiologia Cabeça e Pescoço - Roteiro Exame Físico235211028Ainda não há avaliações
- Hc. 07 Higiene Bucal. Oral. Ocular. Auricular S RespDocumento30 páginasHc. 07 Higiene Bucal. Oral. Ocular. Auricular S RespNicoly TerraAinda não há avaliações
- Importância Da Psicologia No Estudo Do Comportamento HumanoDocumento12 páginasImportância Da Psicologia No Estudo Do Comportamento HumanoBaptista Jaime MilioneAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologia Aplicada Ao MergulhoDocumento52 páginasFisiologia Aplicada Ao MergulhoEverton TudeAinda não há avaliações
- Cranio IIDocumento41 páginasCranio IIRejanniely souza bandeiraAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomia Cavidade Nasal e Vias AéreasDocumento11 páginasAnatomia Cavidade Nasal e Vias AéreasLAÍS LINHARESAinda não há avaliações
- Procedimentos ICD 10Documento2.925 páginasProcedimentos ICD 10Susana CoutoAinda não há avaliações
- Livro-Neuroanatomia 210715 223630Documento140 páginasLivro-Neuroanatomia 210715 223630Rodrigo SouzaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercícios Paralisia FacialDocumento2 páginasExercícios Paralisia FacialRenison Soeiro80% (5)
- 8° EABP pt1 - Nervos CranianosDocumento16 páginas8° EABP pt1 - Nervos CranianosCarolina BortoloniAinda não há avaliações